Actions
Cloudforet has 100+ repositories, 70 of which are for applications and these repositories have github action workflows.
Because of that, it's very difficult to handle one by one when you need to update or run a workflow.
To solve this problem, we created Actions.
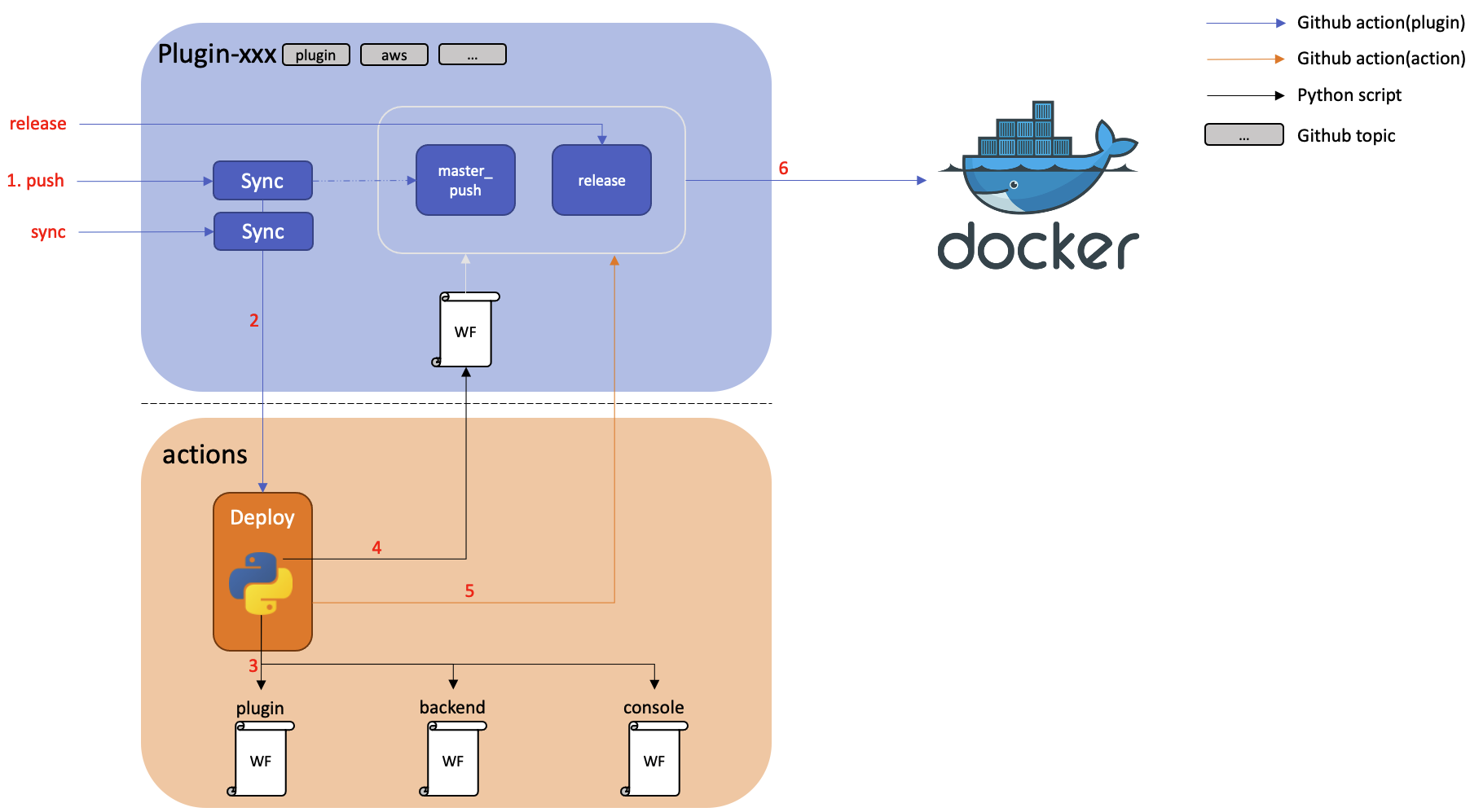
The diagram below shows the relationship between Actions and repositories.
What does actions actually do?
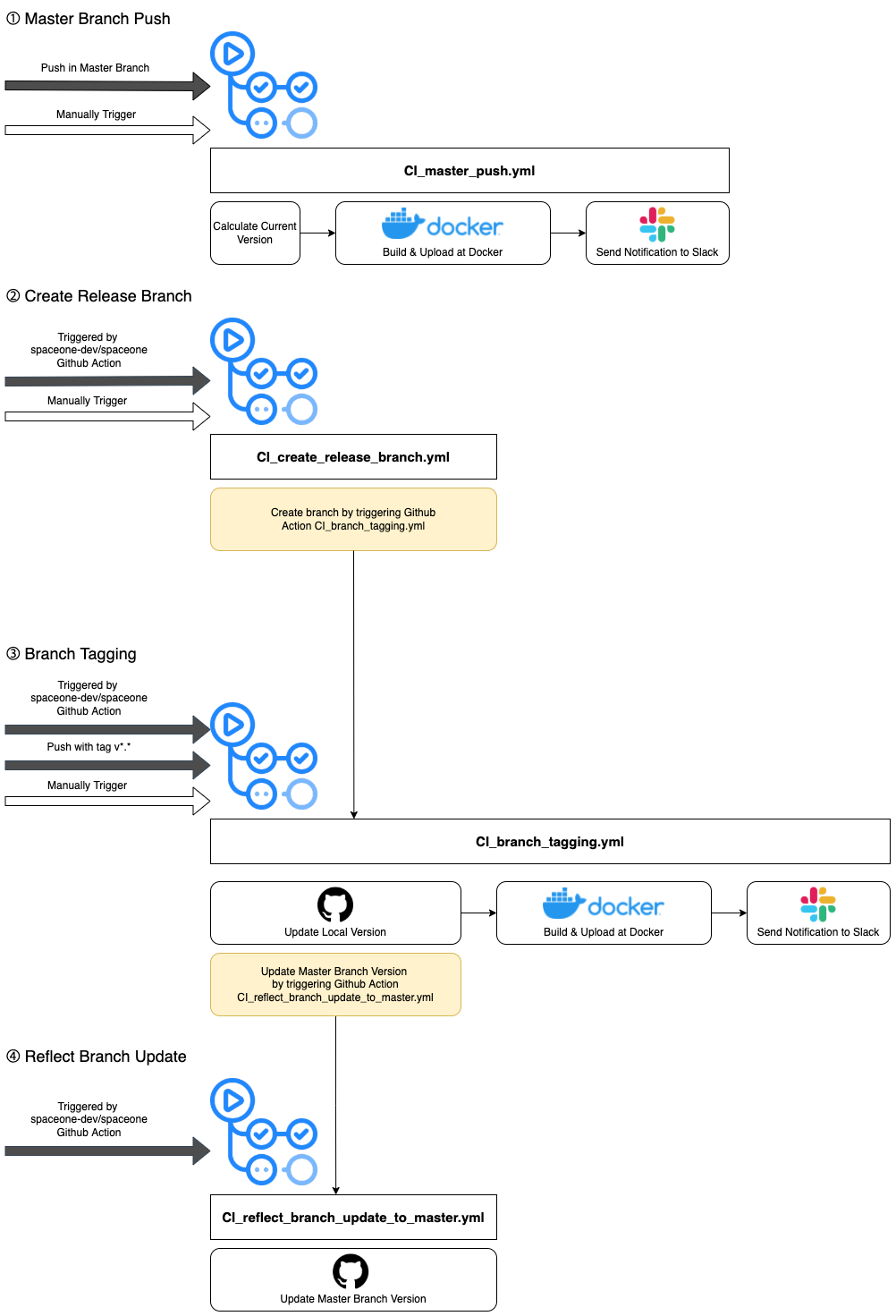
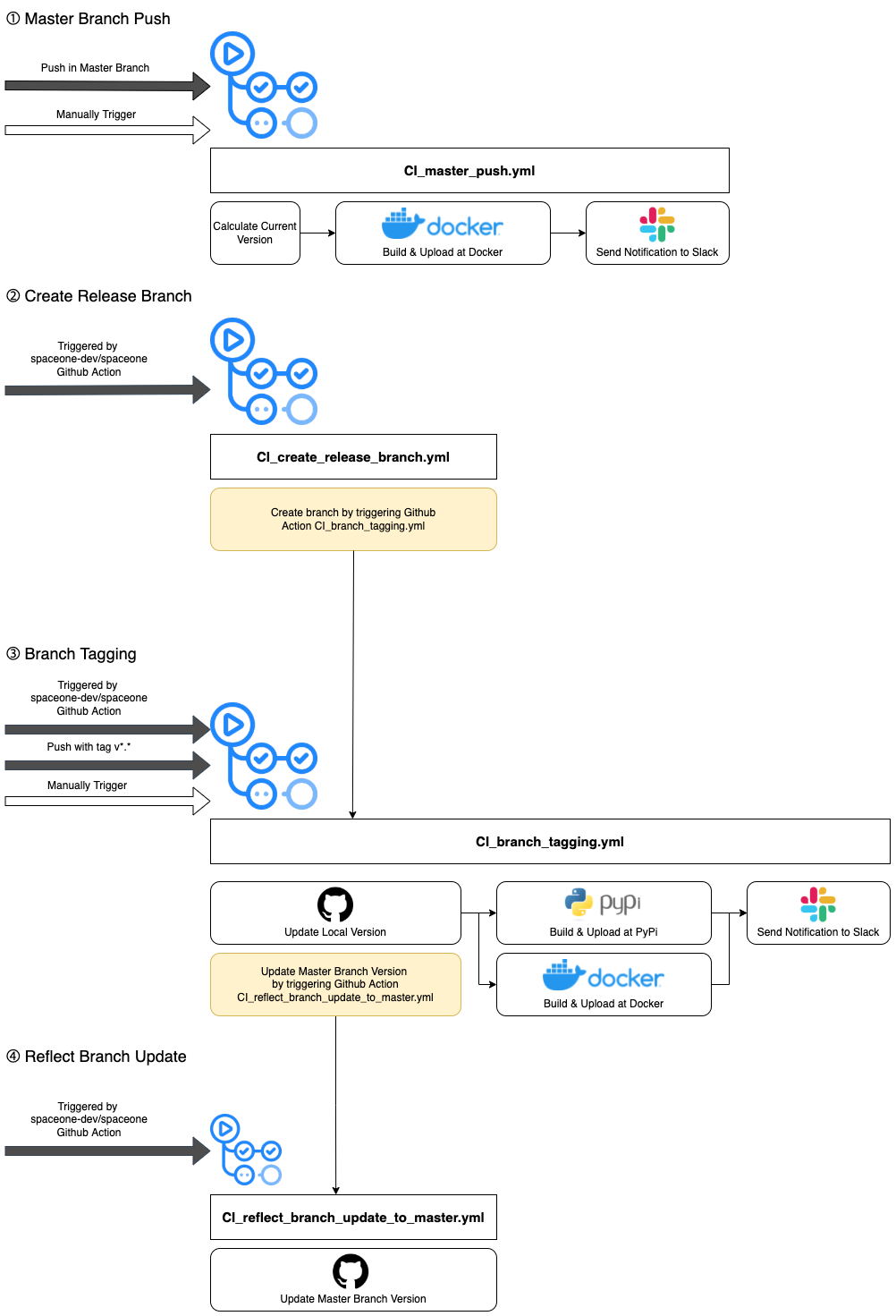
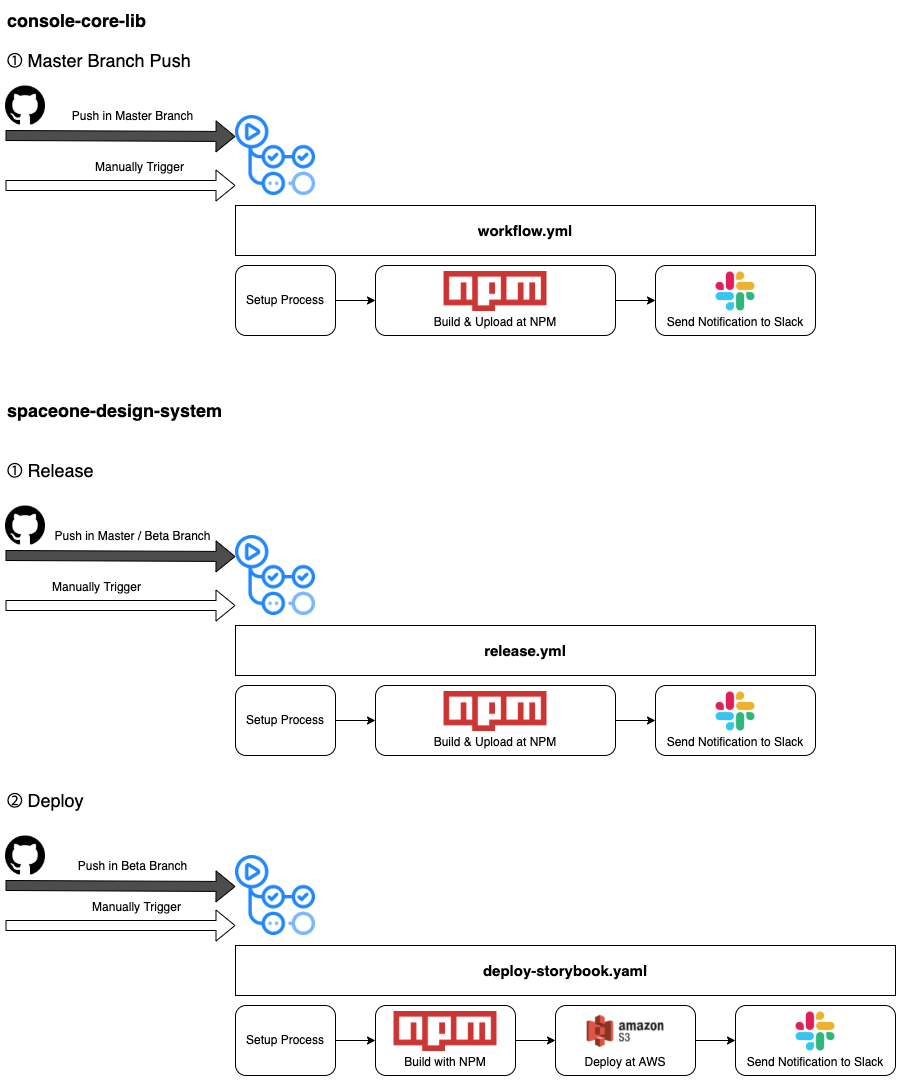
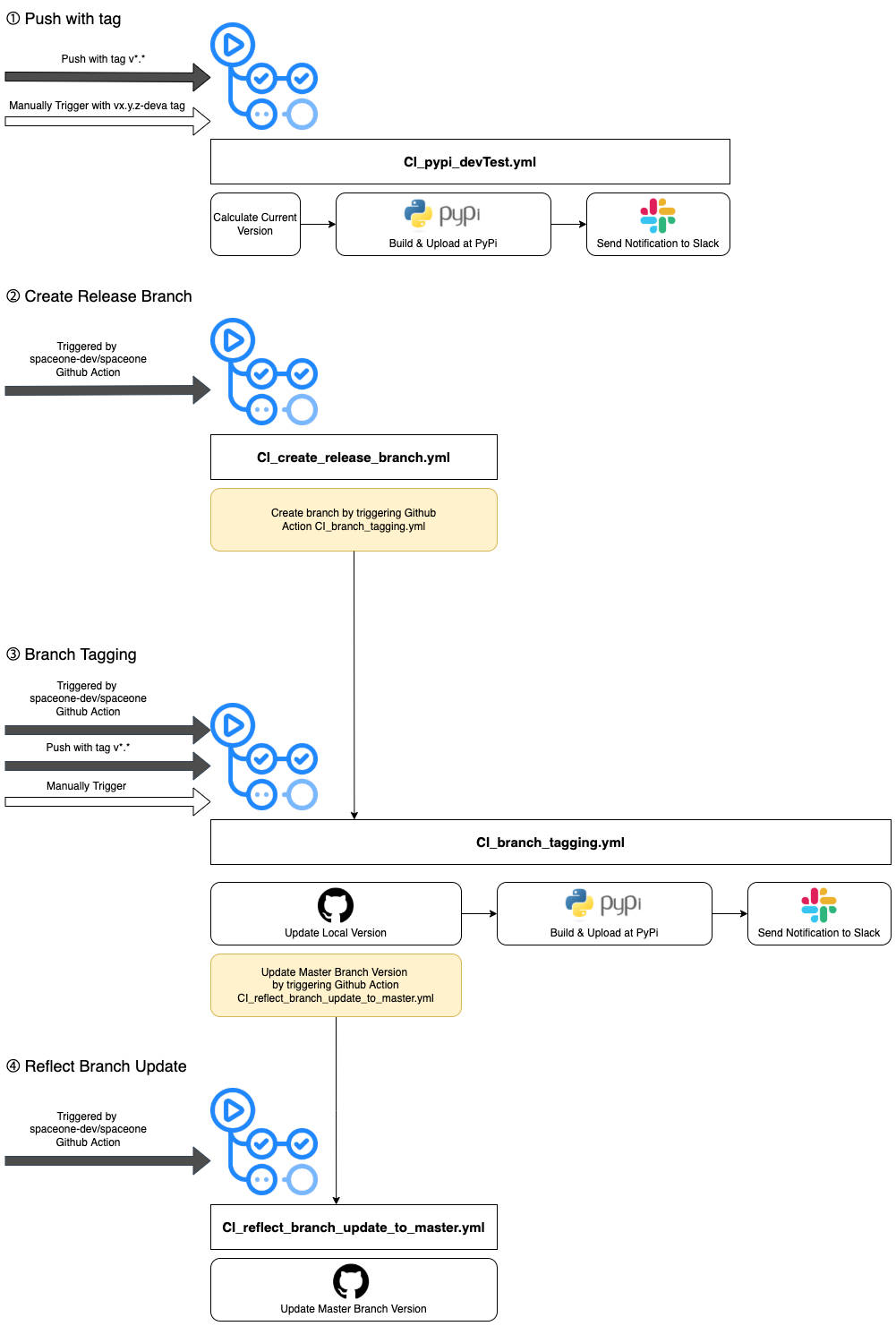
Actions is a control tower that manages and deploys github action workflows for Cloudforet's core services.
It can also bulk trigger these workflows when a new version of Cloudforet's core services needs to be released.
1. Manage and deploy github action workflows for Cloudforet's core services.
All workflows for Cloudforet's core services are managed and deployed in this repository.
We write the workflow according to our workflow policy and put it in the workflows directory of Actions.
Then these workflows can be deployed into the repository of Cloudforet's core services
Our devops engineers can modify workflows according to our policy and deploy them in batches using this feature.
The diagram below shows the process for this feature.
*) If you want to see the Actions script that appears in the diagram, see here.
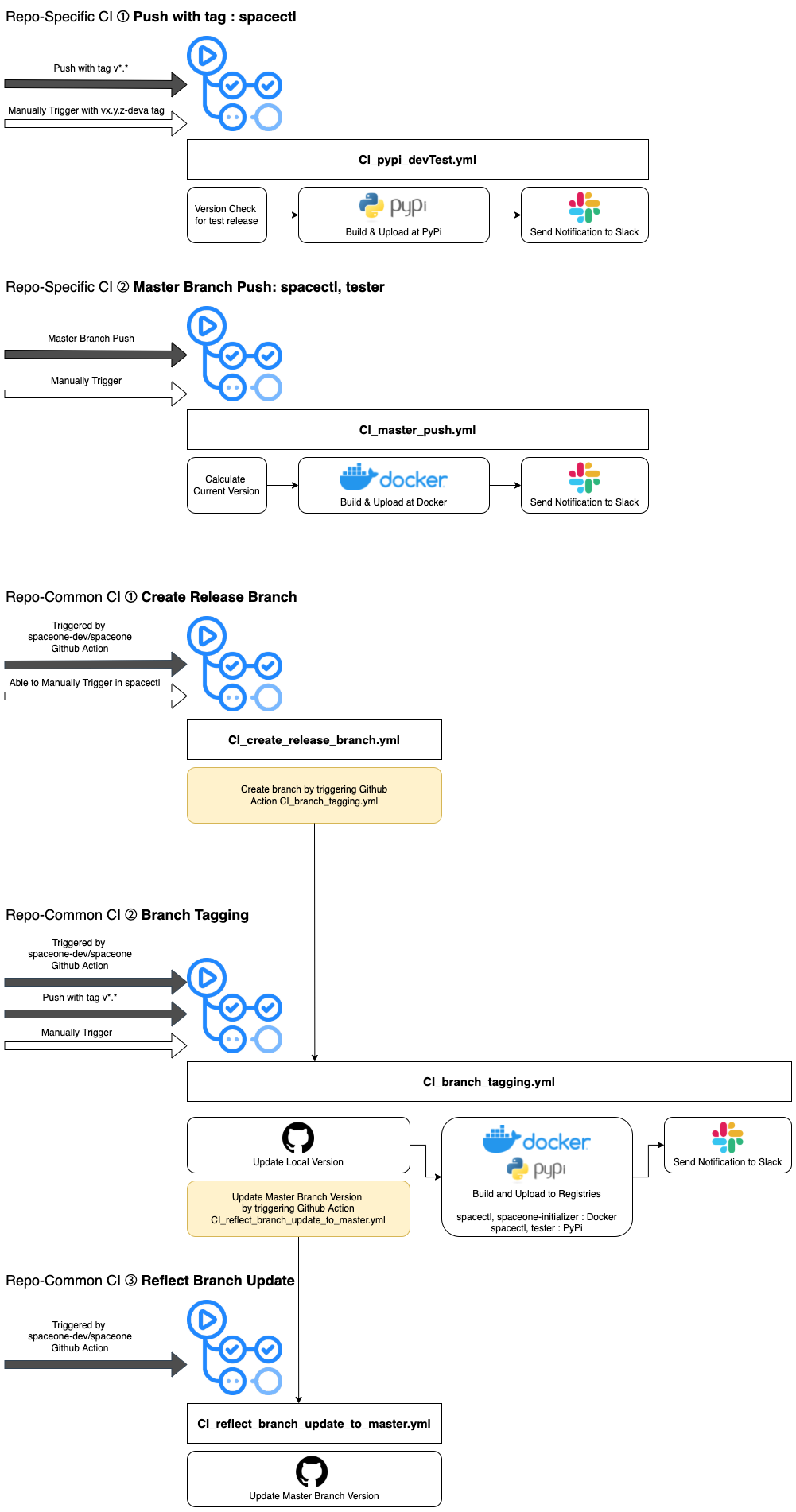
2. trigger workflows when a new version of Cloudforet's core services needs to be released.
When a new version of Cloudforet's core services is released, we need to trigger the workflow of each repository.
To do this, we made workflow that can trigger workflows of each repository in Actions.