Plugin Interface
First, check the interface between the plugin to be developed and the core service. The interface structure is different for each service. You can check the gRPC interface information about this in the API document. (SpaceONE API)
For example, suppose we are developing an Auth Plugin for authentication of Identity.
At this time, if you check the interface information of the Auth Plugin, it is as follows. (SpaceONE API - Identity Auth)
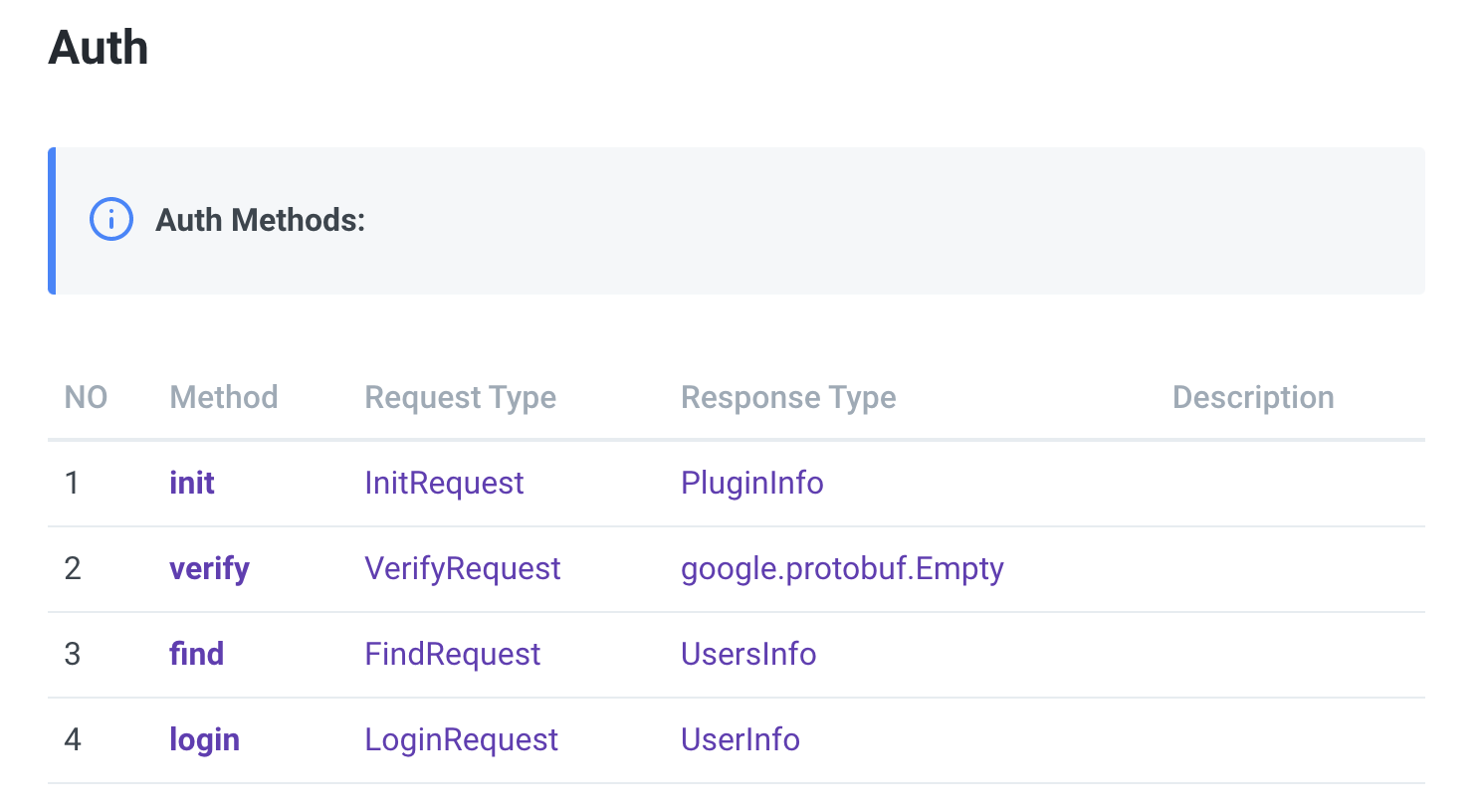
In order to develop Identity Auth Plugin, a total of 4 API interfaces must be implemented.
Of these, init and verify are intefaces that all plugins need equally,
The rest depends on the characteristics of each plugin.
Among them, let's take a closer look at init and verify, which are required to be implemented in common.
1. init
Plugin initialization.
In the case of Identity, when creating a domain, it is necessary to decide which authentication to use, and the related Auth Plugin is distributed.
When deploying the first plugin (or updating the plugin version), after the plugin container is created, the Core service calls the init API to the plugin.
At this time, the plugin returns metadata information required when the core service communicates with the plugin.
Information on metadata is different for each Core service.
Below is an example of python code for init implementation of Google oAuth2 plugin.
Metadata is returned as a return value, and at this time, various information required by identity is added and returned.
@transaction
@check_required(['options'])
def init(self, params):
""" verify options
Args:
params
- options
Returns:
- metadata
Raises:
ERROR_NOT_FOUND:
"""
manager = self.locator.get_manager('AuthManager')
options = params['options']
options['auth_type'] = 'keycloak'
endpoints = manager.get_endpoint(options)
capability= endpoints
return {'metadata': capability}
2. verify
Check the plugin's normal operation.
After the plugin is deployed, after the init API is called, it goes through a check procedure to see if the plugin is ready to run, and the API called at this time is verify.
In the verify step, the procedure to check whether the plugin is ready to perform normal operation is checked.
Below is an example of python code for verify implementation of Google oAuth2 plugin.
The verify action is performed through the value required for Google oAuth2 operation.
The preparation stage for actual logic execution requires verification-level code for normal operation.
def verify(self, options):
# This is connection check for Google Authorization Server
# URL: https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token
# After connection without param.
# It should return 404
r = requests.get(self.auth_server)
if r.status_code == 404:
return "ACTIVE"
else:
raise ERROR_NOT_FOUND(key='auth_server', value=self.auth_server)
