Previous version of Cloudforet,
| Version | Installation Guide |
|---|---|
| v1.12 (stable) | https://cloudforet.io/v1-12/docs/setup_operation/quick_install/ |
| v2.x (development) | Current page |
Overview
This is Getting Started Installation guide with minikube.
Note :- This Guide is for developer only.
Cloudforet-Minikube Architecture
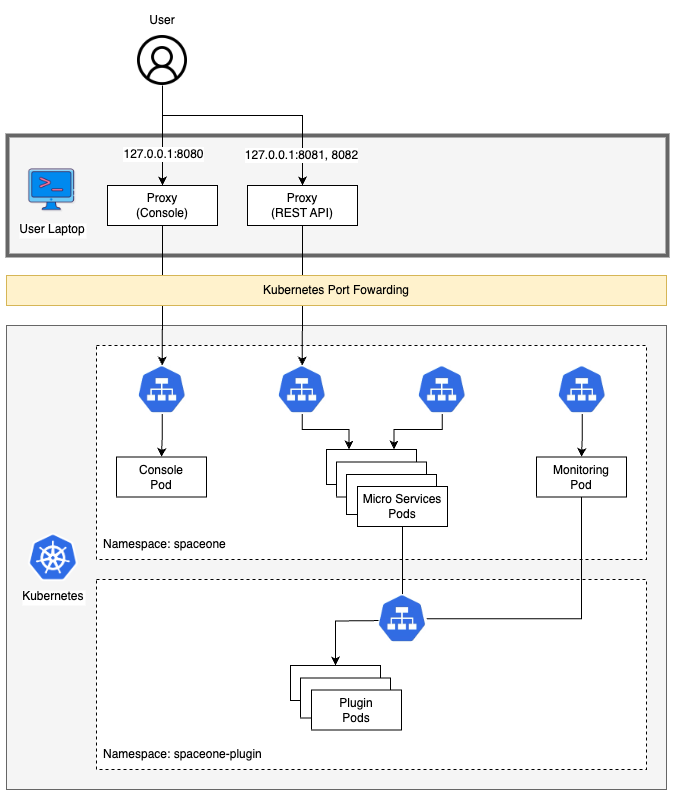
Prerequisites
- Minimum requirements for development (2 cores, 8 GB memories, 30GB disk)
| CSP | Possible Instance Type |
|---|---|
| AWS | t3.large , m5.large |
| GCP | n4-standard-2, n1-standard-2 |
| Azure | d2s-v3 |
- Docker/Docker Desktop
- If you don't have Docker installed, minikube will return an error as minikube uses docker as the driver.
- Highly recommend installing Docker Desktop based on your OS.
- Minikube
- Requires minimum Kubernetes version of 1.21+.
- Kubectl
- Helm
- Requires minimum Helm version of 3.11.0+.
- If you want to learn more about Helm, refer to this.
Before diving into the Cloudforet Installation process, start minikube by running the command below.
minikube start --driver=docker --memory=6000mb
Installation
You can install the Cloudforet by the following the steps below.
1) Add Helm Repository
This command wll register Helm repository.
helm repo add cloudforet https://cloudforet-io.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm search repo cloudforet
2) Create Namespaces
kubectl create ns cloudforet
kubectl create ns cloudforet-plugin
3) Create Role and RoleBinding
First, download the rbac.yaml file.
The rbac.yaml file basically serves as a means to regulate access to computer or network resources based on the roles of individual users. For more information about RBAC Authorization in Kubernetes, refer to this.
If you are used to downloading files via command-line, run this command to download the file. Next, execute the following command.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloudforet-io/charts/master/examples-v2/rbac.yaml -O rbac.yaml
kubectl apply -f rbac.yaml -n cloudforet-plugin
4) Install Cloudforet Chart
Download default YAML file for helm chart. Execute the following command.
Current Cloudforet 2.x is development status, so you need to add
--develoption.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloudforet-io/charts/master/examples-v2/values/release-2x.yaml -O release-2x.yaml
helm install cloudforet cloudforet/spaceone -n cloudforet -f release-2x.yaml --devel
After executing the above command, check the status of the pod.
Scheduler pods are in
CrashLoopBackOfforErrorstate. This is because the setup is not complete.
kubectl get pod -n cloudforet
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
board-5746fd9657-vtd45 1/1 Running 0 57s
config-5d4c4b7f58-z8k9q 1/1 Running 0 58s
console-6b64cf66cb-q8v54 1/1 Running 0 59s
console-api-7c95848cb8-sgt56 2/2 Running 0 58s
console-api-v2-rest-7d64bc85dd-987zn 2/2 Running 0 56s
cost-analysis-7b9d64b944-xw9qg 1/1 Running 0 59s
cost-analysis-scheduler-ff8cc758d-lfx4n 0/1 Error 3 (37s ago) 55s
cost-analysis-worker-559b4799b9-fxmxj 1/1 Running 0 58s
dashboard-b4cc996-mgwj9 1/1 Running 0 56s
docs-5fb4cc56c7-68qbk 1/1 Running 0 59s
identity-6fc984459d-zk8r9 1/1 Running 0 56s
inventory-67498999d6-722bw 1/1 Running 0 57s
inventory-scheduler-5dc6856d44-4spvm 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 3 (18s ago) 59s
inventory-worker-68d9fcf5fb-x6knb 1/1 Running 0 55s
marketplace-assets-8675d44557-ssm92 1/1 Running 0 59s
mongodb-7c9794854-cdmwj 1/1 Running 0 59s
monitoring-fdd44bdbf-pcgln 1/1 Running 0 59s
notification-5b477f6c49-gzfl8 1/1 Running 0 59s
notification-scheduler-675696467-gn24j 1/1 Running 0 59s
notification-worker-d88bb6df6-pjtmn 1/1 Running 0 57s
plugin-556f7bc49b-qmwln 1/1 Running 0 57s
plugin-scheduler-86c4c56d84-cmrmn 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 3 (13s ago) 59s
plugin-worker-57986dfdd6-v9vqg 1/1 Running 0 58s
redis-75df77f7d4-lwvvw 1/1 Running 0 59s
repository-5f5b7b5cdc-lnjkl 1/1 Running 0 57s
secret-77ffdf8c9d-48k46 1/1 Running 0 55s
spacectl-5664788d5d-dtwpr 1/1 Running 0 59s
statistics-67b77b6654-p9wcb 1/1 Running 0 56s
statistics-scheduler-586875947c-8zfqg 0/1 Error 3 (30s ago) 56s
statistics-worker-68d646fc7-knbdr 1/1 Running 0 58s
supervisor-scheduler-6744657cb6-tpf78 2/2 Running 0 59s
To execute the commands below, every POD except xxxx-scheduler-yyyy must have a Running status.
5) Default Initialization (in spacectl POD)
To use Cloudforet, you have to initialize the root domain, which creates a SYSTEM TOKEN.
Login to the spacectl POD and execute the command below.
kubectl exec -it -n cloudforet spacectl-xxxxx -- /bin/sh
spacectl config init -f default.yaml
root domain yaml file (root.yaml)
---
admin:
user_id: admin@example.com
password: Admin123!@#
name: Admin
Execute the command below to create the root domain.
spacectl exec init identity.System -f root.yaml
6) Update Helm Values
Update your helm values file (ex. release-2x.yaml) and edit the values. There is only one item that need to be updated.
For EC2 users: put in your EC2 server's public IP instead of 127.0.0.1 for both CONSOLE_API and CONSOLE_API_V2 ENDPOINT.
- TOKEN (from the previous step)
console:
production_json:
CONSOLE_API:
ENDPOINT: http://localhost:8081 # http://ec2_public_ip:8081 for EC2 users
CONSOLE_API_V2:
ENDPOINT: http://localhost:8082 # http://ec2_public_ip:8082 for EC2 users
global:
shared_conf:
TOKEN: 'TOKEN_VALUE_FROM_ABOVE' # Change the system token
After editing the helm values file(ex. release-2x.yaml), upgrade the helm chart.
helm upgrade cloudforet cloudforet/spaceone -n cloudforet -f release-2x.yaml --devel
After upgrading, delete the pods in cloudforet namespace that have the label app.kubernetes.io/instance and value cloudforet.
kubectl delete po -n cloudforet -l app.kubernetes.io/instance=cloudforet
7) Check the status of the pods
kubectl get pod -n cloudforet
8) Create User Domain (In spacectl POD)
Create a user domain yaml file (domain.yaml)
---
name: spaceone
admin:
user_id: admin@domain.com
password: Admin123!@#
name: Admin
execute the command below to create the user domain.
spacectl config init -f default.yaml
spacectl config set api_key {SYSTEM_TOKEN}
spacectl exec create identity.Domain -f domain.yaml
If all pods are in Running state, the setup is complete.
Port-forwarding
Installing Cloudforet on minikube doesn't provide any Ingress objects such as Amazon ALB or NGINX ingress controller. We can use kubectl port-forward instead.
Run the following commands for port forwarding.
# CLI commands
kubectl port-forward -n cloudforet svc/console 8080:80 --address='0.0.0.0' &
kubectl port-forward -n cloudforet svc/console-api 8081:80 --address='0.0.0.0' &
kubectl port-forward -n cloudforet svc/console-api-v2-rest 8082:80 --address='0.0.0.0' &
Start Cloudforet
Log-In User Domain
For EC2 users: open browser with http://your_ec2_server_ip:8080
Open browser (http://127.0.0.1:8080)
| ID | PASSWORD |
|---|---|
| admin@domain.com | Admin123!@# |