This the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
User Guide
- 1: Get started
- 2: Dashboards
- 2.1: Dashboard Templates
- 2.2: Create Dashboard
- 2.3: Customize Dashboard
- 2.4: Review & Quick Configuration
- 3: Project
- 4: Asset inventory
- 4.1: Quick Start
- 4.2: Cloud service
- 4.3: Server
- 4.4: Collector
- 4.5: Service account
- 5: Cost Explorer
- 5.1: Cost analysis
- 5.2: Budget
- 6: Alert manager
- 6.1: Quick Start
- 6.2: Dashboard
- 6.3: Alert
- 6.4: Webhook
- 6.5: Event rule
- 6.6: Maintenance window
- 6.7: Notification
- 6.8: Escalation policy
- 7: Administration
- 7.1: [IAM] User
- 8: My page
- 8.1: Account & profile
- 8.2: Notifications channel
- 9: Information
- 9.1: Notice
- 10: Advanced feature
- 10.1: Custom table
- 10.2: Export as an Excel file
- 10.3: Search
- 11: Plugin
1 - Get started
Learn more about Cloudforet through a user guide.
To use Cloudforet's services, the following three prerequisites must be met:
- User settings
- Project settings
- Service account settings
User settings
Cloudforet users are classified into three types: internal users, external users, and API users.
This section only introduces how to add internal users, and how to add external users and API users can be found in [IAM] user guide.
Adding a user
(1) Click the [Create] button on the [Admin > Users] page.
(2) In the [Create user] modal, select the [Local] tab.
(2-1) After entering the ID, click the [Check ID] button to check if the ID is valid.
(2-2) After entering the name, email, and password to identify the user, click the [OK] button to complete the user creation.
Assign administrator’s privileges
If you want to give a user administrator’s privileges, you can assign them by selecting them from the [Assign admin role] dropdown.
If nothing is selected, no privileges will be granted to that user.
For a more detailed information on permissions, see here.
Project settings
Create project and Project group for systematic resource management .
Creating a project group
Since a project must belong to one project group, you must first create a project group before creating a project.
(1) Click the [Create project group] button on the [Project] page.
(2) After entering the project group name in the [Create project group] modal dialog, click the [OK] button to create the project group.
Creating a project
After creating a project group, create a project that will belong to it.
(1) Select the previously created project group from the list of project groups on the left and click the [Create project] button at the top right.
(2) After entering the project name in the [Create project] modal dialog, click the [OK] button to create the project.
Inviting project group members
You can invite users to a project group to register as a Member of the project group.
Roles of project group members
Invited members must have one role for the project group. This role is equally applied to all project groups and projects that fall under that project group.
For more information, see here.
(1) Select the previously created project group from the [Project group] list on the left.
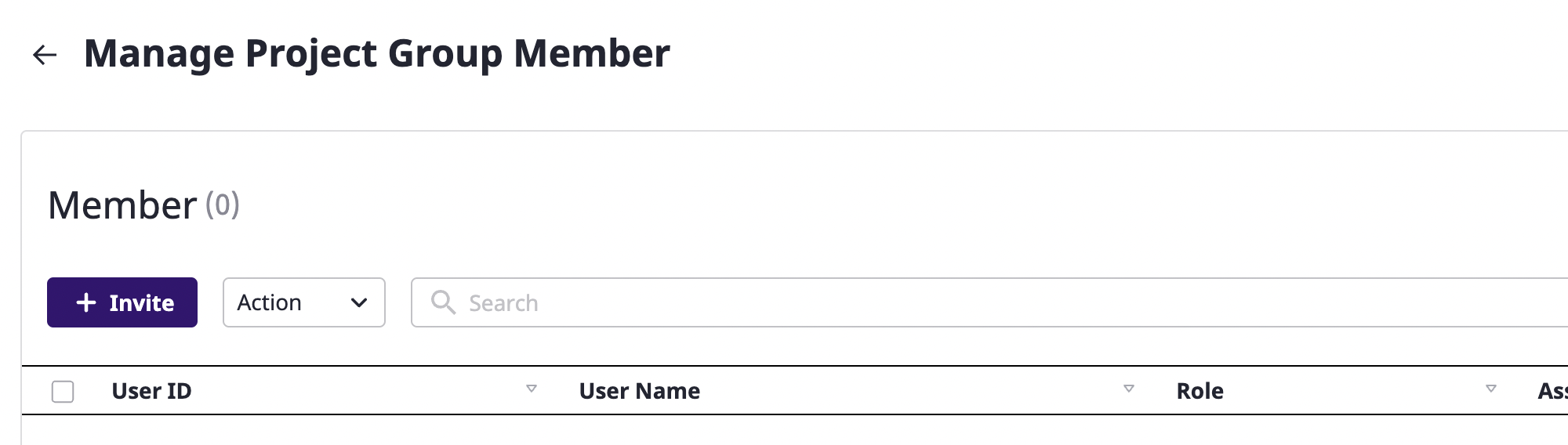
(2) Click the [Manage project group members] icon button at the top right.
![]()
(3) Click the [Invite] button on the [Manage project group members] page to open the [Invite members] modal dialog.
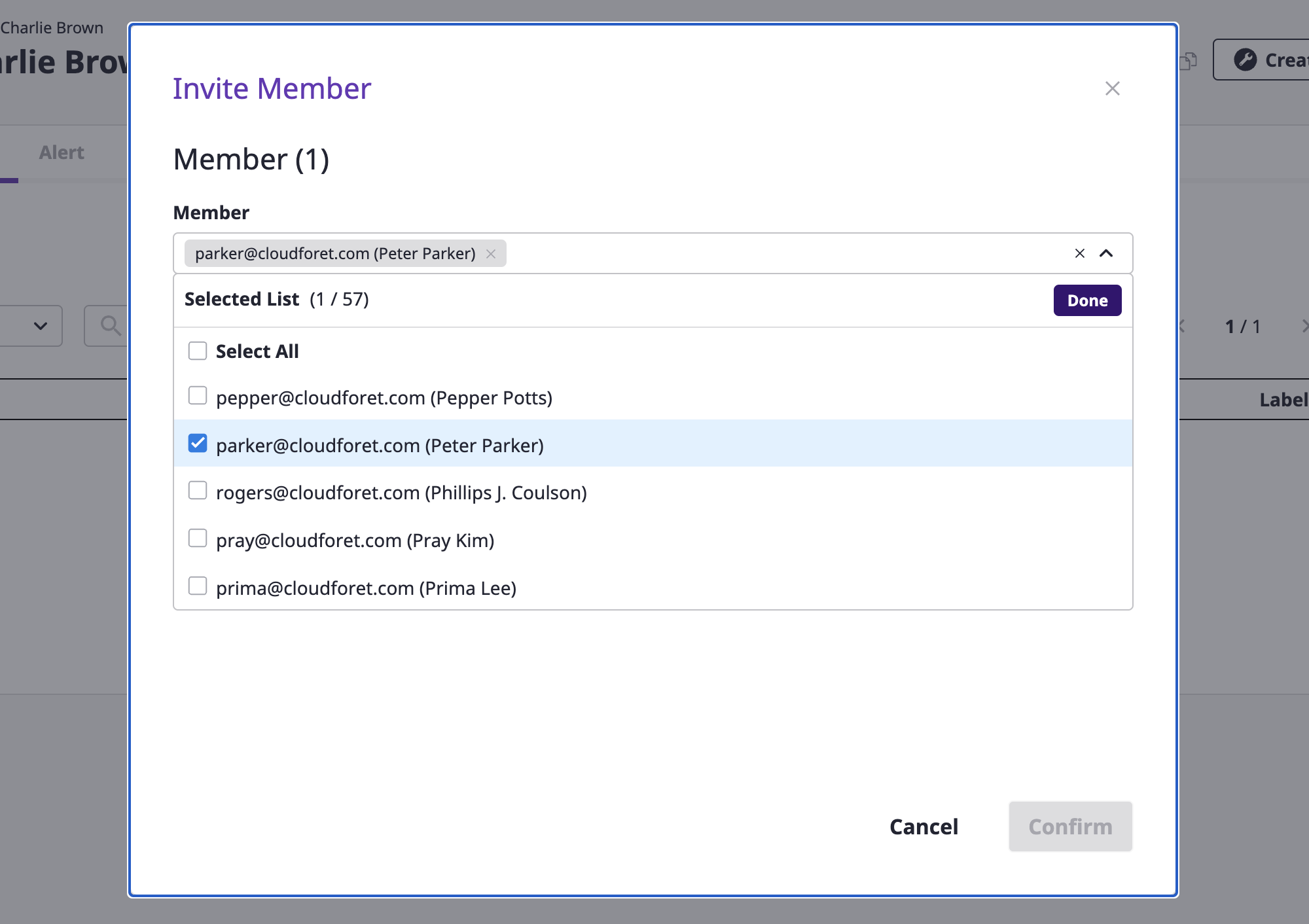
(3-1) Select the member you want to invite. You can select and invite multiple members at once.
(3-2) Select the role to be granted to the members to be invited.
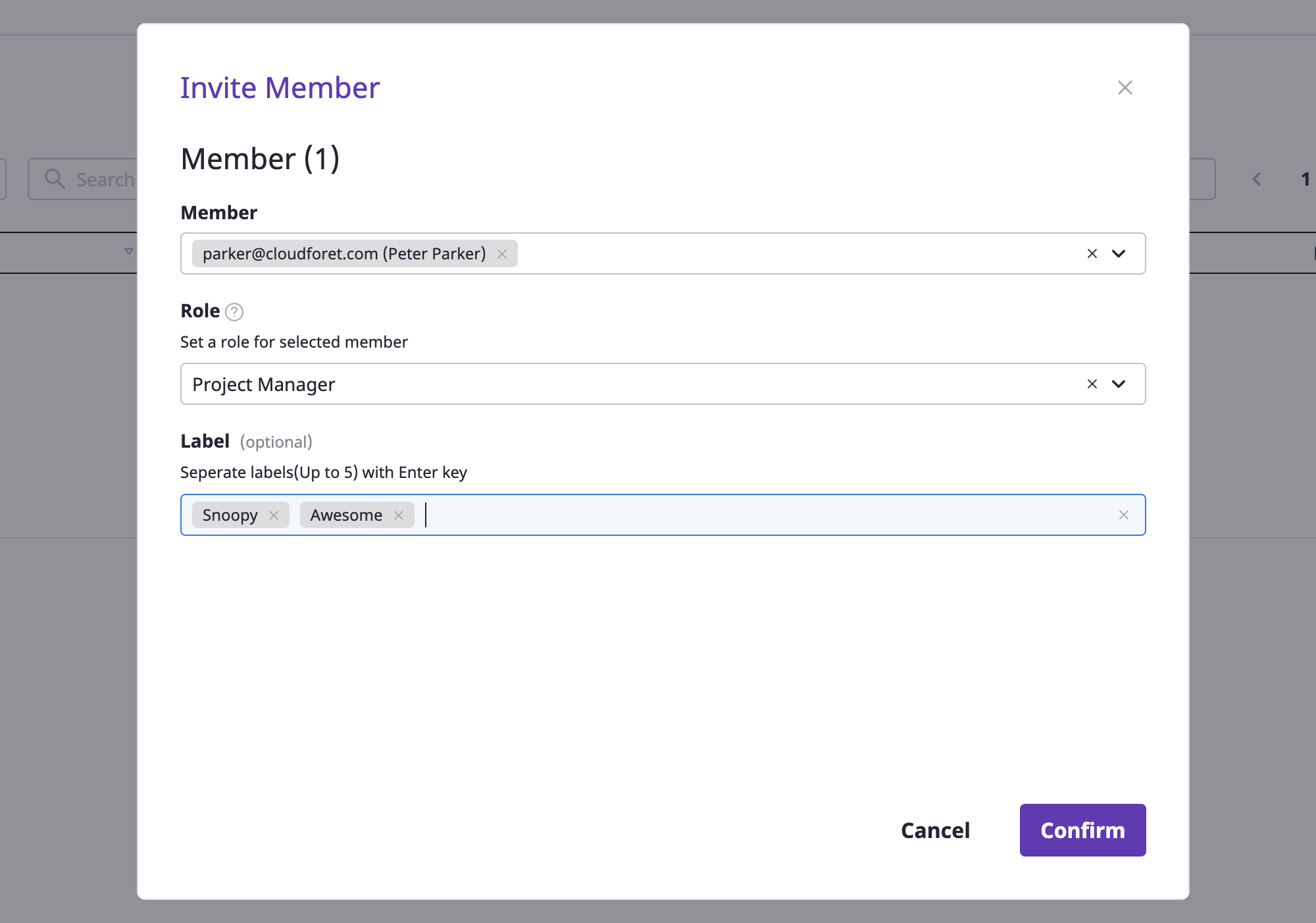
Member’s role
A project member can only be granted auser type role.
For a detailed description of role types, see here.(3-3) After entering the labels for the members to invite, press the Enter key to add them.
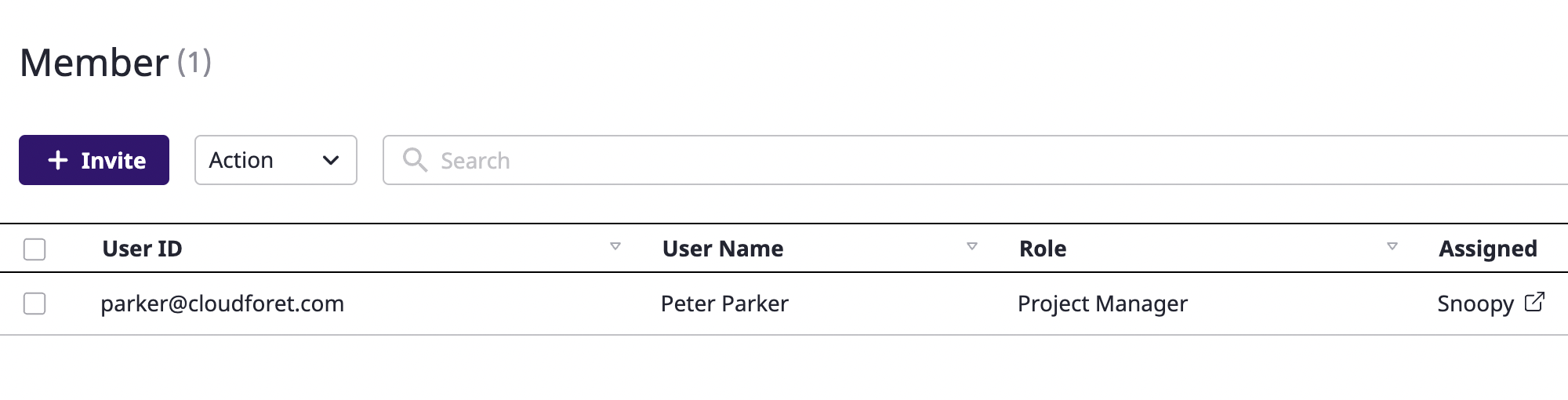
(3-4) Click the [OK] button to complete member invitation.
Service account settings
Service Account means the Cloud service account required to collect resources for the cloud service.
Adding cloud service account
(1) On the [Asset Inventory > Service account] page, select the cloud service you want to add.
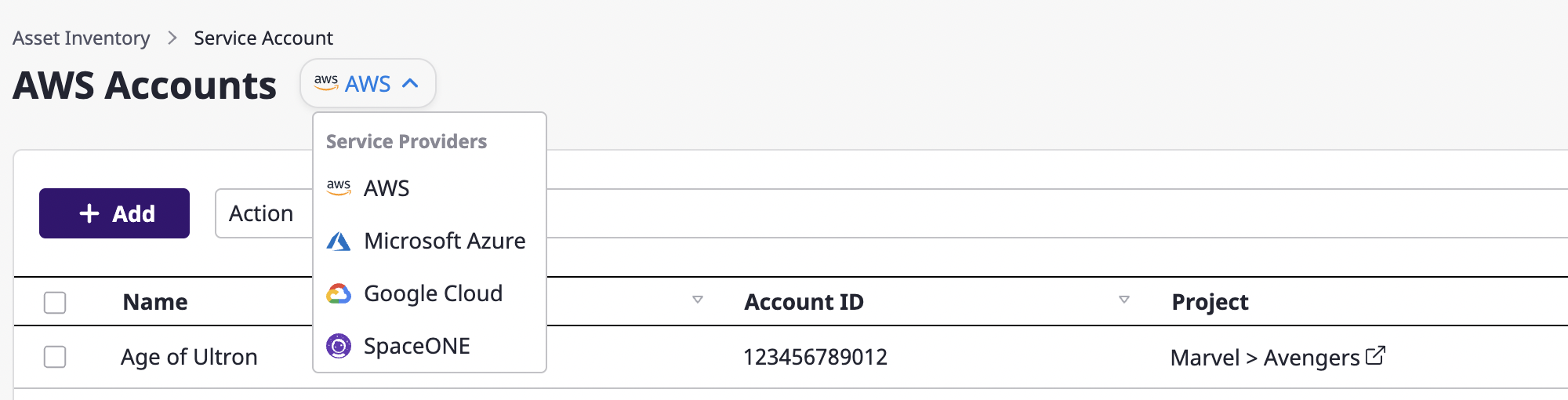
(2) Click the [Add] button.
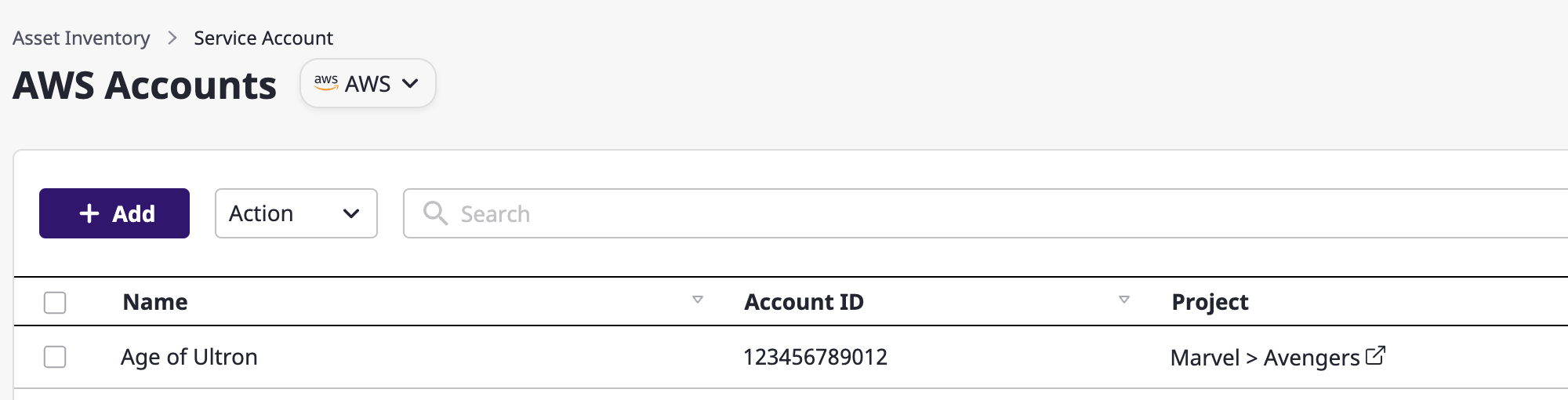
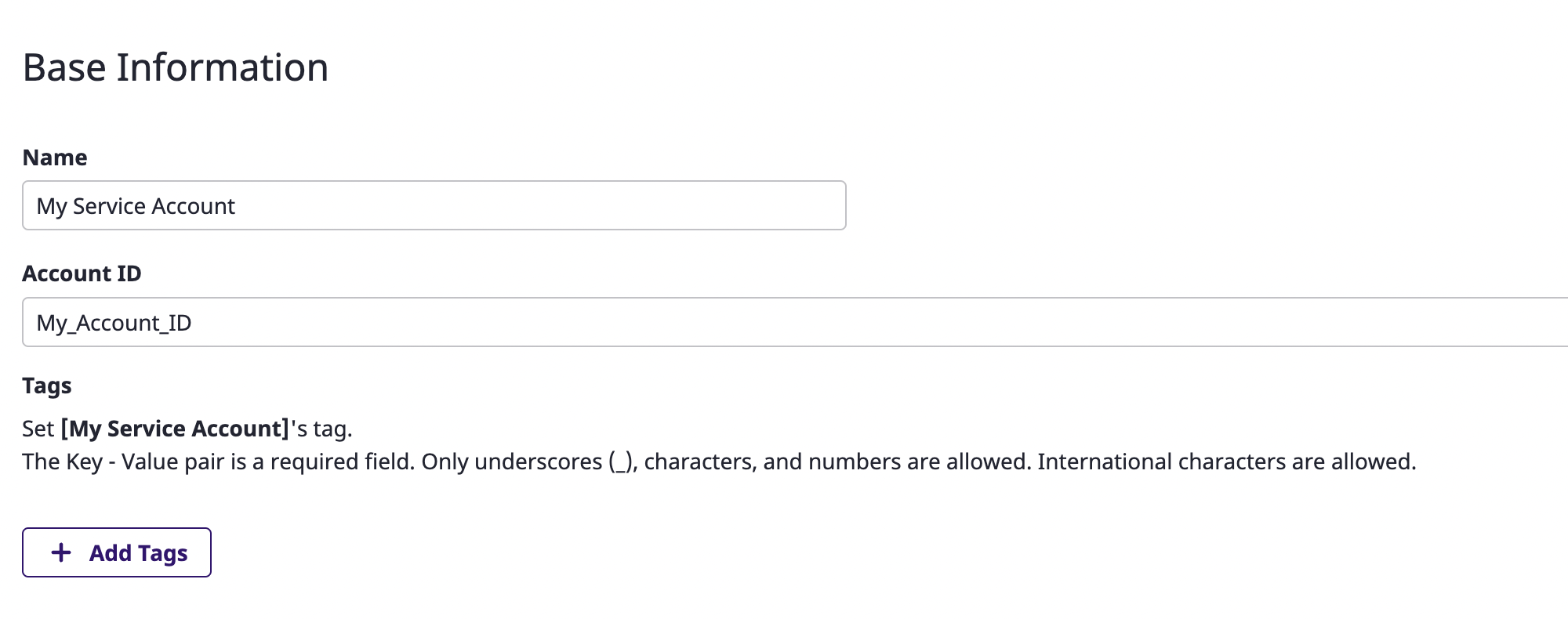
(3) Fill out the service account creation form.
(3-1) Enter basic information.
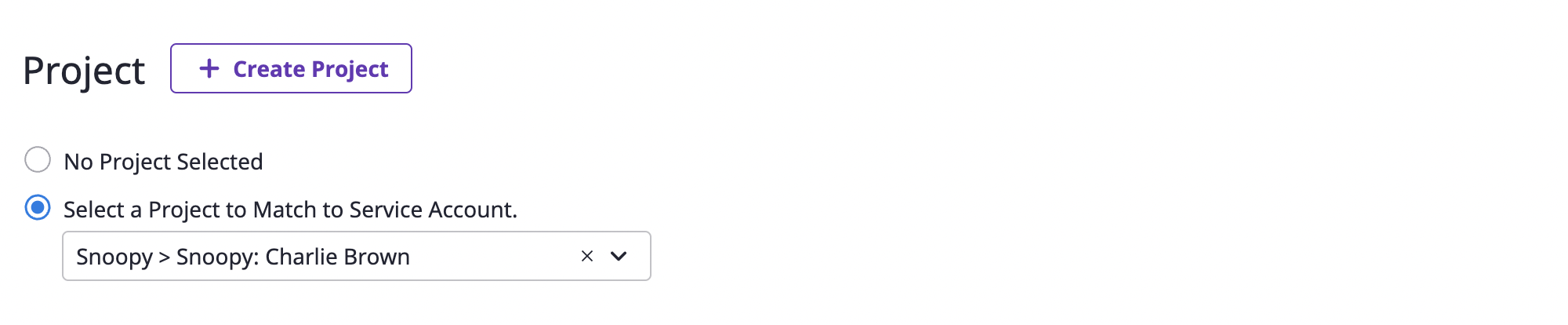
(3-2) Specify the project to collect resources from according to the service account.
(3-3) Enter encryption key information.
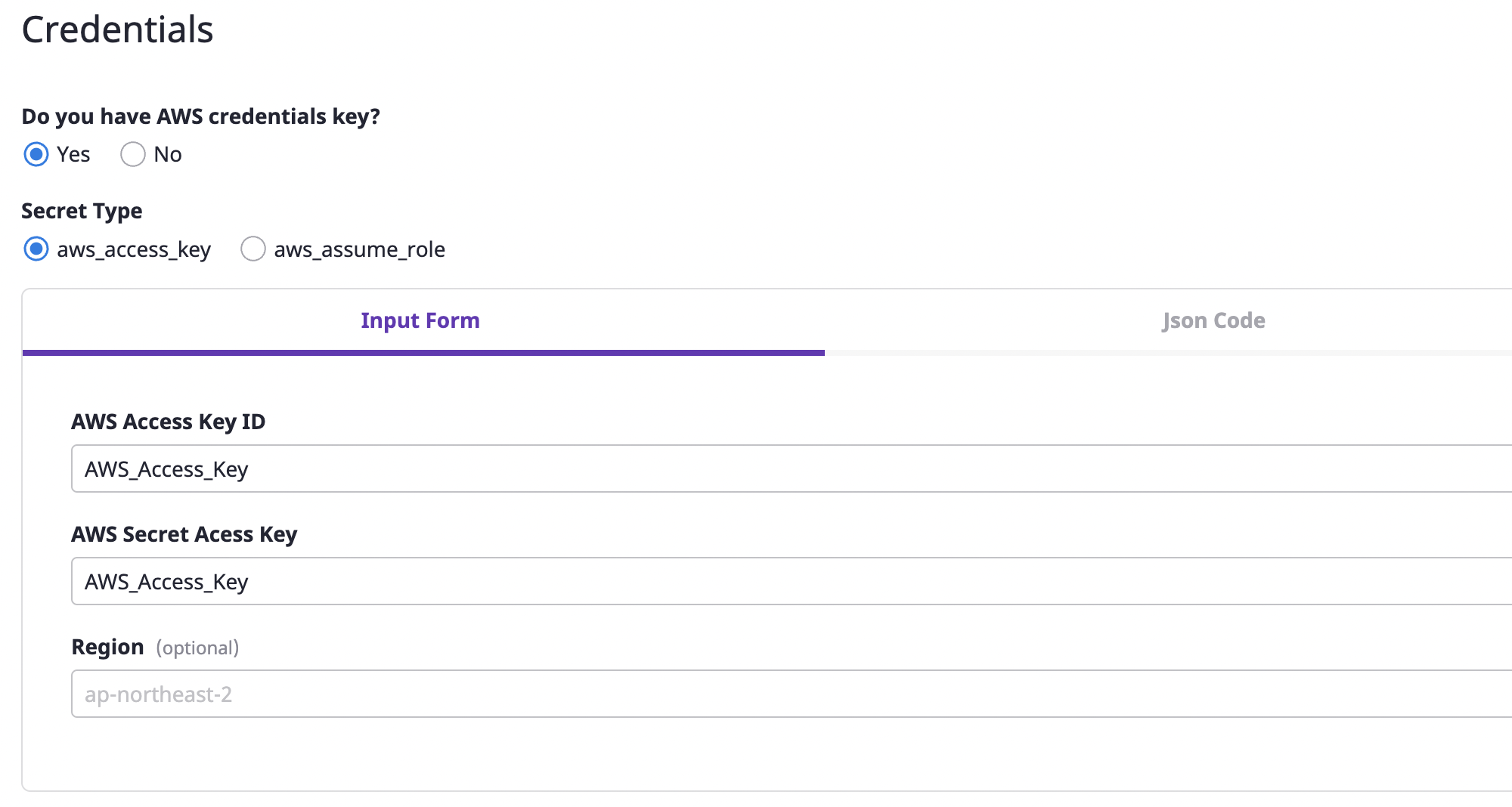
(4) Click the [Save] button to complete.
Add account by cloud service
Account information required for each cloud service may differ. You can see detailed information from the link below:
• AWS (link)
• Azure (link)
• GCP (link)
• OCI (link)
• Alibaba Cloud (link)
After completing the above steps, if you want to use Cloudforet’s services more conveniently and in a variety of ways, please see the following guide:
2 - Dashboards
You can create customized dashboards by combining specific widgets to gain a quick overview of your desired data in addition to the default provided dashboards. Furthermore, you can have precise control over variables, date ranges, and detailed options for each widget for each dashboard, allowing you to build and manage more accurate and professional dashboards tailored to your organization's requirements.
2.1 - Dashboard Templates
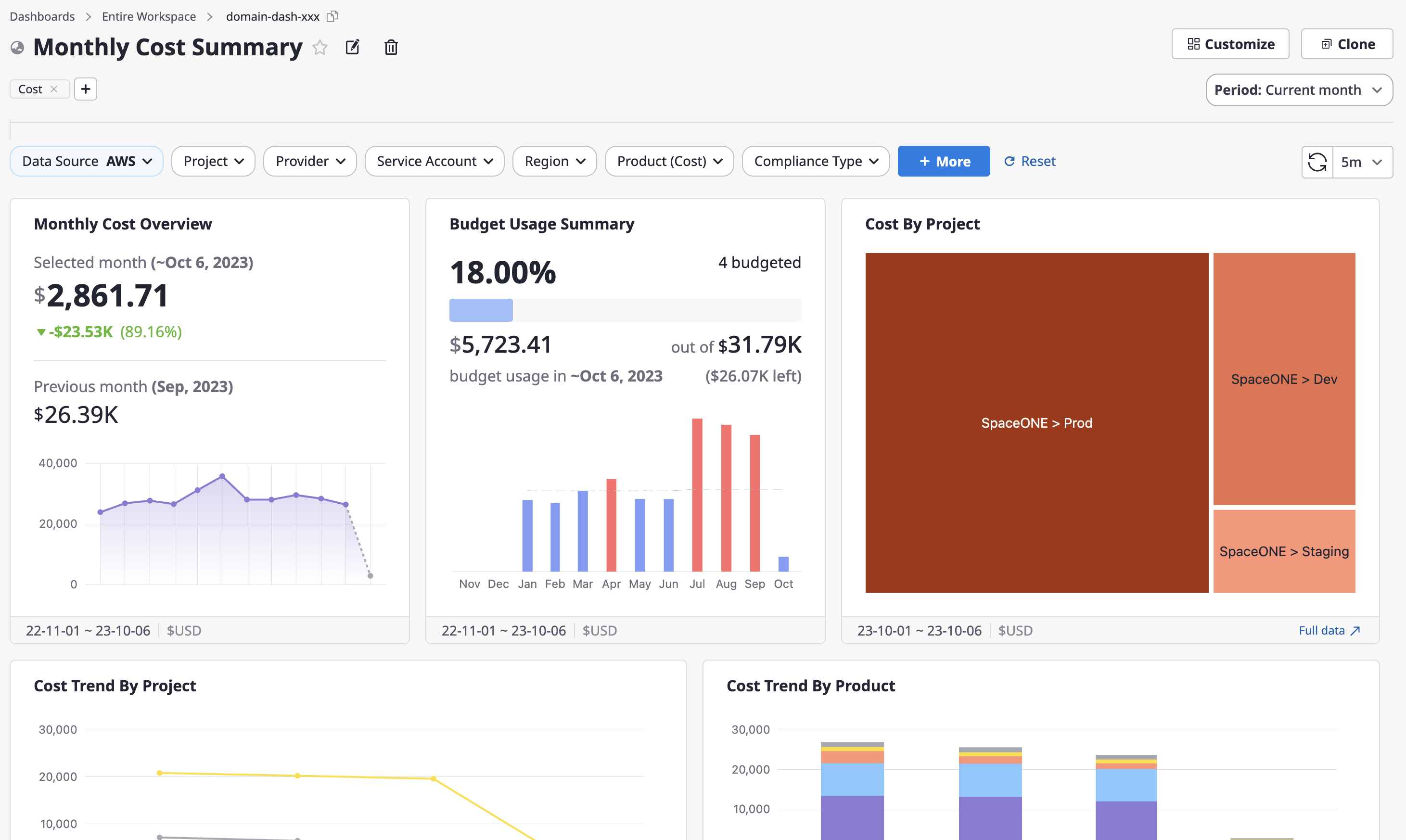
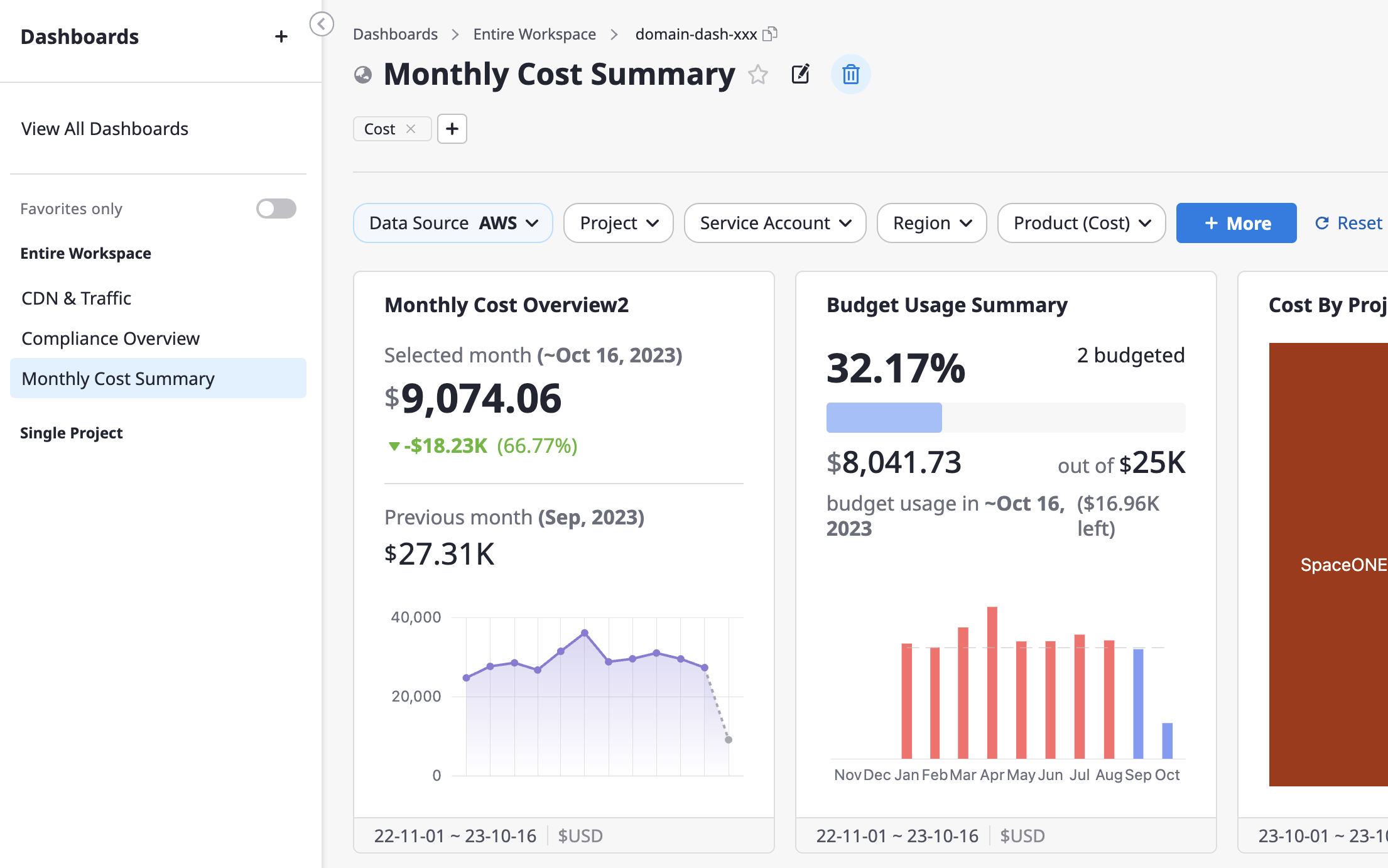
Monthly Cost Summary
This is a dashboard that visualizes cloud cost status and budget utilization based on various group-specific statistical criteria in the form of charts.
It is comprised of cost-related widgets, and among the dashboard variables, one specific Data-Source must be selected.
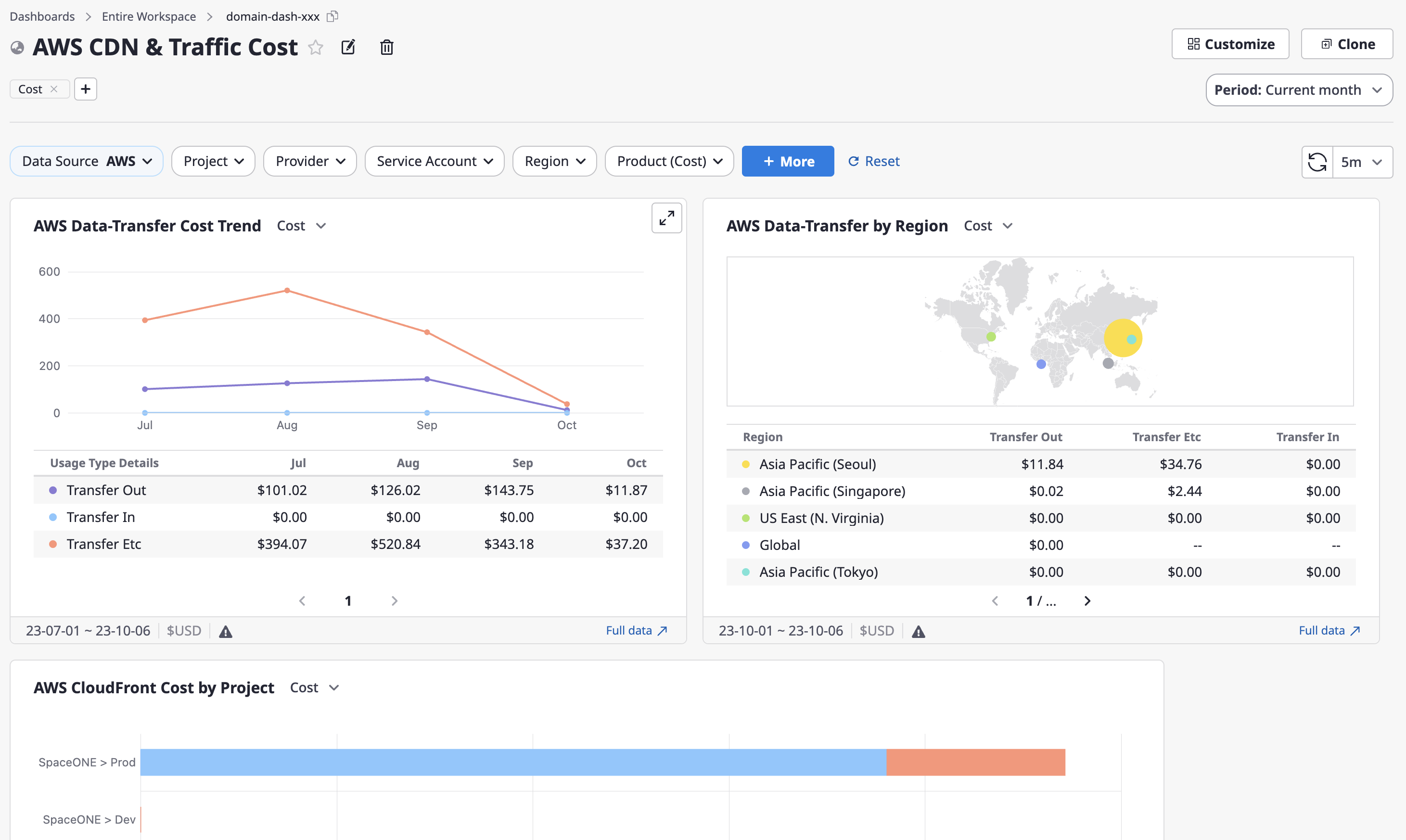
CDN & Traffic
This is a dashboard that charts the status of CDN and traffic-related costs and usage for a specific cloud product. One specific Data-Source must be selected.
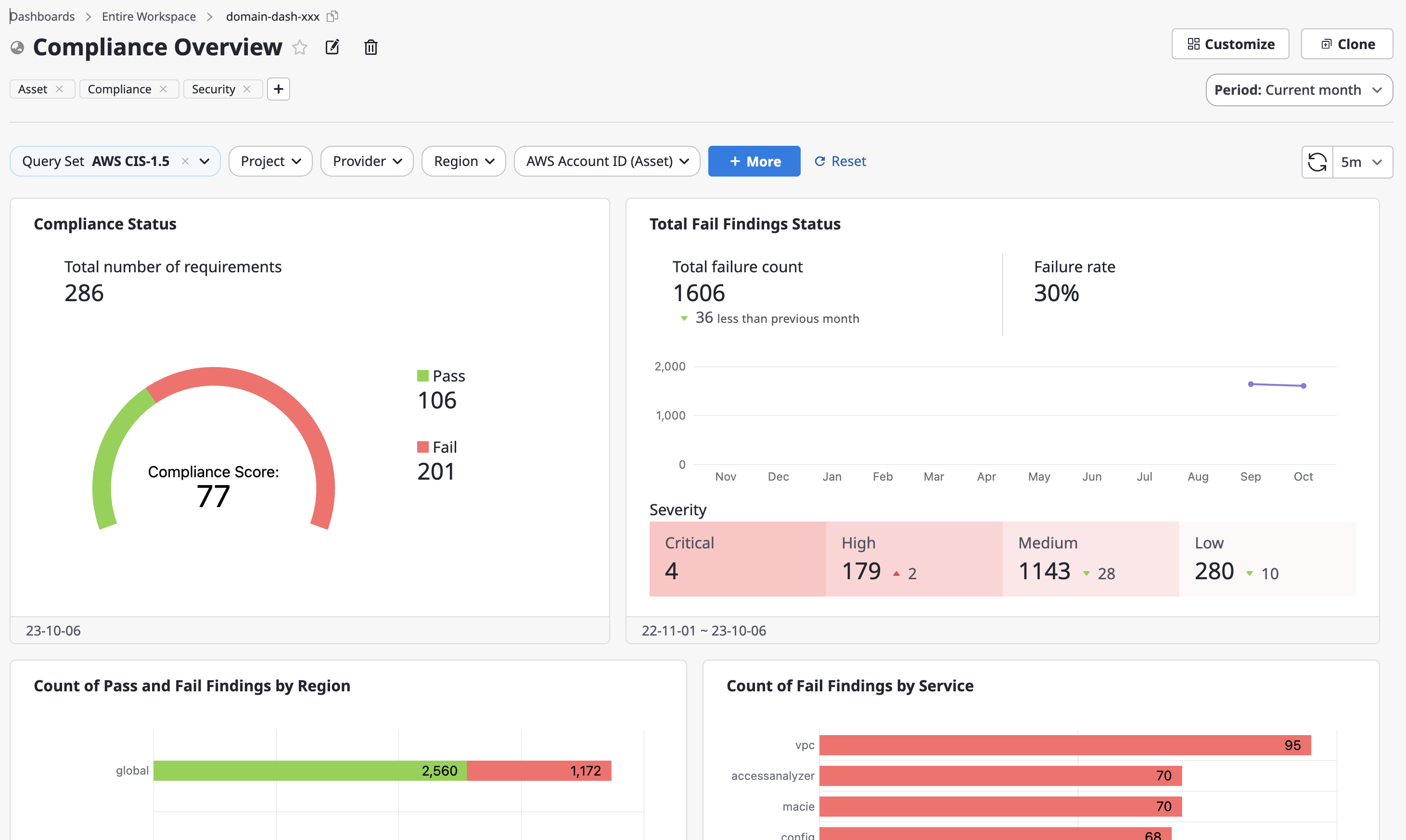
Compliance Overview
This is a dashboard that visualizes compliance configuration audit and monitoring results. One specific Data-Source must be selected.
2.2 - Create Dashboard
Creating a new dashboard
You can create a dashboard following the steps below.
(1) To create a new dashboard, you can either click on [Dashboard > Create New Dashboard] in the top menu or click the [+] button at the top of the left-hand menu within the dashboard service to go to the creation page.
(2) On the "Create New Dashboard" page, select the dashboard scope and choose whether it should be public or not.
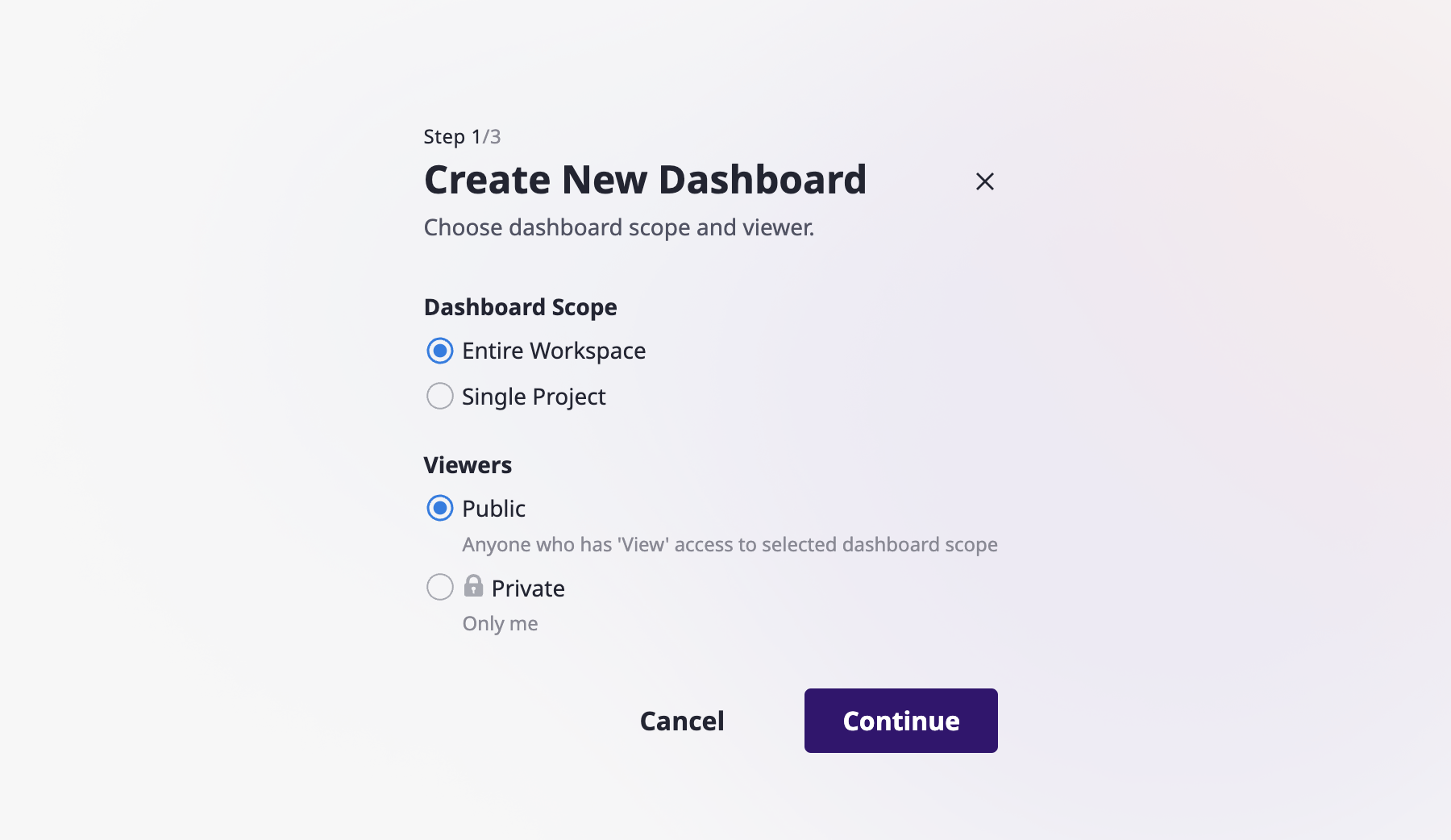
- Entire Workspace : The data for the entire workspace's projects will be displayed.
- Single Project : The dashboard will be configured using only the data from a chosen project.
(3) You can select from the default templates provided by Cloudforet or choose to duplicate an existing dashboard. After selecting your preferred options, click the [Continue] button.
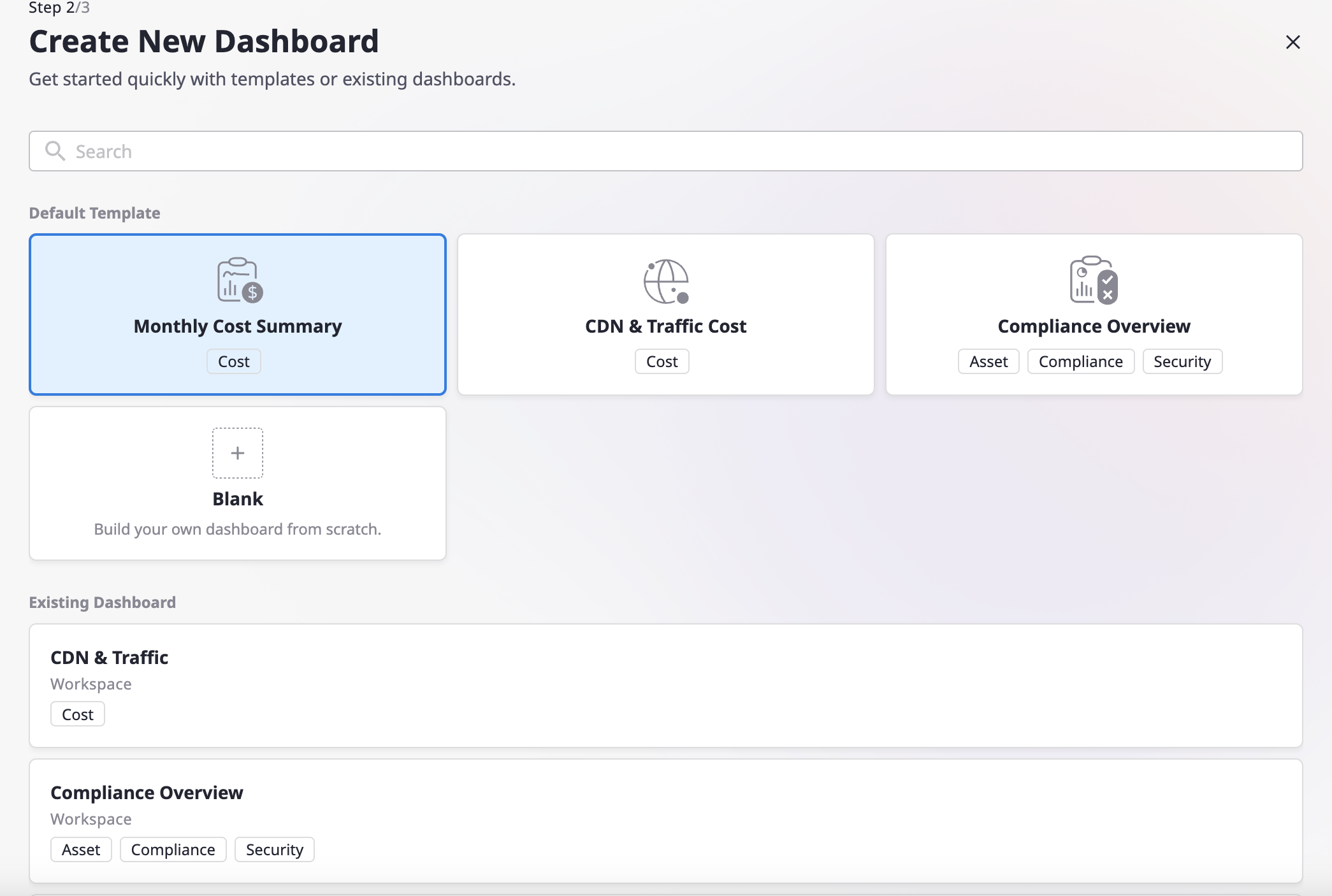
(4) After entering the dashboard name, you can complete creating the dashboard using the provided widgets. For detailed editing instructions, refer to here.
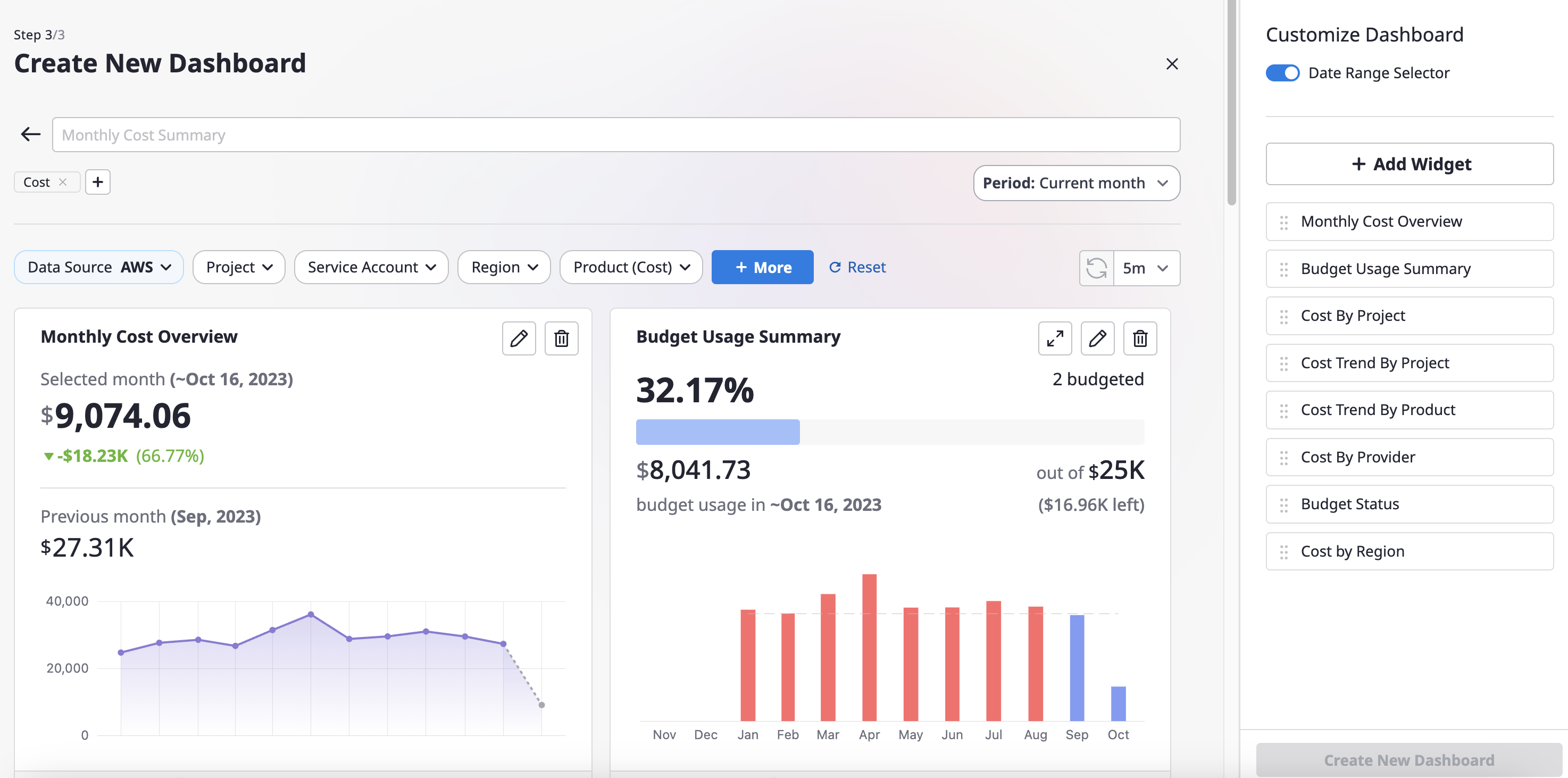
(5) The created dashboard can be found on the [View All Dashboards] page, categorized based on [viewers] and [scope].
To review the created dashboard and make quick adjustments, please refer to here.
2.3 - Customize Dashboard
Customizing your dashboard
Switch to 'Customize' mode
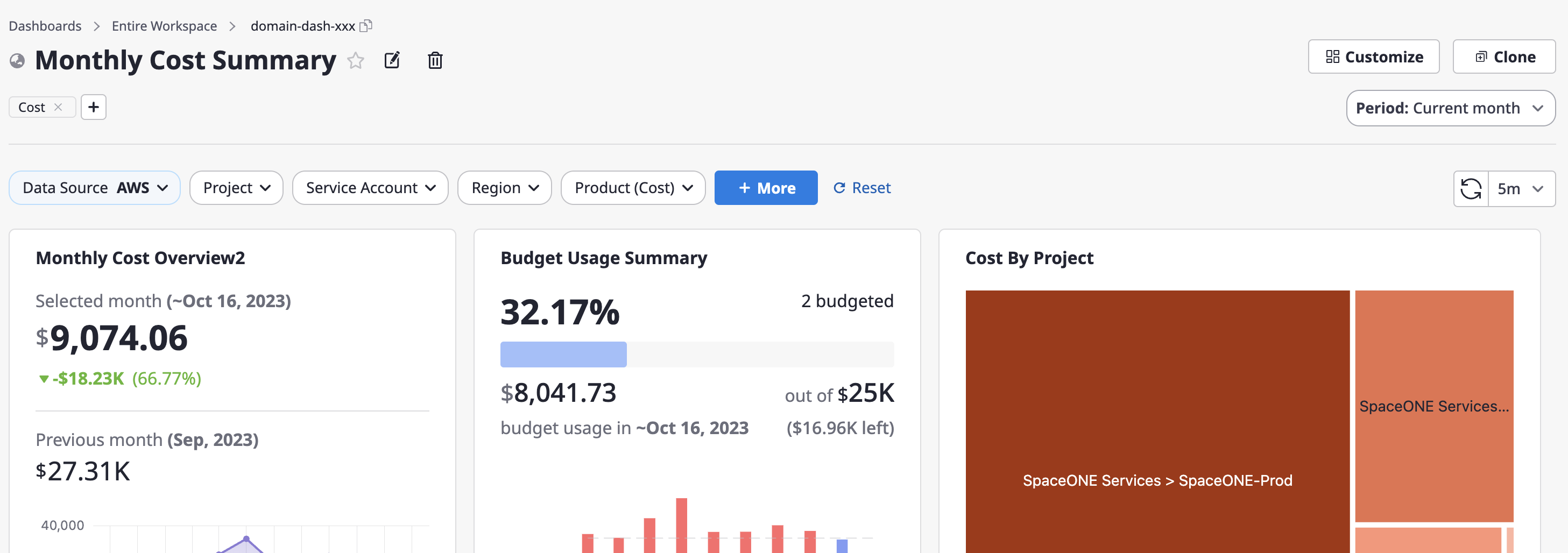
Clicking the [Customize] button on the right side of a dashboard page will take you to the dashboard editing page.
Rename the dashboard
You can click the [Edit] icon button next to the dashboard title to make changes.
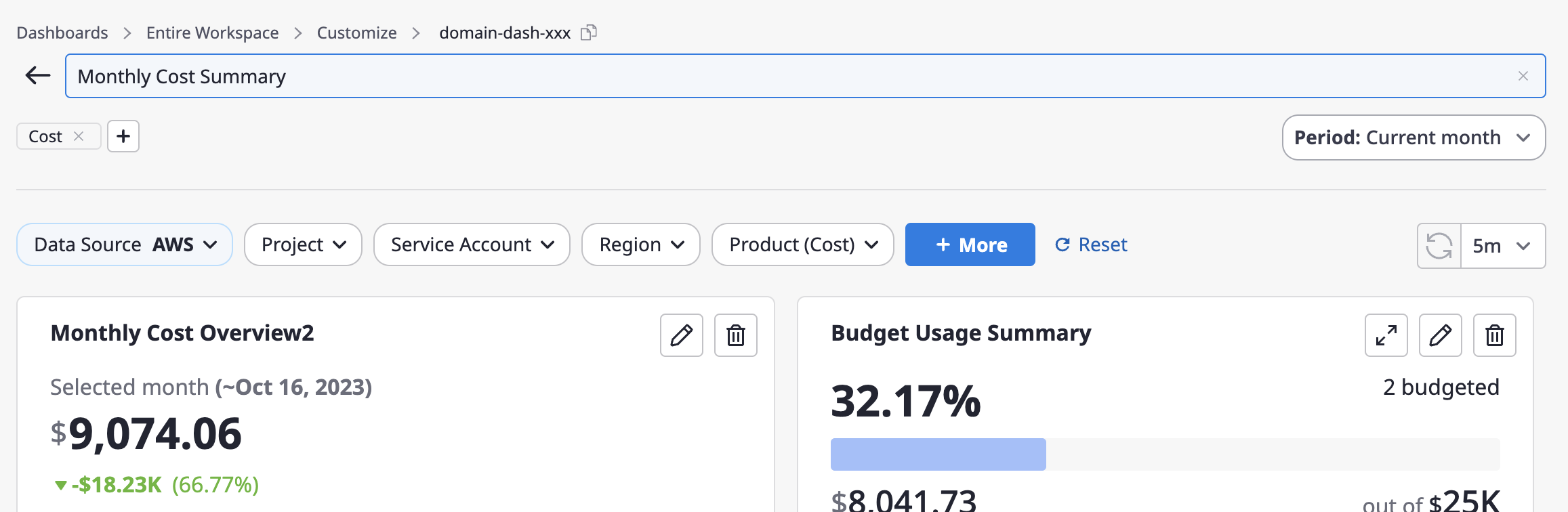
Manage labels
You can add or remove labels just below the dashboard title at the top. Labels are used to categorize and differentiate dashboard-related categories and features, making them useful for dashboard searches.
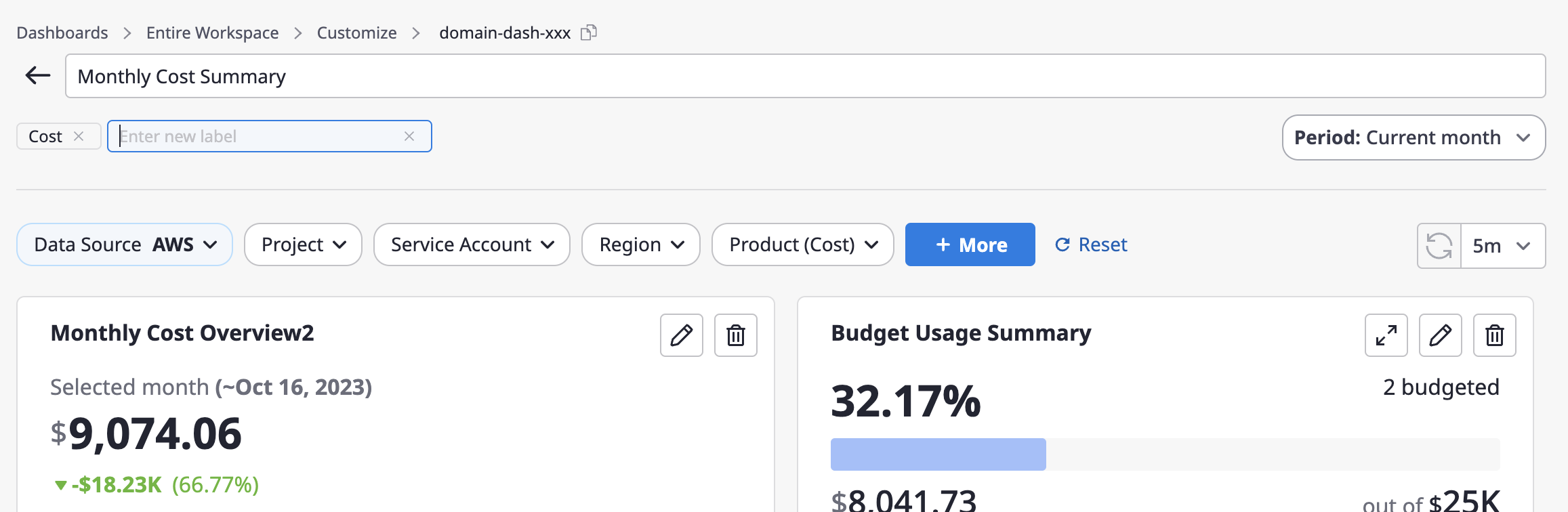
Apply a period range
(1) When you activate the [Date Range Selector] option from the right side panel, a dropdown button for setting the period will be displayed on the dashboard.
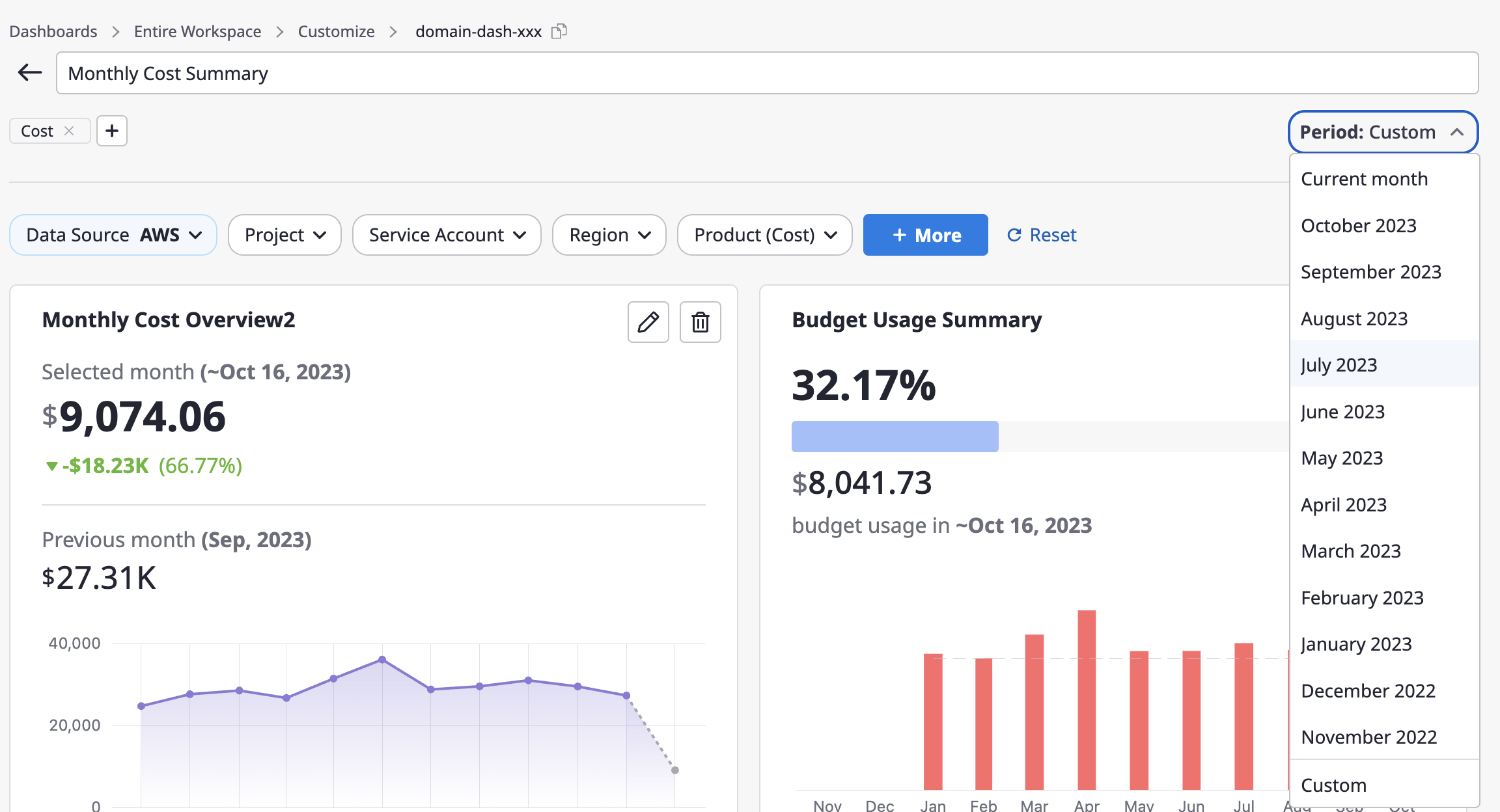
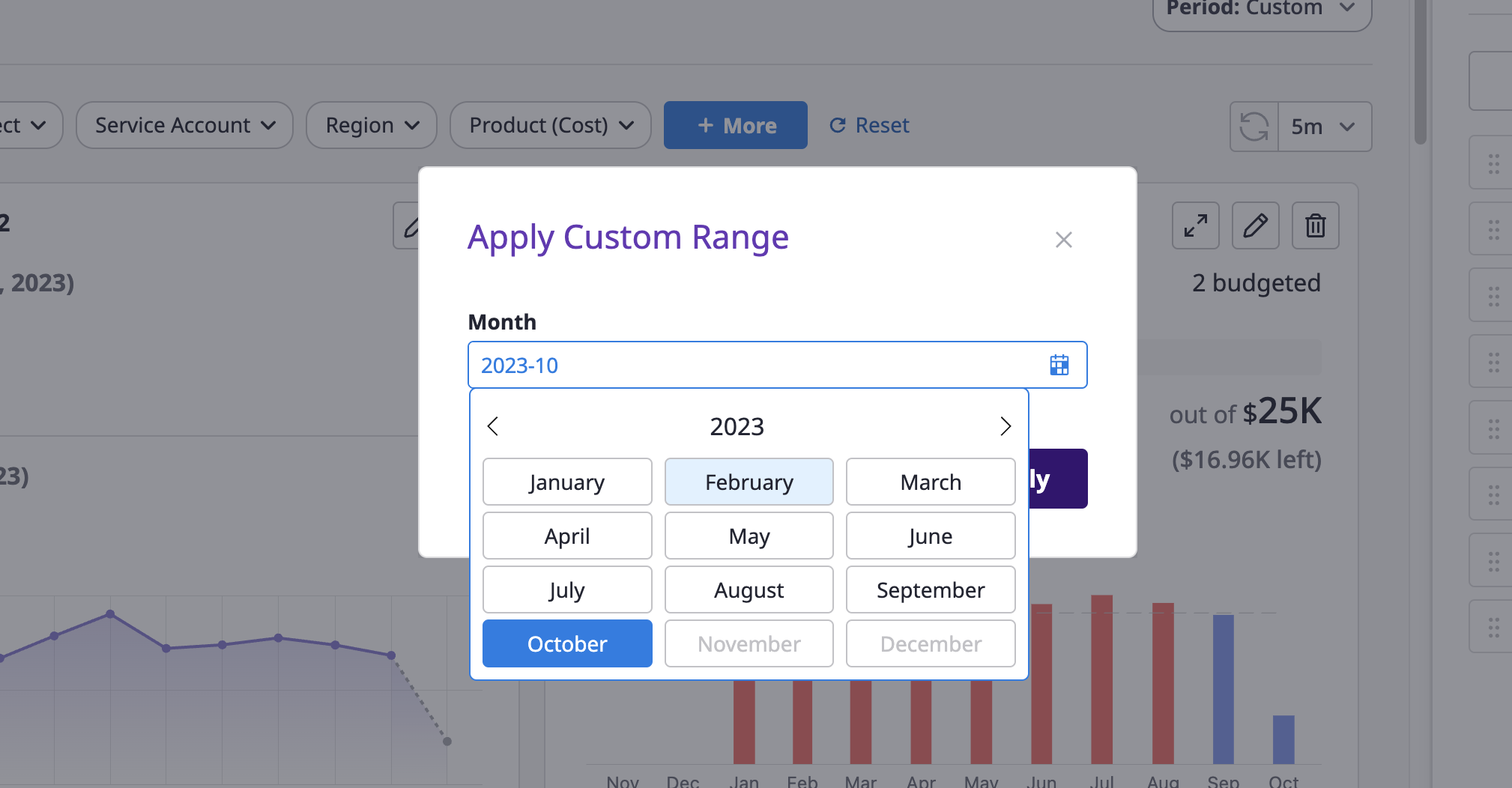
(2) You can select a specific month from the drop-down or choose a specific month within the last 3 years using the [Custom] menu.
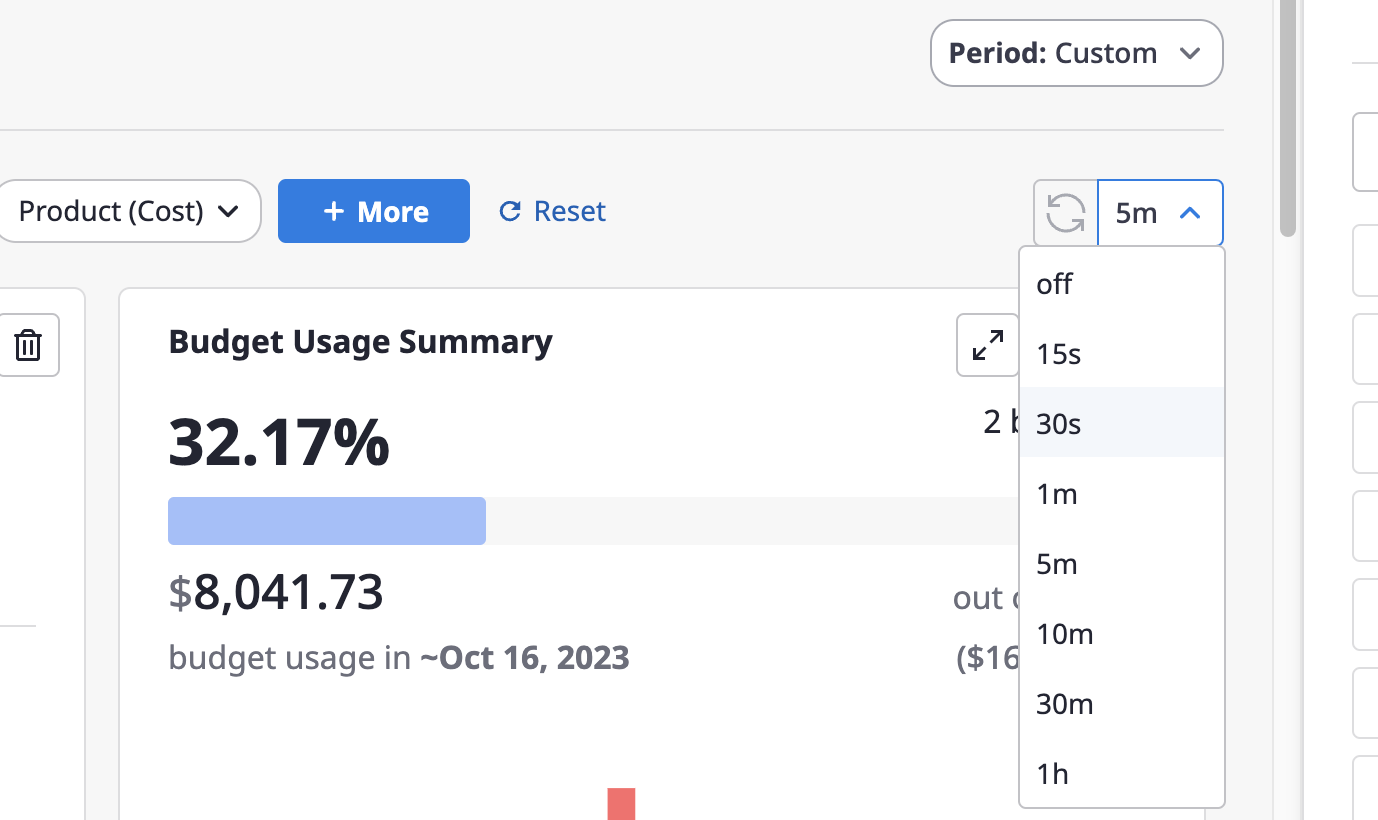
Configure auto data refresh
You can choose the data refresh interval from the [Refresh] dropdown in the upper right corner of the dashboard.
Add widgets
(1) Click the [+ Add Widget] button on the right-hand dashboard editing page.
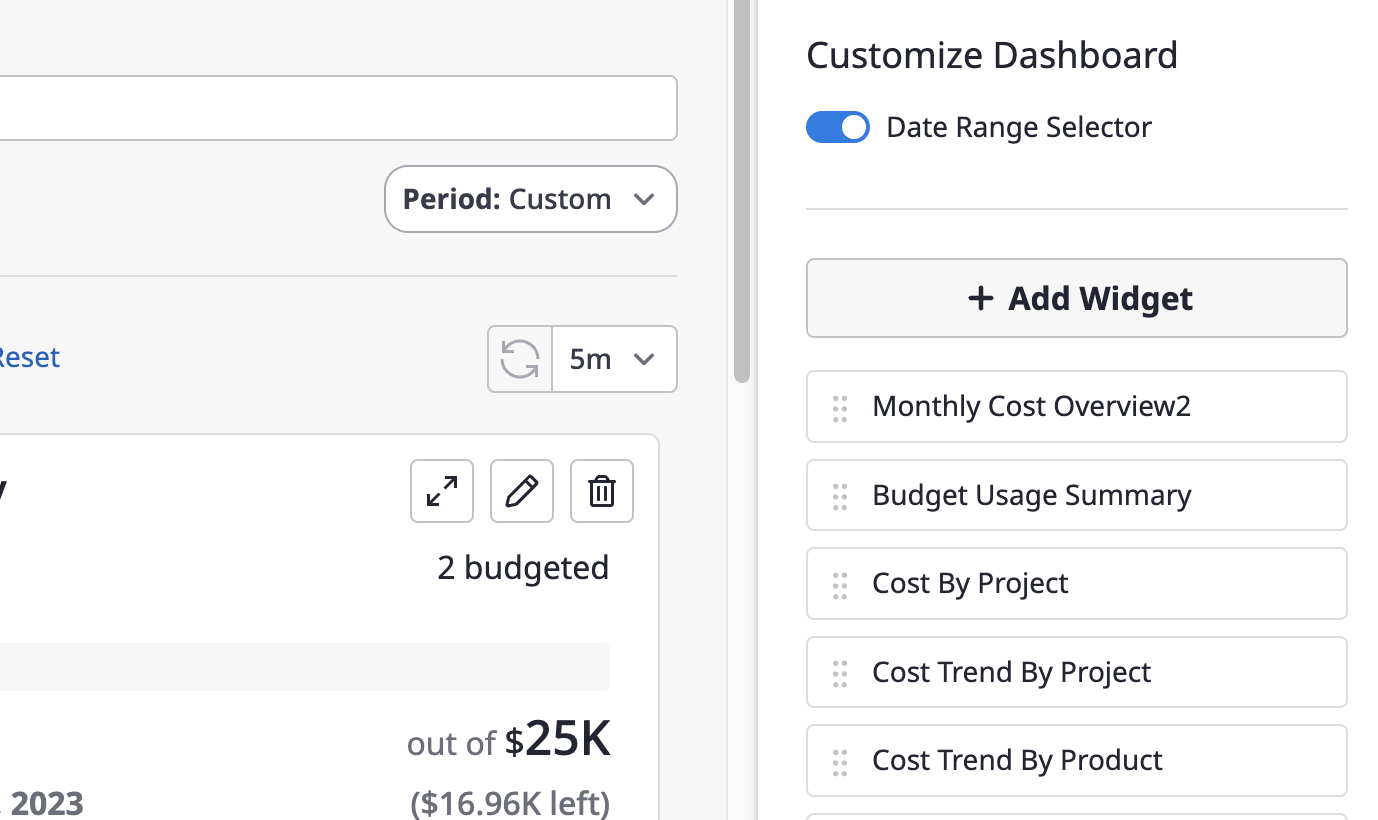
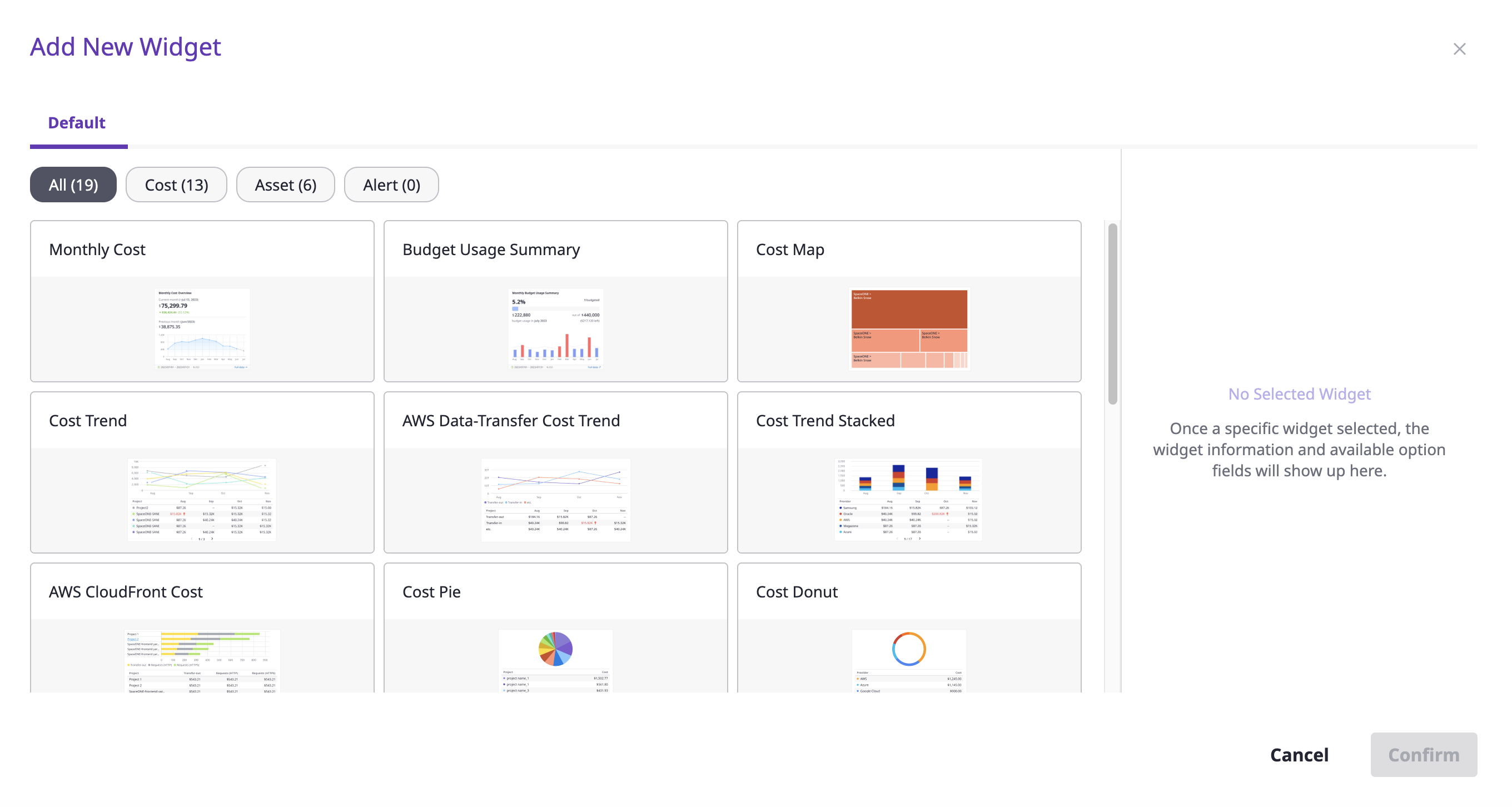
(2) Select a specific widget from the list on the left and add it.
(2-2) If you have selected a specific widget, you can enter the [Name] and set the detailed options.
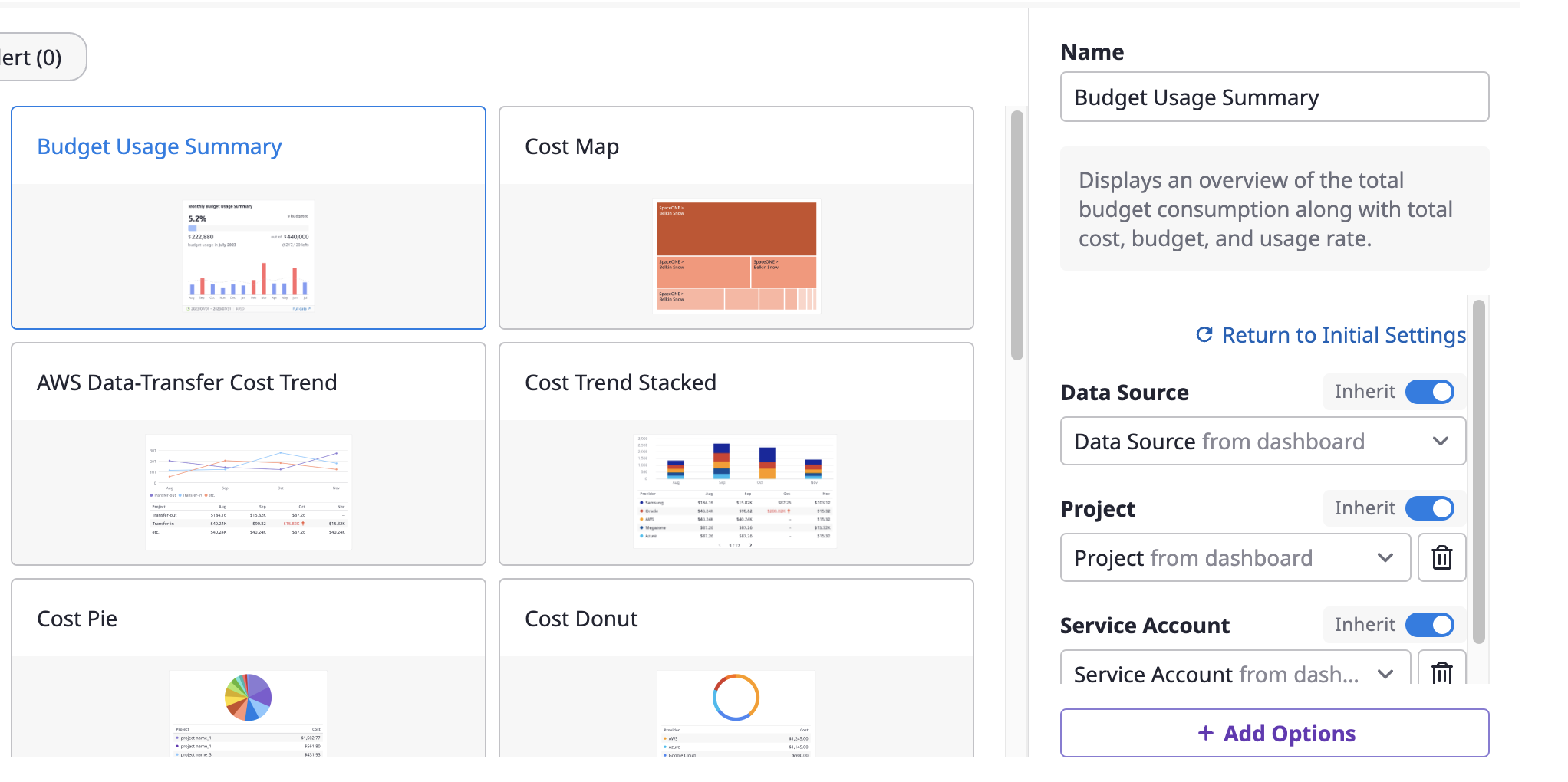
e.g. In the Cost Map widget, the
Project option is set to 'Inherit' and if you filter Project to 'Project A' at the dashboard level, the widget will now display data relevant to 'Project A' only.(2-3) If there are no additional options you want, you can click the [+Add Option] button to add them.
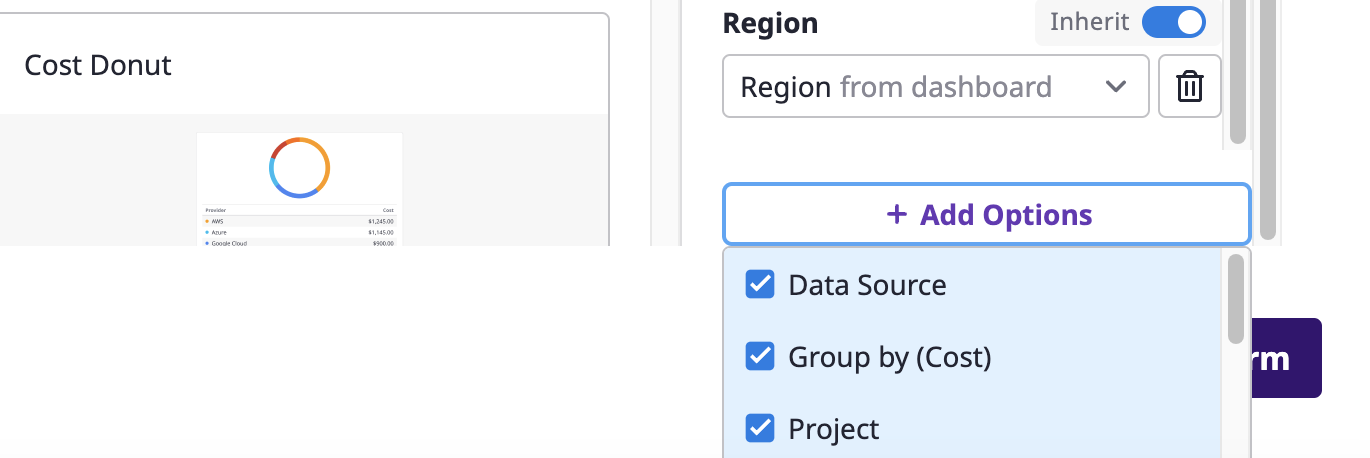
(2-4) When you've finished the configuration, click the [Confirm] button to complete adding widgets to the dashboard.
Rearrange the widget order
You can change the order by drag & drop the widget name button from the widget list in the right panel.
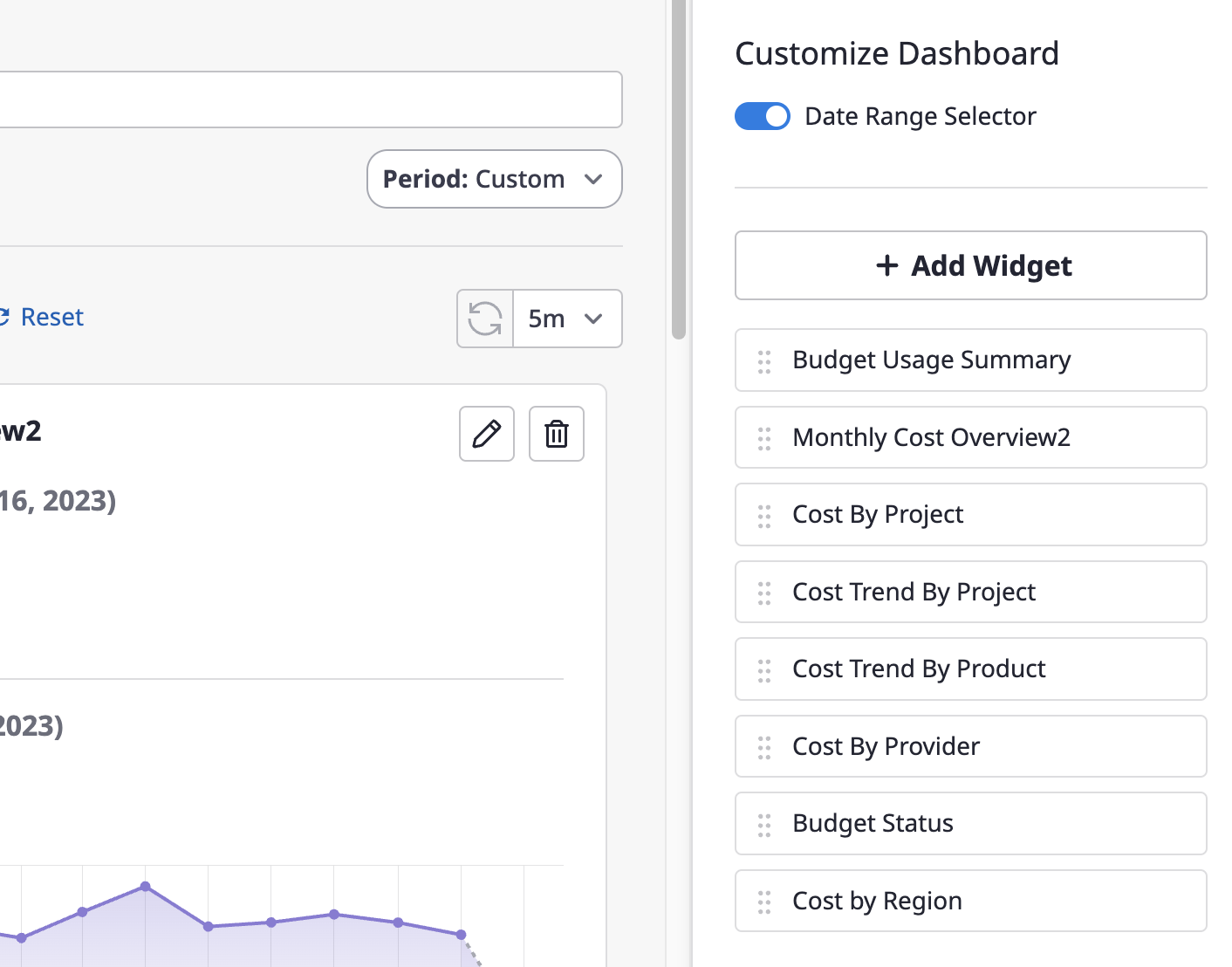
Enlarge widget size
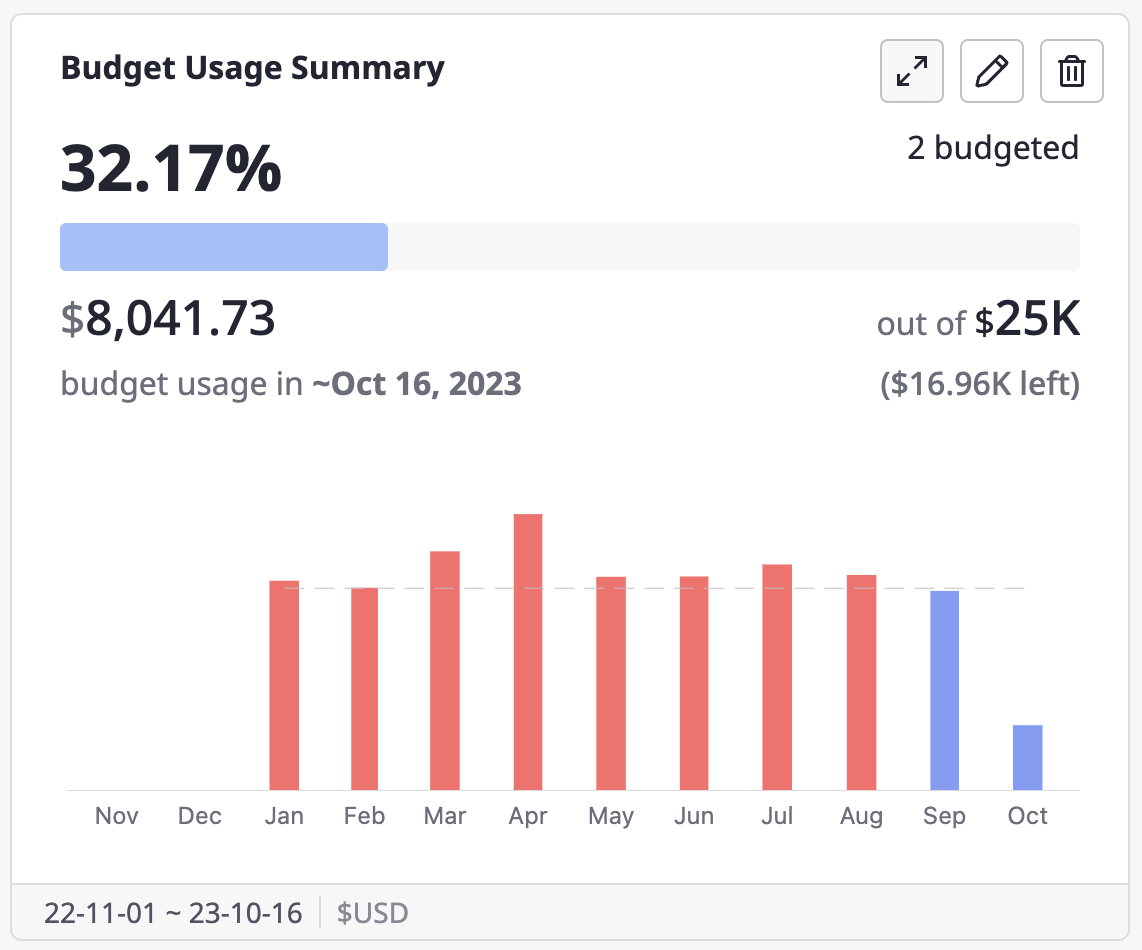
If you want to view a widget in full-screen, click the [Full Screen] icon button in the top right corner of the widget.
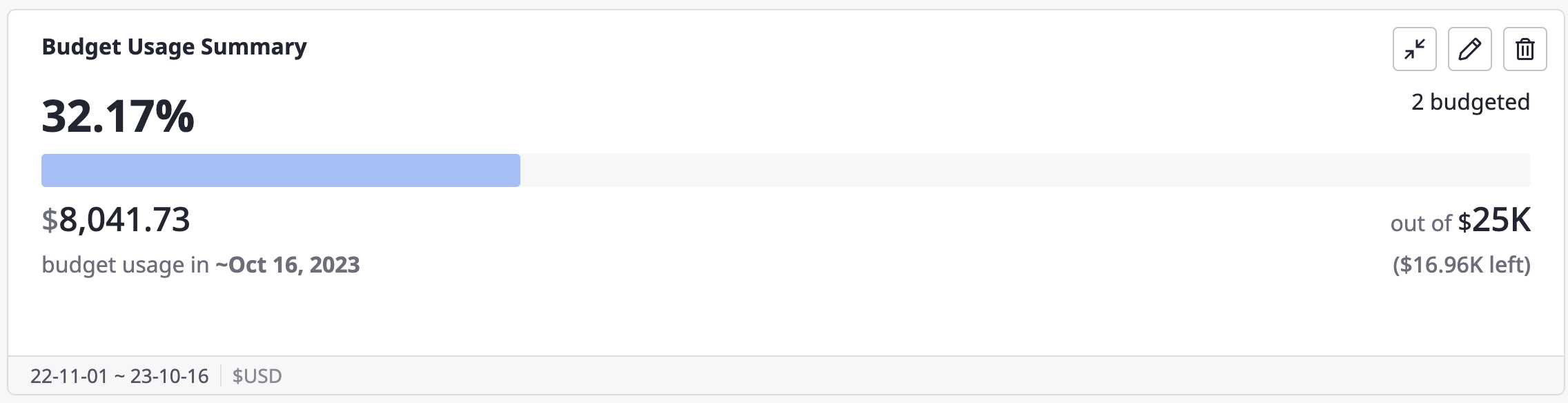
Edit a widget
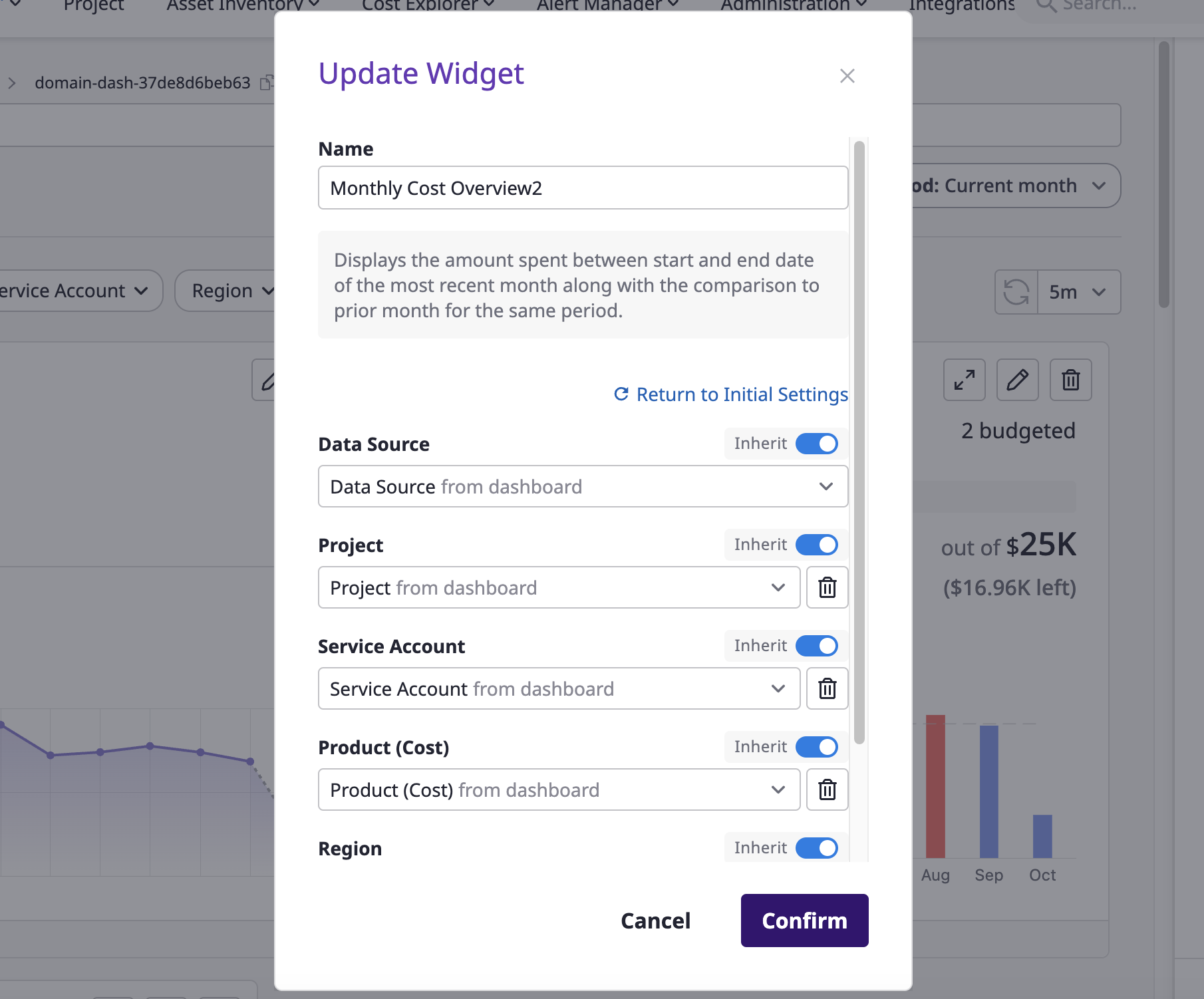
(1) Click the [Edit] icon button in the top right corner of the widget to edit it.
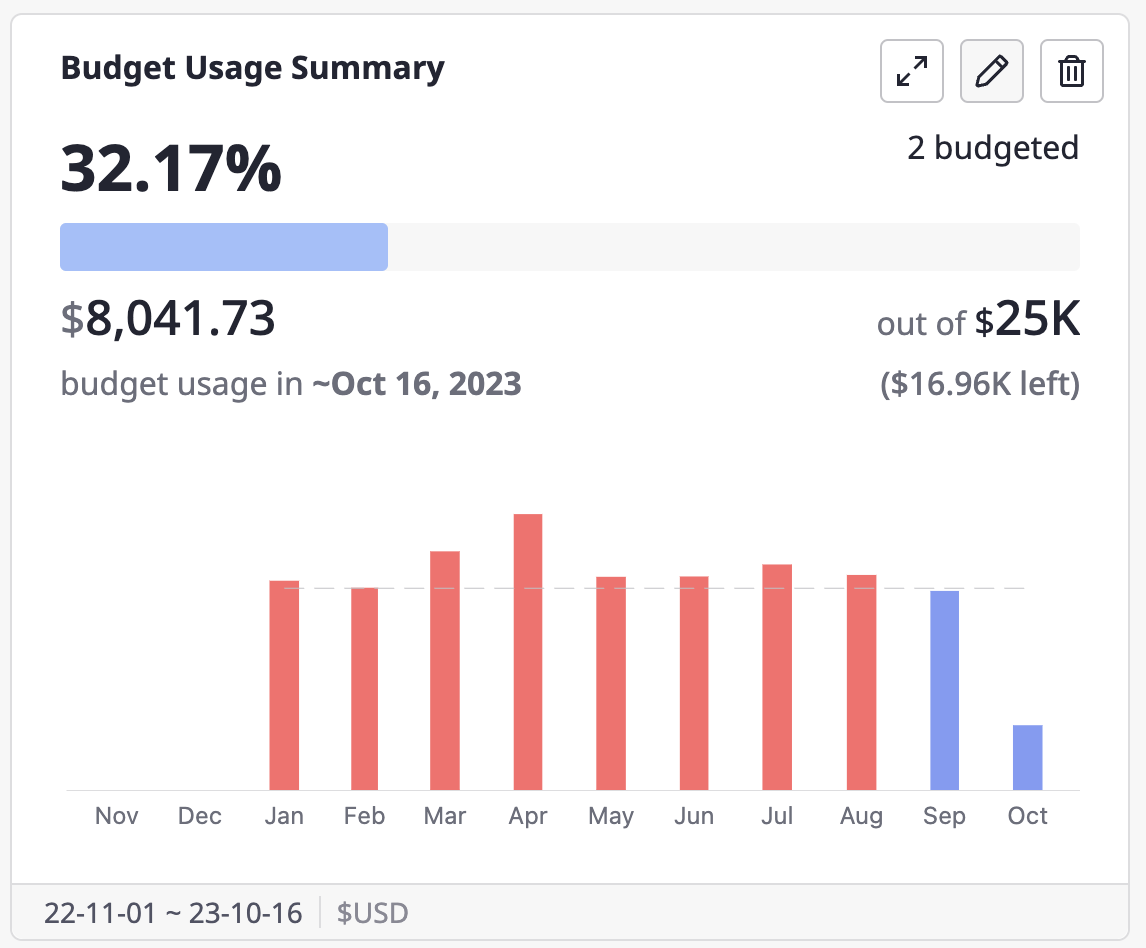
(2) You can edit the widget name and options, then click the [Confirm] button to save your changes. However, if you don't [Save] the dashboard in [Customize] mode, the edited widget won't be reflected in the final version.
- For information on widget option settings, please refer to here.
2.4 - Review & Quick Configuration
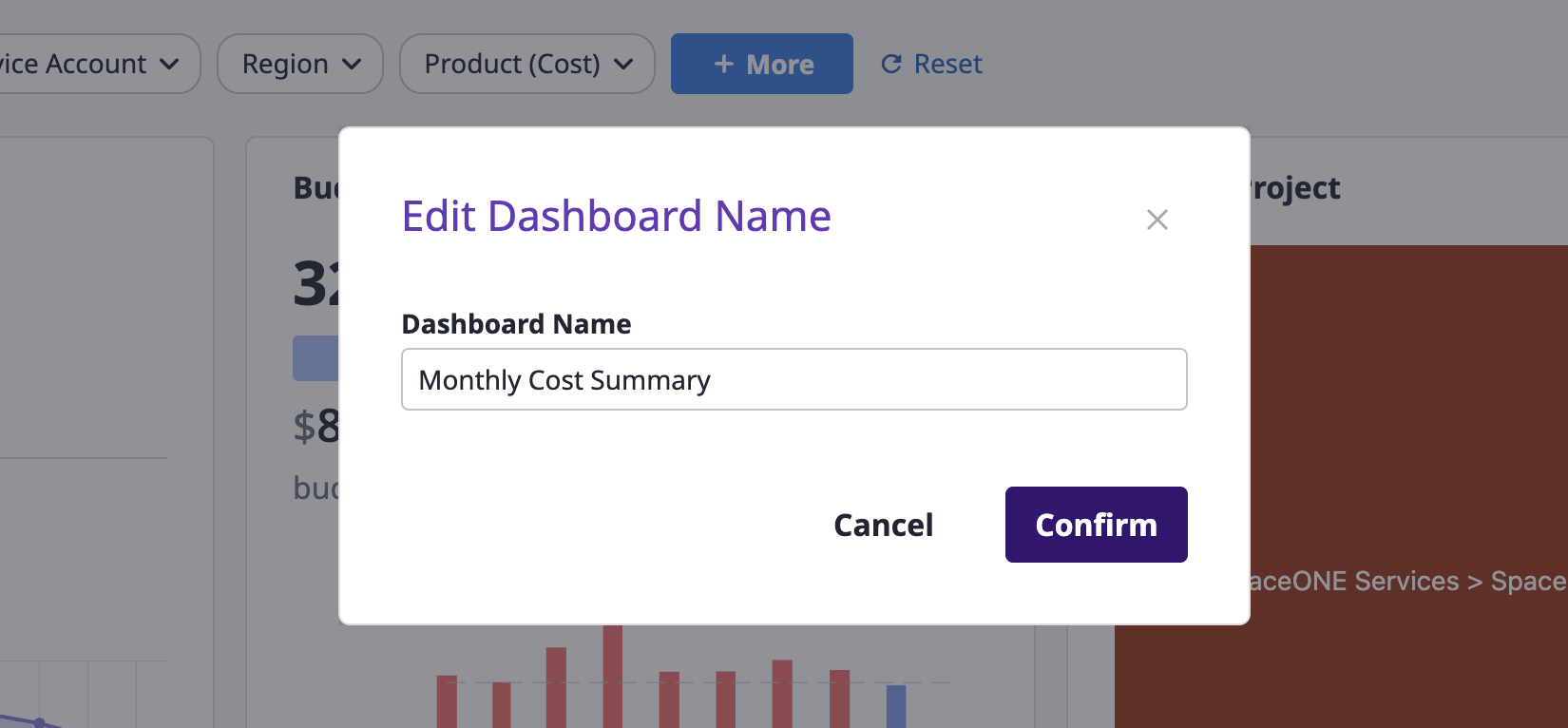
Editing a dashboard's name or Deleting/Duplicating
Editing a dashboard's name
(1) Click the [Edit] icon button next to the dashboard name.
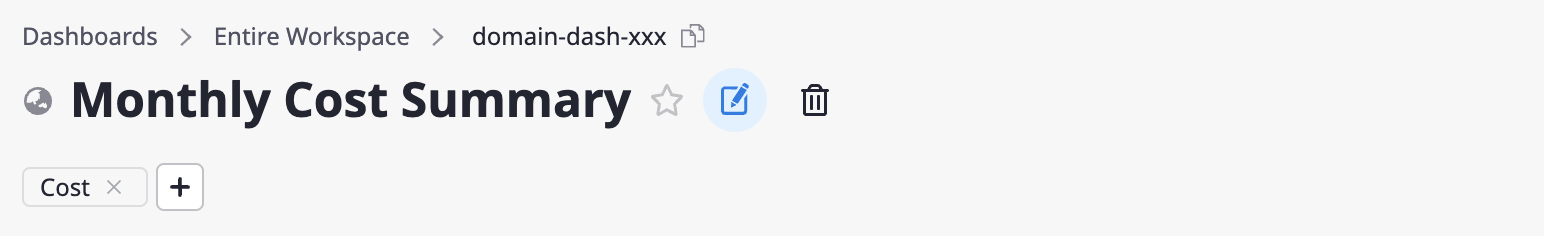
(2) After changing the dashboard's name, click the [Confirm] button.
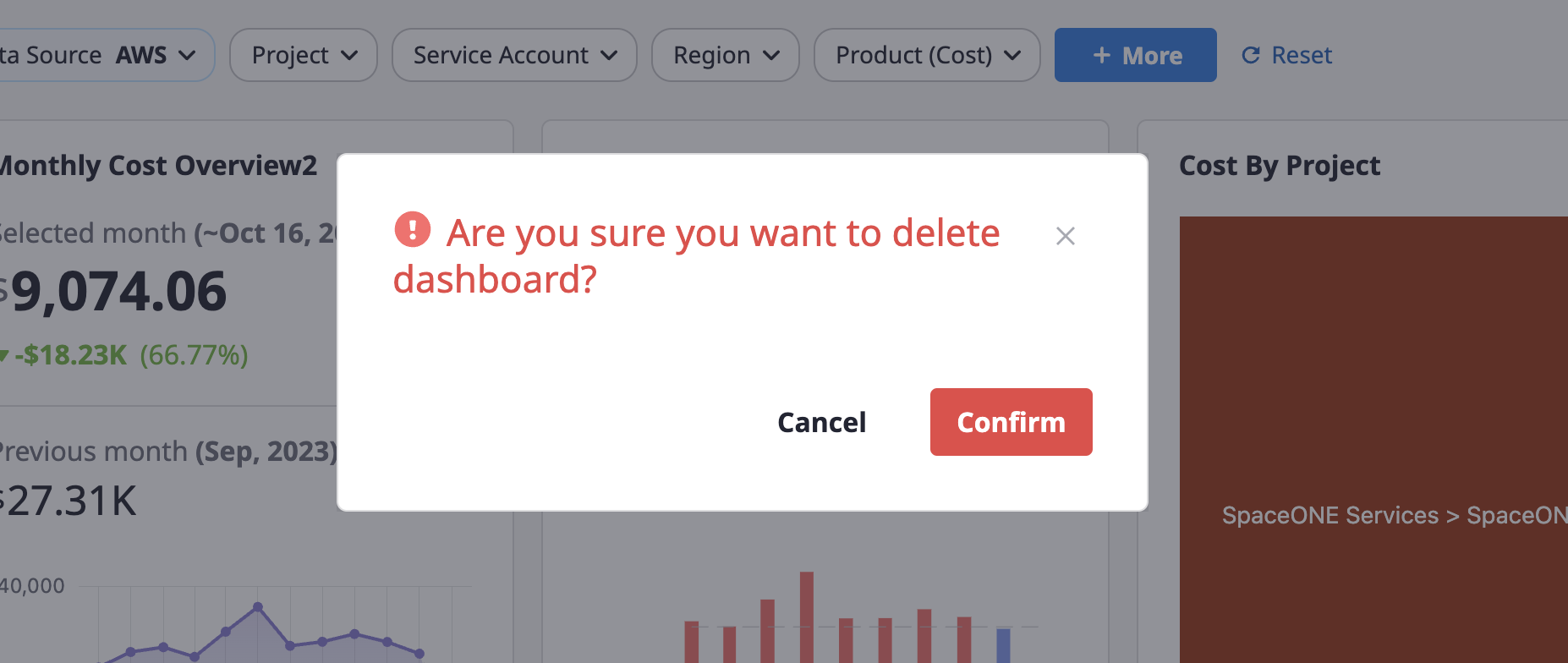
Deleting
(1) Click the [Trash] icon button next to the dashboard name.
(2) Click the [Confirm] button in the [Delete Dashboard] modal to delete the dashboard.
Duplicating
(1) Click the [Clone] button on the right side of a dashboard.

(2) Select the following options and complete the cloning.
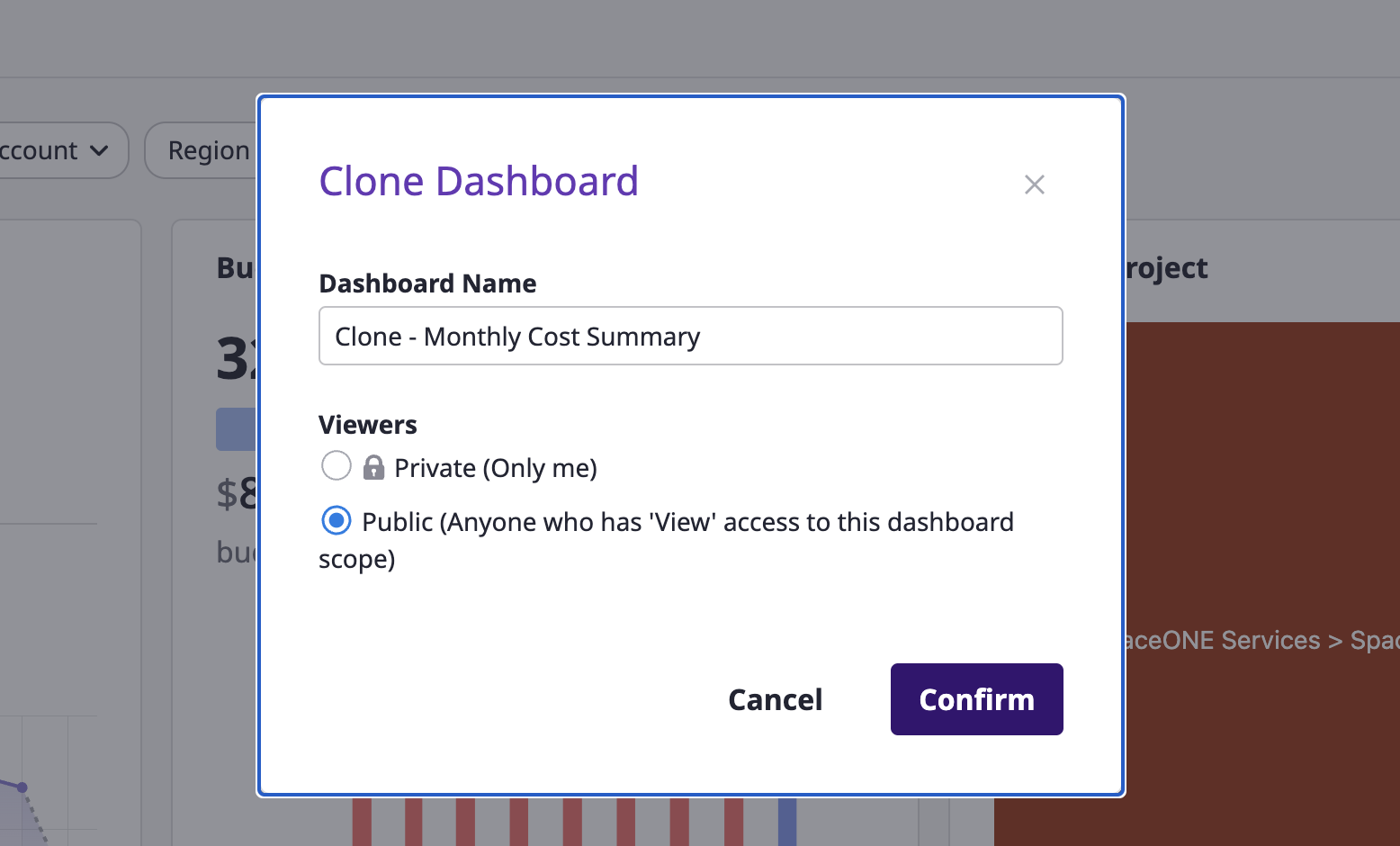
- Dashboard name
- Viewers: Select one between
PrivateandPublic.
Managing labels
Label addition/removal can be done in the same way as on here.

Setting filters
When you set up filters, you can view the dashboard data filtered by the desired conditions.
(1) Choose the specific options of the desired item from the Variables section at the top of the dashboard.
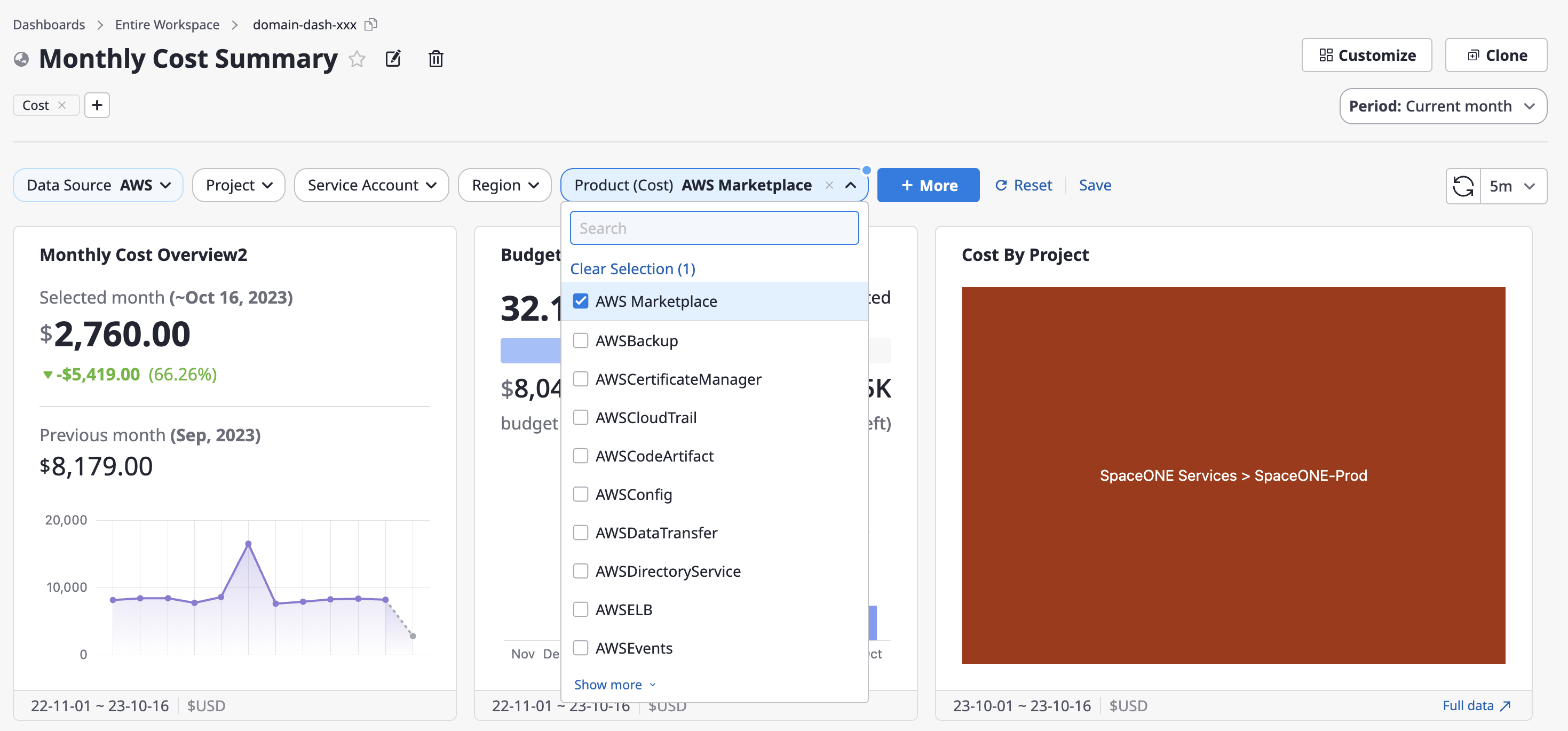
(2) If there are differences from the previously saved settings, the [Save] button on the right side will be activated, allowing you to quickly save the changes.

(3) If you want to revert your changes to the most recently saved values while in the process of changing options, click the [Reset] button.
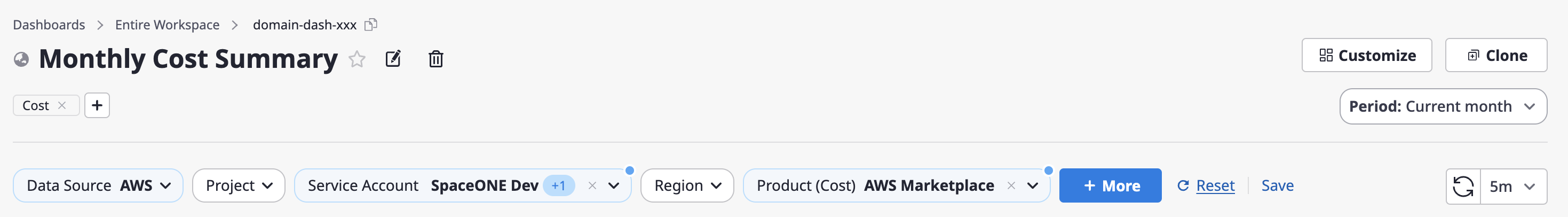
(4) Click the [+ More] > [Manage Variables] button to review all available variables or add custom variables.
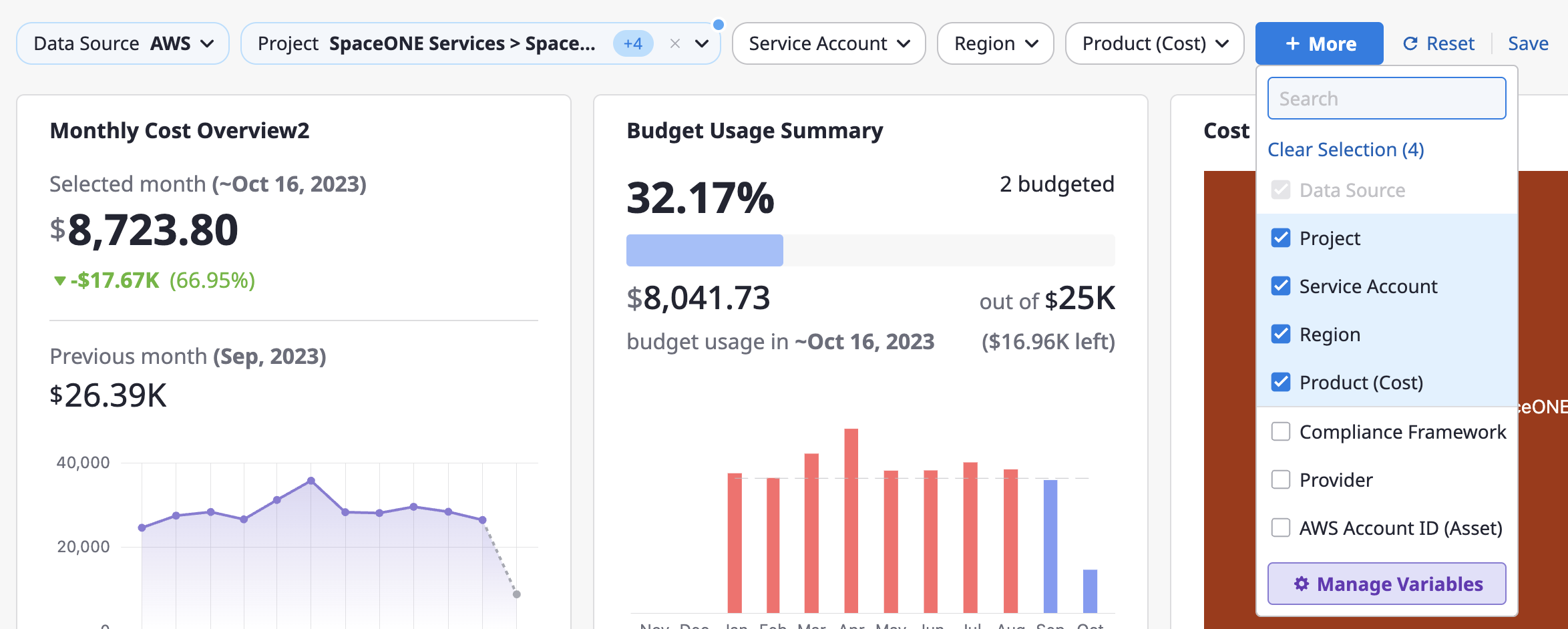
(4-1) If you need to add custom variables, click the [+ Add Variable] button in the upper right corner of the [Manage Variables] window.
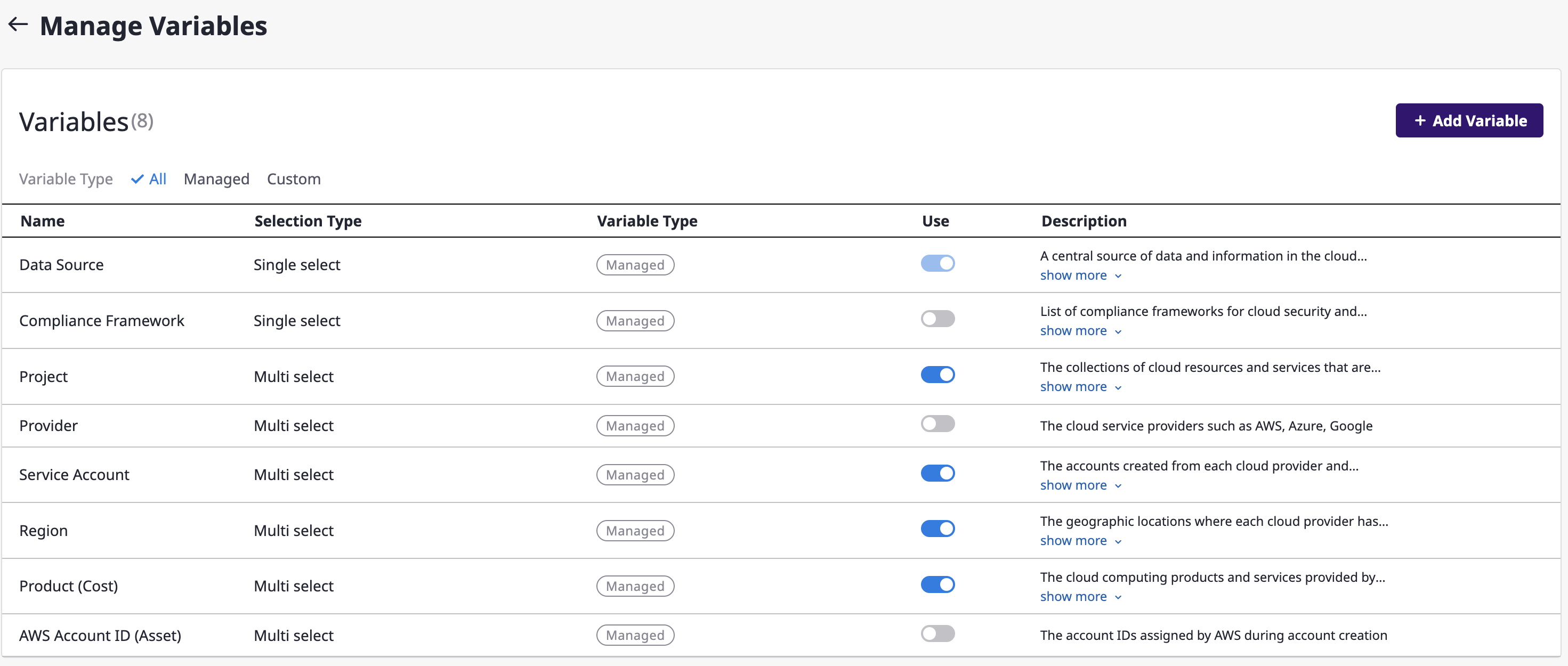
(4-2) After entering the basic information for the variable you want to add, click the [Save] button.
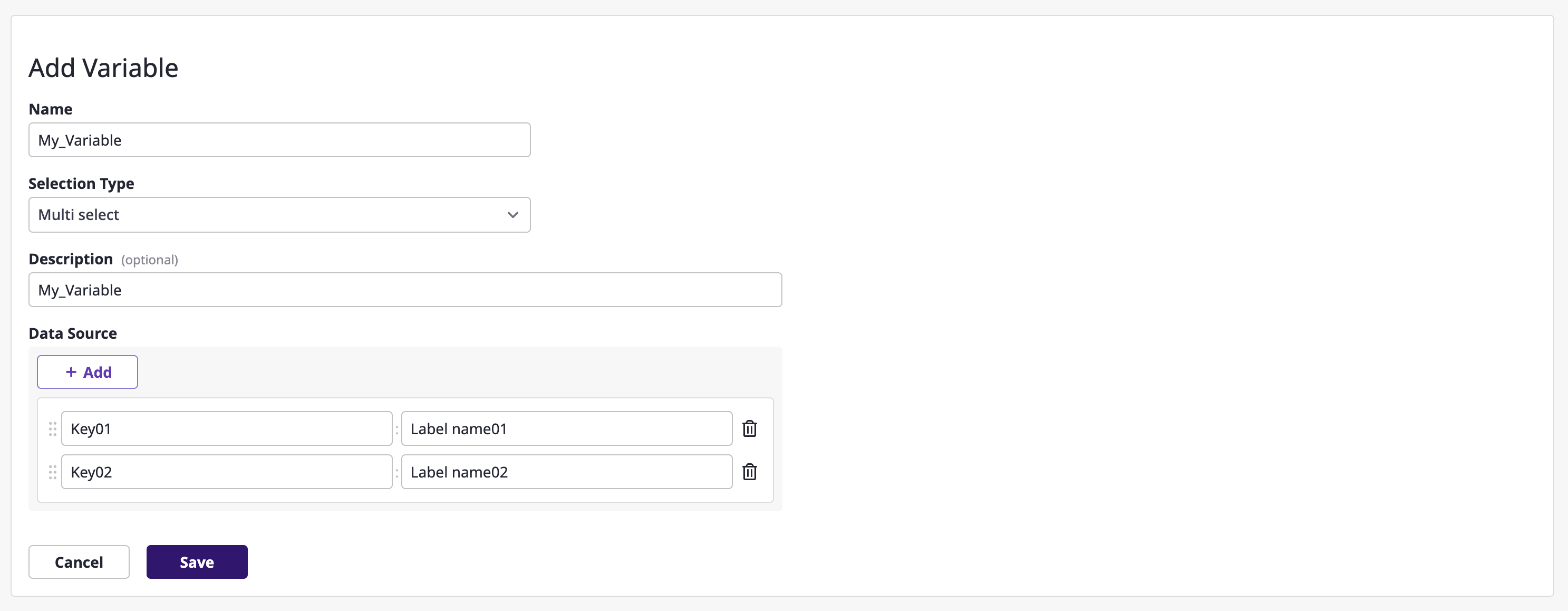
Setting the period
In the dashboard's top-right [Period] dropdown, you can select a specific month or choose a specific month within the last 3 years using the [Custom] menu.
Configuring auto data refresh
You can select the data refresh interval from the [Refresh] dropdown in the top right corner of the dashboard.
Viewing and editing widget settings
(1) Click the [Full Screen] icon button in the top-right corner of a specific widget
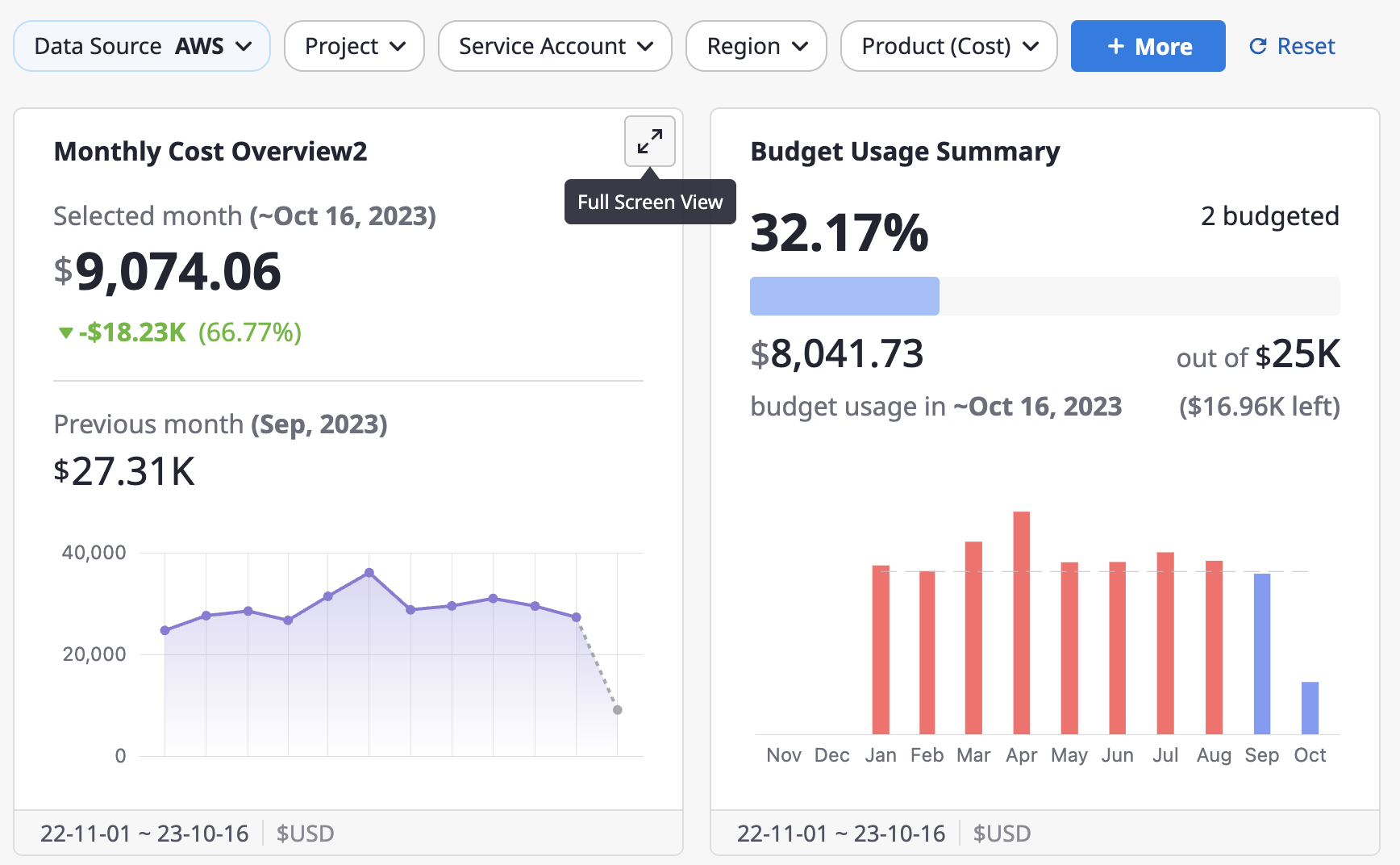
(2) In full-screen mode, you can examine detailed widget data. The top filter options are the same as the dashboard variables, and you can explore each option to get a closer look at the widget's data.
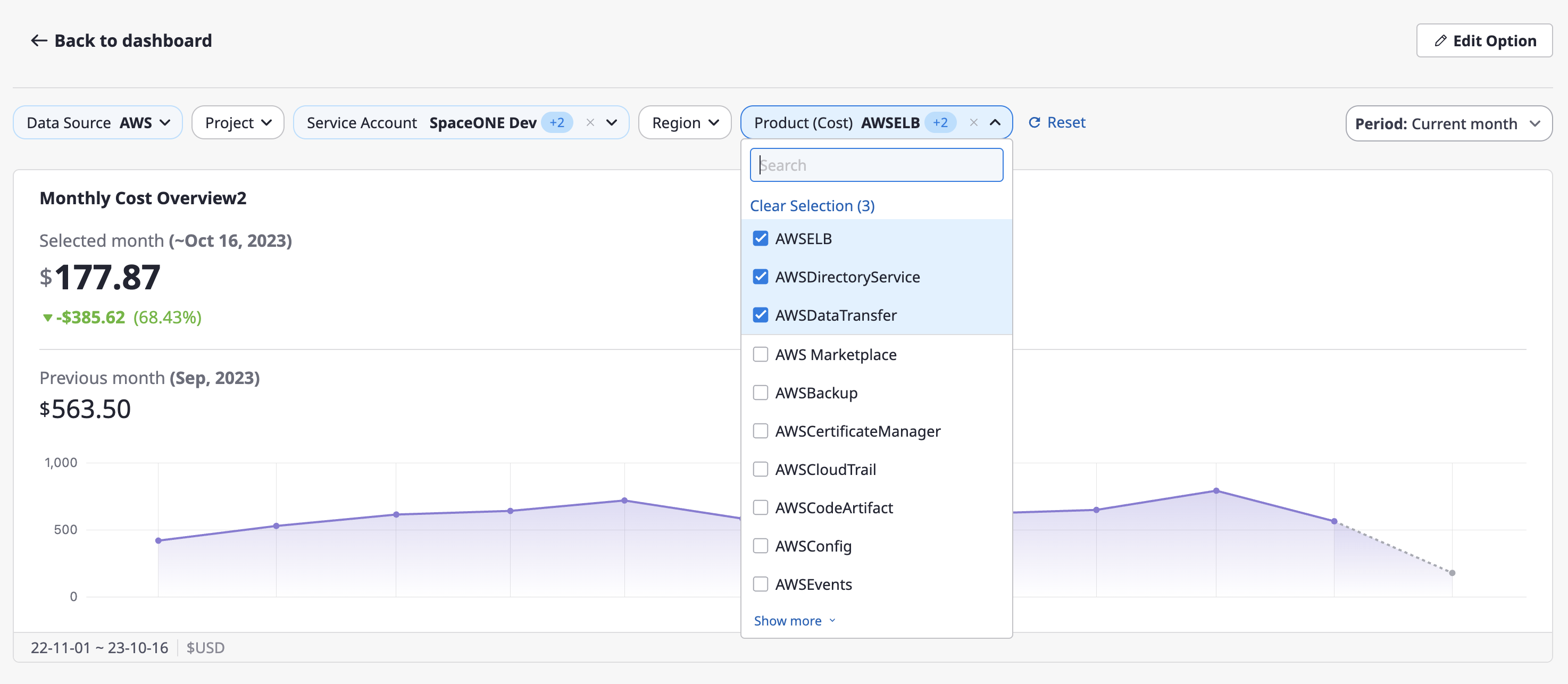
(3) If detailed editing of the widget is required, click the [Edit Options] button in the top-right corner.

(4) Similar to [Customize] mode, you can edit and save the specific items of the widget.
- For information on widget option settings, please refer to here.
3 - Project
Create a Project group and a Project on the project page of Cloudforet, and invite your member.
3.1 - Project
A project must belong to a specific Project group, and there can be no more hierarchies below the project.
Invite a Member to the project and assign a Role that differentiates their access privilege to project resources.
Creating a project
(1) From the [Project group] list on the left side of the [Project] page, select a project group for which you will create a project.
(2) Click the [Create project] button at the top right.
(3) After entering a project name in the [Create project] modal dialog, click the [OK] button to create the project.
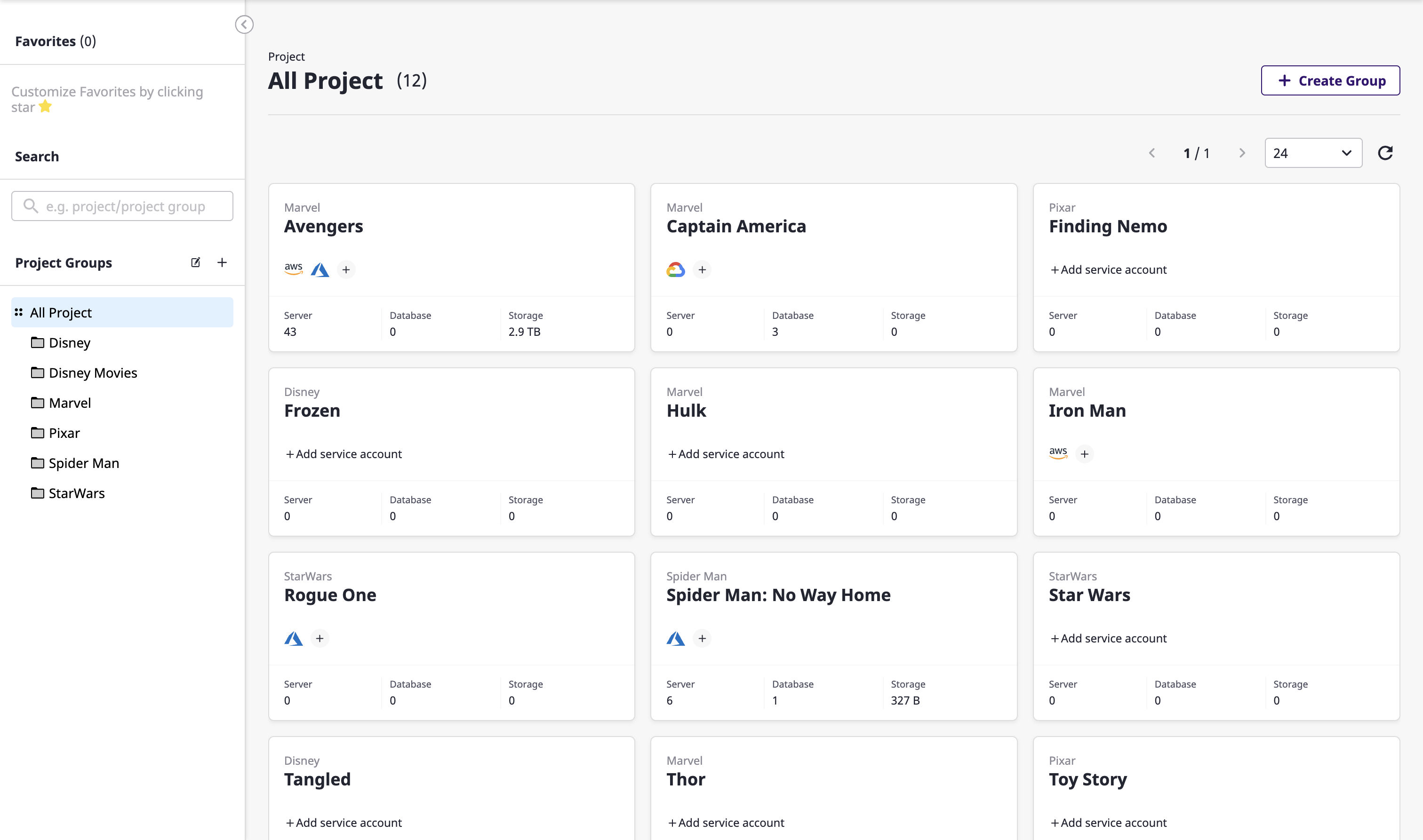
Viewing the project list
From the project list, you can easily check the resource status of the major categories of each project.
You can also enter a search word to see a list of project groups and projects that match your criteria.
Getting a list of all projects
You can view a list of the entire projects by selecting [All projects] from [Project groups] on the left.

Viewing a list of projects in a project group
You can select the project group you want from the [Project group] list on the left to view projects belonging to that group only.
If there are other project groups under the selected project group, the projects belonging to such other project groups are not displayed here.
- Project Group A
- Project Group B
- Project B-1
- Project B-2
- Project A-1
- Project A-2
For example in the above structure, if you select Project Group A, only Project A-1 and Project A-2 would be displayed in the list.
Exploring projects
Select a project from a list of projects to enter the project detail page.
Project Dashboard
In the [Summary information] tab, you can check the aggregated information of the resources belonging to the project through the project dashboard.
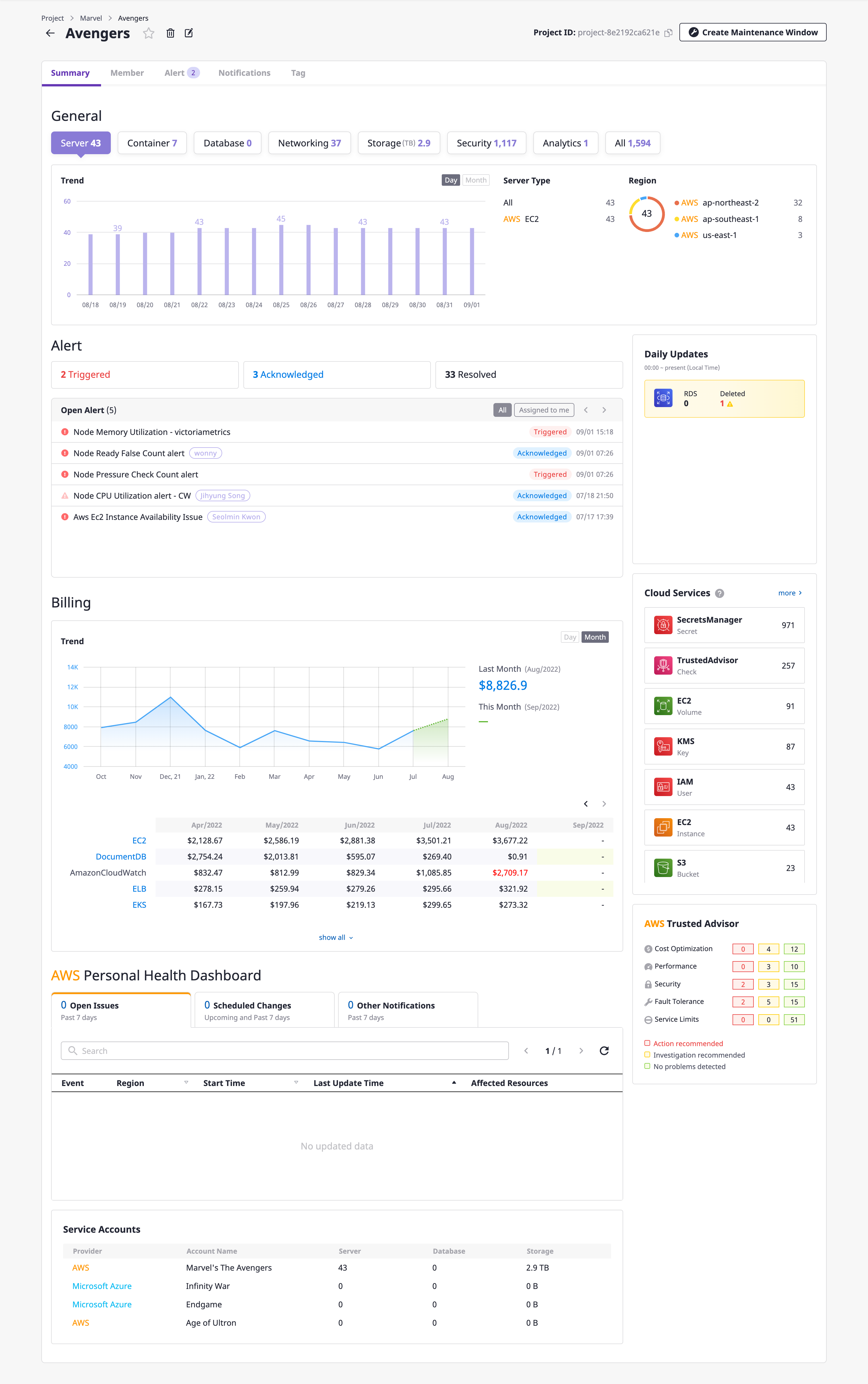
The project dashboard shows the status of resource usage and trends by category and region.
In addition, statistical information about the project in diverse formats through multiple widgets helps to manage resources more efficiently and minimize costs.
Below is a list of widgets on the project dashboard.
| Project dashboard widget name | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert | Information on alerts that occurred in the project |
| Cost | Cost information for the project |
| Today's resource updates | Resource information updated from midnight local time to the present |
| Cloud services | Information on major cloud services among the services |
| AWS Personal Health Dashboard | Information on AWS Personal Health Dashboard |
| AWS Trusted Advisor | Information on AWS Trusted Advisor |
Edit project
Changing project name
(1) Click the [Edit] icon button to the right of the project name.
![]()
(2) After entering the name to be changed in the [Change project] modal dialog, click the [OK] button to change the project name.
Managing project tags
You can manage it by adding tags to your project.
(1) Click the [Edit] button inside the [Tag] tab.
(2) Click the [Add Tag] button on the [Tag] page.
(3) Enter the value to be added in the form of ‘key:value.’
(3-1) If you want to add more tags, click the [Add tag] button as many as the number of tags you want.
(4) Click the [Save] button to finish adding tags.
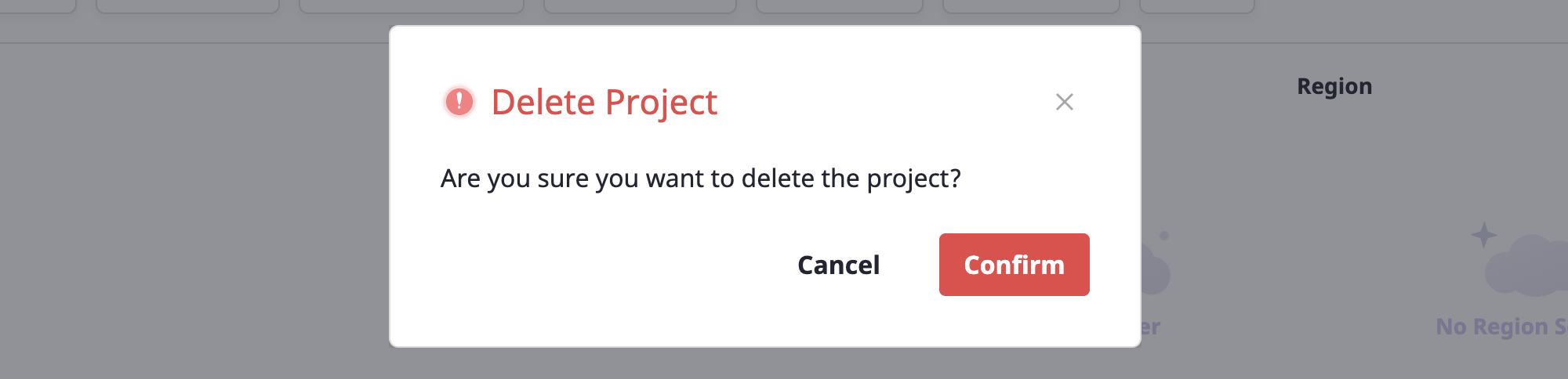
Deleting a project
(1) Click the [Delete] icon button to the right of the project name.
![]()
(2) Click the [OK] button in the [Delete project] modal dialog to delete the project.
3.2 - Member
Members are always assigned at least one role for each, which allows them to manage access to the project and project group.
• Roles of project group members are equally applied to all project groups and projects under such roles.
• Roles of project members are applied only to corresponding projects.
• If roles of members exist for multiple project groups that exist in the upper hierarchy, the roles granted to each are merged and then applied.
Manage project group members
You can manage members by entering the [Manage project group members] page.
(1) Select the project group whose members you want to manage from the [Project group] list on the left side of the [Project] page.
(2) Click the [Manage project group members] icon button at the top right.
![]()
(3) Enter a search word on the [Manage project group members] page to view a list of projects that meet the criteria, invite new members, or edit/delete members.

Inviting project group members
(1) Click the [Invite] button on the [Manage project group members] page to open the [Invite members] modal dialog.
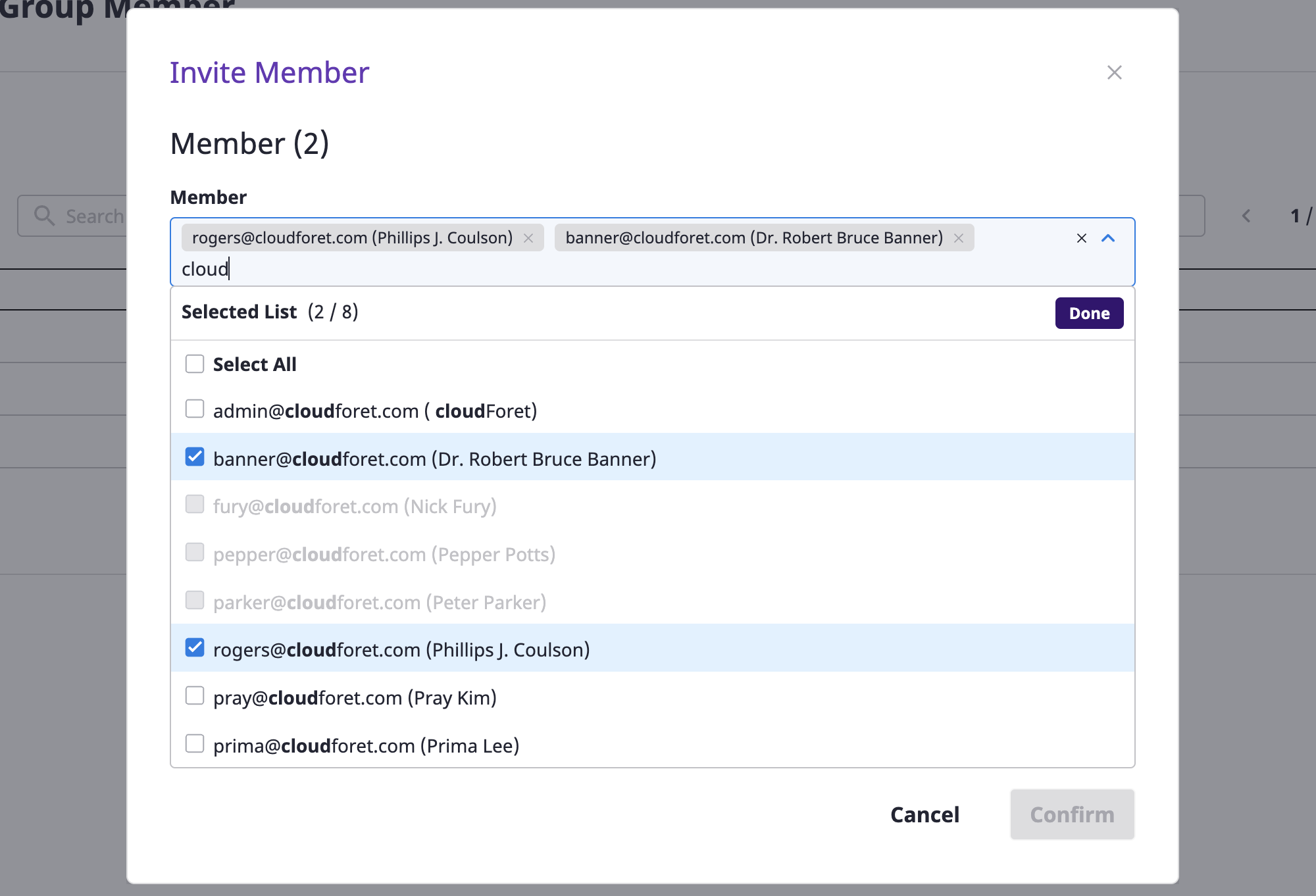
(2) Select the member you want to invite. You can select and invite multiple members at once.
(3) Select the roles to be granted to members that you want to invite.
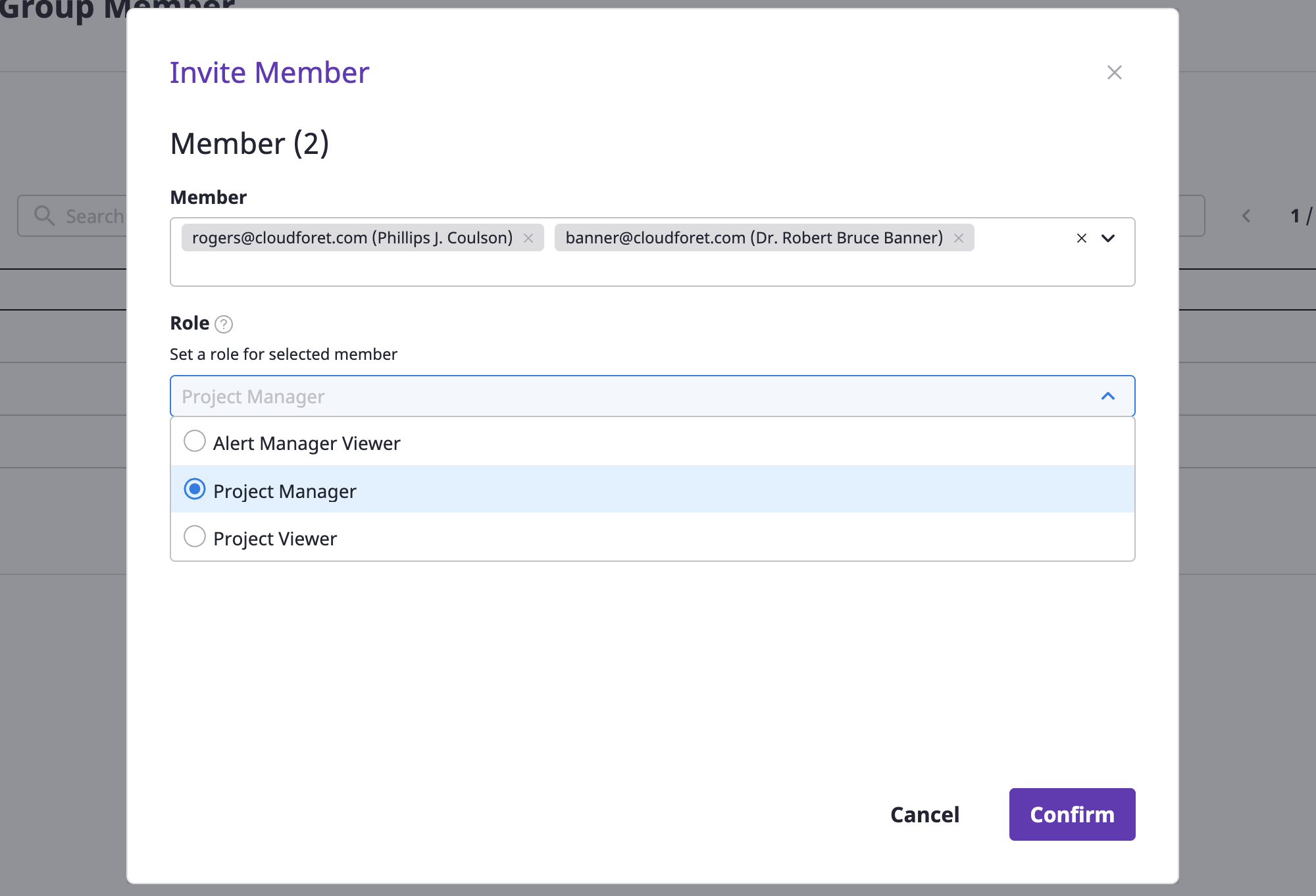
roles of members
Roles that can be granted to members of the project can only be of a user type.
For detailed instructions, see here.
(4) After entering labels for members to invite, press the Enter key to add them.
(5) Click the [OK] button to complete member invitation.
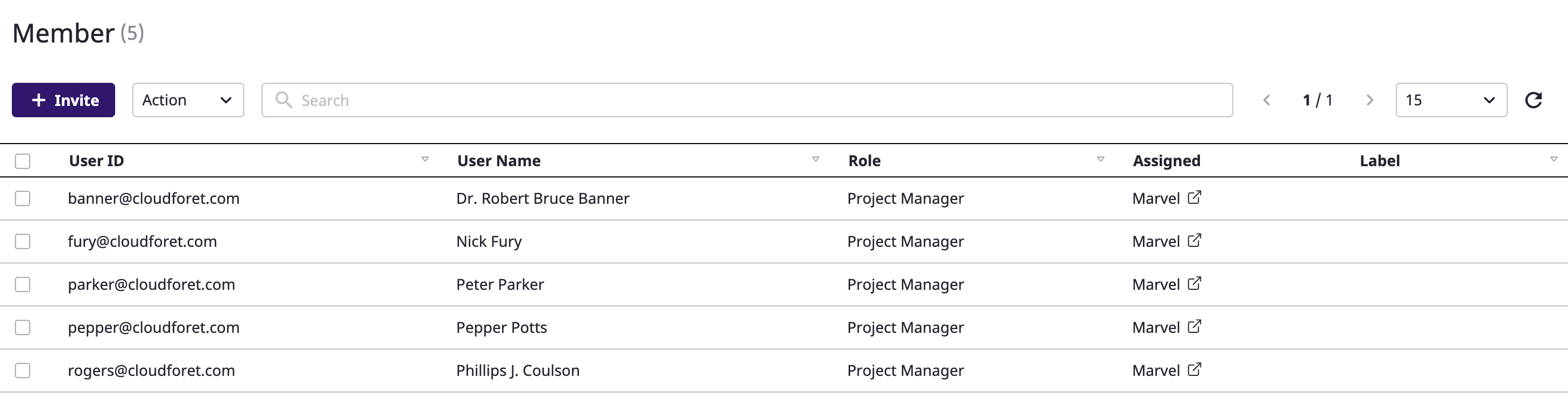
Editing project group members
You can change the roles and labels granted to members for the project group.
(1) In the [Manage project group members] page, select the member you want to edit.
(2) Select [Edit] from the [Action] dropdown.
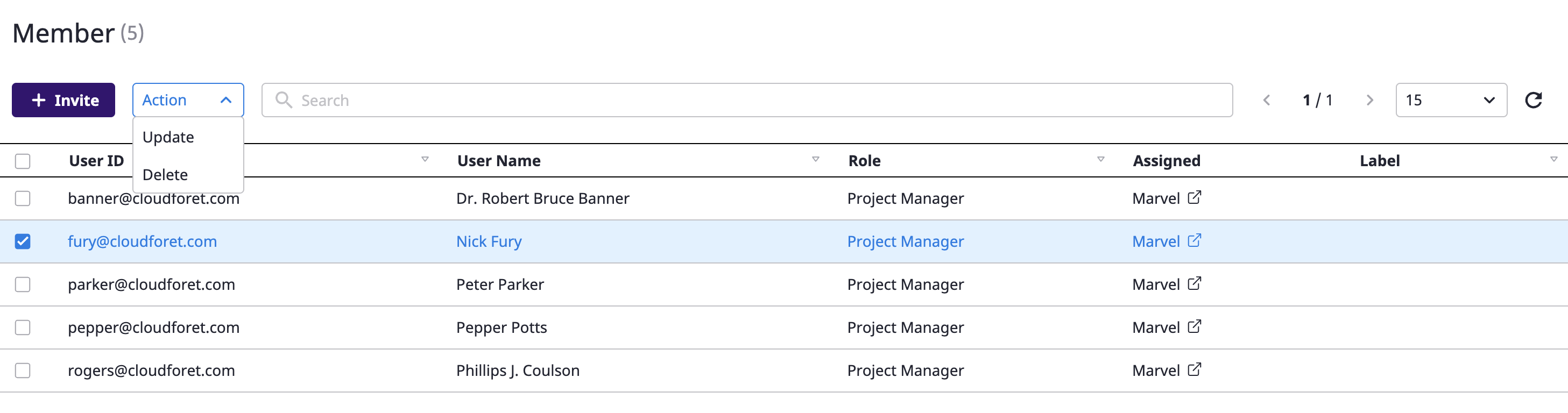
(3) In the [Change member information] modal dialog, enter the contents you want to change and click the [OK] button to complete the change.
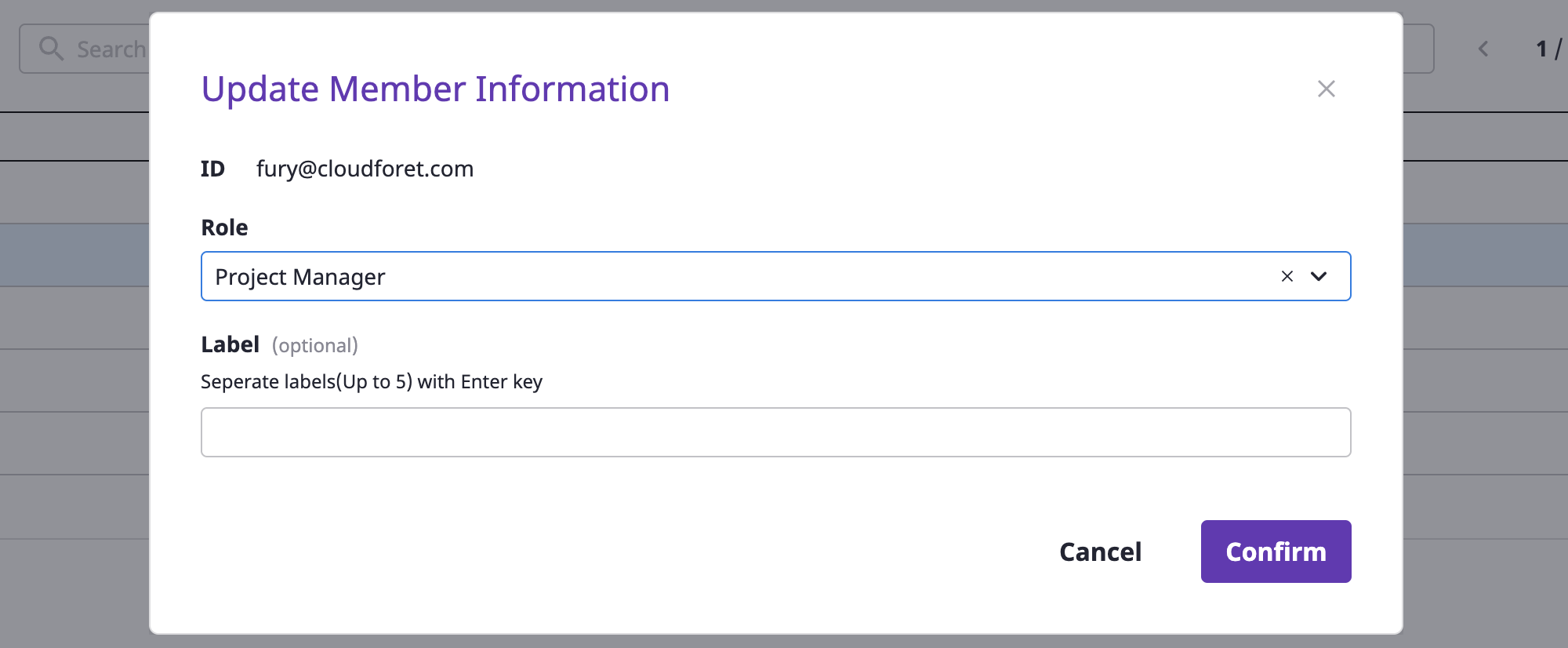
Deleting project group members
(1) In the [Manage project group members] page, select the member you want to delete. Multiple selections are possible.
(2) Select [Delete] from the [Action] dropdown.
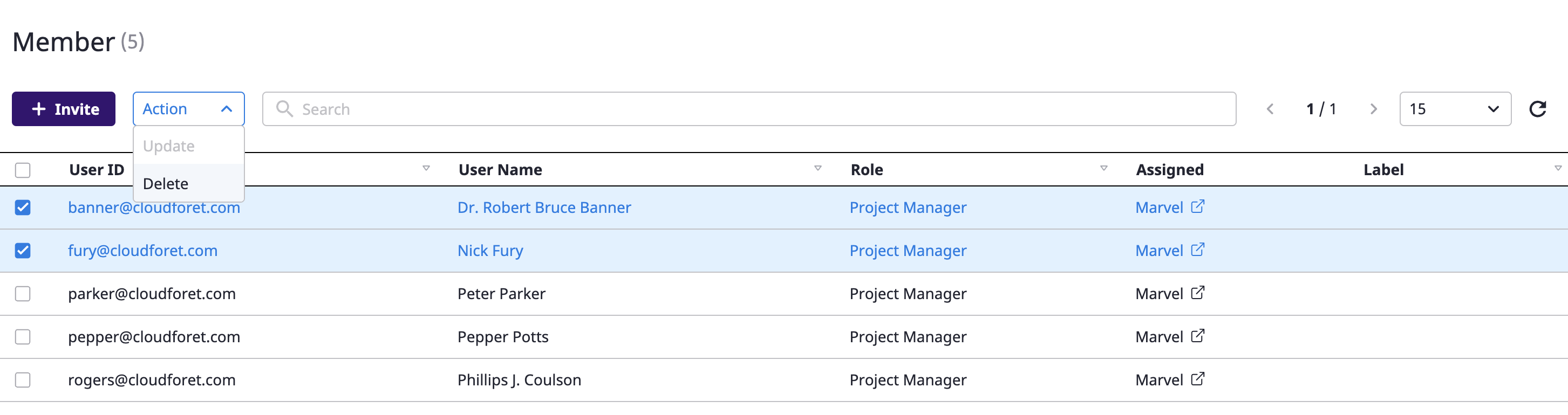
(3) Click the [OK] button in the [Remove member] modal dialog to remove the member.
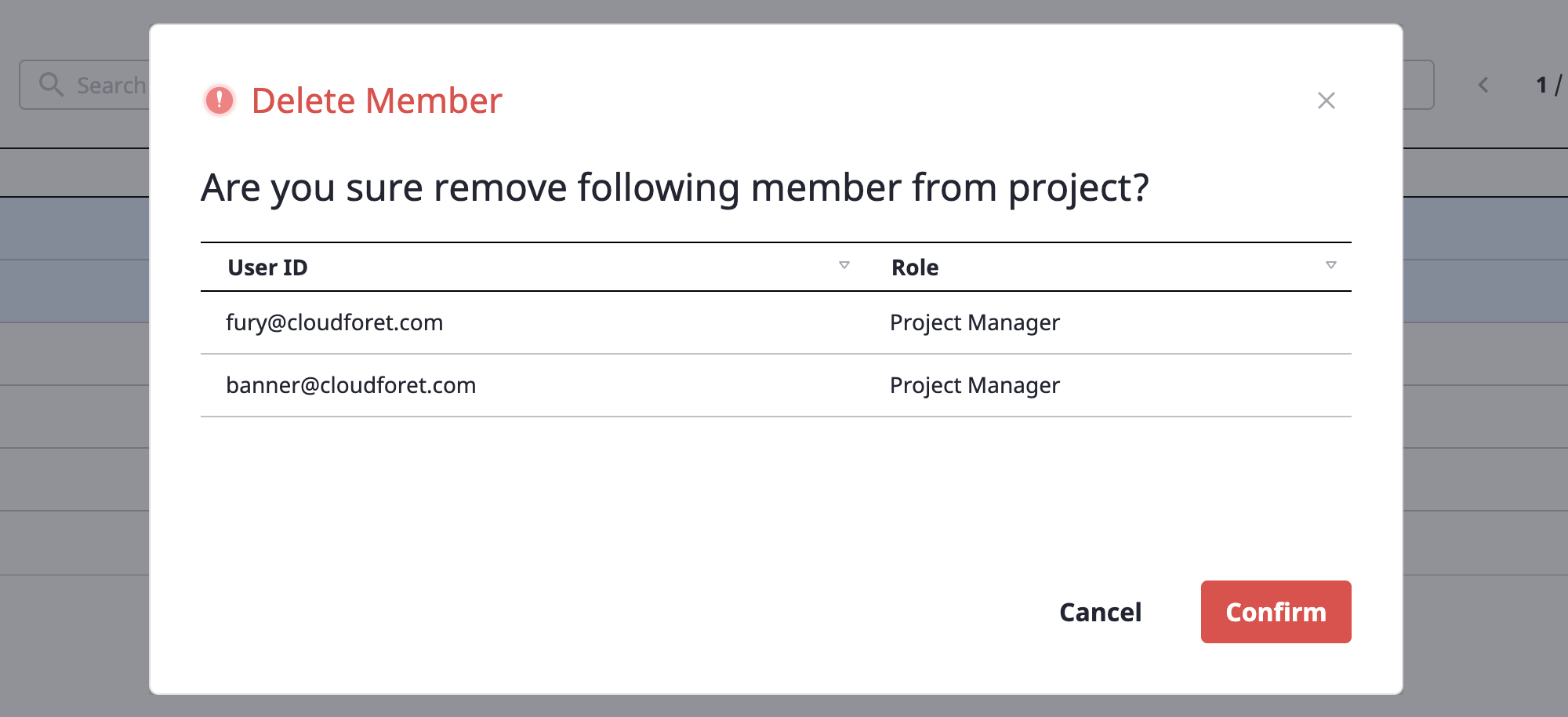
Managing project members
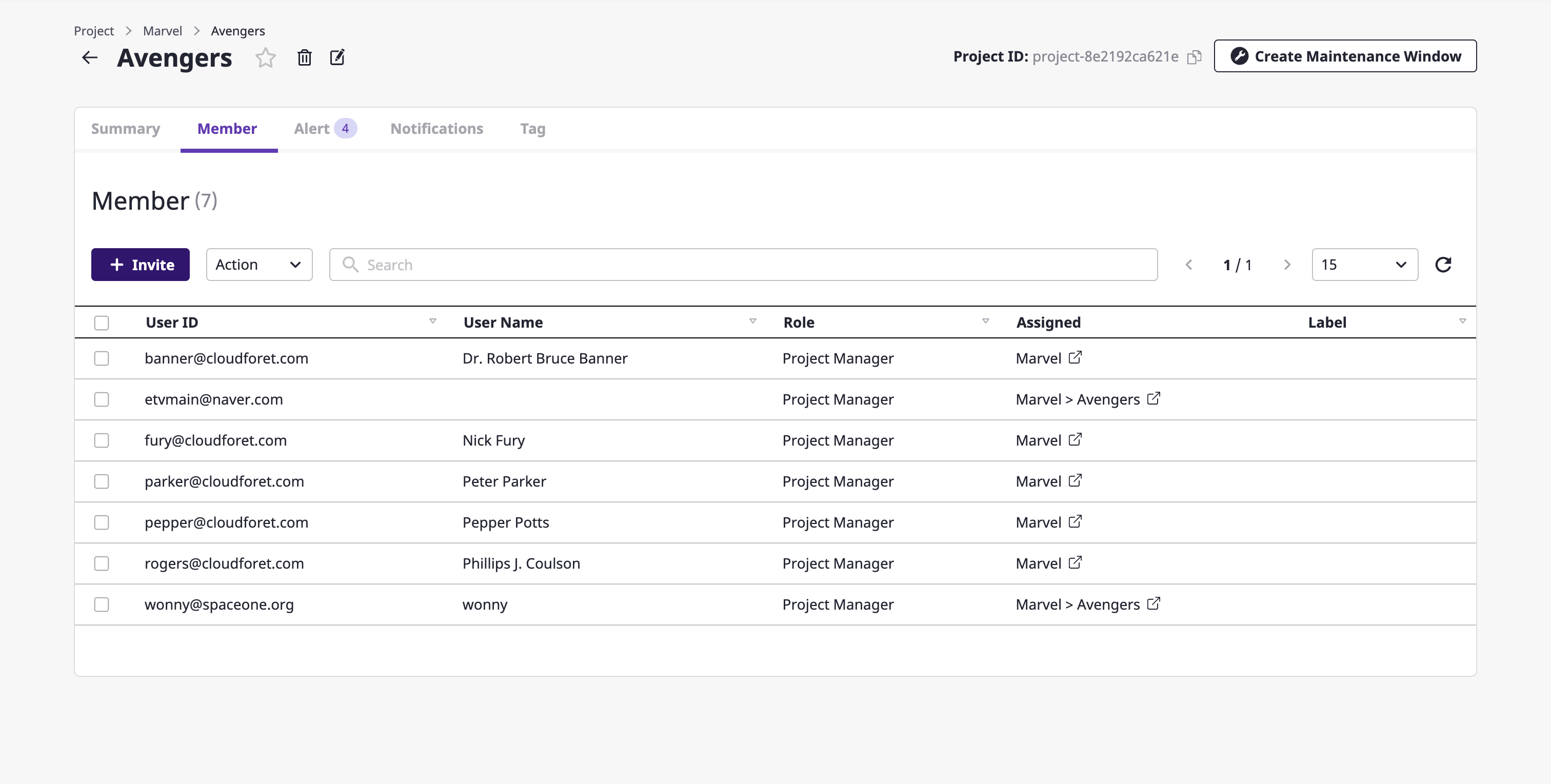
You can manage members by entering the [Members] tab of the project detail page, and all methods and contents are the same as the managing project group members (link).
(1) On the [Project] page, select the project whose members you want to manage and go to the project detail page.
(2) Select the [Member] tab.
4 - Asset inventory
Cloud provider: refers to a cloud provider offering cloud services such as AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, etc.
Cloud service: refers to a cloud service that a cloud provider offers, as in the case of AWS EC2 Instance.
Cloud resource: refers to resources of cloud services, as in the case of servers of AWS EC2 Instance.
4.1 - Quick Start
Creating a service account
Add a cloud service account in the [Asset inventory > Service account] page.
(1) Select a cloud service to add.
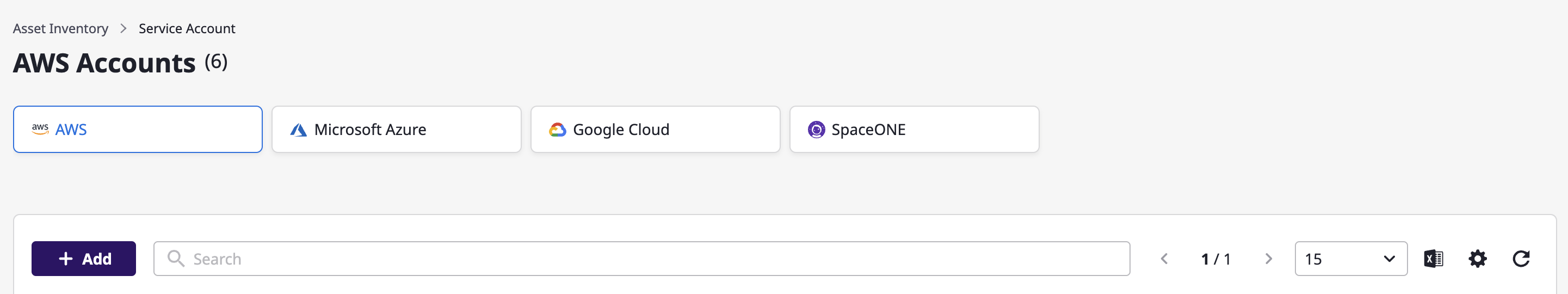
(2) Click the [Add] button.
(3) Fill out the service account creation form.
(3-1) Enter basic information.
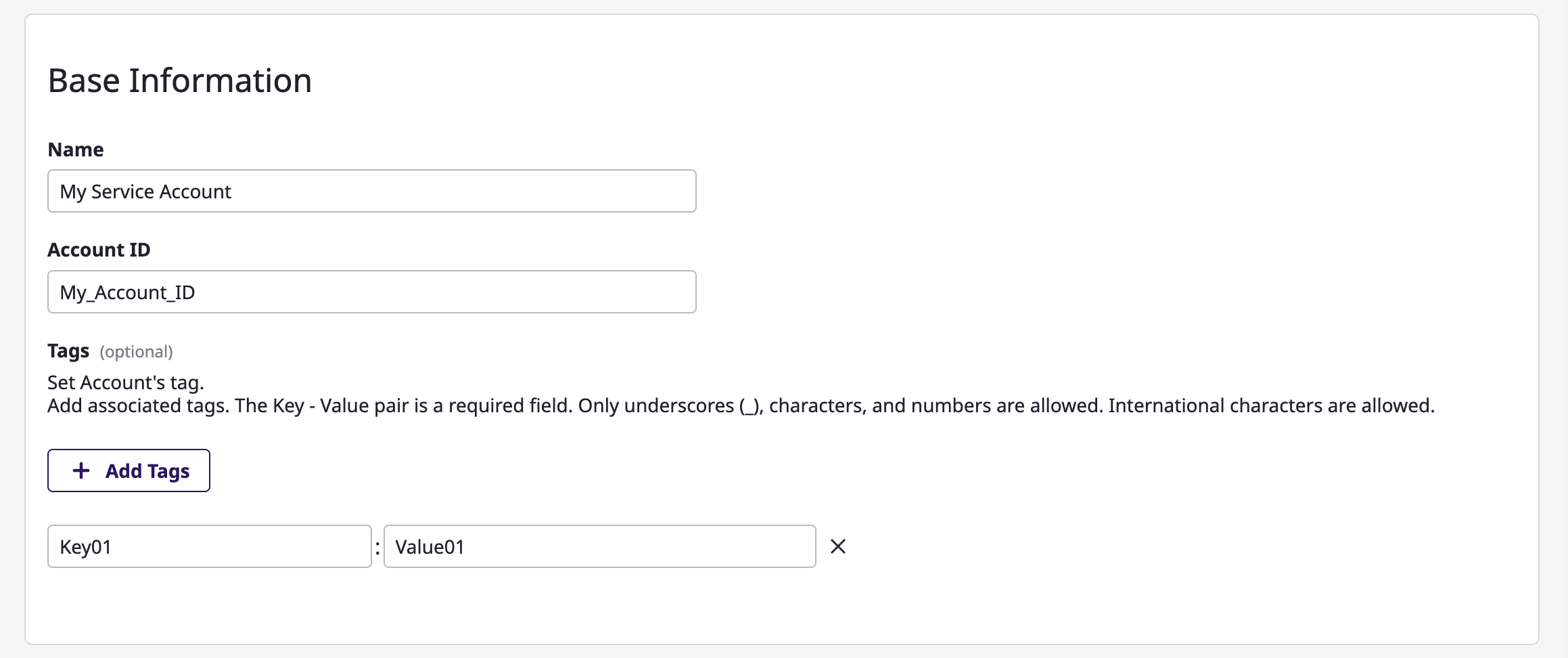
(3-2) Specify the project to collect resources from according to the service account.
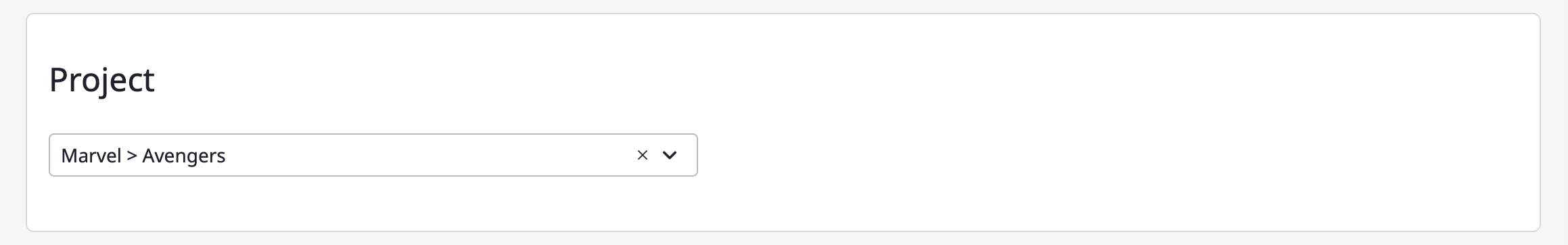
(3-3) Enter encryption key information.
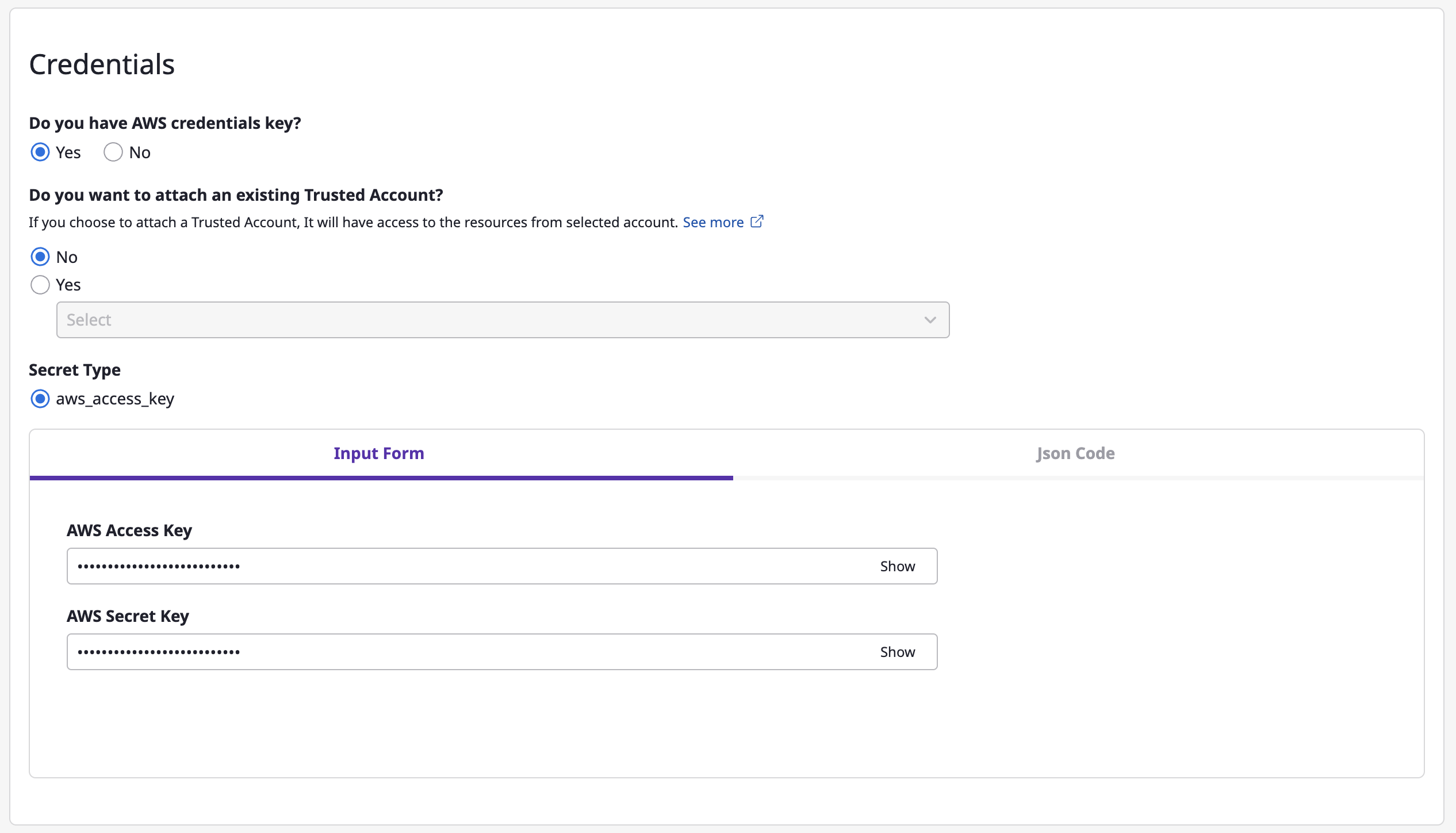
Creating a collector
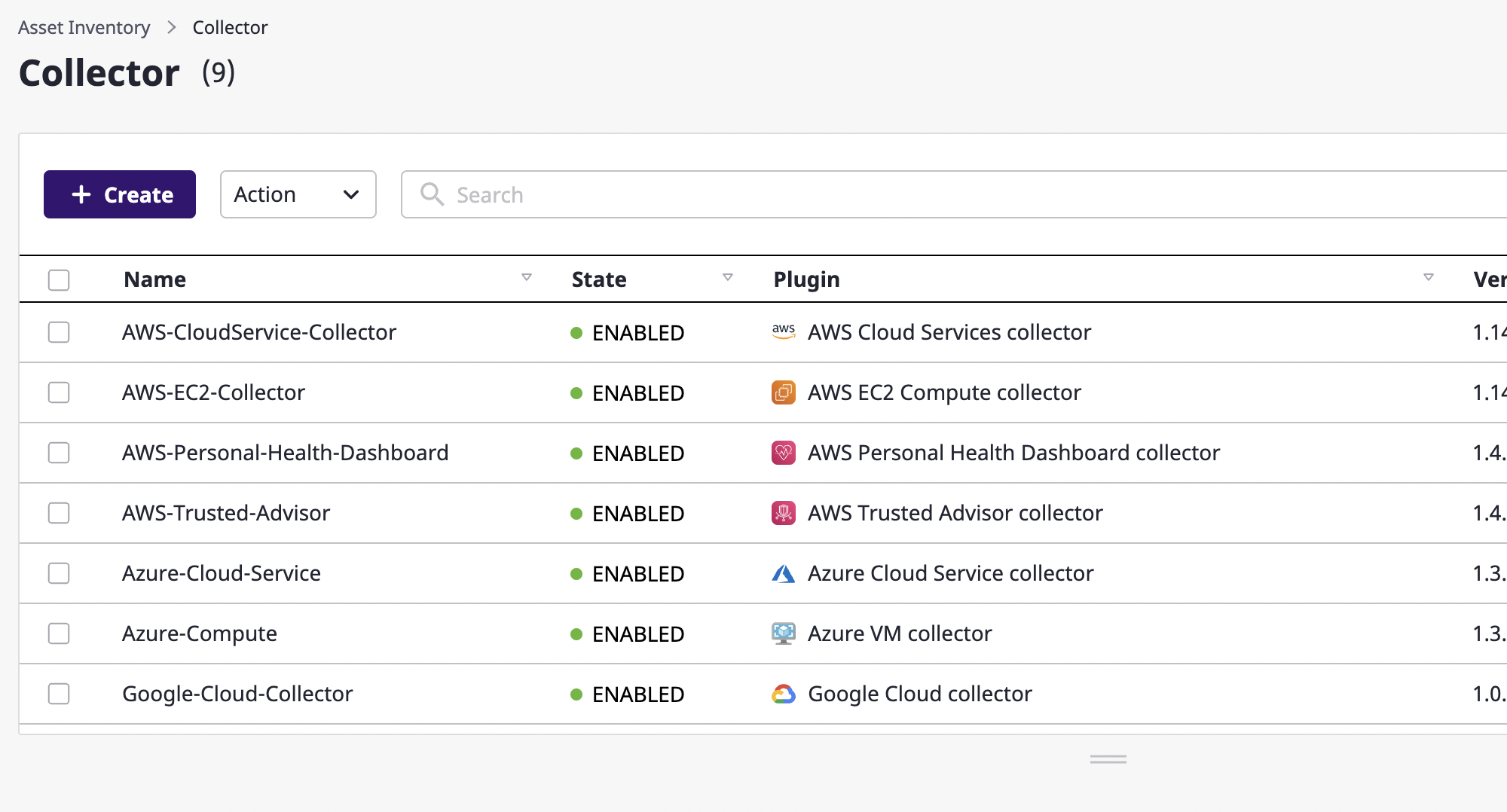
On the [Asset Inventory > Collector] page, create a collector to collect resources.
(1) Click the [Create] button.
(2) Select the plugin to use when collecting resources.
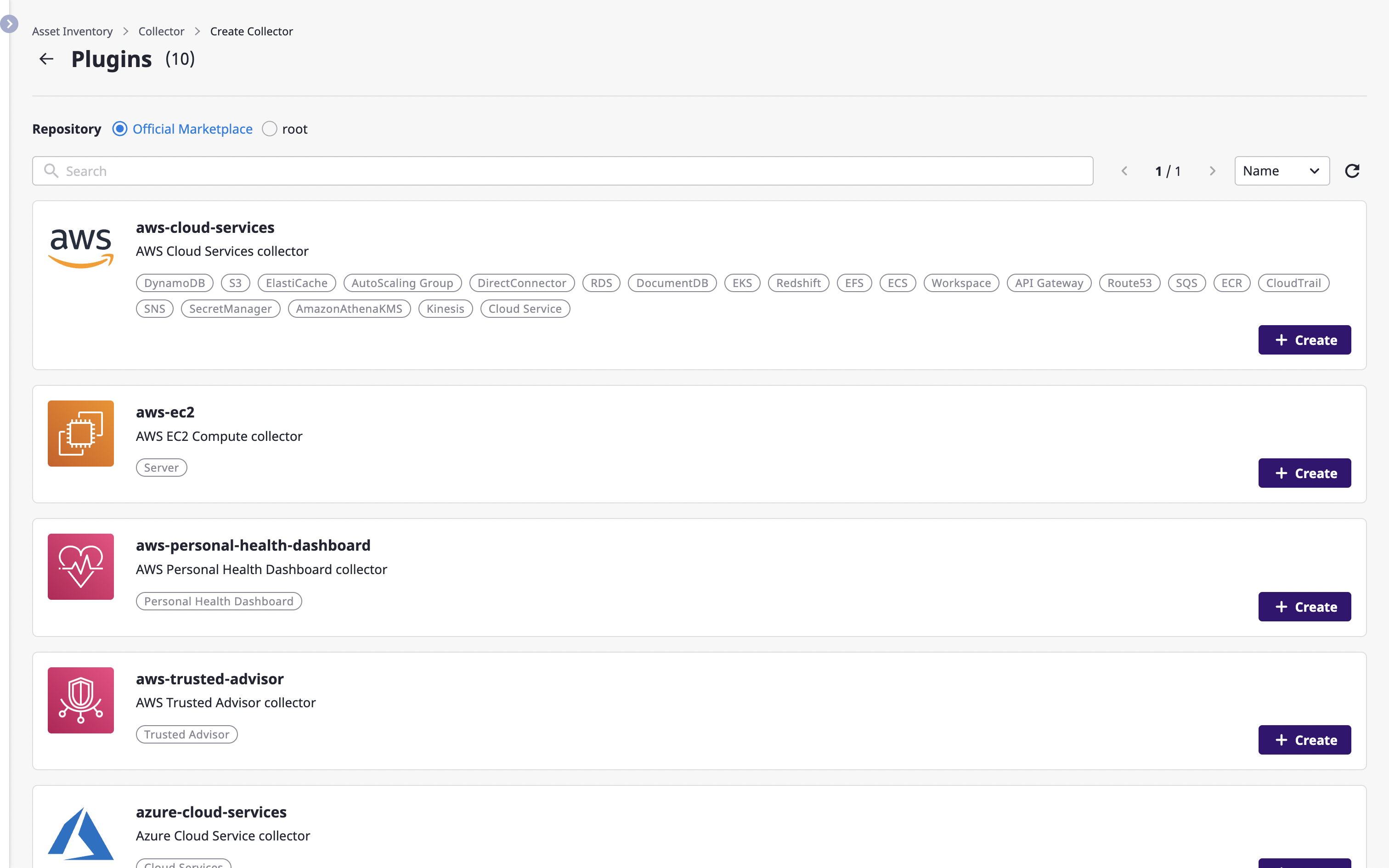
(3) Fill out the collector creation form. (3-1) Enter basic information such as a name and a version.
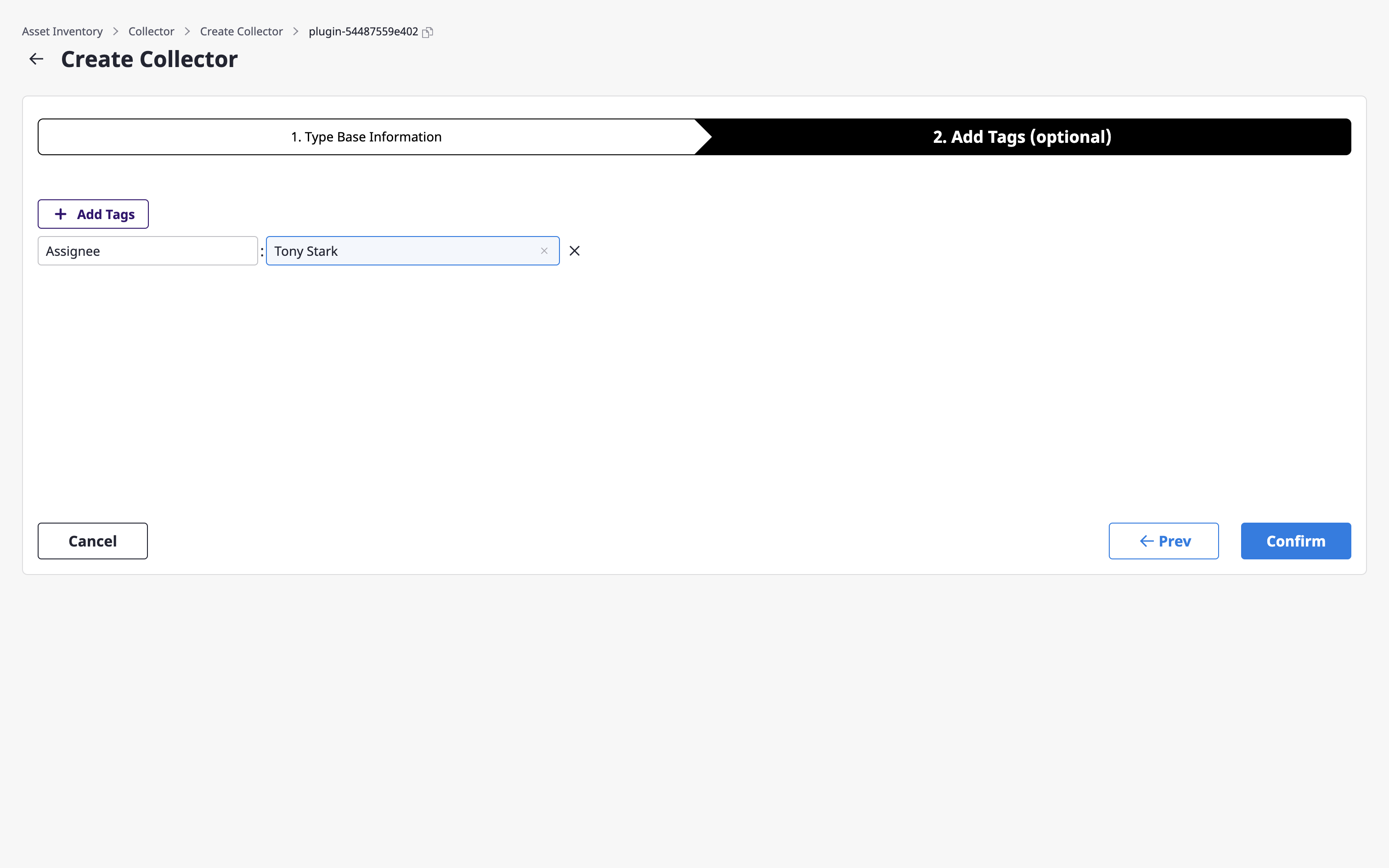
(3-2) Add tags if necessary.
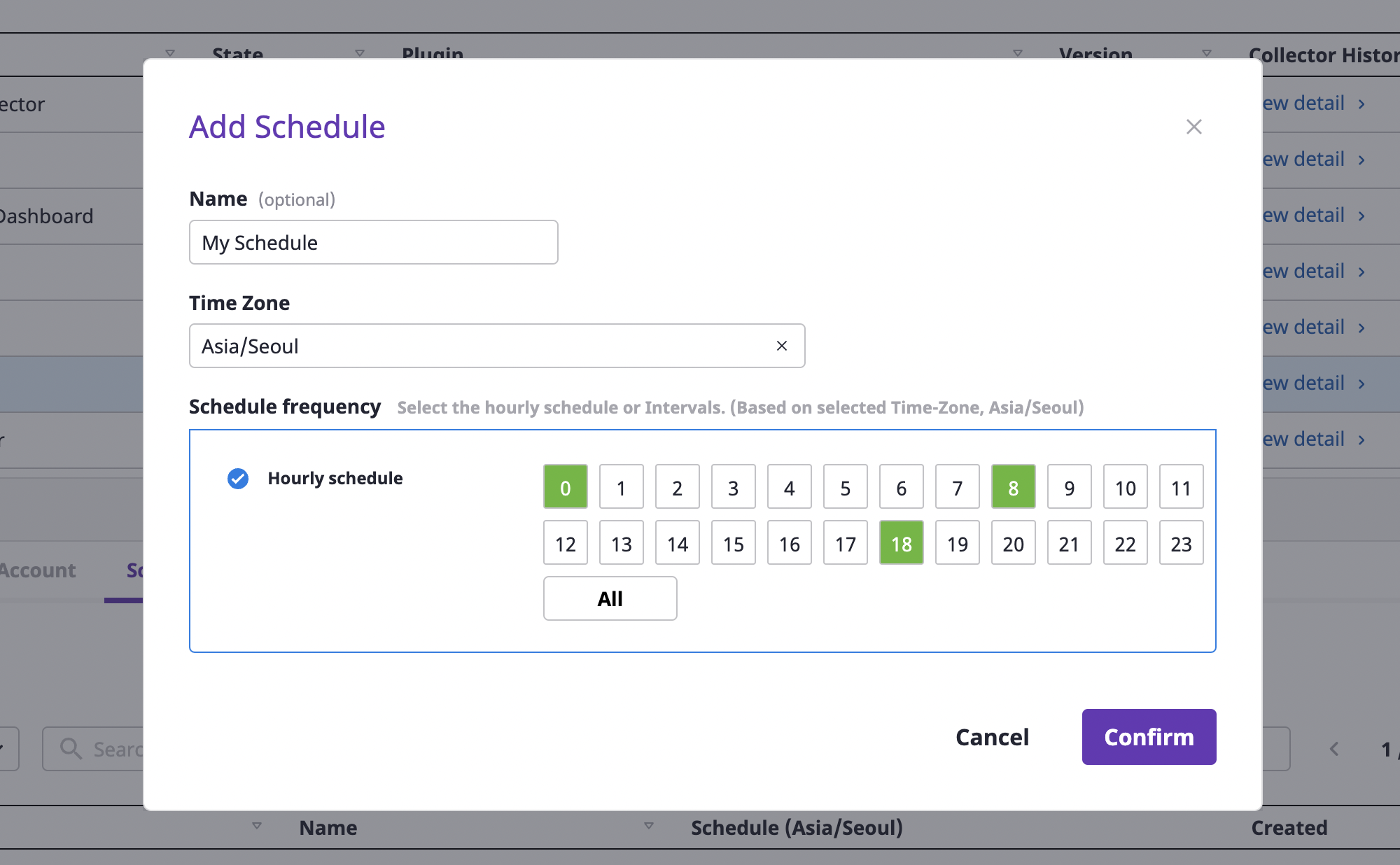
(4) Create a schedule for running the collector.
(4-1) On the [Asset inventory > Collector] page, select one collector from the table, and then click the [Add] button in the [Schedule] tab.
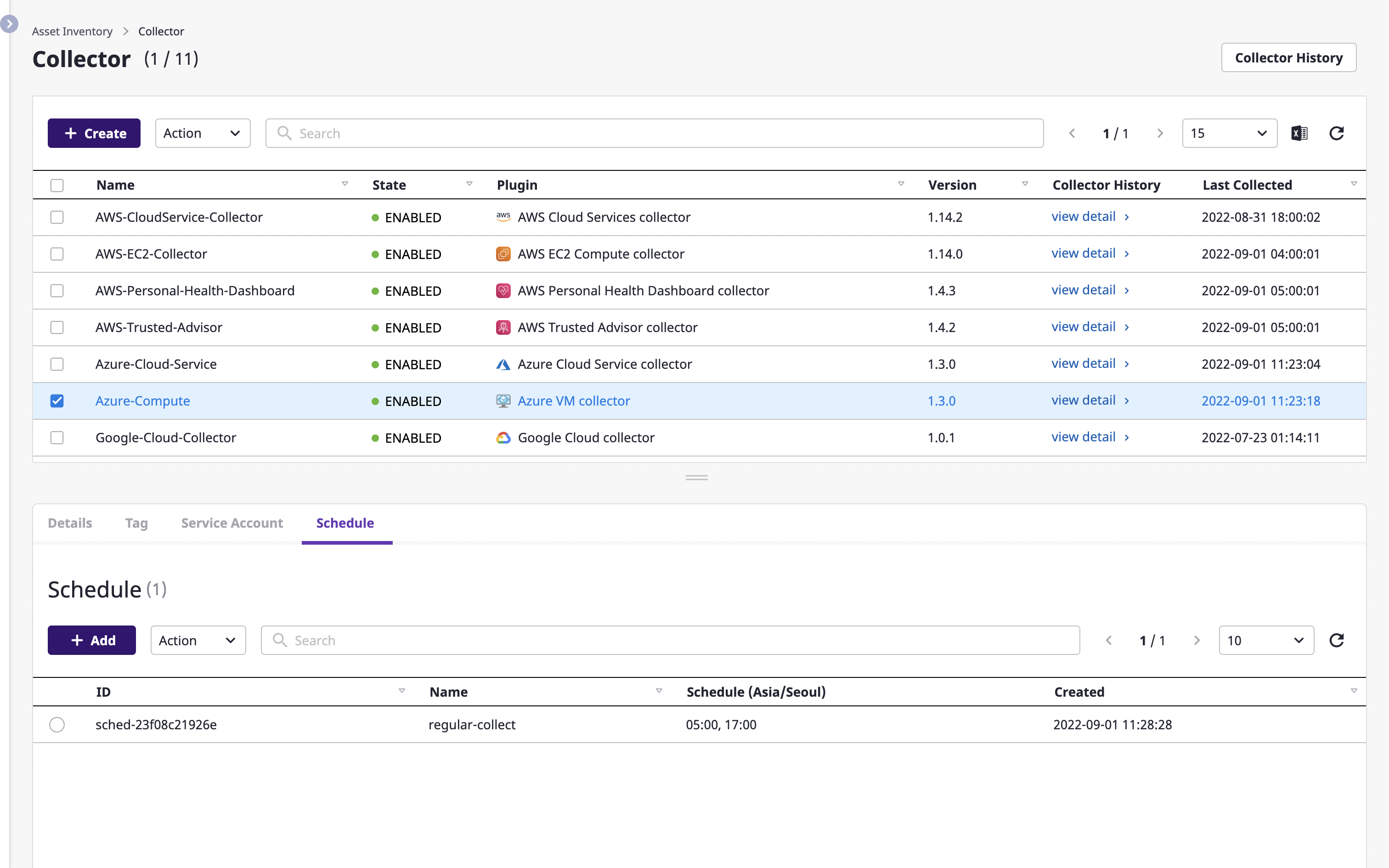
(4-2) In the [Add schedule] modal dialog, set the time to run the collector and click the [OK] button.
Verifying collected resources
You can view the collected resources in [Asset inventory > Cloud service].
4.2 - Cloud service
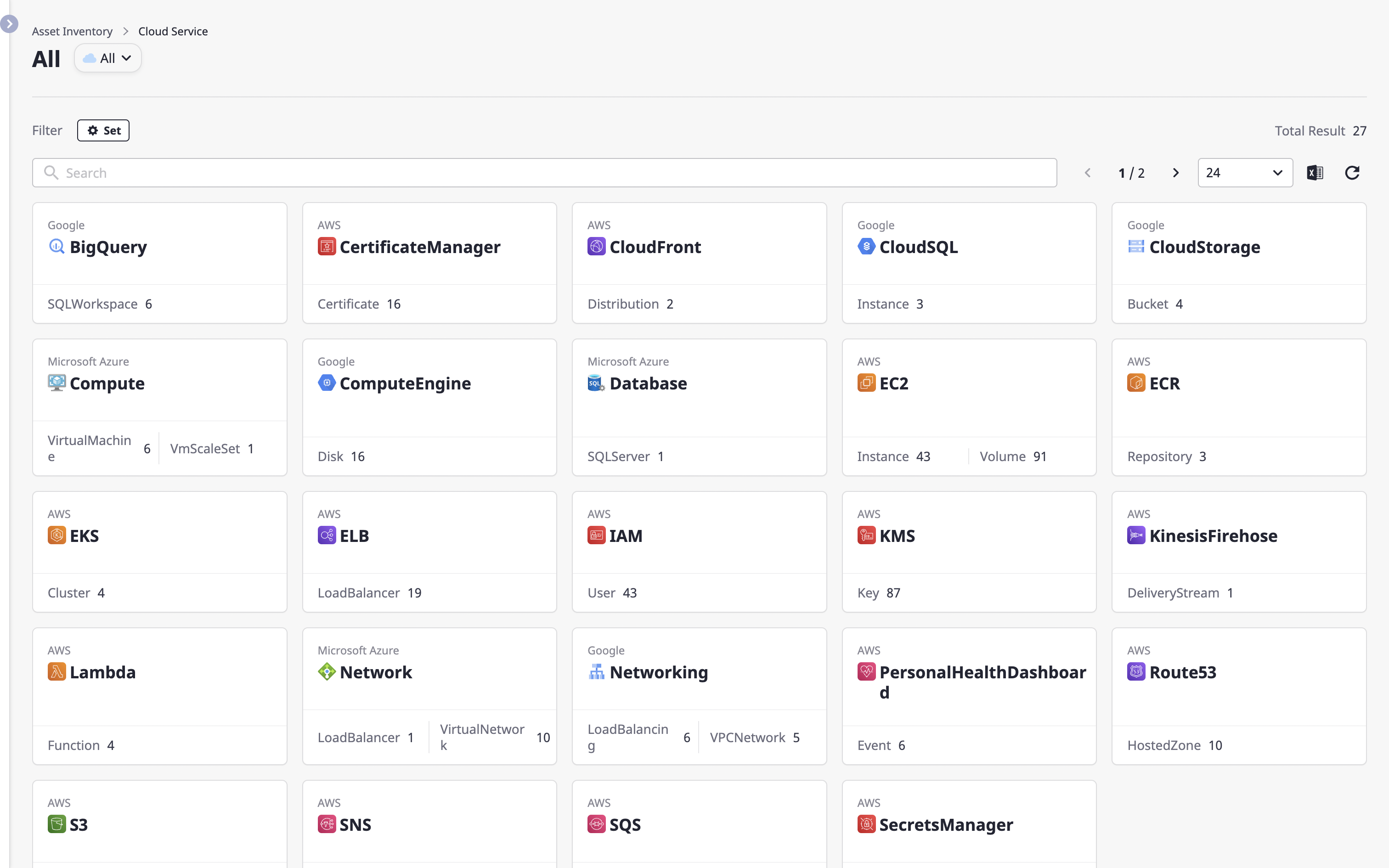
Viewing a list of cloud services
The cloud service page displays the status of cloud service usage by Provider.
Advanced Search and filter settings allow you to filter the list by refined criteria.
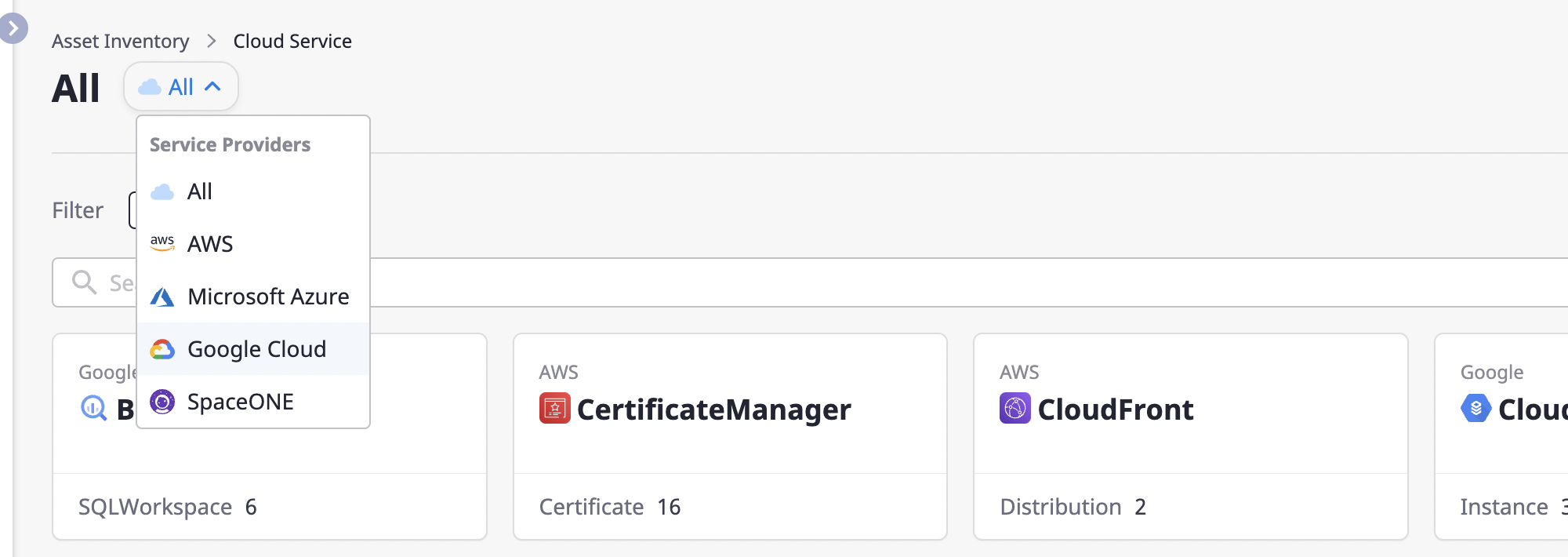
Choosing a Provider
Select a provider to view cloud services provided through a certain provider only.
Filter settings
You can search with more detailed conditions by setting service classification and region filters.
(1) Click the [Settings] button to open the [Filter Settings] modal dialog.
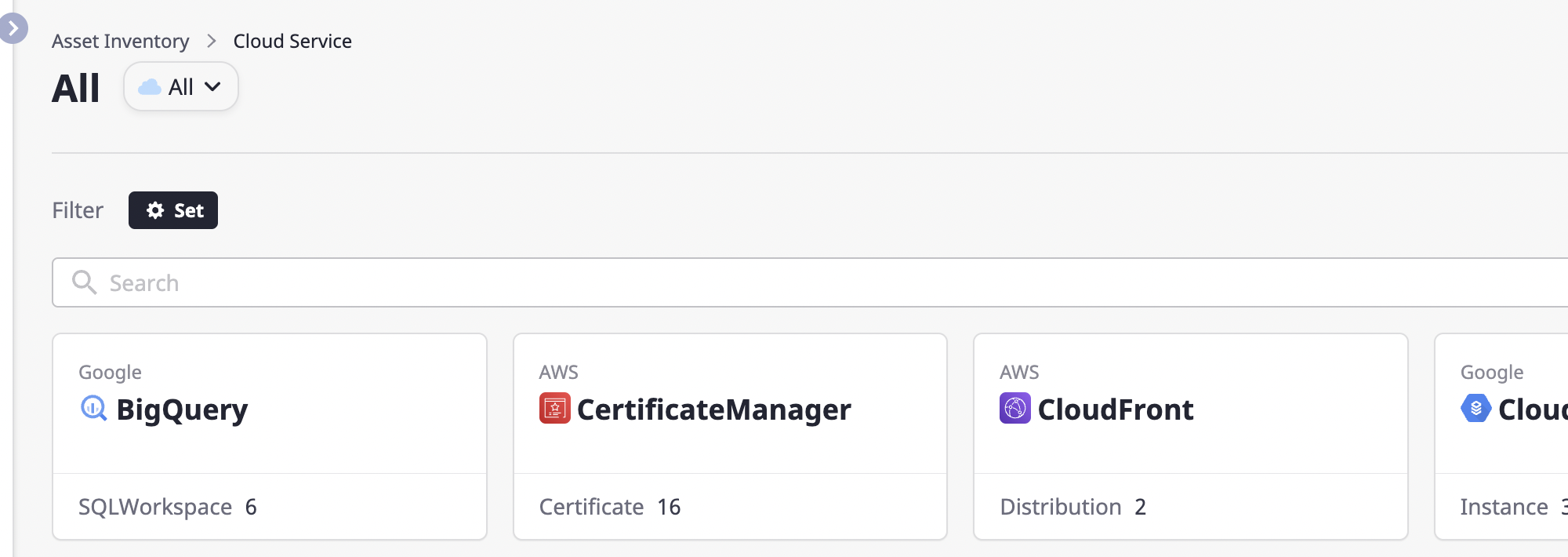
(2) After selecting the desired filter, click the [OK] button to apply it.
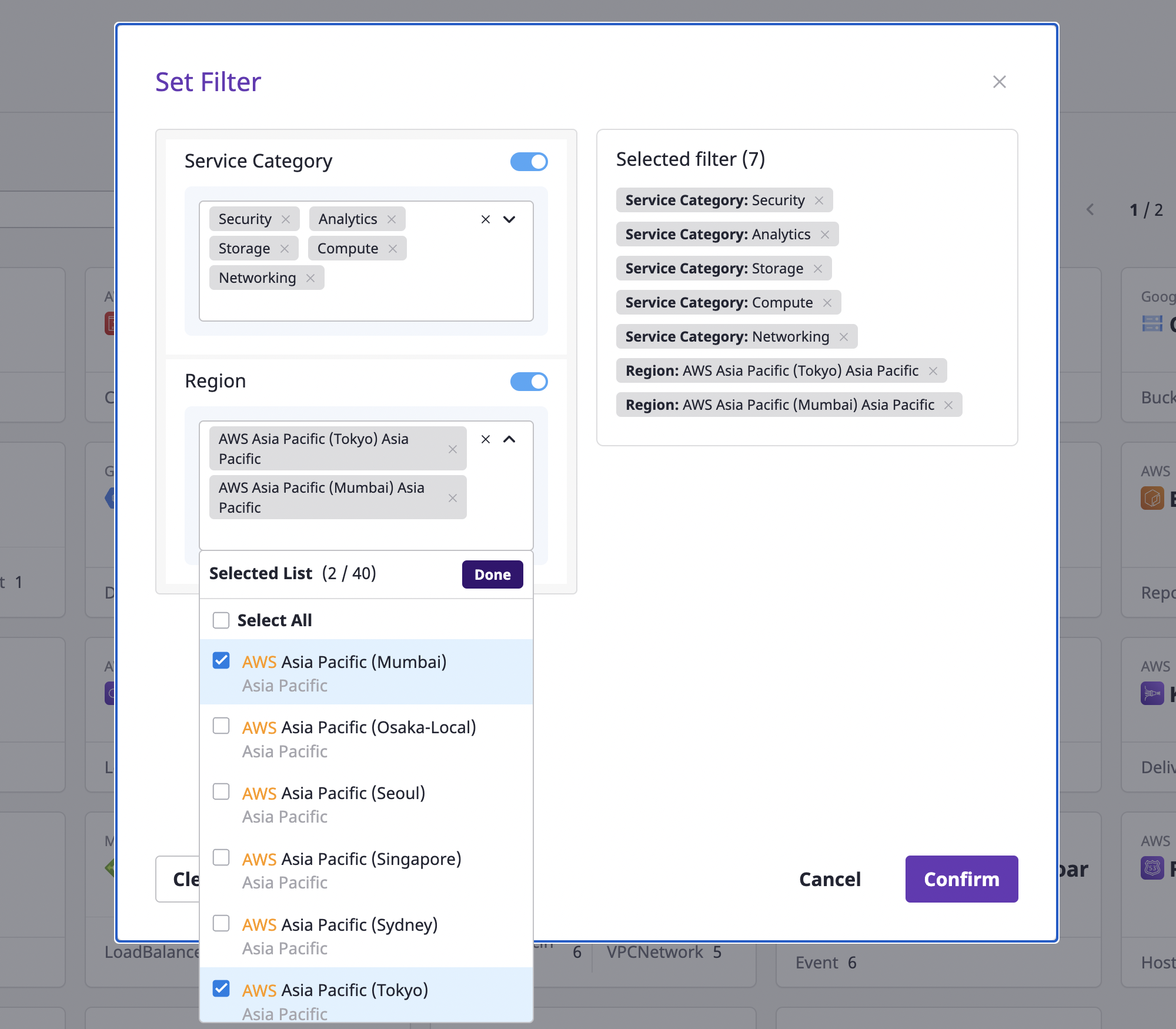
Exploring Cloud Service
You can check the details of certain cloud services on the cloud service detail page.
Click a card on the cloud service page to go to the detail page.
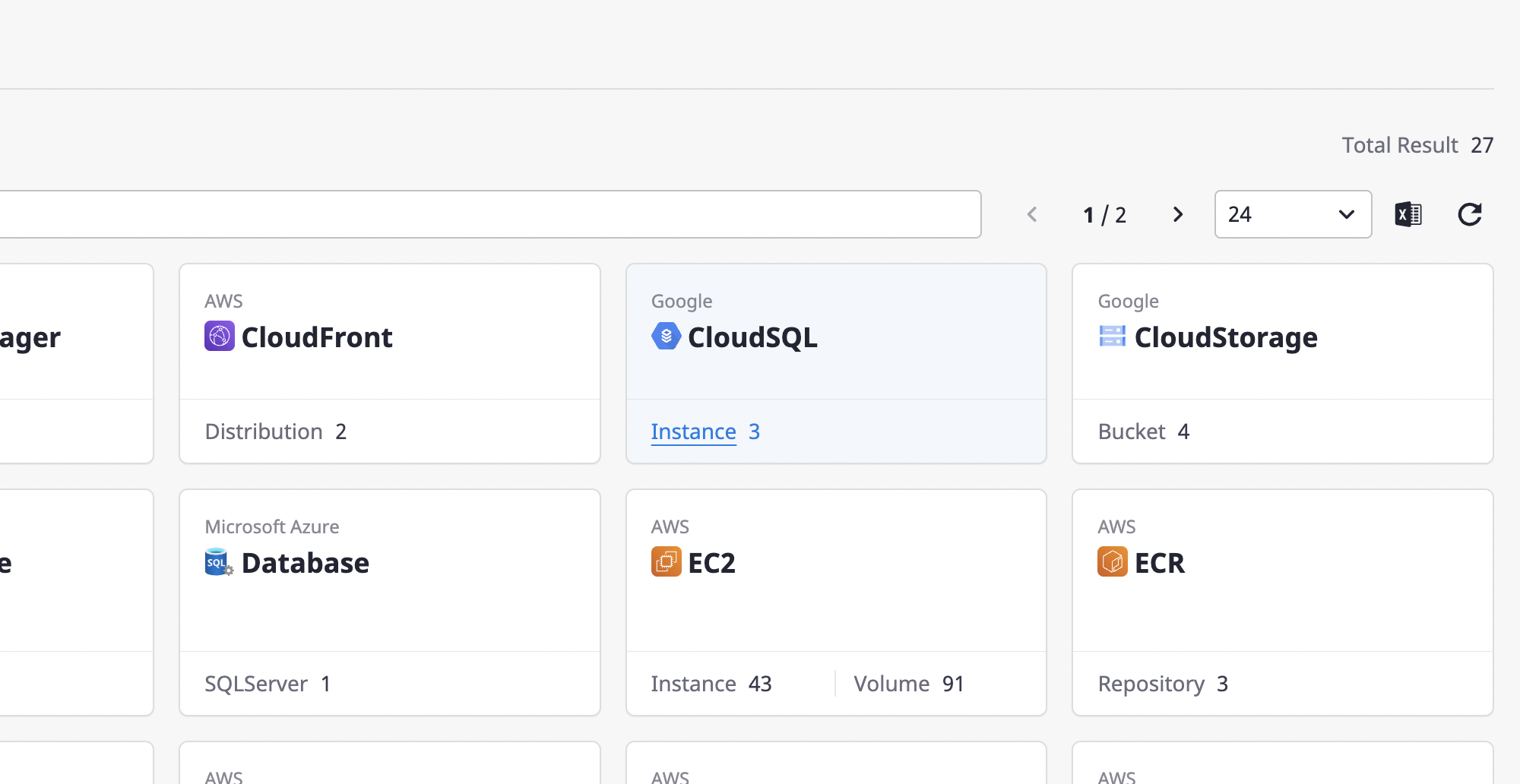
You can check detailed information about the selected cloud service in the cloud service list on the left.
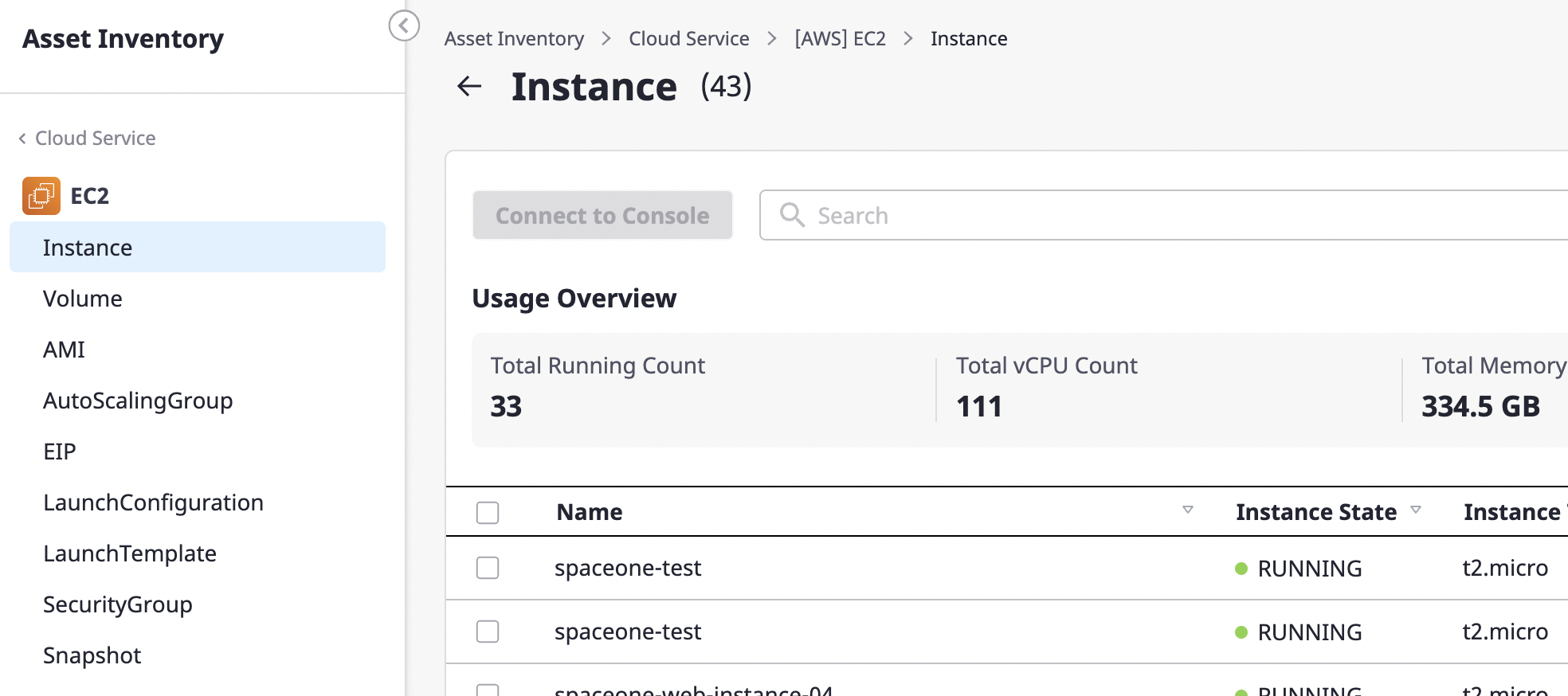
Viewing a list of resources in cloud services
You can enter a search word to see a list of cloud resources that match your criteria.
See here for a detailed description of Advanced search.
Click the [Excel] icon button to [Export as an Excel file] for a list of resources (/ko/docs/guides/advanced/excel-export) or click the [Settings] icon button to [Personalize table fields](/ko/ docs/guides/advanced/custom-table).
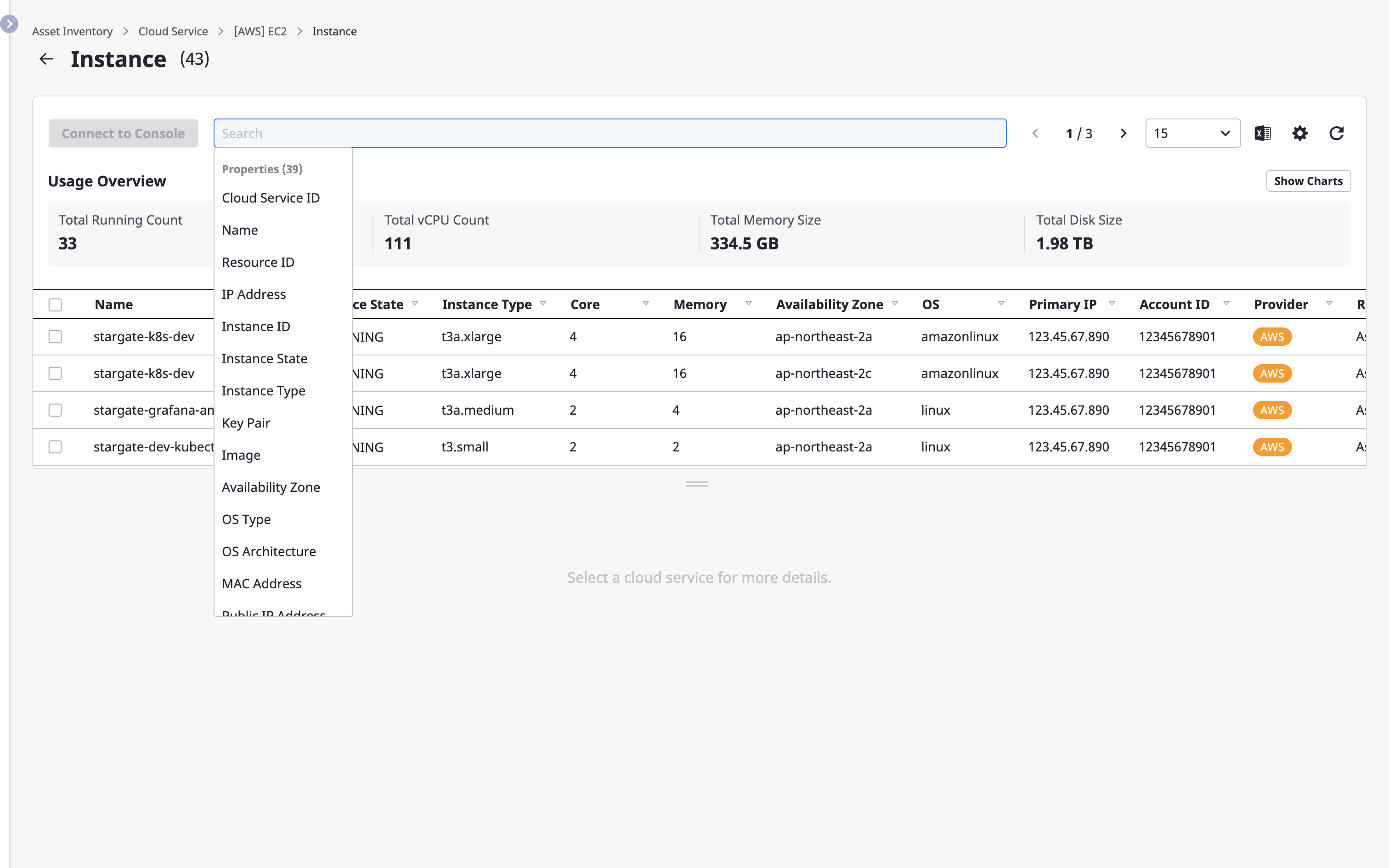
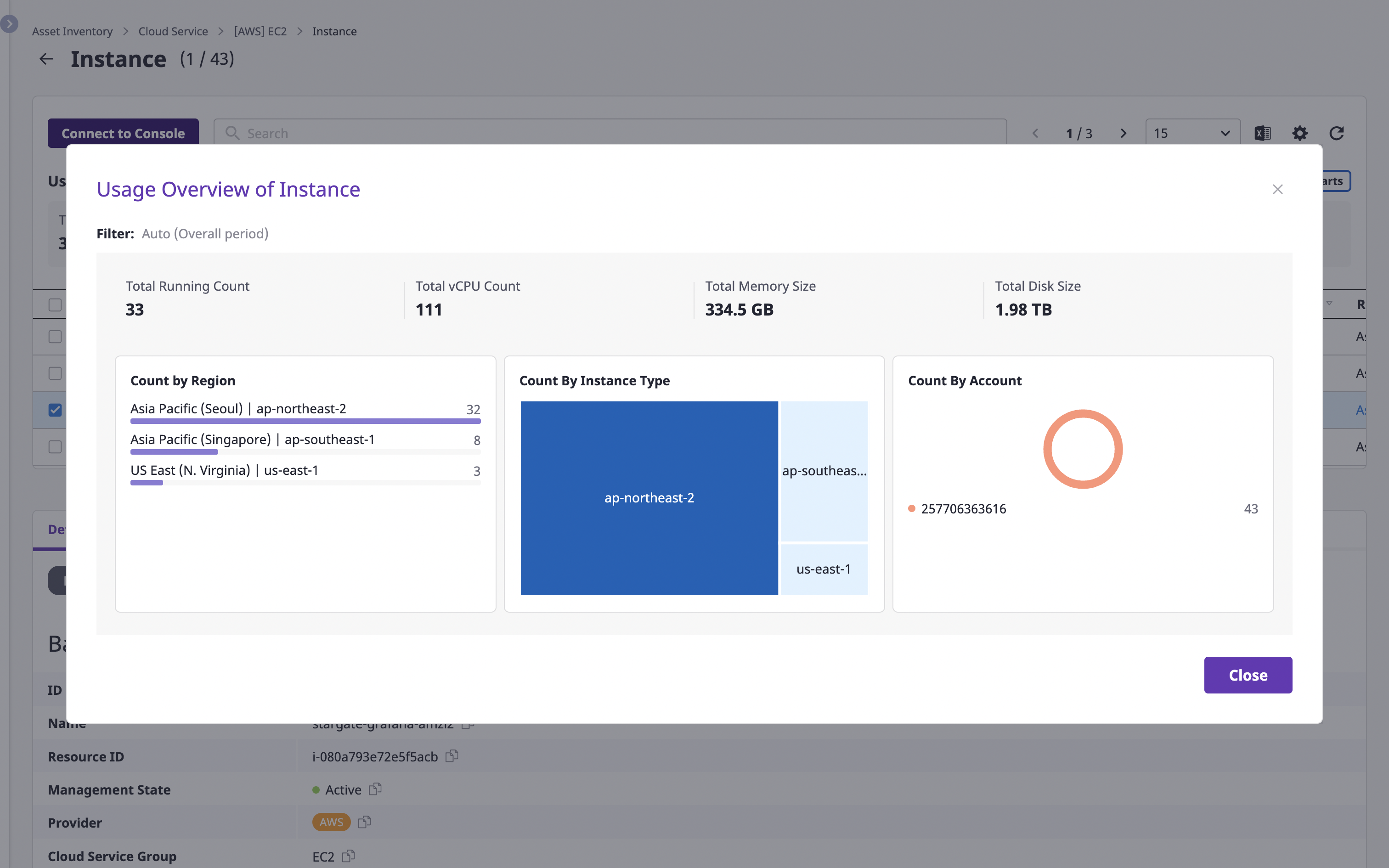
Viewing the status of cloud service usage
You can check statistical information about the selected cloud service.
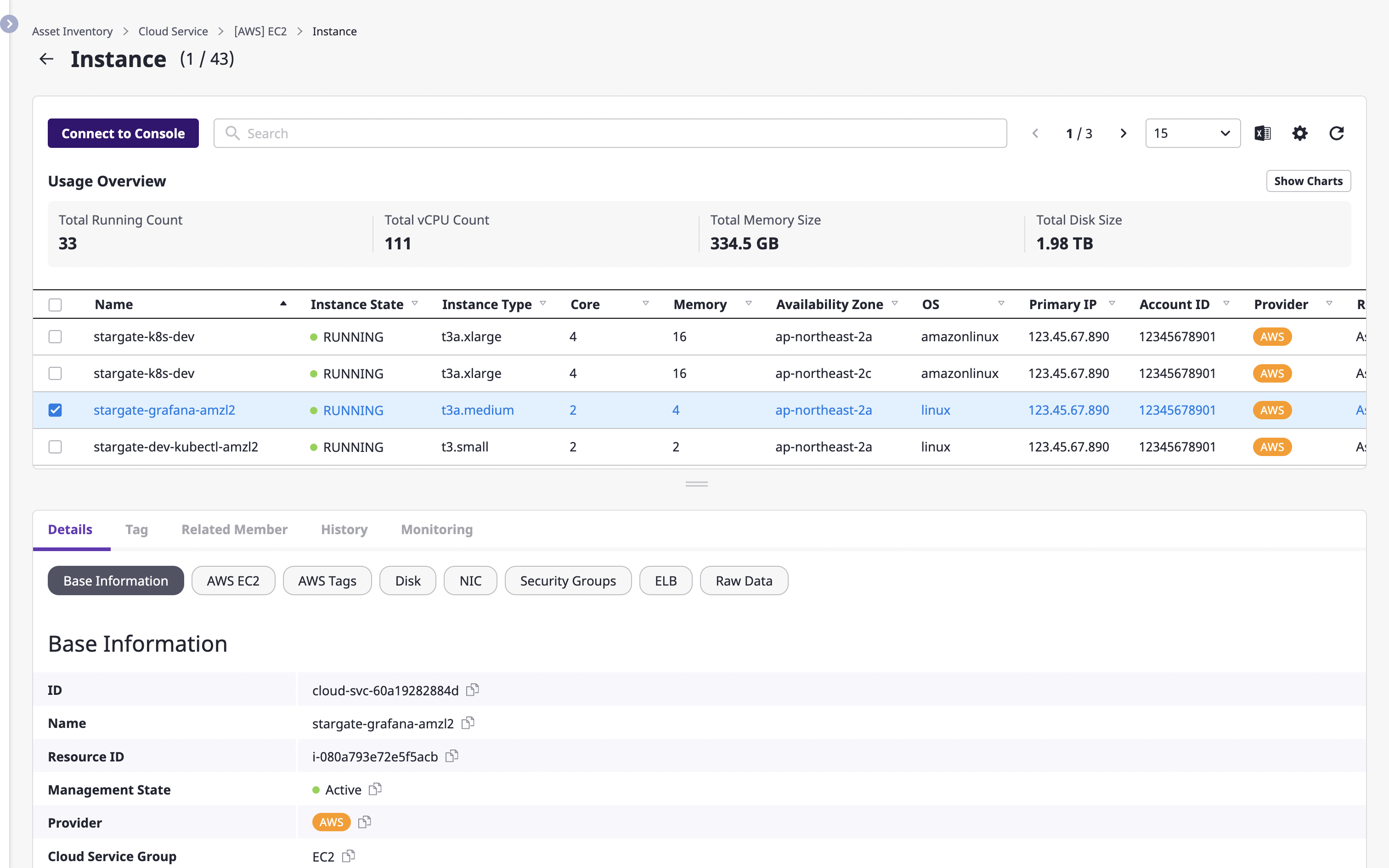
For more detailed information, click the [View chart] button on the right.
Opening cloud resources console
Sometimes you need to work in a console provided by a cloud resources provider.
(1) Select the cloud resource to which you want to connect the console.
(2) Click the [Console connection] button.
(3) By clicking the button, open the provider's console in a new tab where you can continue working with the cloud resource.
Below is an example of the AWS EC2 Instance console that was opened.
Exploring resources in cloud services
If you select an item you want to look at in the list of cloud resources, you can check information about that resource at the bottom.
- [Details] (#check-cloud-resources-details)
- [Tag] (#manage-cloud-resources-tag)
- [Associated member] (#check-cloud-resource-associated-member)
- [Change history] (#check-cloud-resource-associated-member)
- [Monitoring] (#check-cloud-resource-monitoring-information)
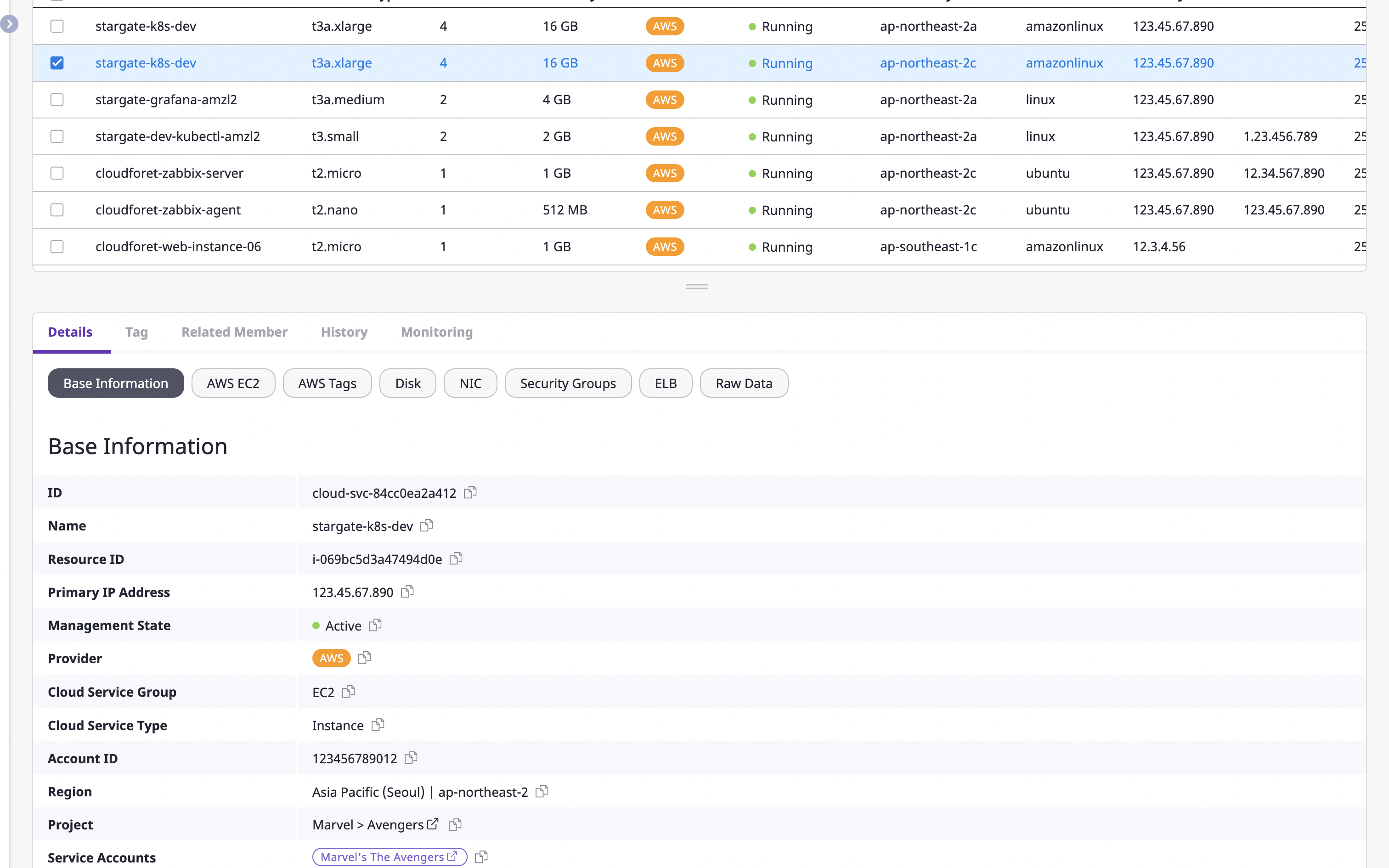
Checking cloud resource details
Detailed information about the selected resource is displayed.
The information displayed here is divided into a Basic tab and a More information tab.
- Basic tab: This is provided as default in the cloud resources details, and the [Basic information] and [Original data] tabs are applicable.
- More information Tab: All tabs except the main tab are determined by the collector plugin that gathers resources. For detailed information, see here.
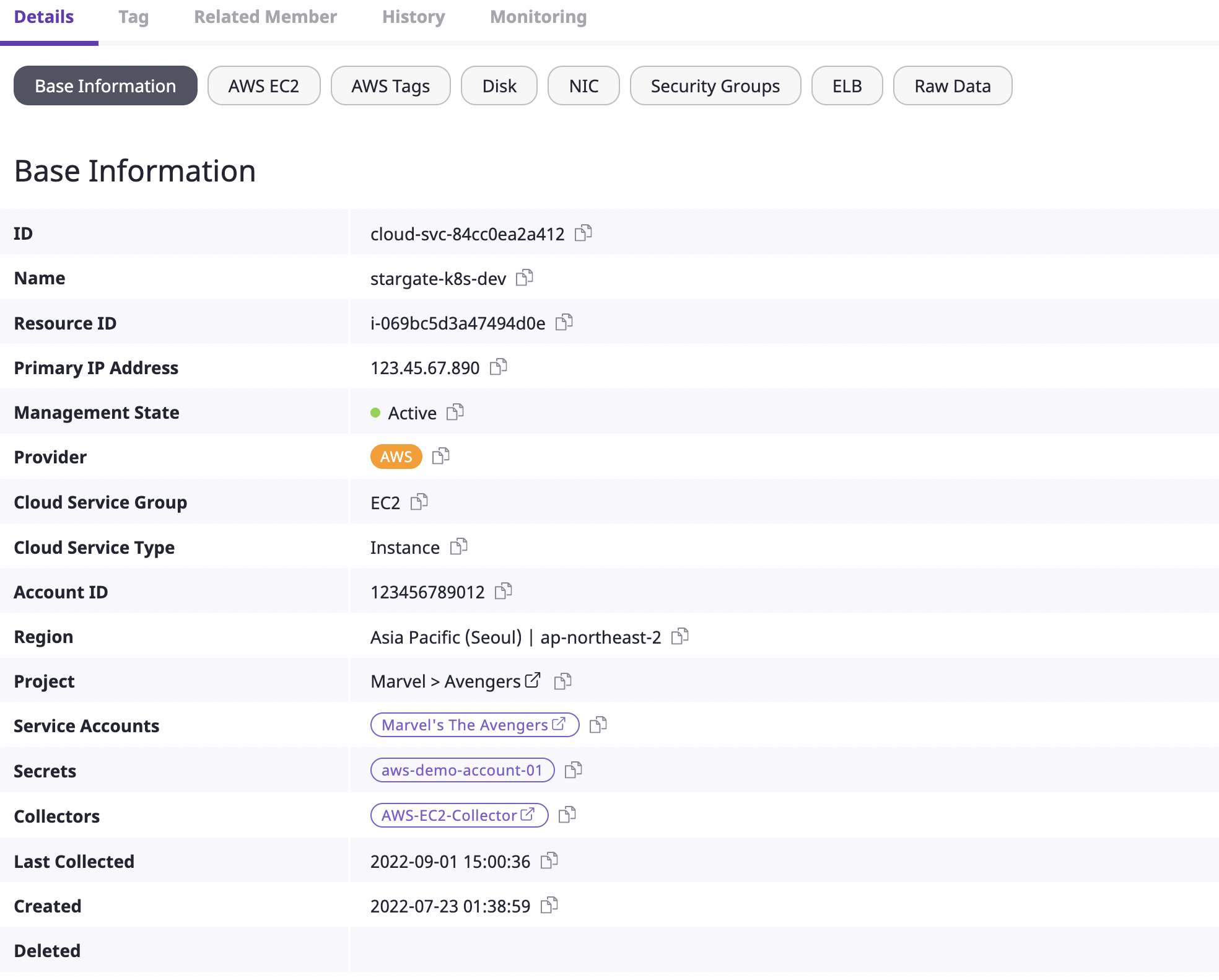
The image above is an example of cloud resources details.
Except for the [Basic information] tab and [Original data] tabs, all other tabs (AMI, Permissions, Tags) offer information added by the collector plugin.
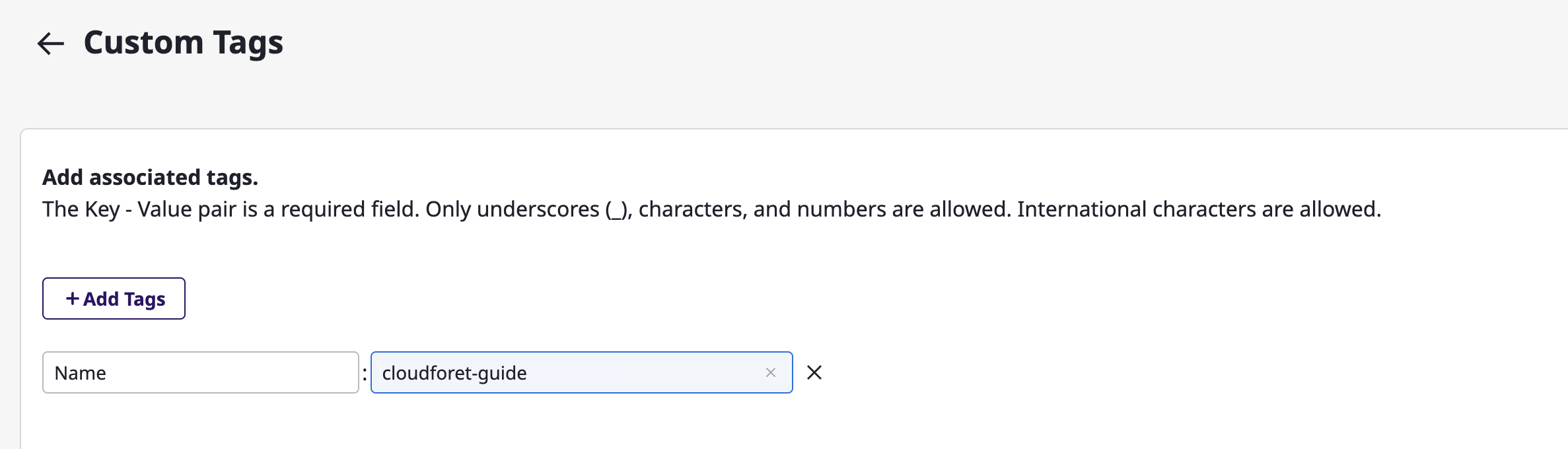
Managing cloud resources tags
There are two types of tags for cloud resources: Managed and Custom.
For each cloud resource, you can either view the Managed tags added from the provider or add Custom tags.
Each tag in the form of key: value can be useful when searching for specific resources.
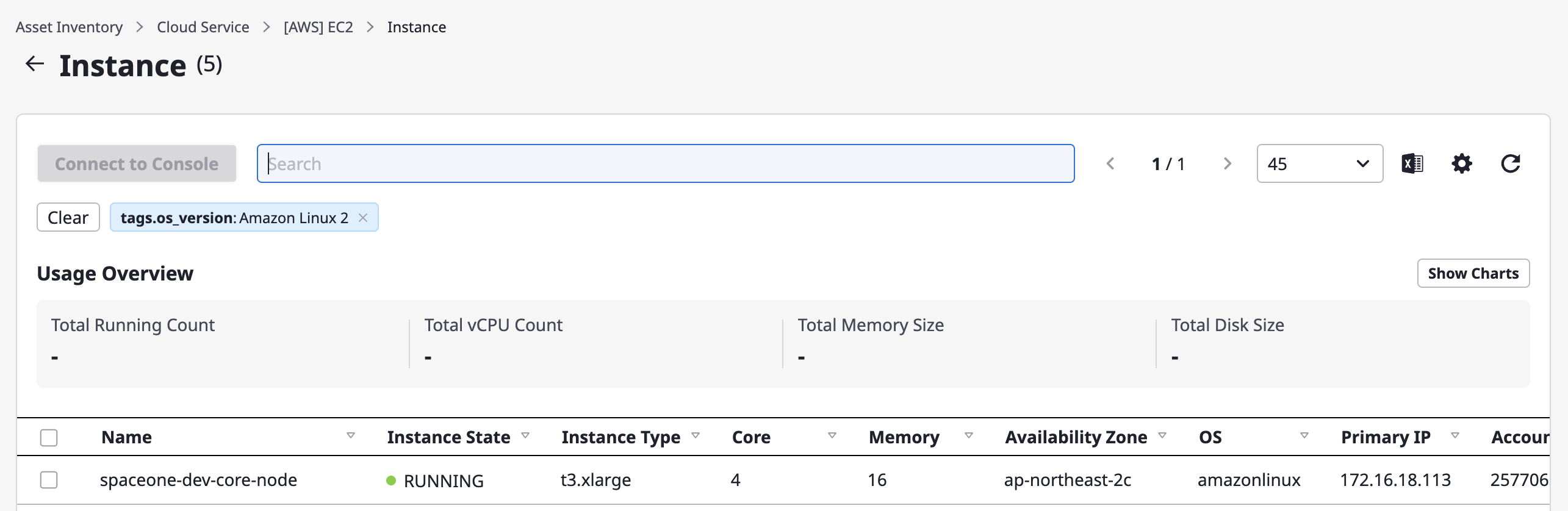
[ Viewing Managed Tags ]
- The
Managedtags can't be directly edited or removed in Cloudforet.
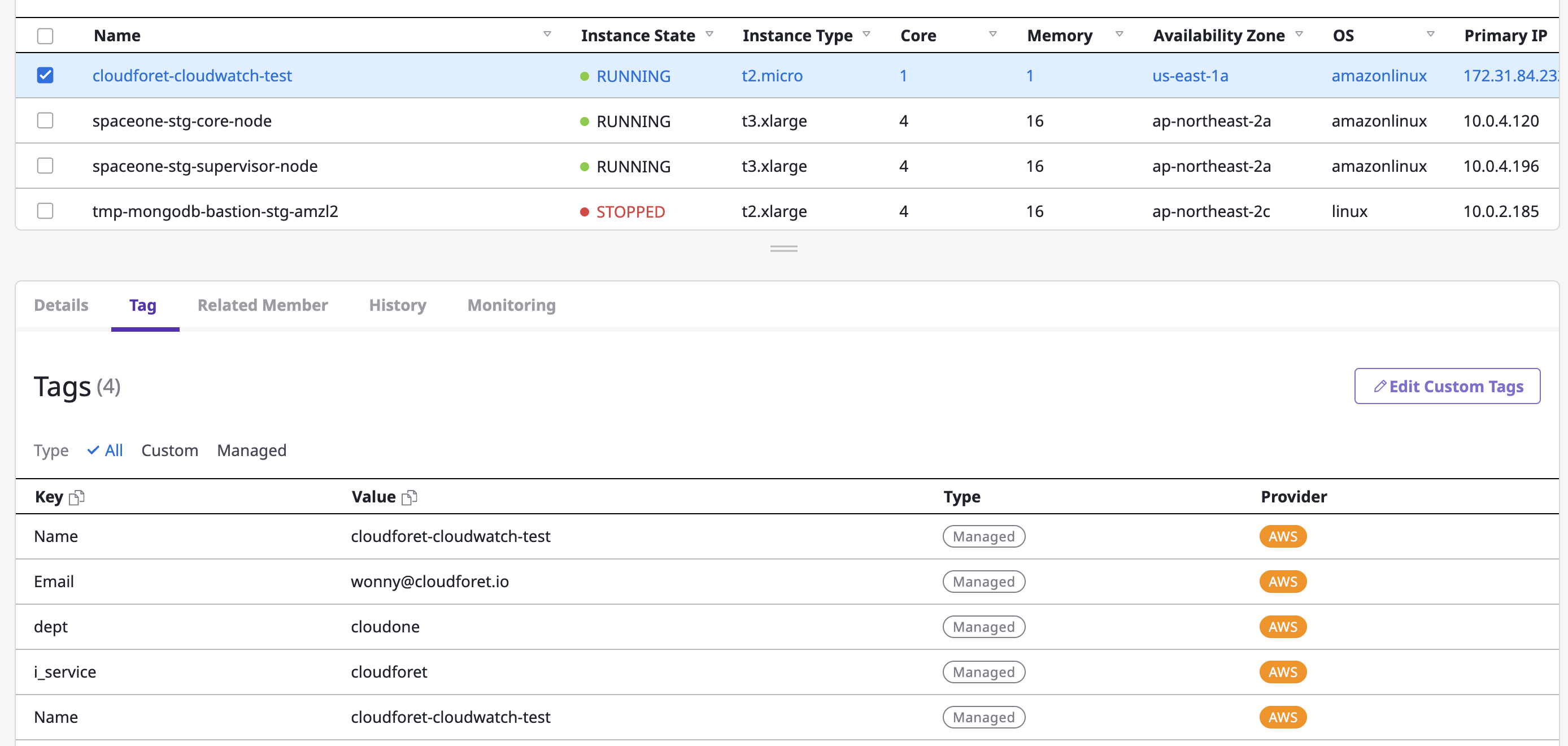
[ Creating & Viewing Custom Tags ]
(1) Click the [Edit Custom Tags] button

(2) After entering the tag in the form of key:value on the tag page, click the [Save] button to complete this process.
Checking members associated with cloud resources
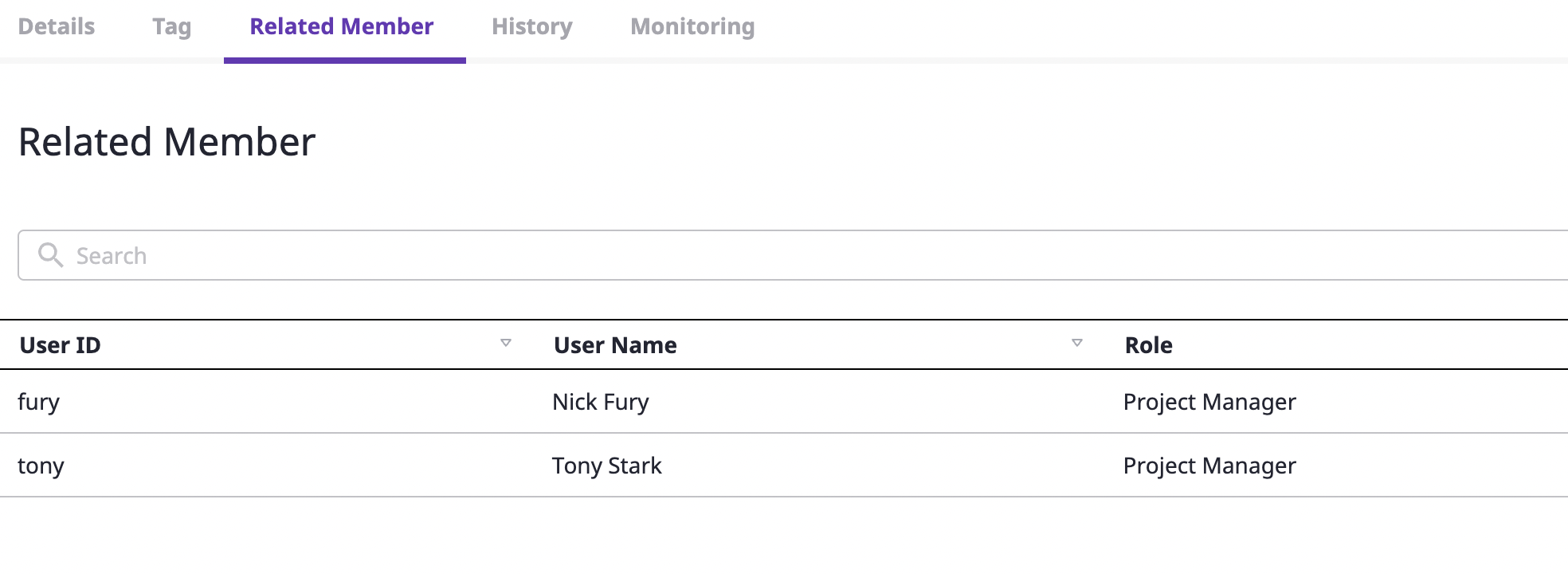
In the [Associated members] tab, you can check user information that meets the conditions below:
- A user who has access to the cloud resource as a Project member
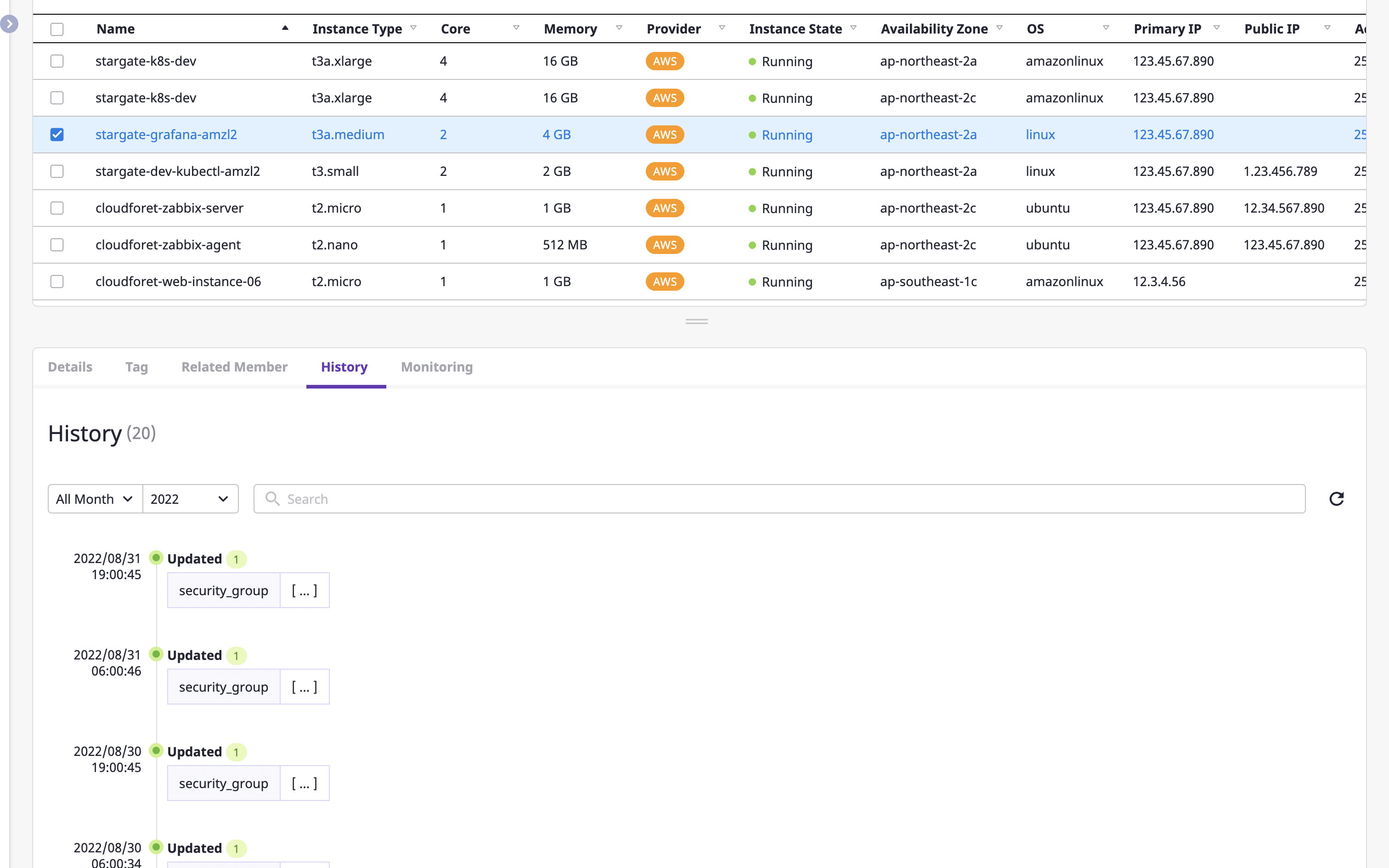
Viewing history of changing cloud resources
In the [Change history] tab, you can quickly identify changes by date/time of the selected cloud resource.
(1) You can select a certain date or search for the content you want to check.
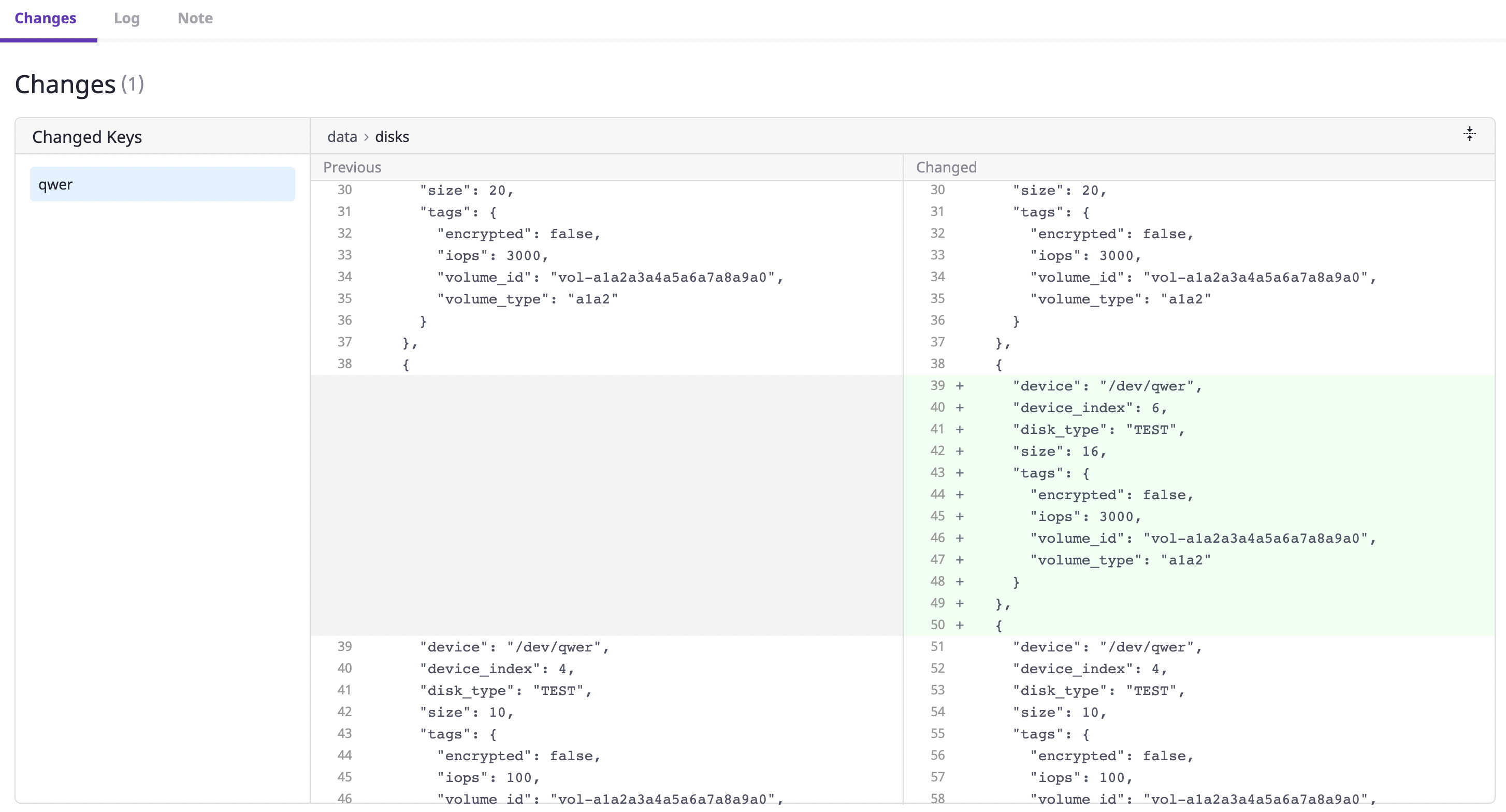
(2) When you click a certain key value or time period, you can check the details of the corresponding history of changes.
(2-1) Contents of changes: You can check the details of which key values of the resource were updated and how.
(2-2) Logs: As we support detailed logs by providers such as AWS CloudTrail, you can check which detailed events have occurred within/without of the selected time. This has a great advantage when identifying users who have made changes to a particular resource.
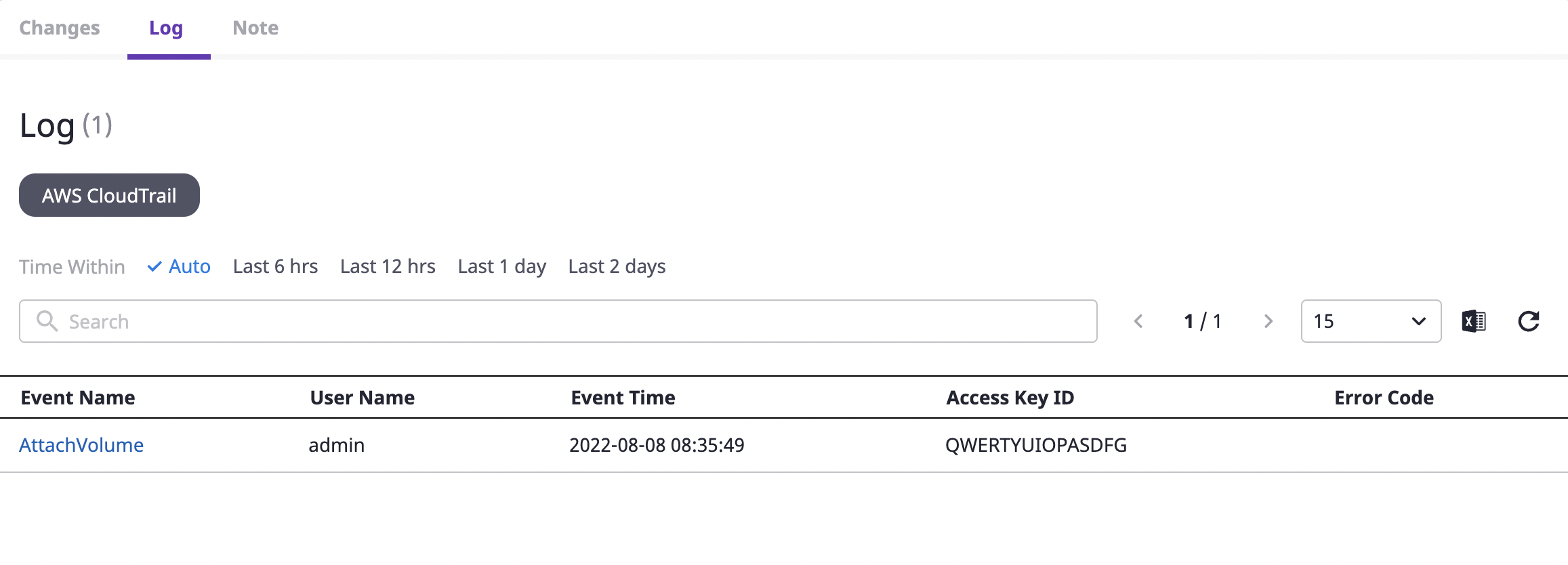
You can check the detailed log by clicking the value key you want to check.
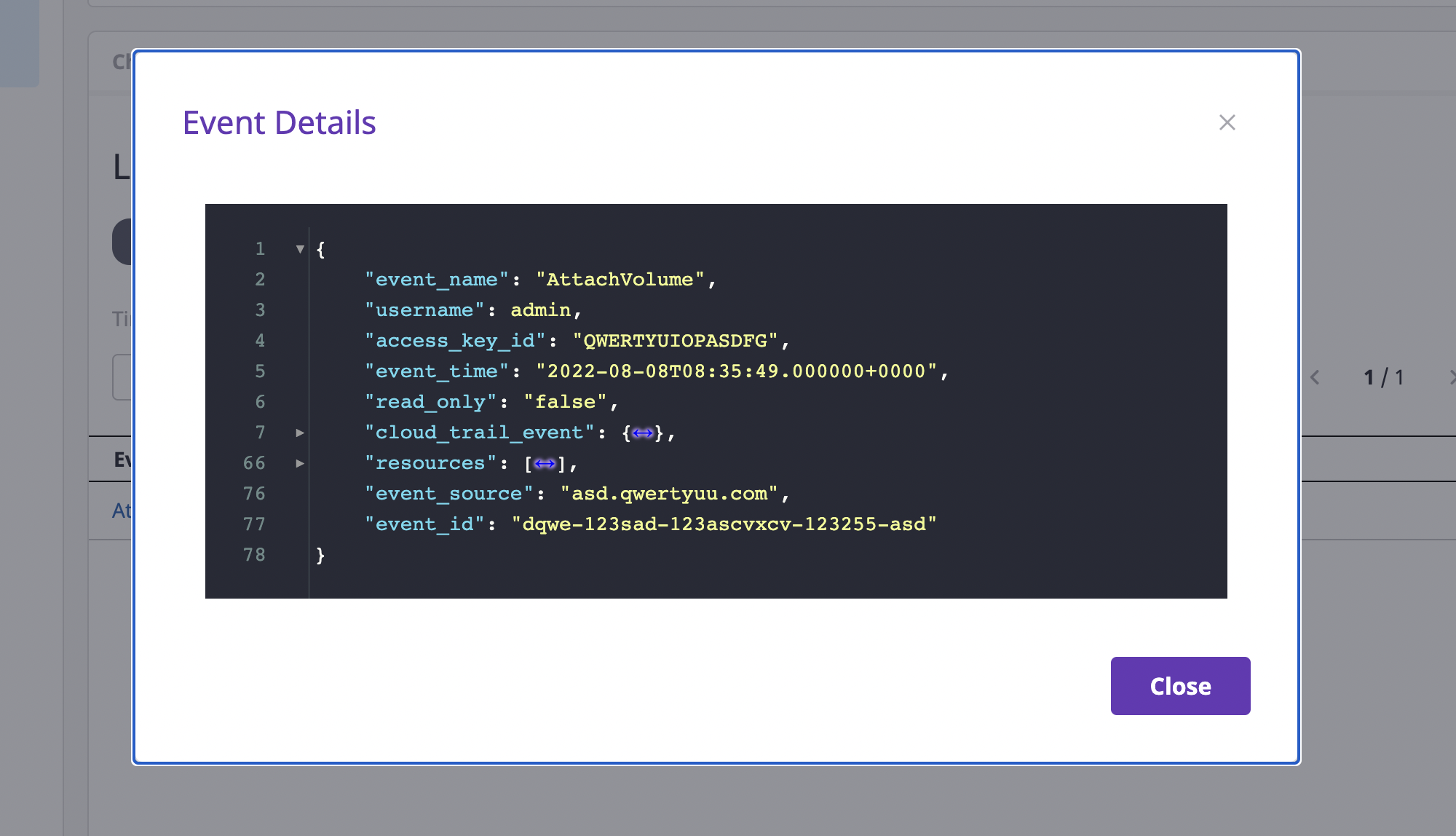
(2-3) Notes: By adding/managing notes at a selected time, you can freely manage the workflow for each company, such as which person in charge is related to the change, which process you will choose to solve the issue, etc.
Checking cloud resource monitoring information
The [Monitoring] tab shows various metrics for cloud resources.
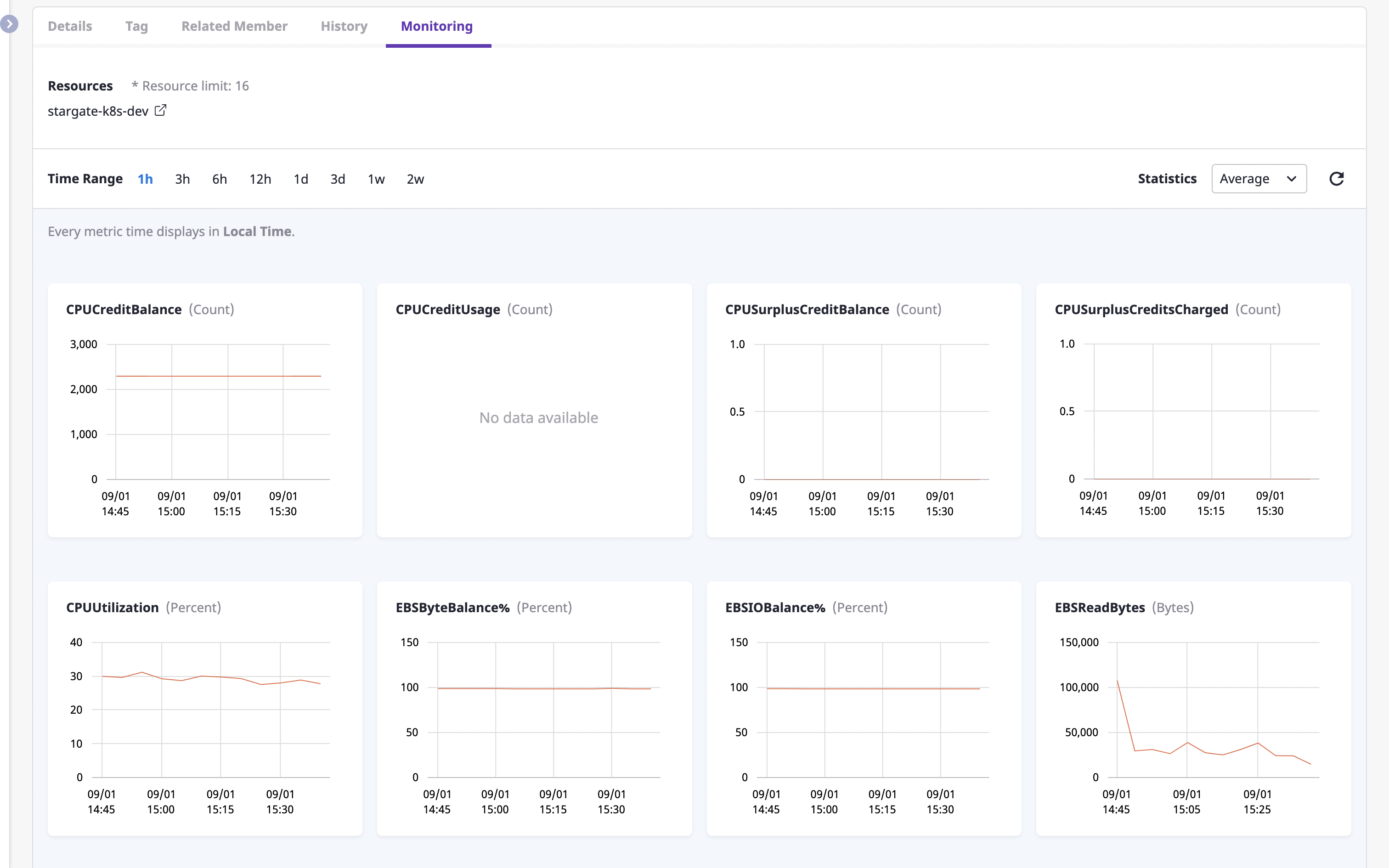
You can also view metrics for different criteria by changing the [Time range] filter, or by selecting a different statistical method from the [Statistics] dropdown.
If you select multiple resources by clicking the checkbox on the left from the list of cloud resources at the top, you can compare and explore metric information for multiple resources.
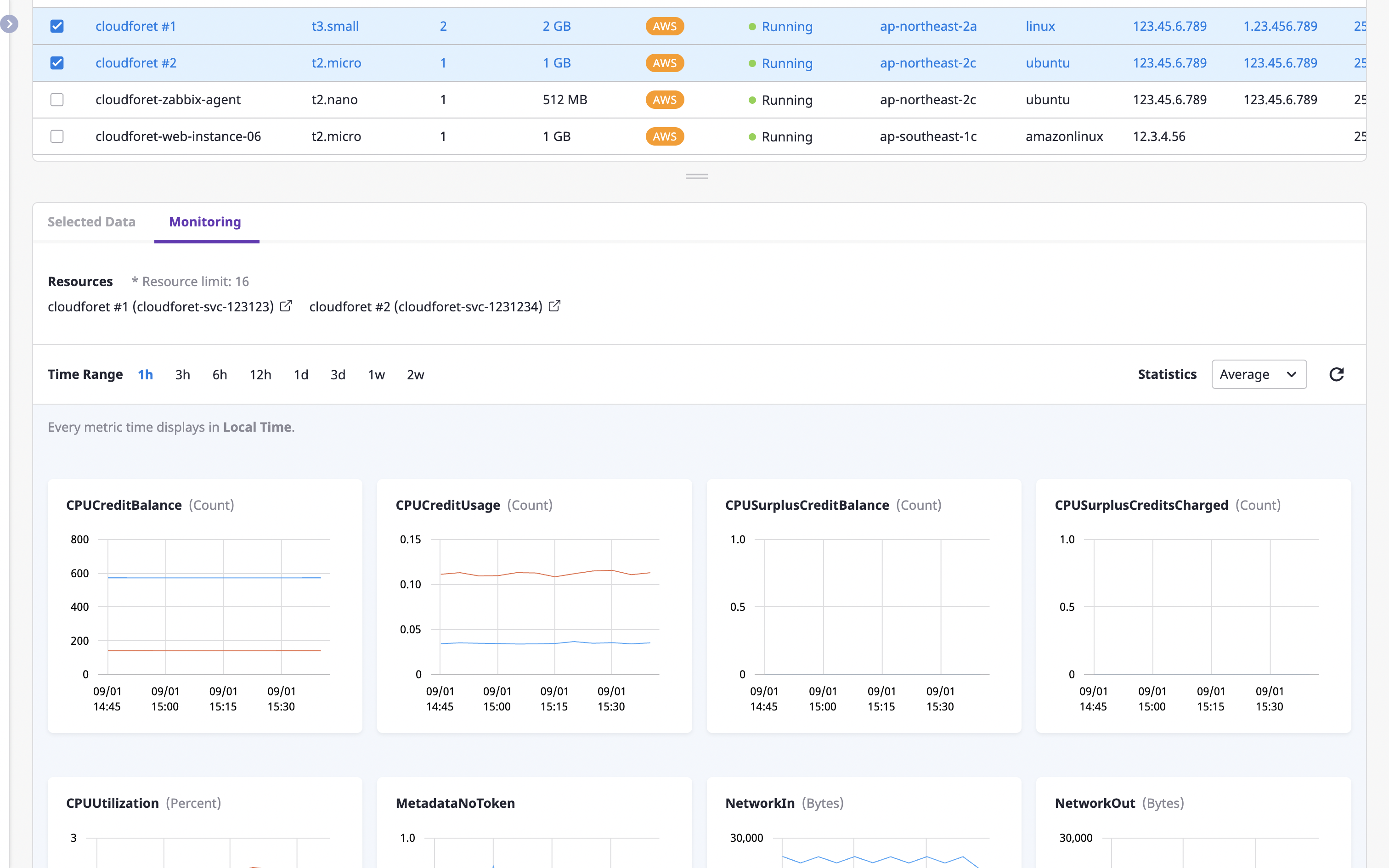
Metrics information is collected by the Monitoring plugin, and for detailed information, see here.
4.3 - Server
Getting a list of server resources
You can check a list of server resources by entering the server page through the [Asset inventory > Server] menu.
Advanced search allows you to filter the list by elaborate criteria.
Click the [Excel] icon button to [Export as an Excel file] for a list of resources (/ko/docs/guides/advanced/excel-export) or click the [Settings] icon button to [Personalize table fields](/ko/ docs/guides/advanced/custom-table).
Opening the server resources console
Sometimes you need to work on a console site that a server resources provider offers.
(1) Select the server resource to which you want to connect the console.
(2) Click the [Console connection] button.
(3) Click the button to open the provider's console in a new tab where you can continue working with the server resource.
Below is an example of the AWS EC2 Instance console that was opened.
Explore server resources
If you select the item you want to look at from a list of server resources, you can check information about the resource at the bottom.
It is equivalent to the Explore cloud service resources in the [Asset inventory > Cloud service] menu.
4.4 - Collector
Overview
To collect data with a collector, you need two elements:
Collector plugin
This is an element that defines the specifications of what resources to collect from the Cloud provider, and how to display the collected data on the screen.
Since each provider has a different structure and content of data, a collector completely relies on Collector plugin to collect resources.
For detailed information on this, see here.
Service account
To collect resources, you need to connect to an account on the Cloud provider.
Service Account is your account information to link to your provider's account.
A collector accesses the provider account through the service account created for each provider.
For detailed information on this, see here.
Create a collector
(1) Click the [+ Create] button at the top left.
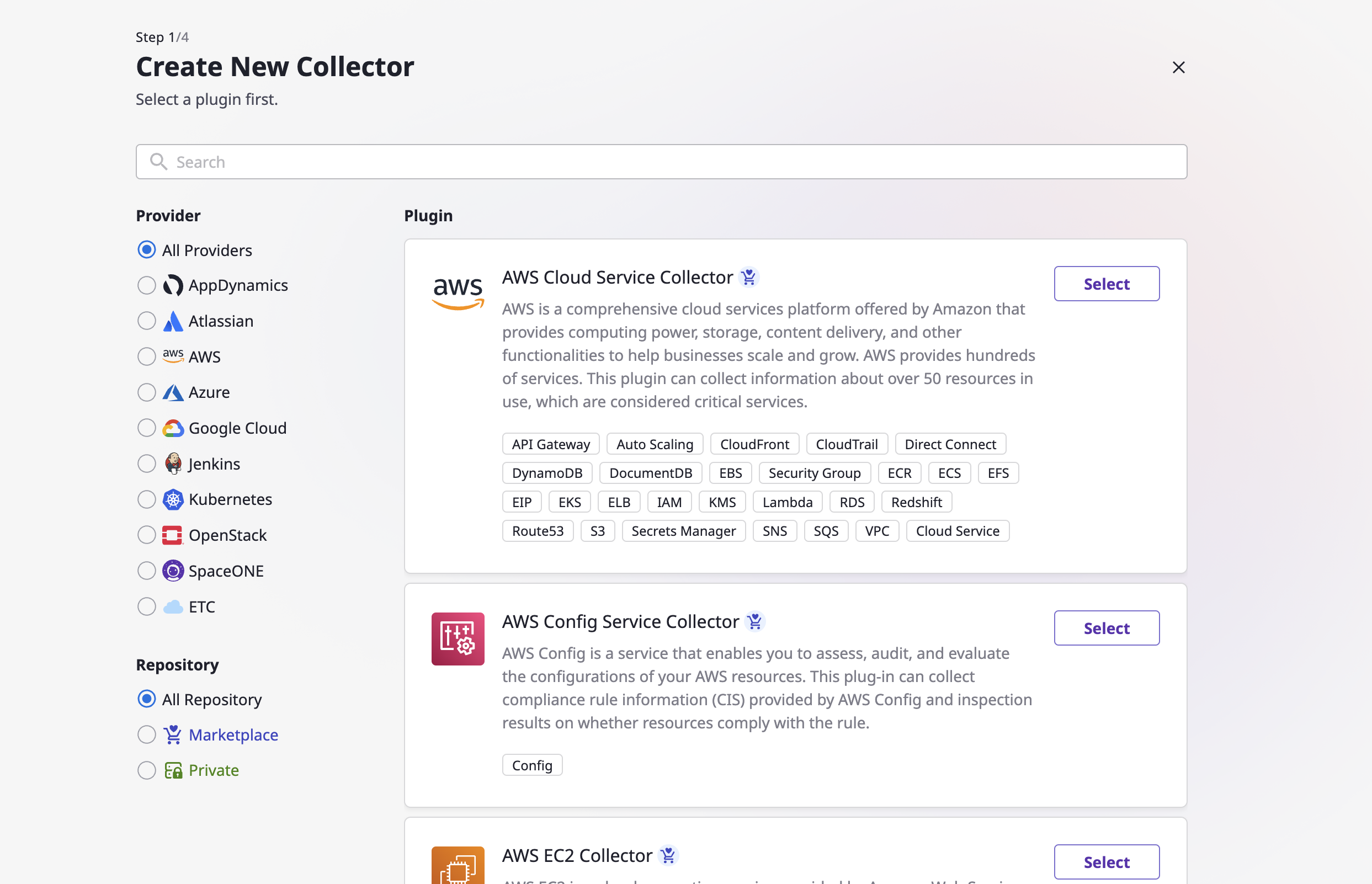
(2) Follow the steps on the "Create New Collector" page.
(2-1) On the Plugin List page, find a required collector plugin and click the [Select] button.
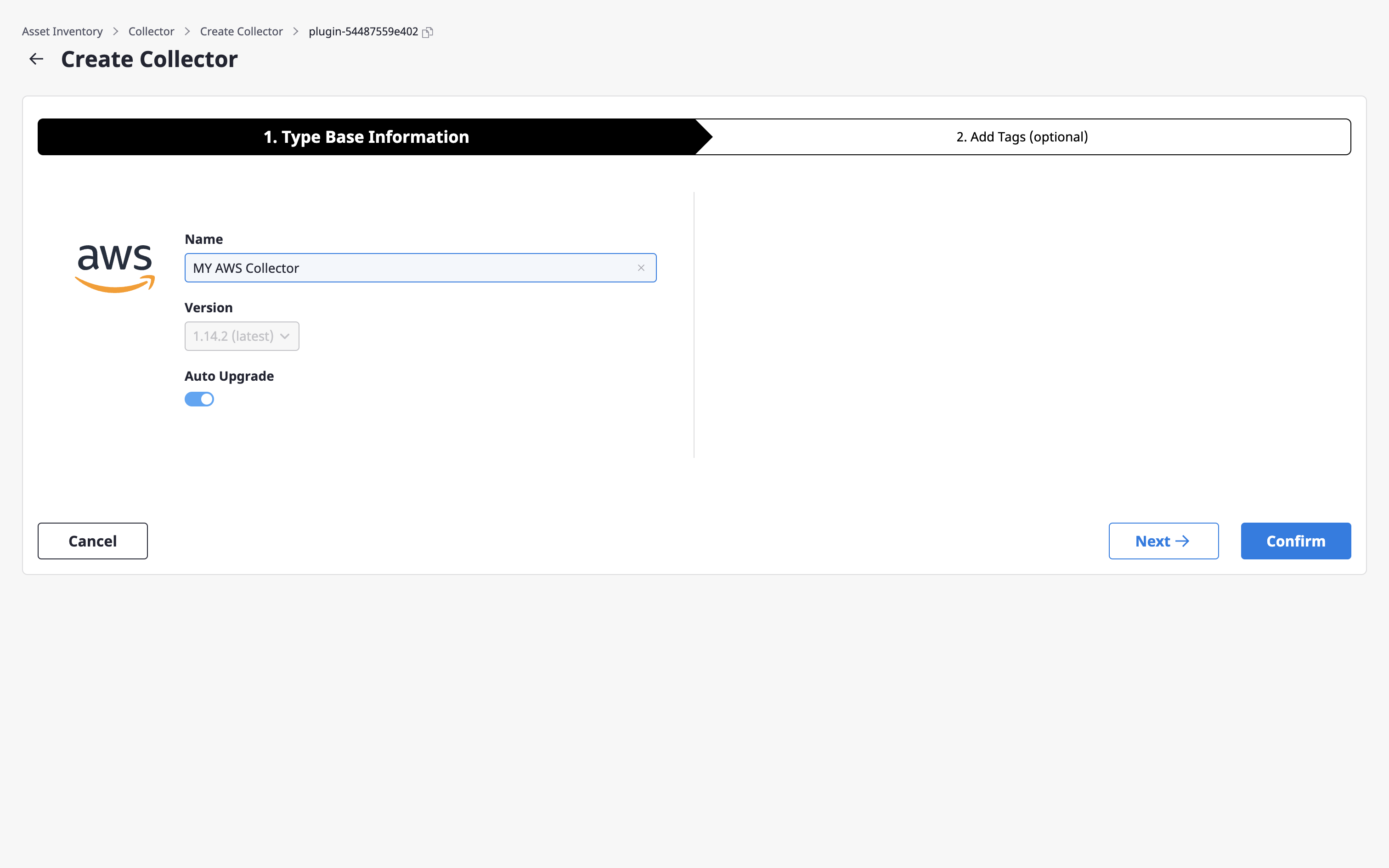
(2-2) Enter the name and version of the collector and click the [Continue] button.
(Depending on the collector, it can be required to select a specific cloud provider.)
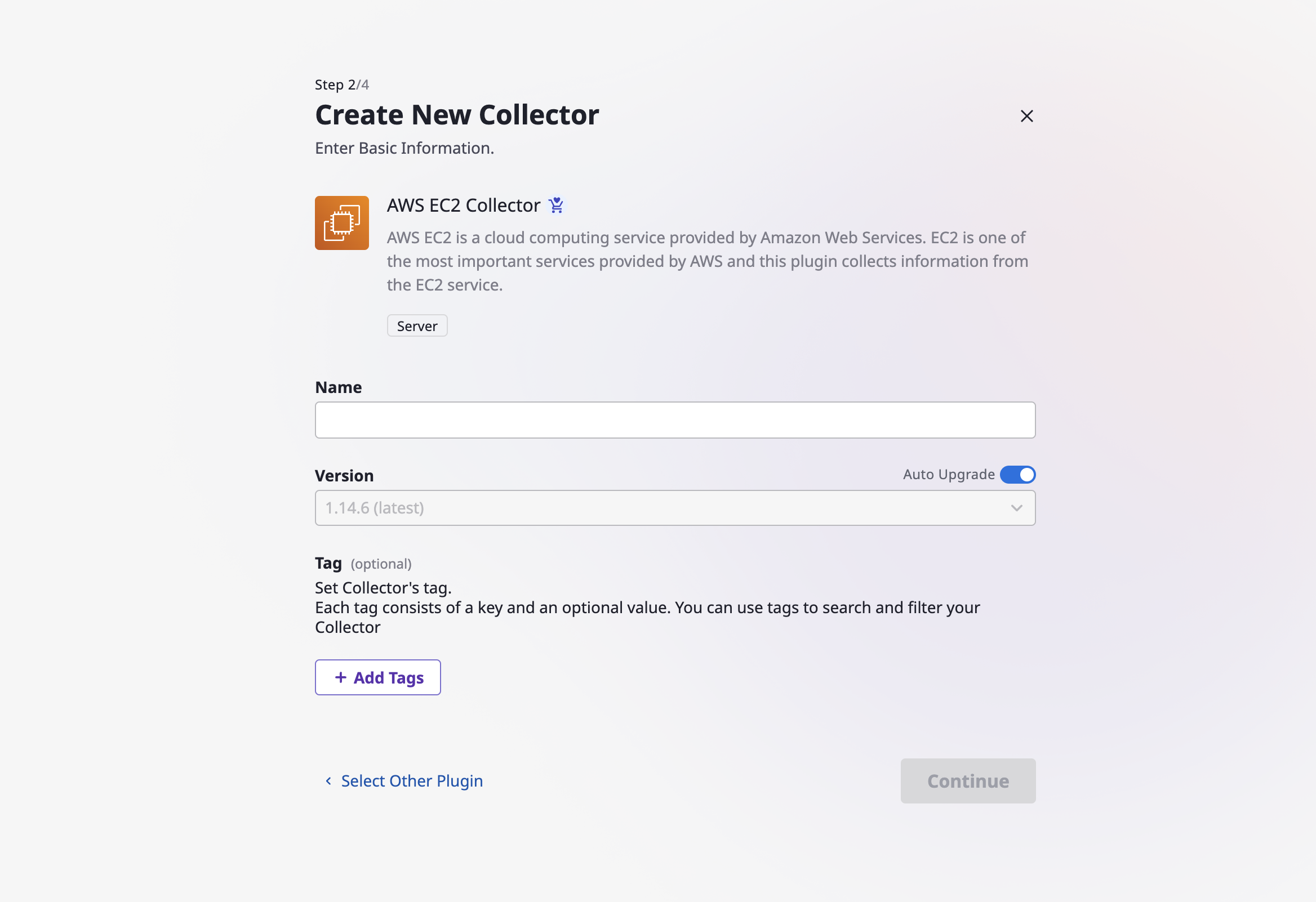
Version and auto upgrade
Version refers to the version of the previously selected collector plugin, which can be chosen by disabling auto upgrade. In this case, the data is always collected with the specified version of the plugin.
On the other hand, if you enable auto upgrade, your data will always be collected with the latest version of the plugin.
(2-3) Select additional options for the collector and click the [Continue] button.
(2-3-1) Service Account: Select either "All" or Specific Service Accounts. If you choose "All," the service accounts associated with the provider related to the collector will be automatically selected for data collection.
(2-3-2) Additional Options: Depending on the collector, there may or may not be additional options to select.
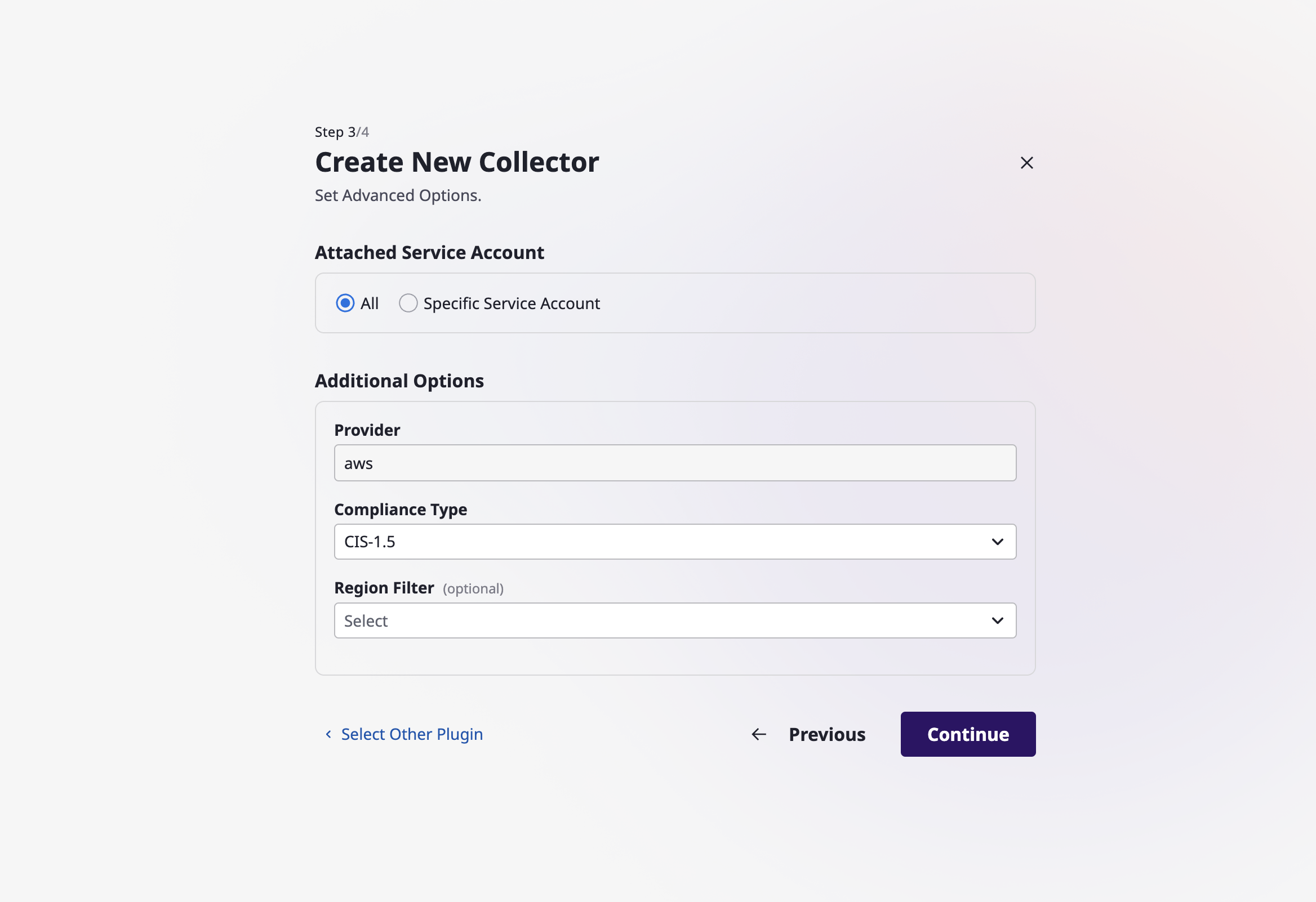
(2-4) You can set up a schedule to automatically perform data collection (optional). Once you have completed all the steps, click the [Create New Collector] button to finalize the collector creation.
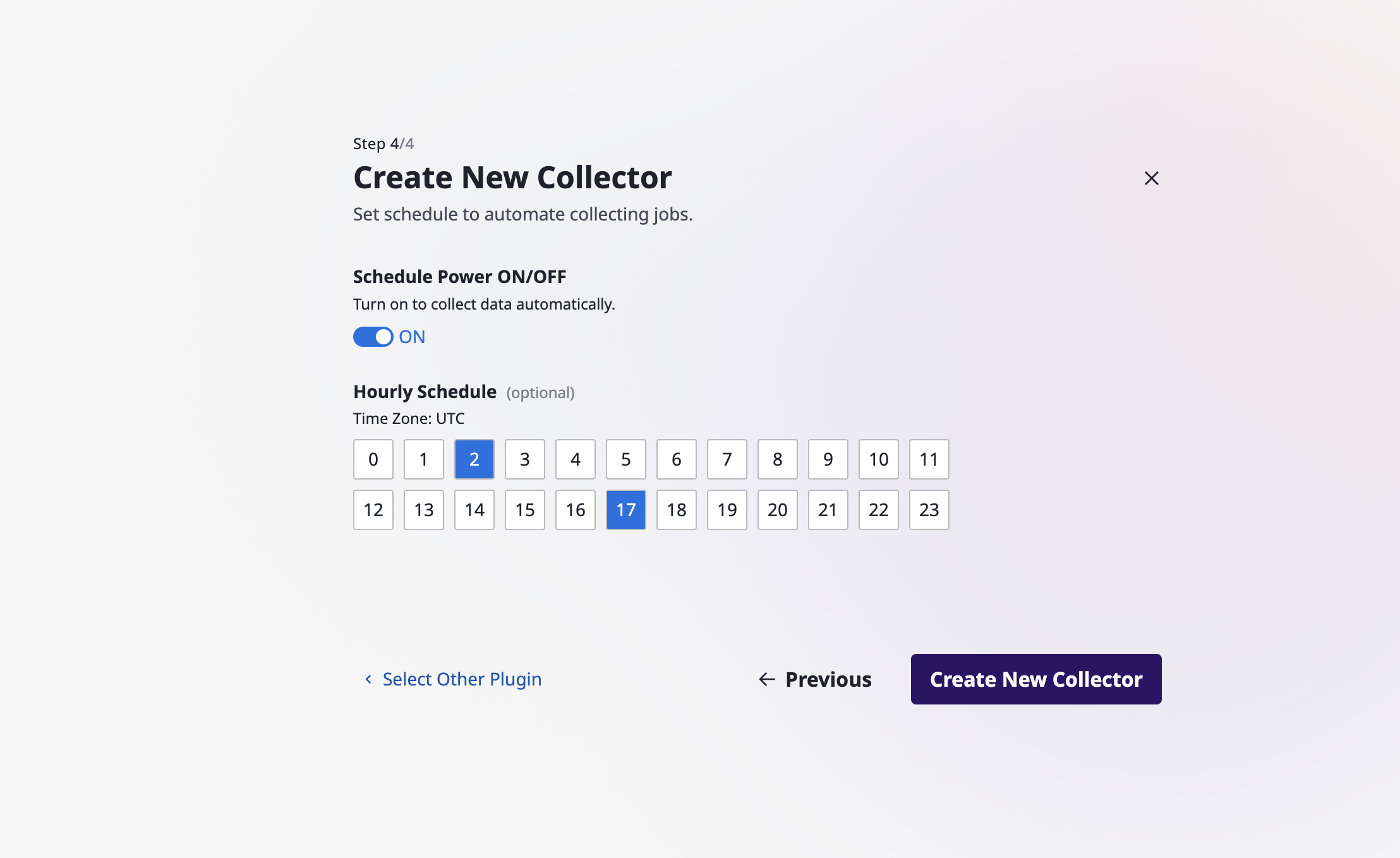
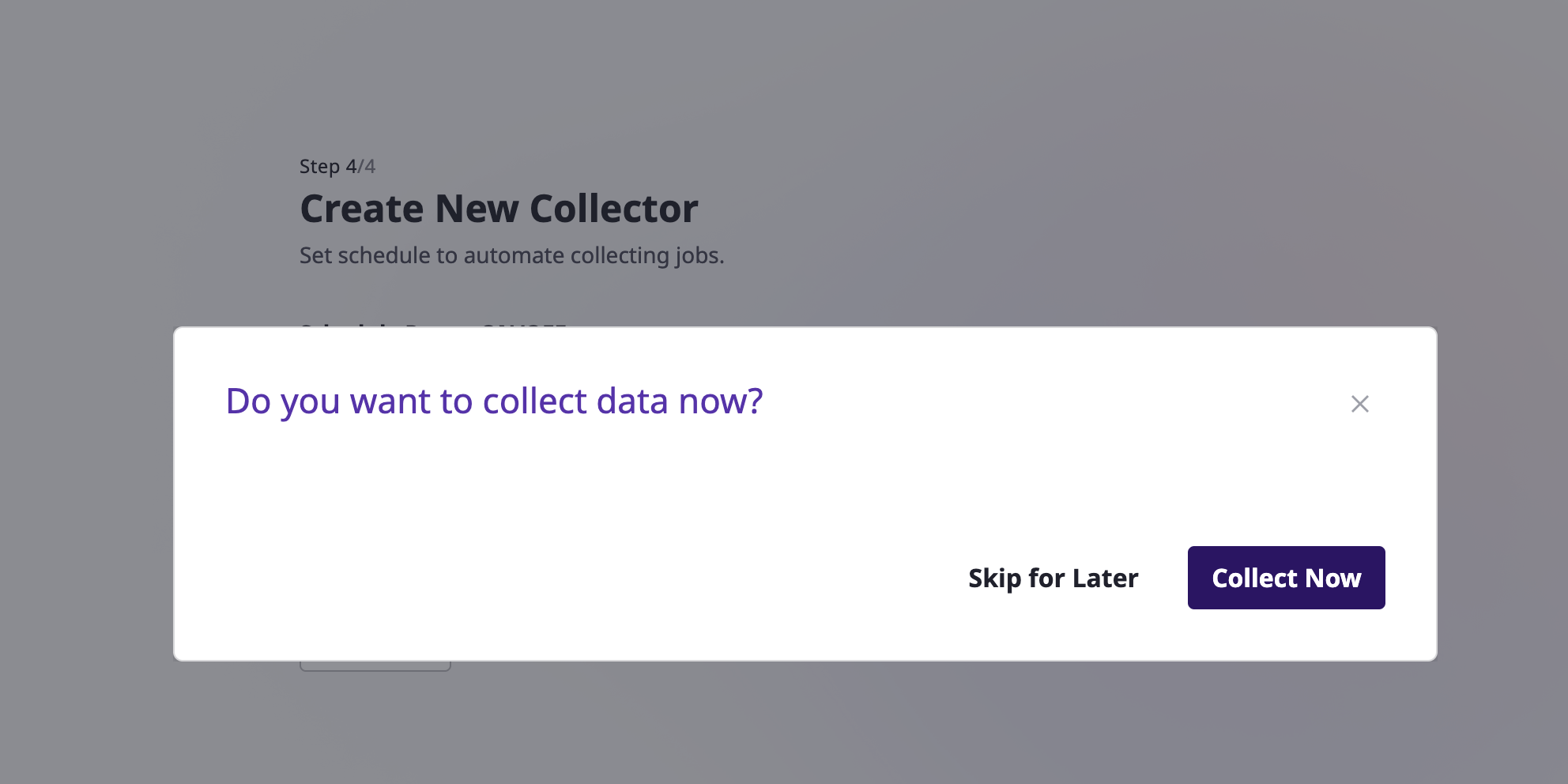
(2-5) Once collector is created, you can collect data immediately.
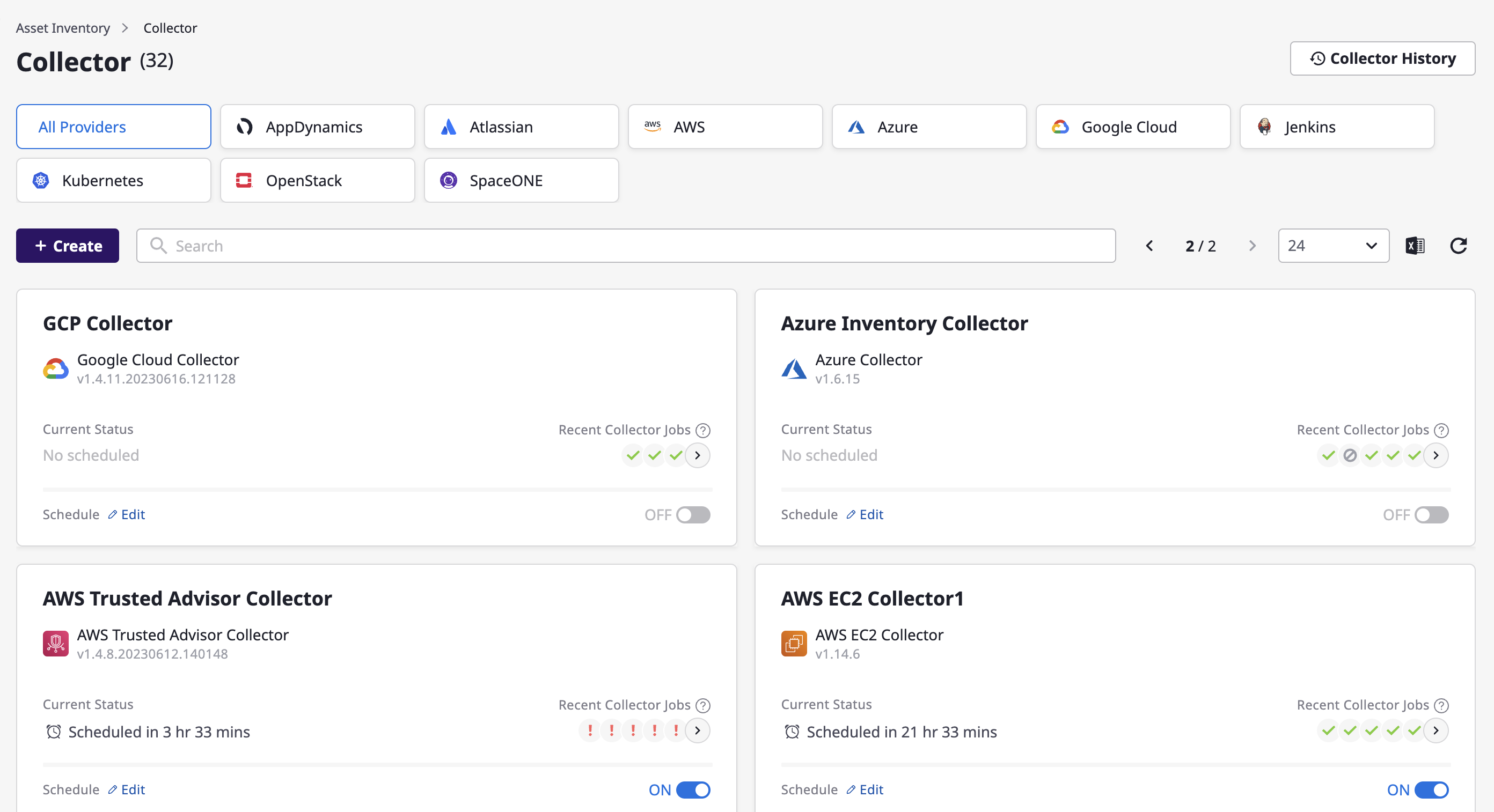
Get a list of collectors
You can view a list of all collectors that have been created on the collector page.
Advanced search allows you to filter the list by elaborate criteria. For a detailed explanation, see here.
View/Edit/Delete collector
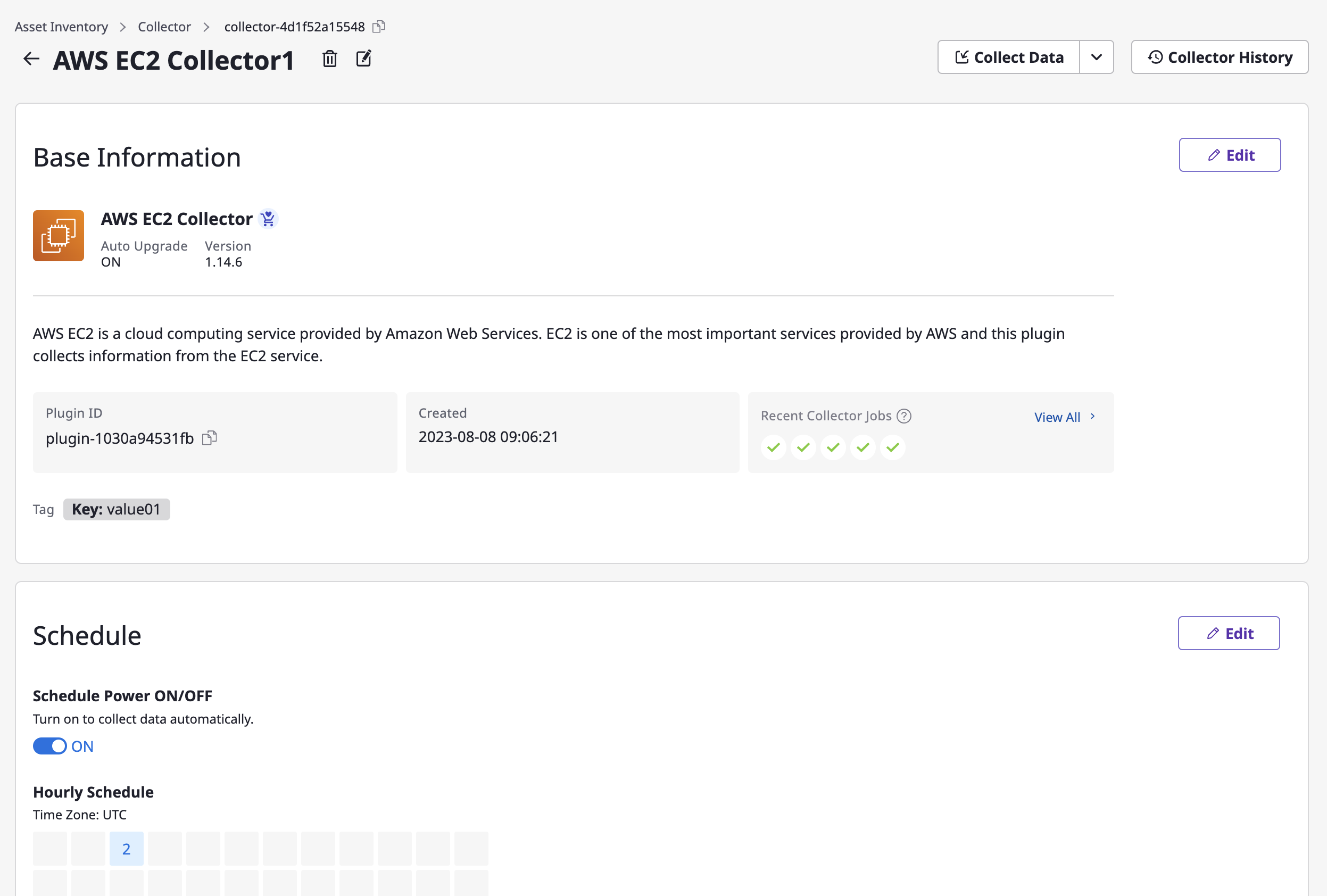
(1) View Details
(1-1) Select a specific collector card from the list to navigate to its detailed page.
(1-2) You can view the basic information, schedule, additional options, and attached service accounts.
(2) Edit or Delete
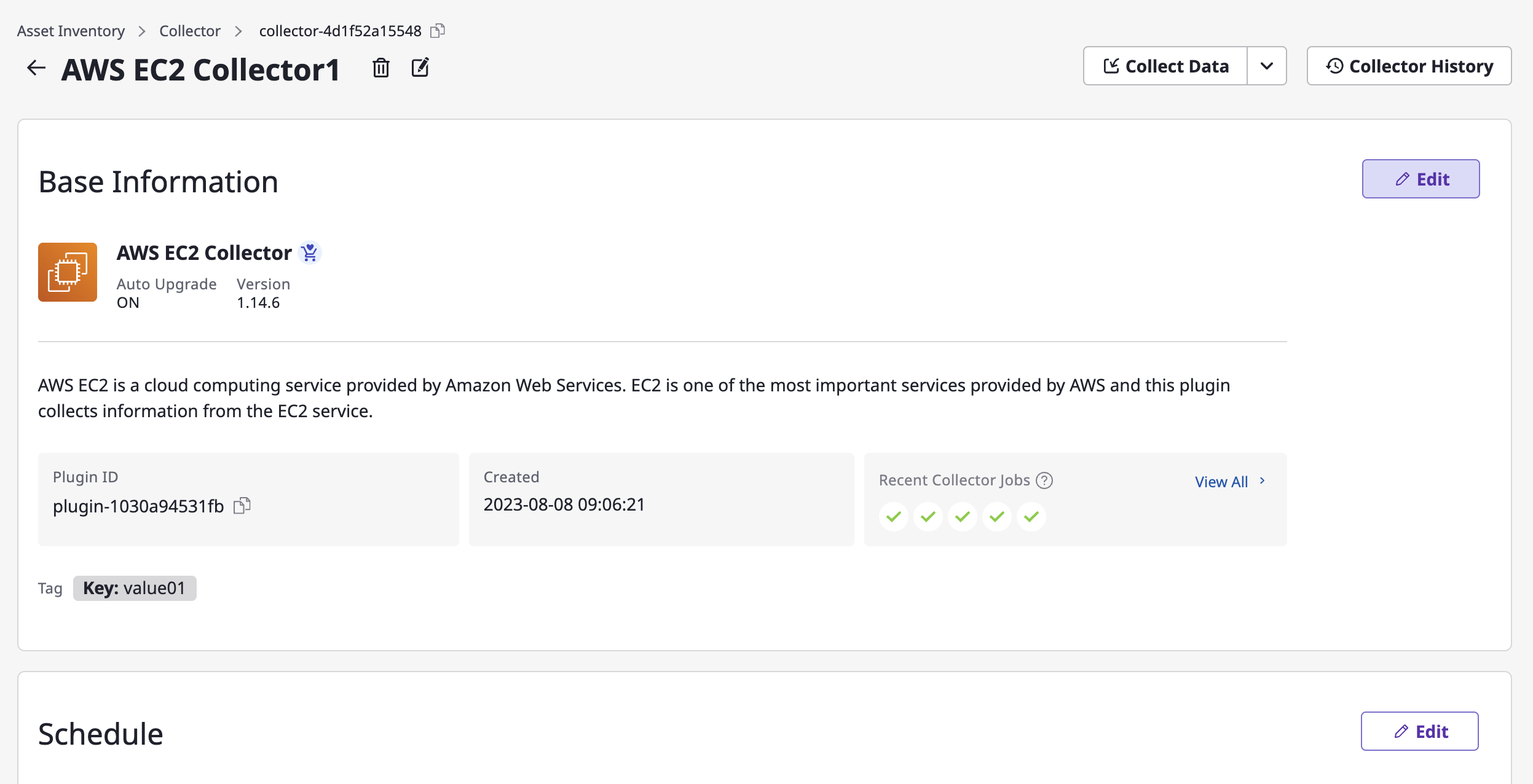
(2-1) Click on the [Edit] icon at the top and modify the collector name.

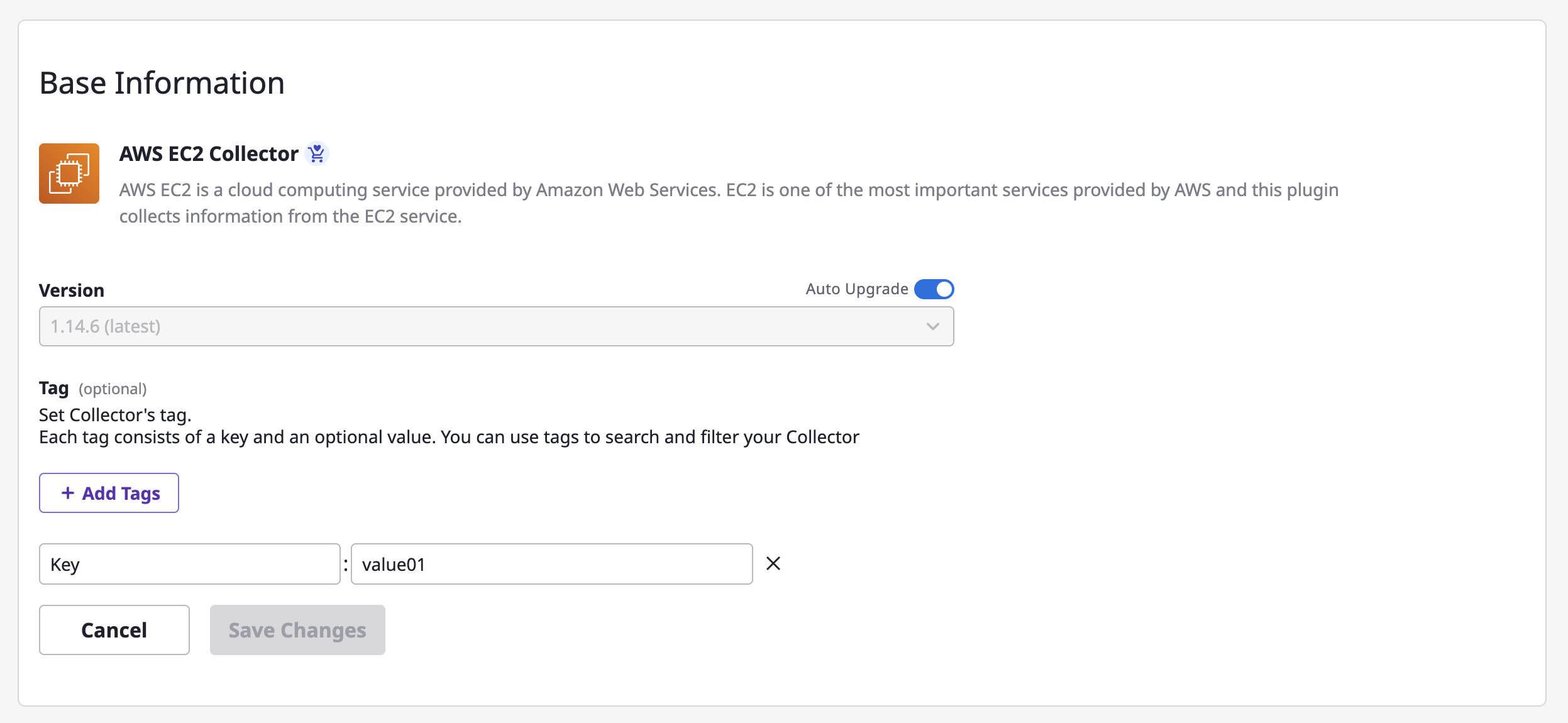
(2-2) If you need to edit details such as base information, schedule, additional options or service accounts, click the [Edit] button in each area.
(2-3) After making the changes, click the [Save Changes] button to complete the modification.
(2-4) If you need to delete a collector, click the [Trash] icon on the top.

Set up automated data collection
After creating a collector, you can still modify the automated data collection schedule for each individual collector.
(1) In the collector list page, you can enable or disable automated data collection for each collector by using the schedule toggle button(Switch On/Off) in the collector card section. You can quickly set and modify the frequency by clicking the [Edit] button.
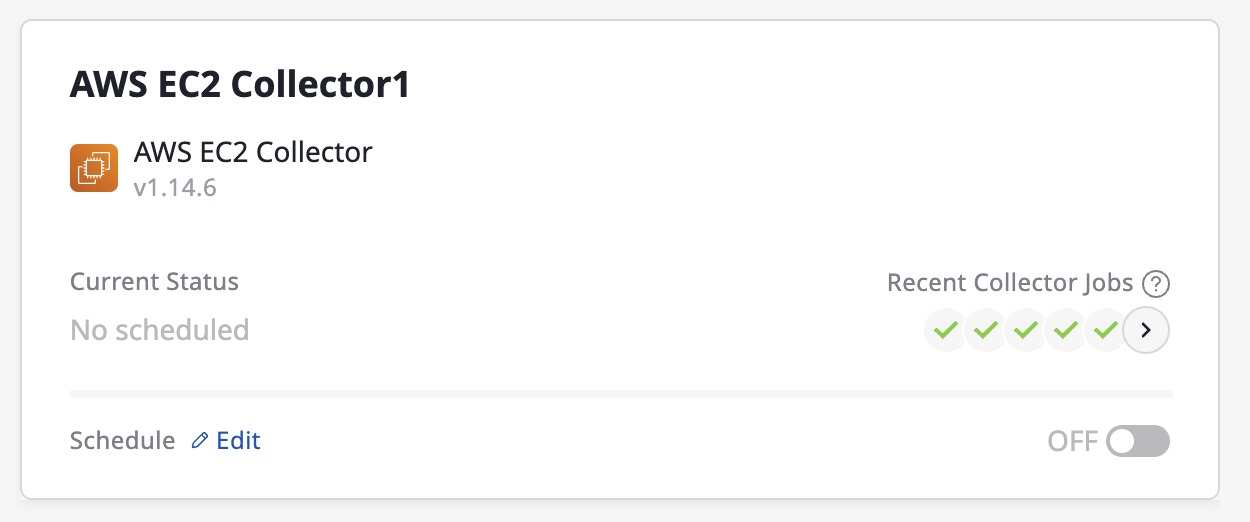
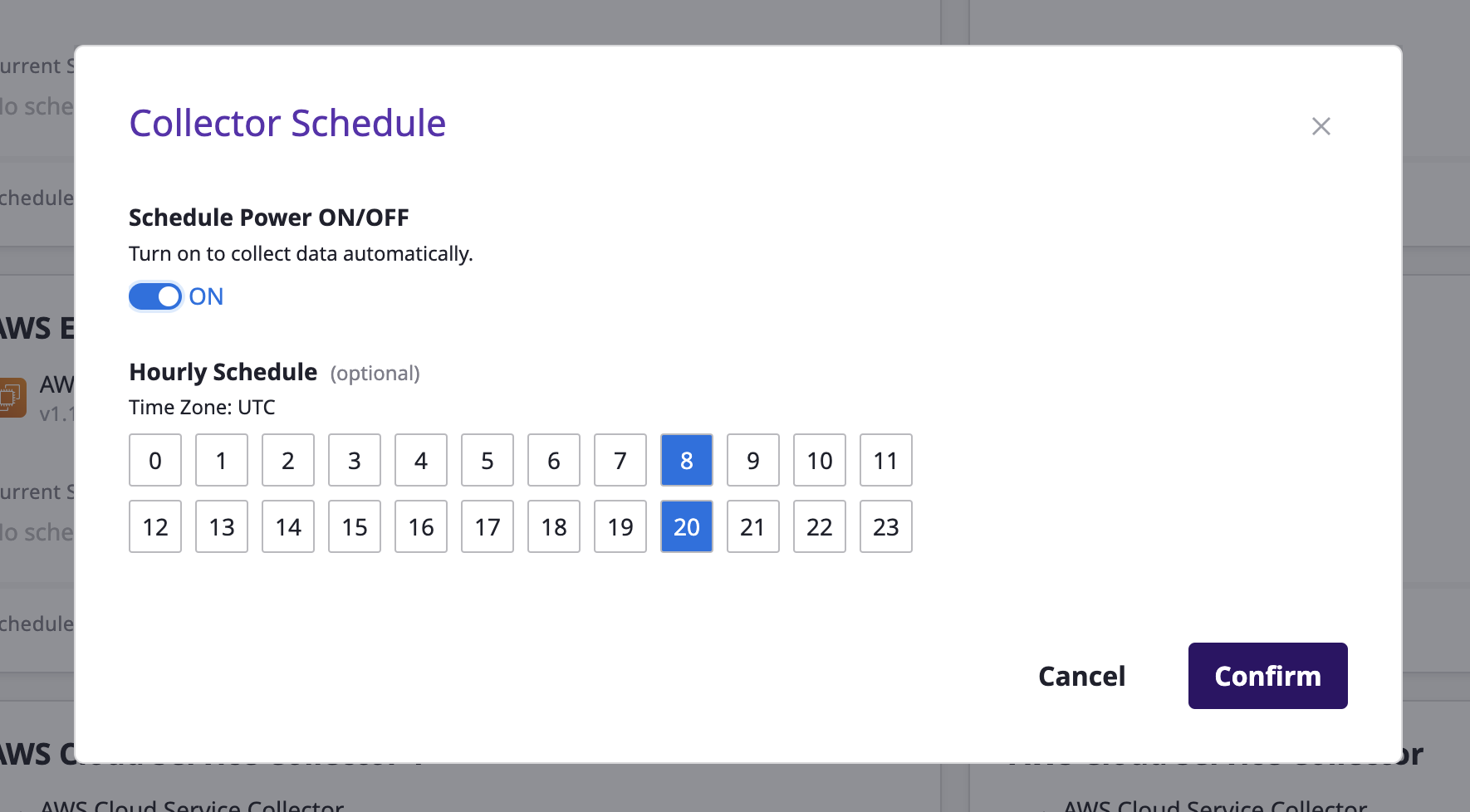
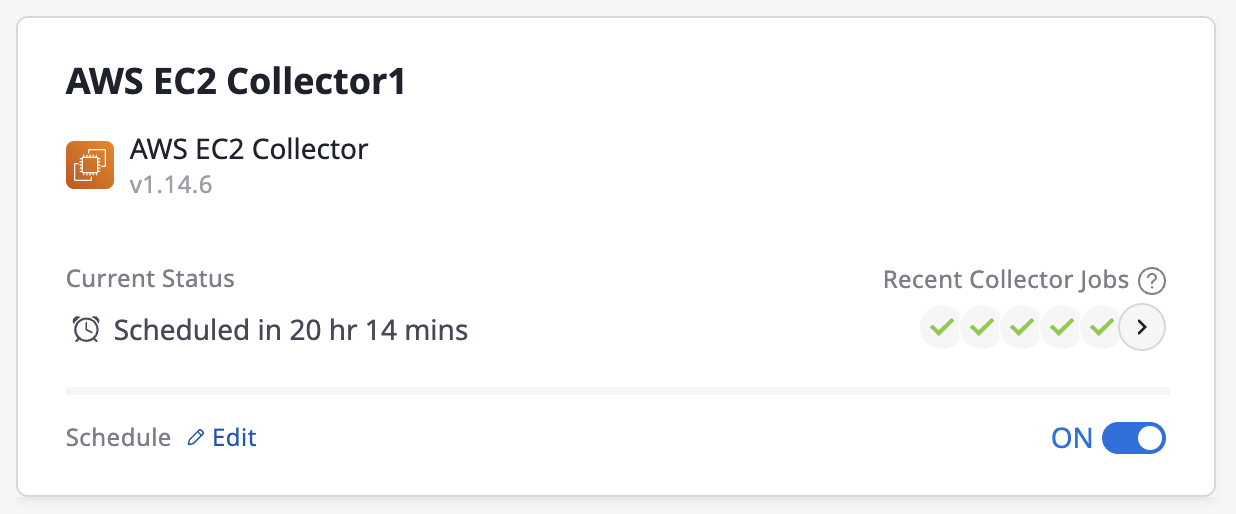
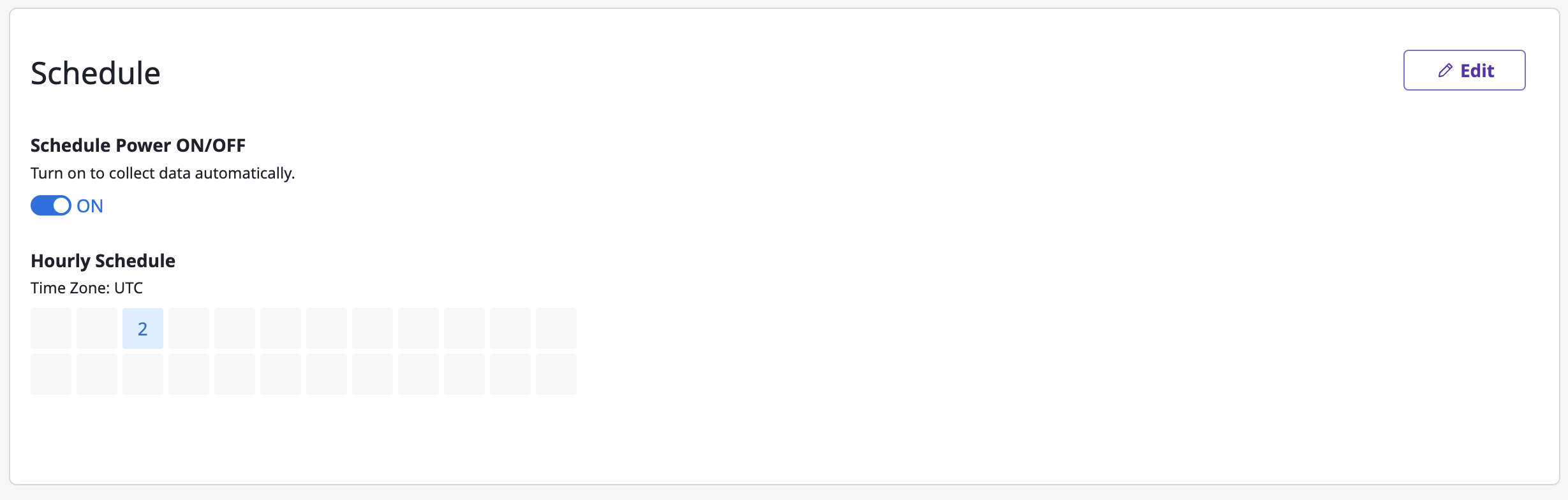
(2) You can also navigate to the detailed page of each collector and change the schedule.
Start data collection immediately
You can collect data on a one-time basis without setting up automated data collection.
It allows data collection to take place even when the collector does not have an automated data collection schedule.
Data collection works in two ways:
Collect data for all attached service accounts
Collector needs account information from a Provider for data collection, which is registered through Service account.
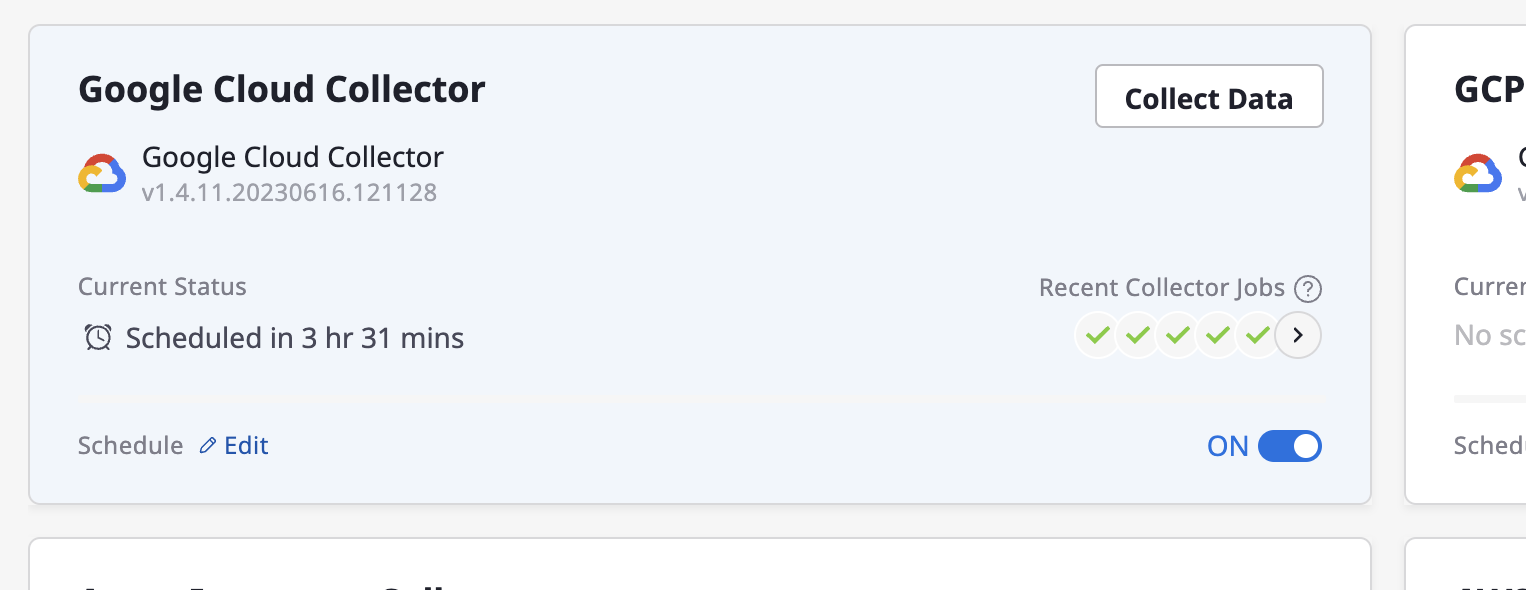
(1) Click on [Collect Data]
(Collector list Page) Hover over the collector card area for data collection, and then click the [Collect Data] button.
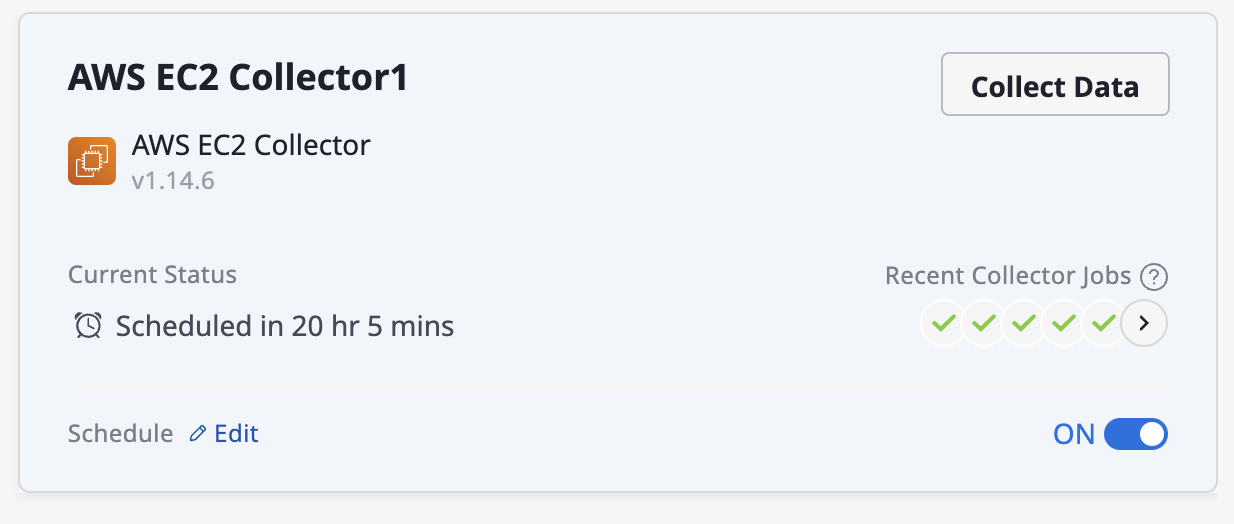
(Collector Detail Page) Click the [Collect Data] button located in the top right corner of the detailed page.

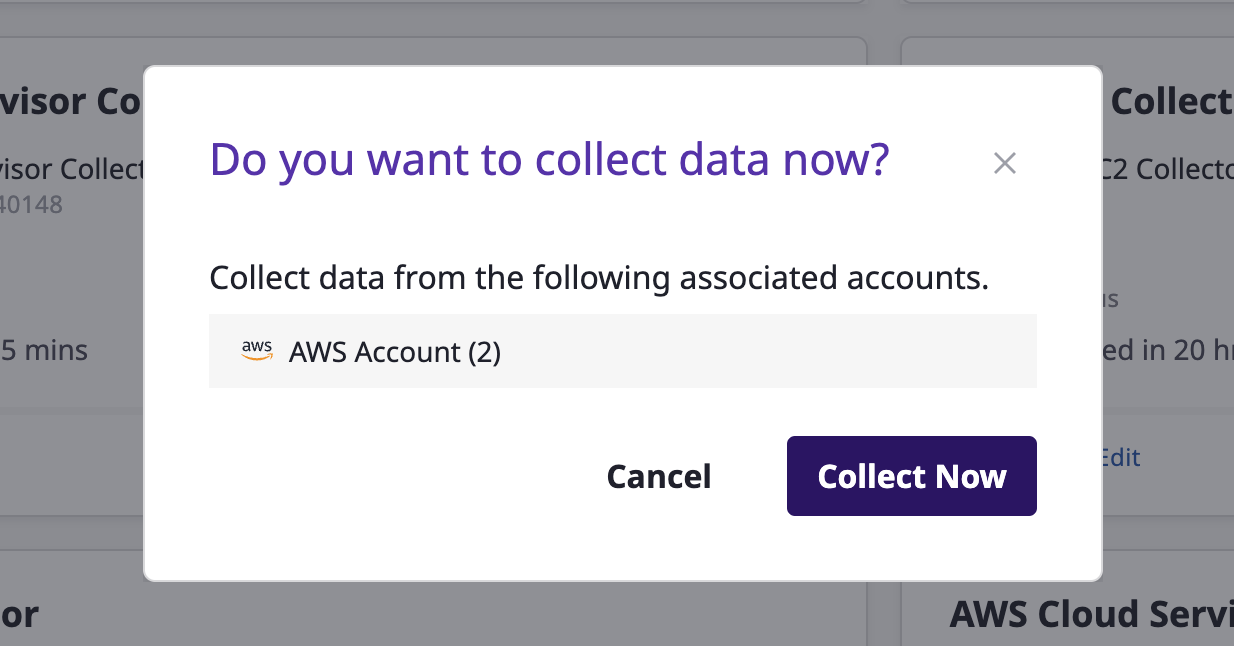
(2) Proceed with data collection.
(2) Whether or not the collector has completed a data collection can be checked in Collector history. You can click the [View details] link of a selected collector to go to that page.
Collect data for a single service account
When collecting data with a collector, you may only collect data from a specific cloud provider’s account.
(1) Select a collector from the collector list page, and go to detail page.
(2) You can find the list of attached service accounts on the bottom of detail page.
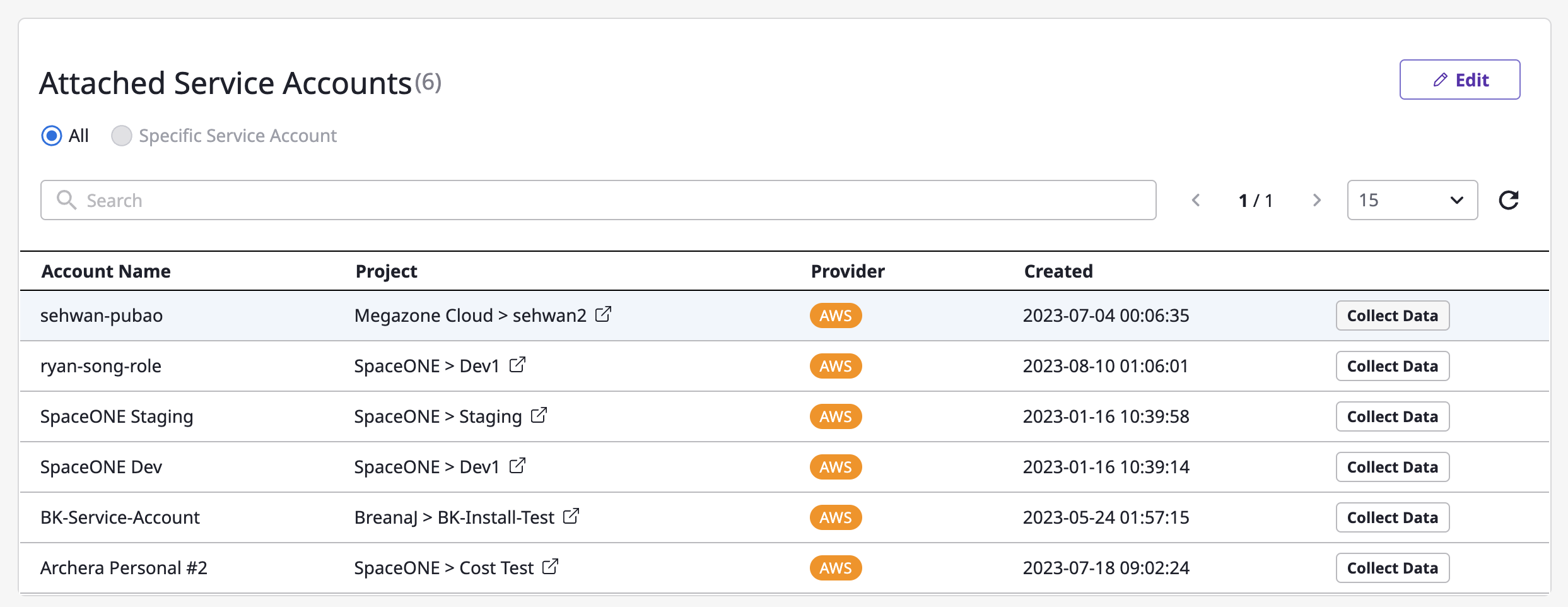
Service account
Service account has access information for the provider account required for data collection.
If no information can be found here, this means there is no account information for accessing the provider, and as a result, no data collection occurs even when the collector is running.
Therefore, to collect data with a collector, you must first register the account information of the provider in the [Service account] menu.
(3) In order to start data collection, Click the [Collect Data] button on the right side of the service account for which you want to collect data.
Checking data collection history
You can check your data collection history on the Collector history page.
You can go to the collector history page by clicking the [Collector history] button at the top of the collector page.

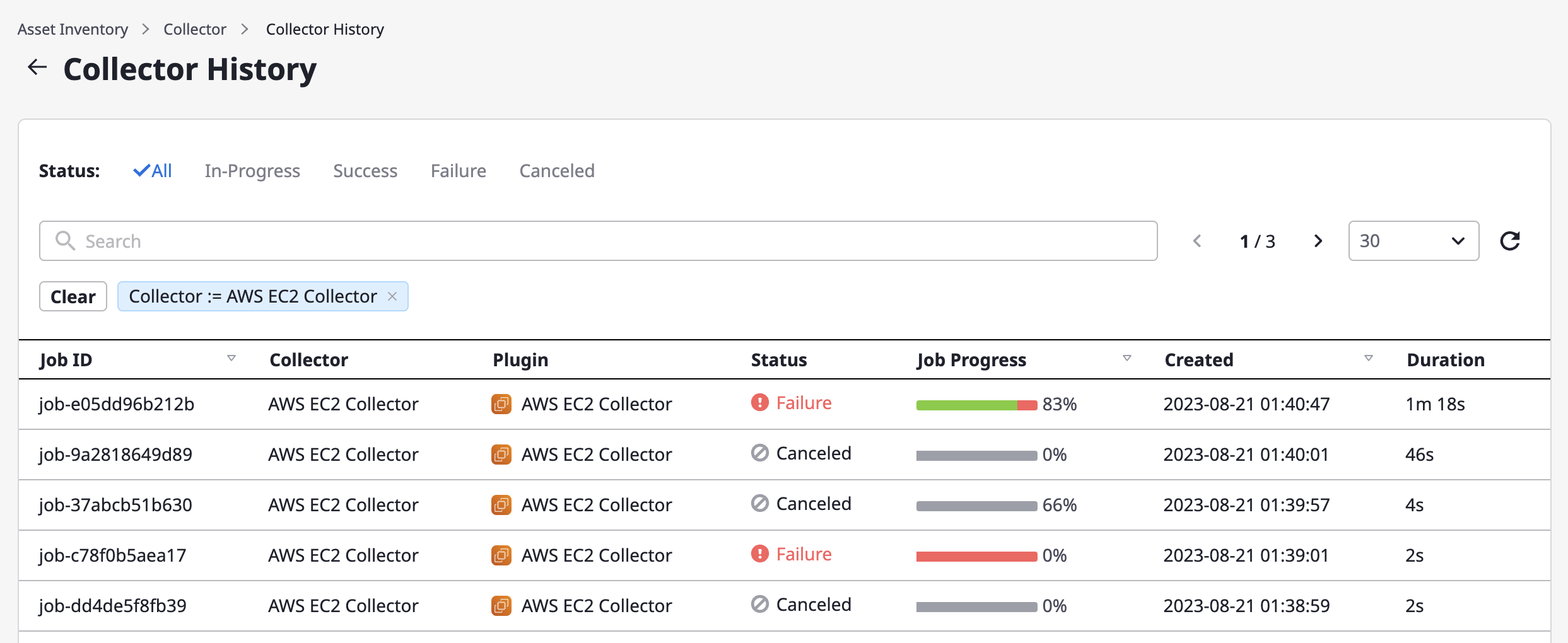
Checking the details of data collection history
If you select a collection history from the list of data collections above, you will be taken to the collection history details page.
You can check data collection status, basic information, and Collection history by service account.
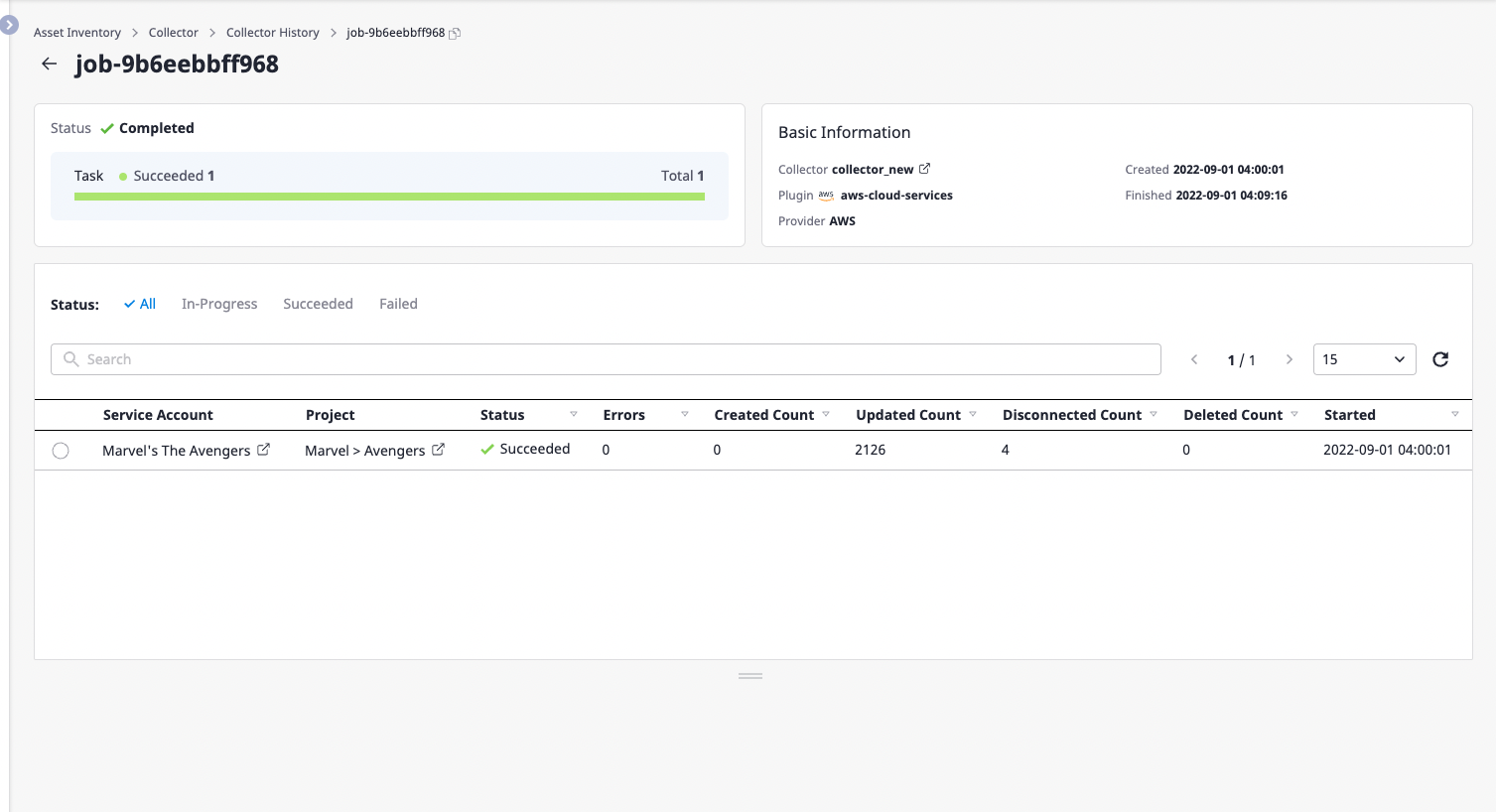
Checking collection history for each service account
When you run the collector, each collection is performed for each associated service account.
Here you can find information about how the collection was performed by the service account.
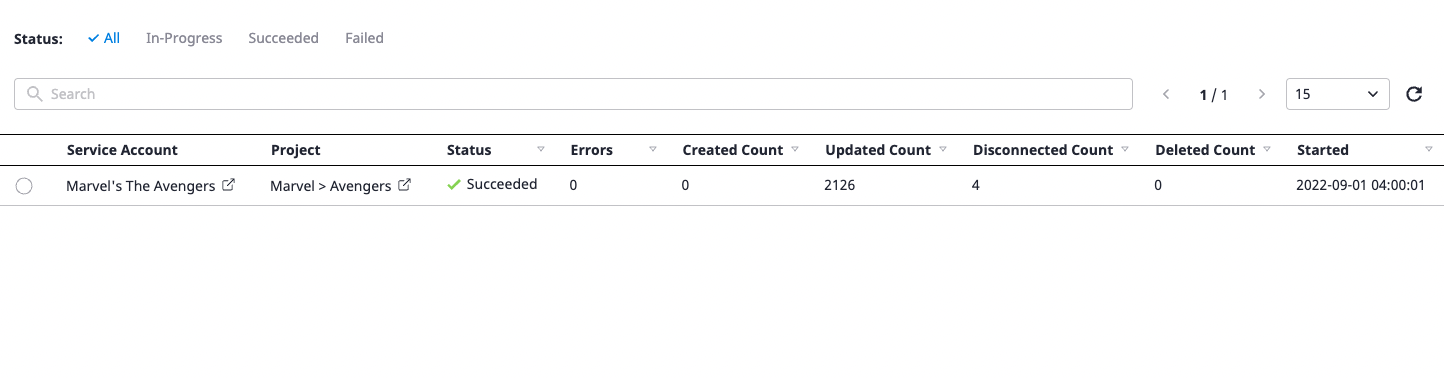
Key field Information
- Created Count: The number of newly added resources
- Updated Count: The number of imported resources
- Disconnected Count: The number of resources that were not fetched
- Deleted Count: Number of deleted resources (in case of a resource failing to fetch multiple times, it is considered deleted.)
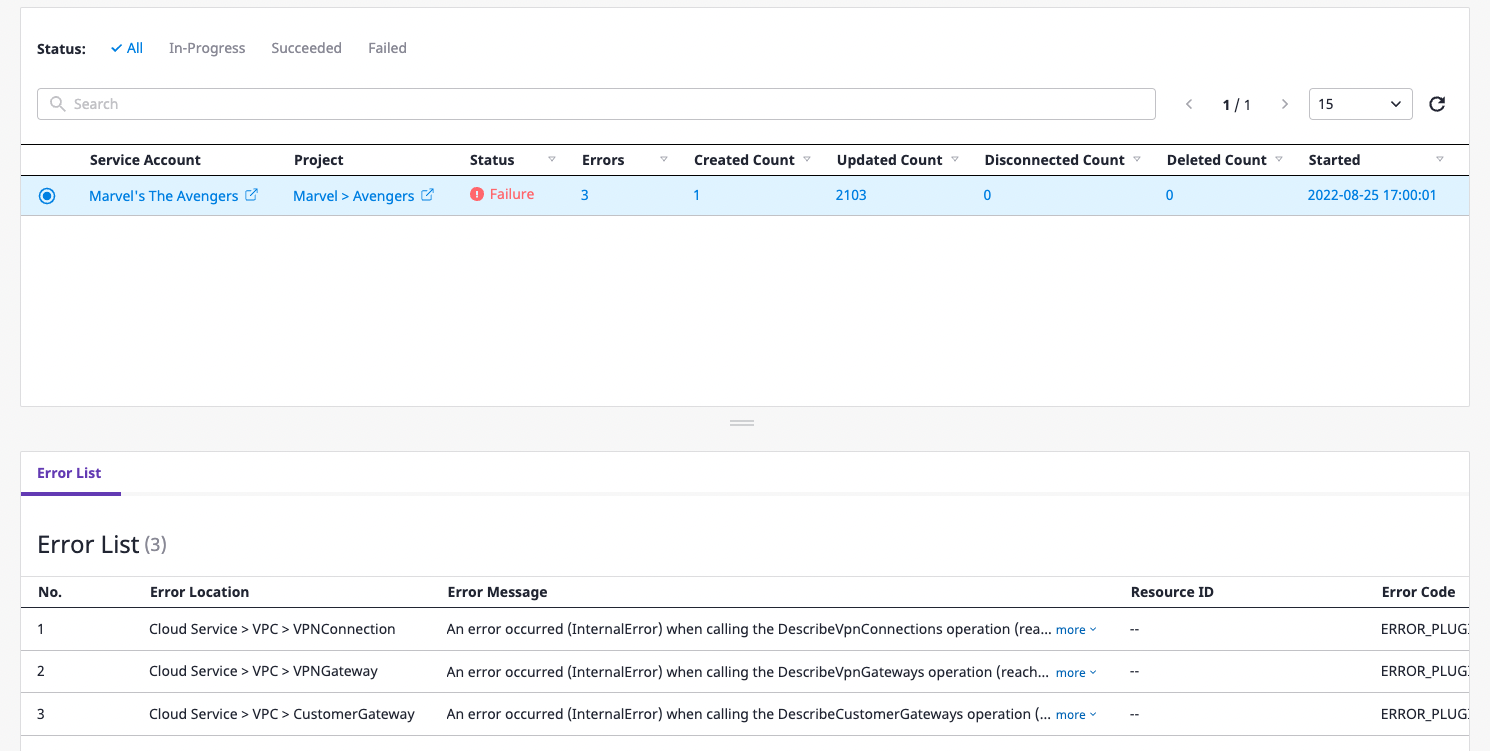
Check the content of collection errors
(1) Select the item you want to check for error details from a list of collections for each account.
(2) You can check the details of errors in the [Error list] tab below.
4.5 - Service account
Add service account
There are two types of service accounts for different needs and better security.
General Account:Option 1) You can create account with its own credentials.
Option 2) Create account using credentials from an existing
Trusted Account.Option 3) You can also create account without credentials.
Trusted Account:You can create an account that enables trusted access,
then other general accounts can refer to its credential key by attaching it.
Create General Account
(1) On the [Asset inventory > Service account] page, select the cloud service you want to add.
(2) Click the [Add] button.
(3) Fill out the service account creation form.
(3-1) Select General Account.
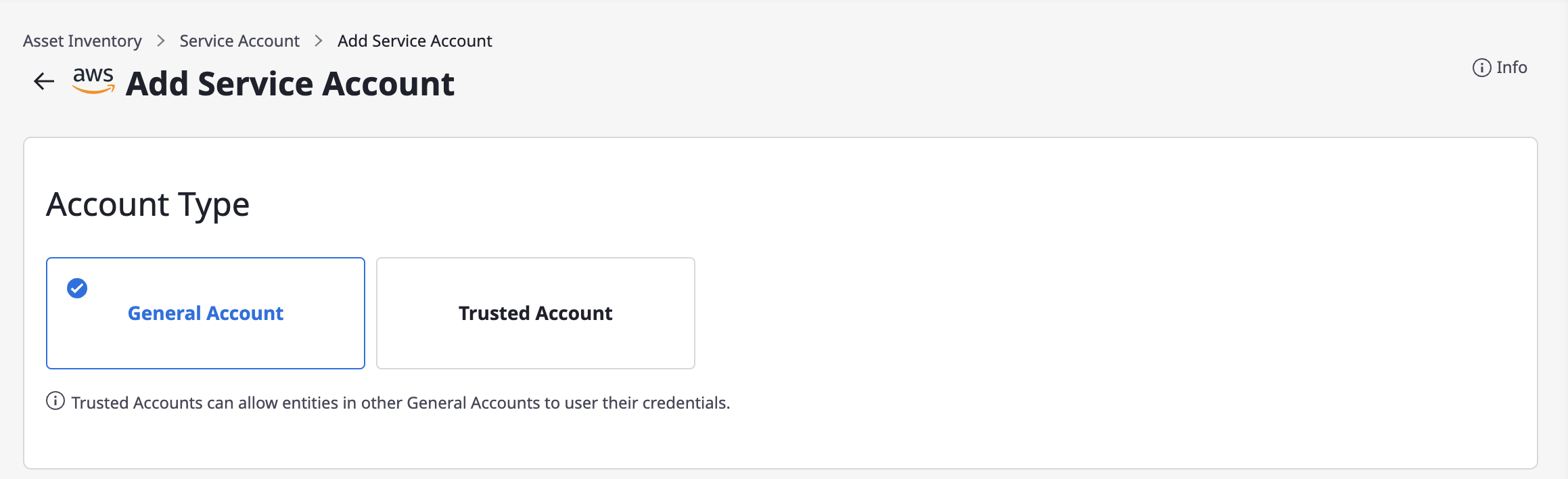
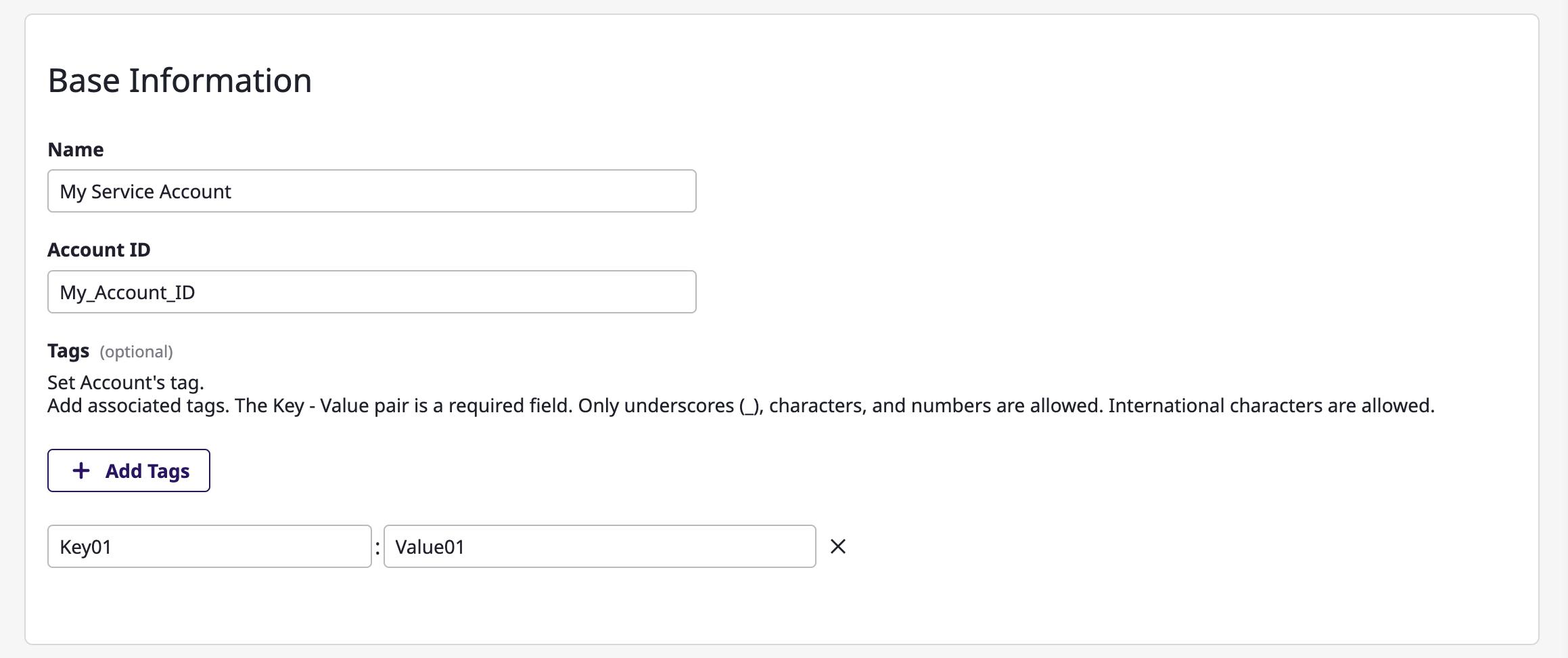
(3-2) Enter basic information.
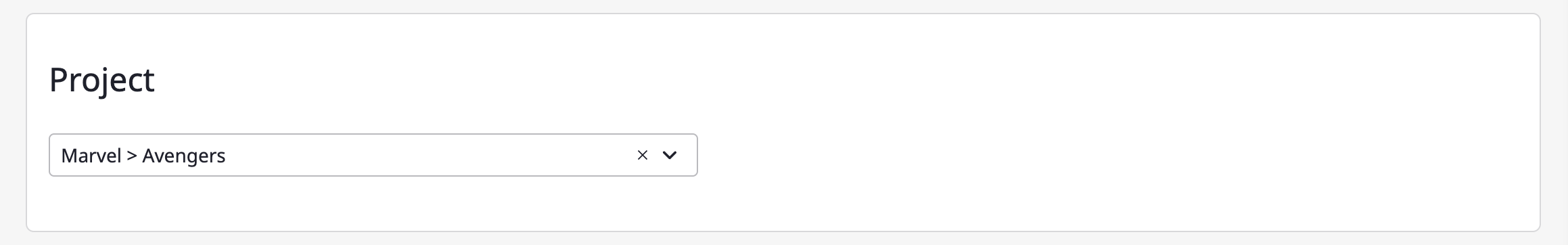
(3-3) Specify the project to collect resources from according to the service account.
(3-4) Enter encryption key information.
Option 1) You can create account with its own credentials.
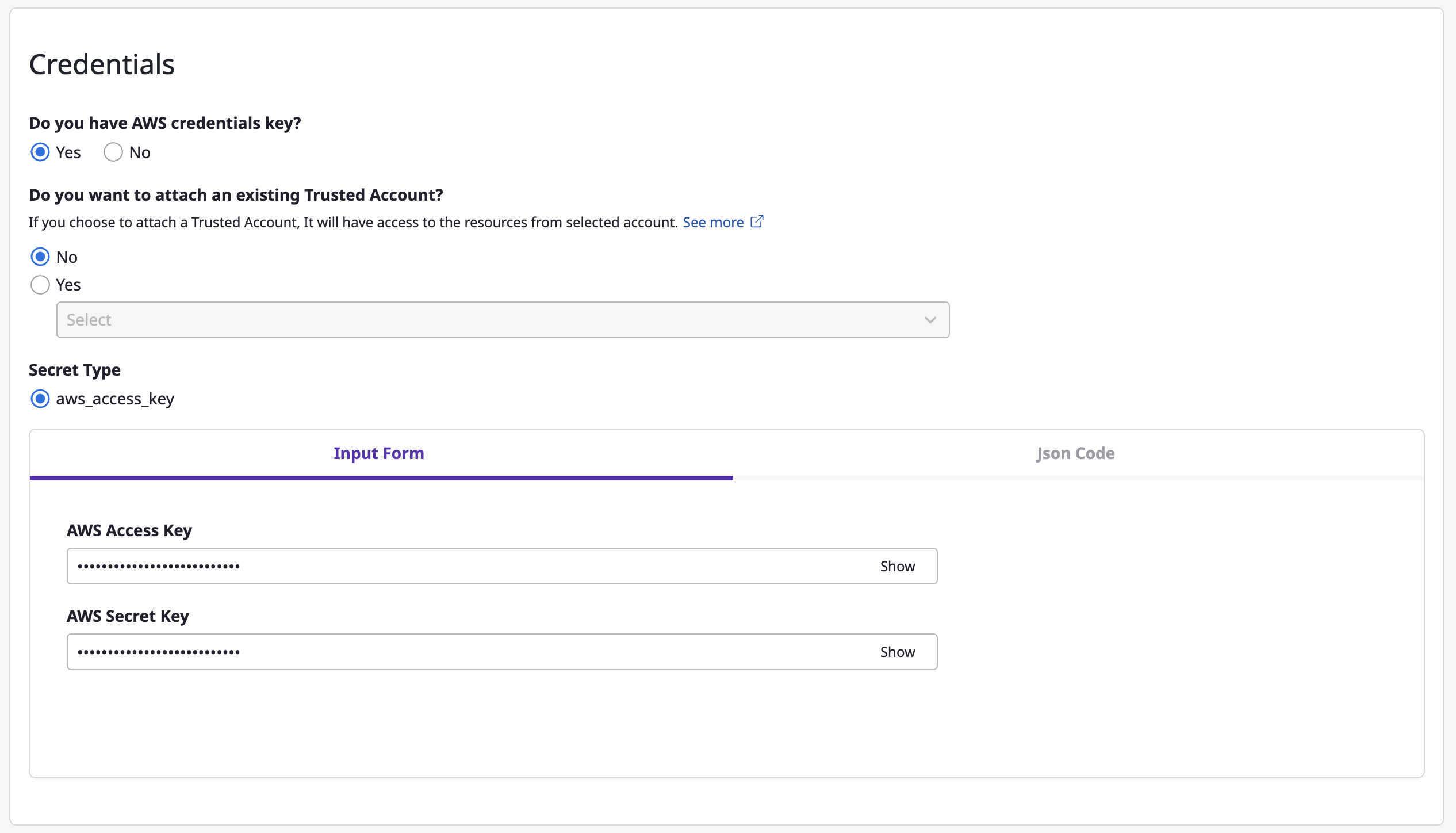
Option 2) Create account using credentials from an existing
Trusted Account.In the case of AWS, you can easily create Assume Role by attaching an exisiting
Trusted Account. If you select a certainTrusted Account, its credential key will automatically get inserted, then you will only need to enter the rest of information.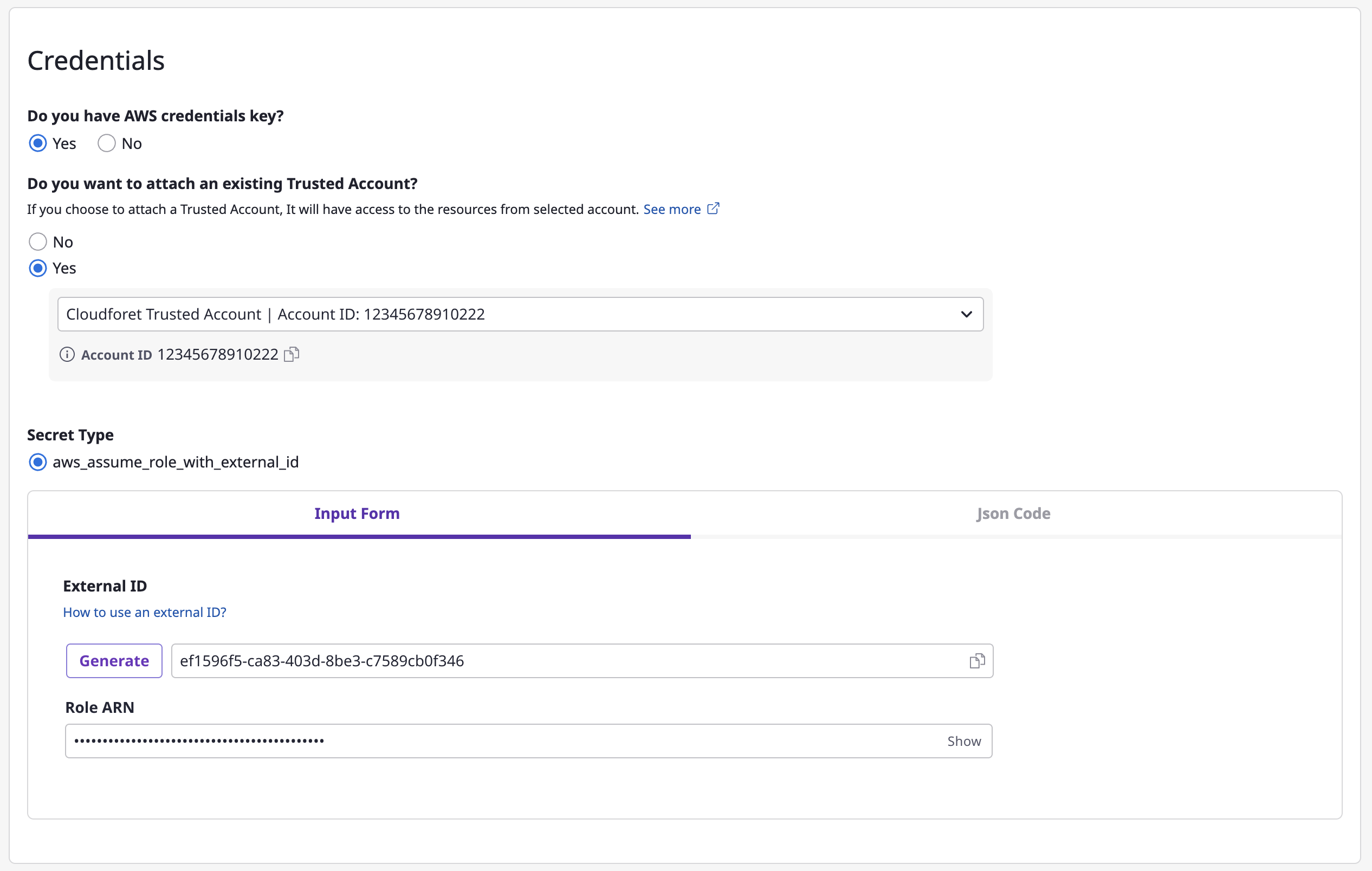
Option 3) You can also create account without credentials.
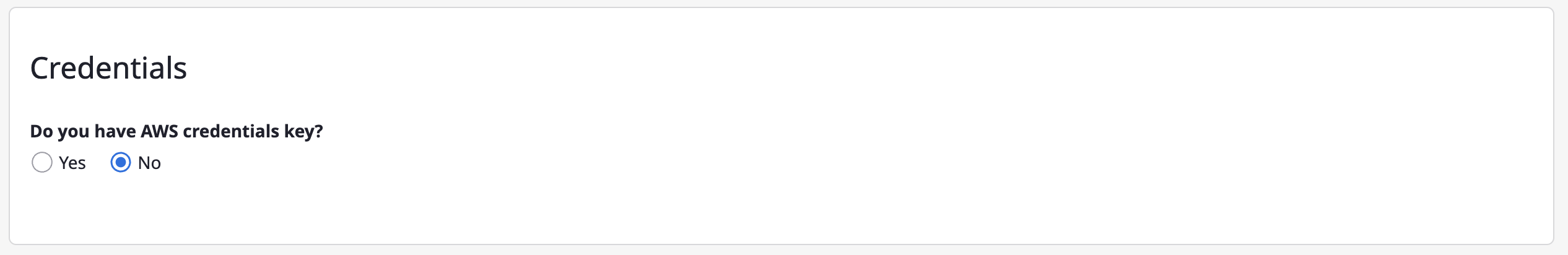
(4) Click the [Save] button to complete.
Create Trusted Account
(1) On the [Asset inventory > Service account] page, select the cloud service you want to add.
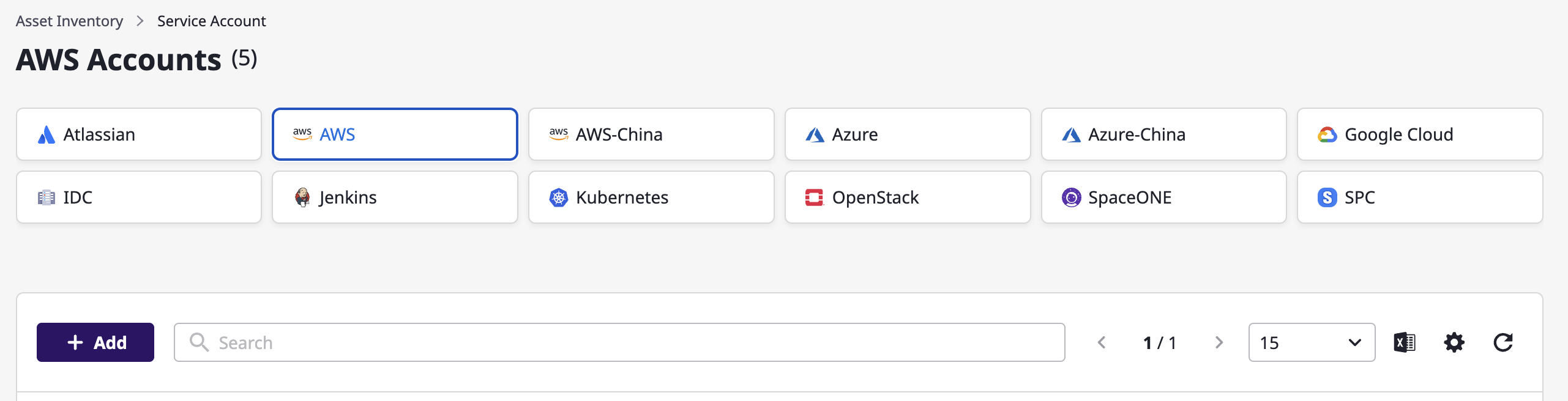
(2) Click the [Add] button.

(3) Fill out the service account creation form.
(3-1) Select Trusted Account.
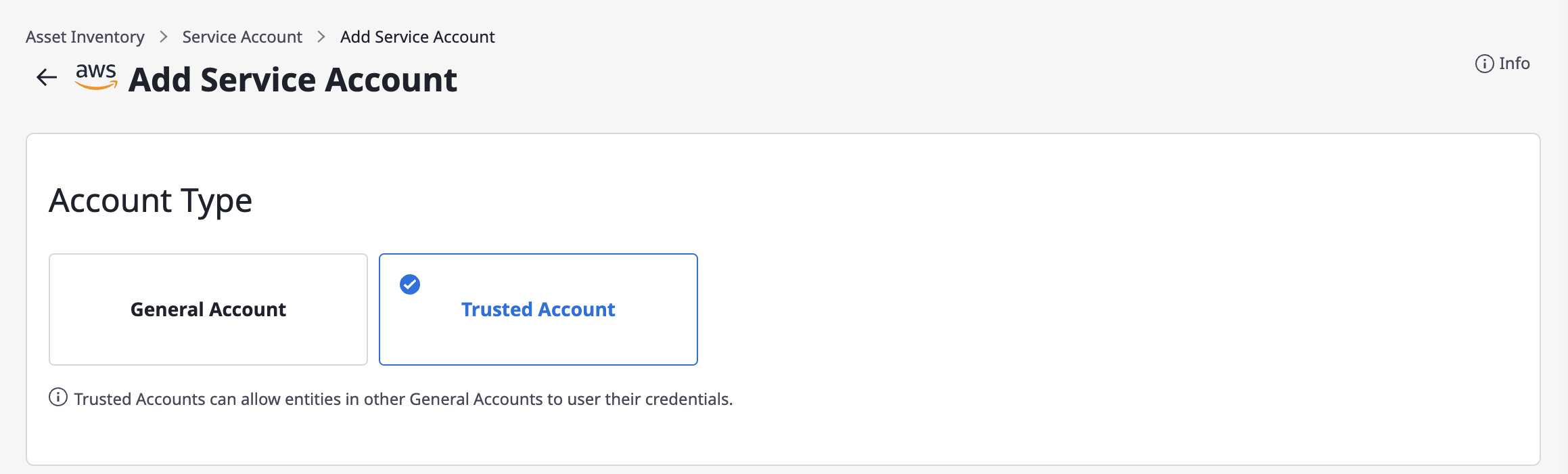
(3-2) Enter basic information.
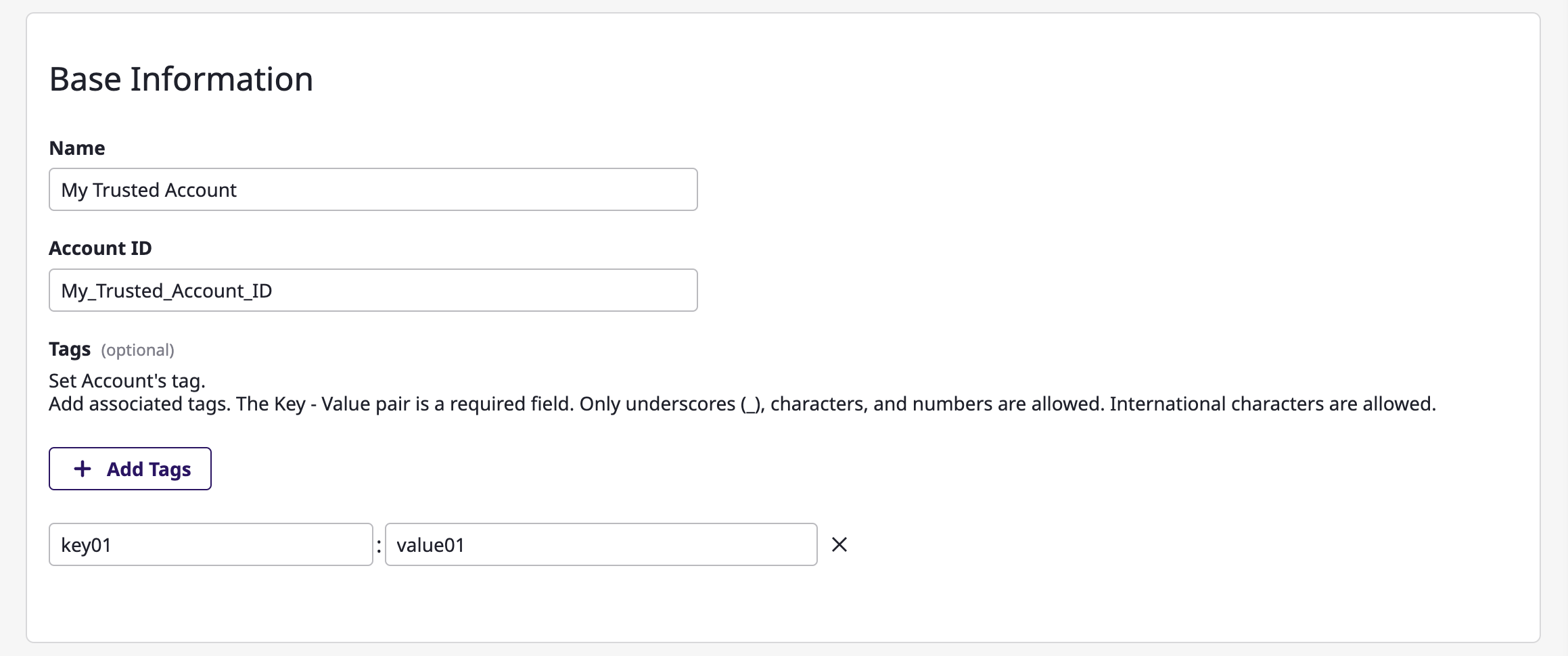
(3-3) Specify the project to collect resources from according to the service account.

(3-4) Enter encryption key information.
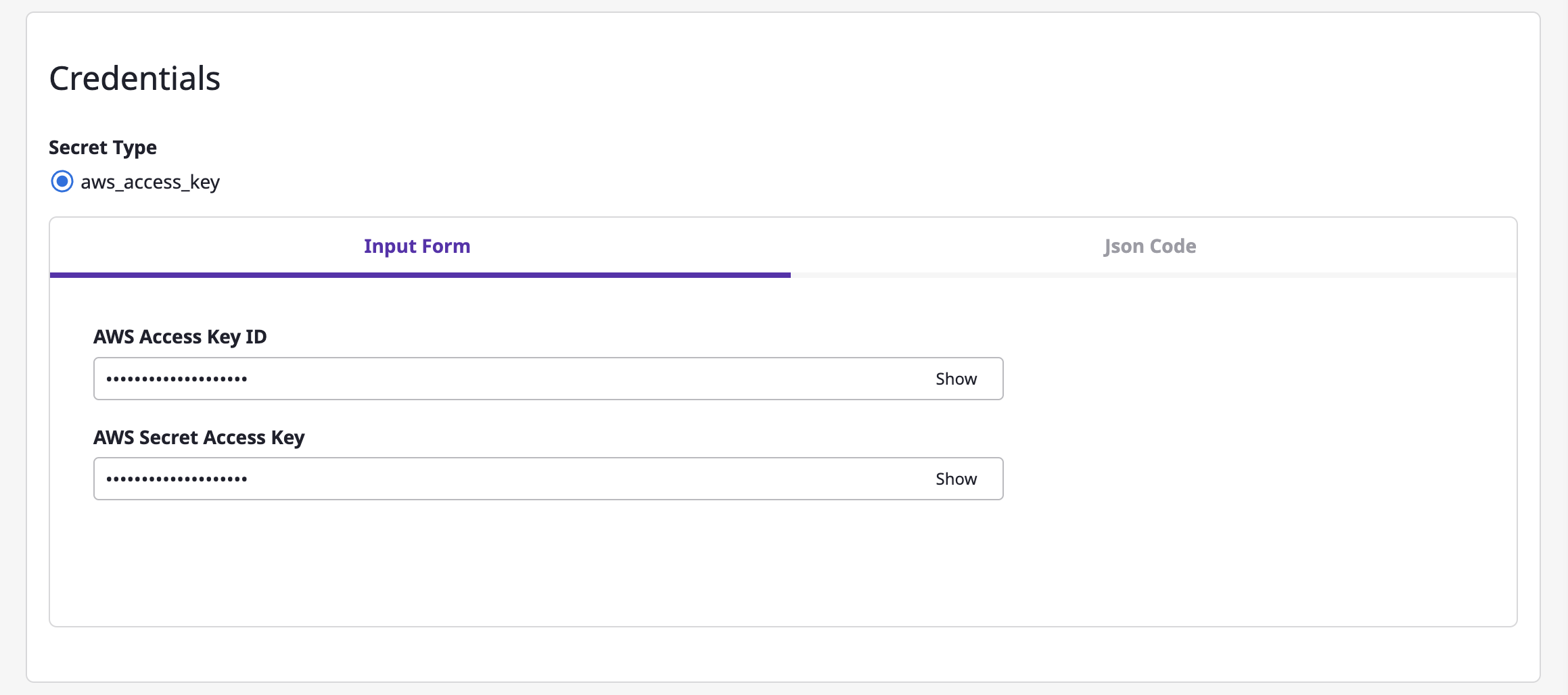
(4) Click the [Save] button to complete.
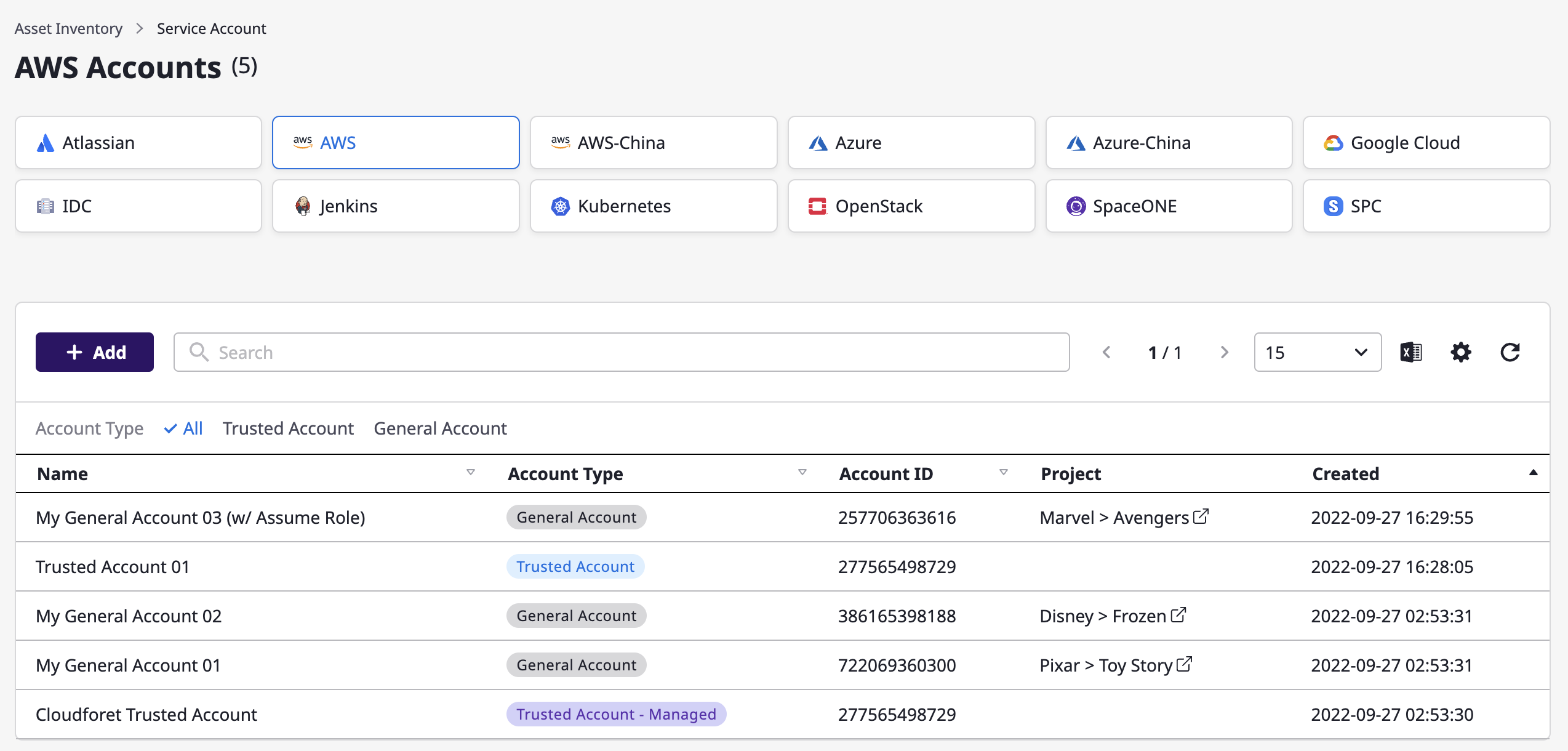
Viewing service account
You can view a list of service accounts that have been added, and when you click a certain account, you can check the detailed information.
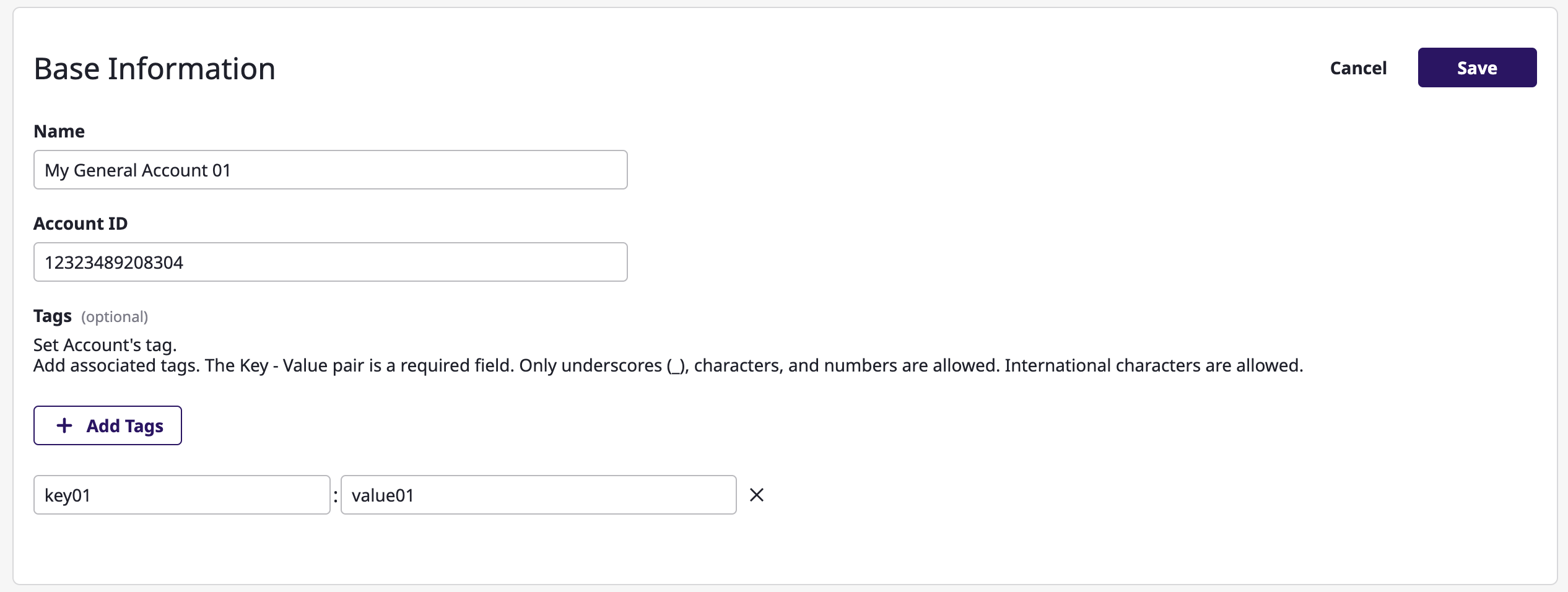
Editing service account
Select a service account you want to edit from the list.
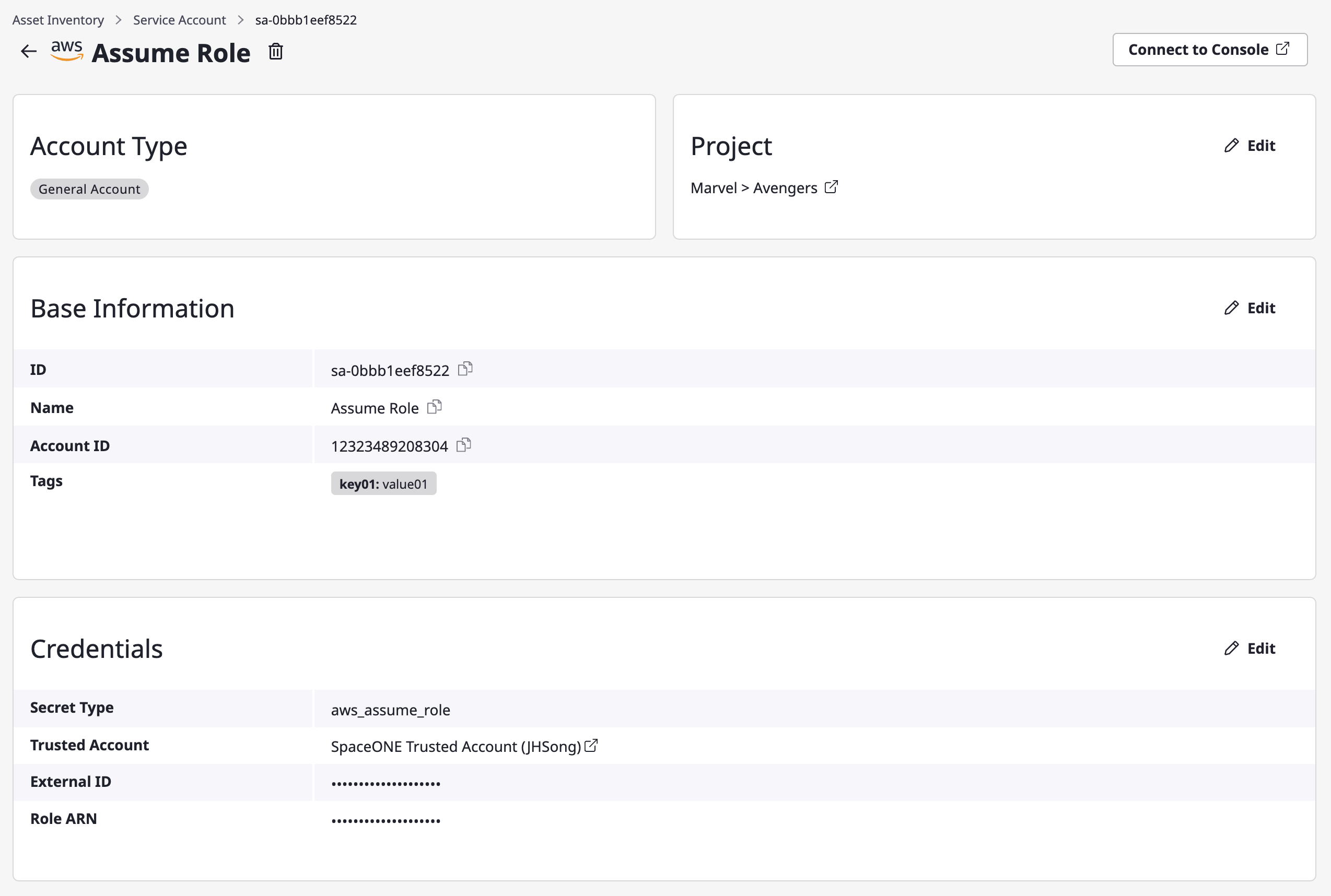
Editing each part
You can edit each part of detail information by clicking [Edit] button.
Removing service account
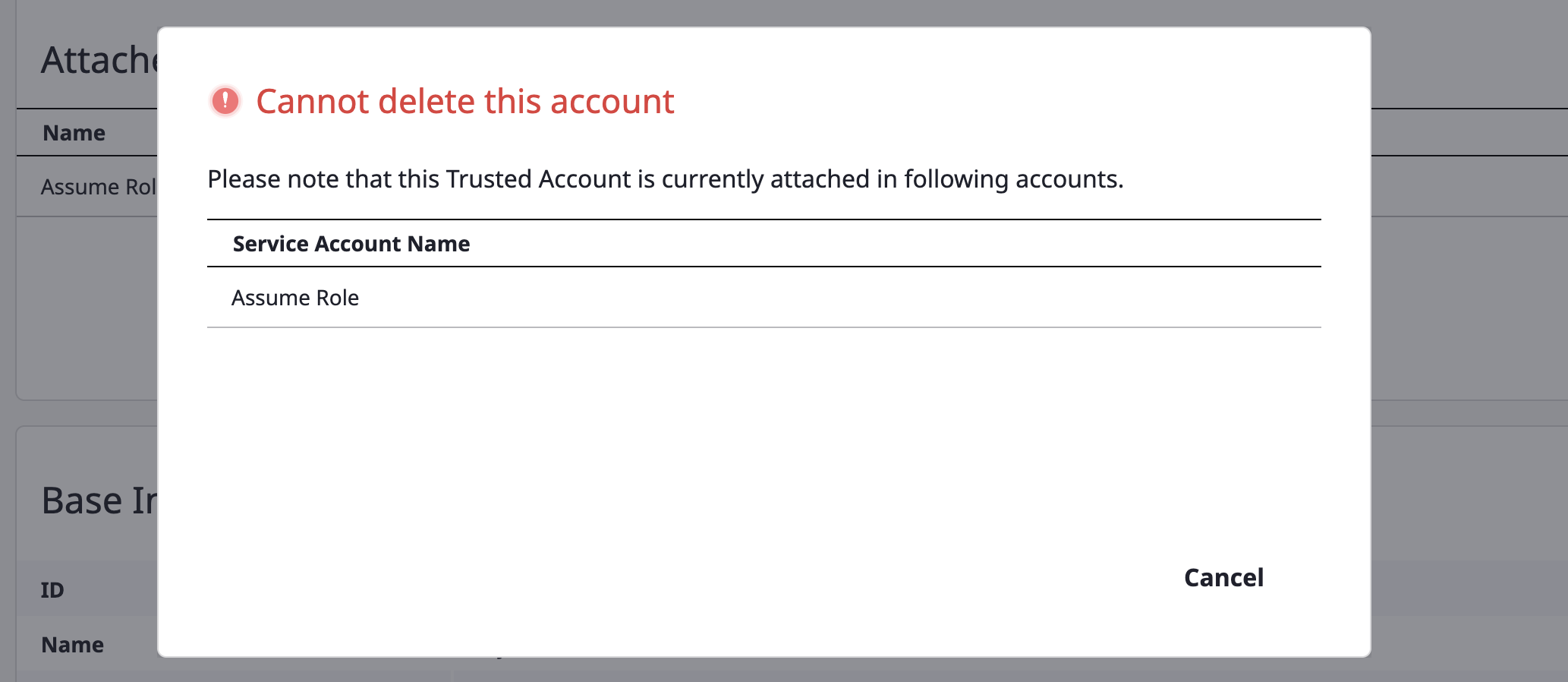
Select a service account you want to remove from the list.
You can delete it by clicking the delete icon button.

If the service account is Trusted Account type and currently attached to more than one General Account, it can't be removed.
5 - Cost Explorer
The amount used by period can be checked based on a Budget set by a user and Budget use notification can also be set up.
5.1 - Cost analysis
By grouping or filtering data based on diverse conditions, you can view the desired cost data at a glance.
Verifying cost analysis
Selecting a data source
If you have more than one billing data source connected, you can perform a detailed cost analysis by selecting each data source from the "Cost Analysis" section in the left menu.
Selecting the granularity
Granularity is criteria set for how data will be displayed. The form of the provided chart or table varies depending on the detailed criteria.
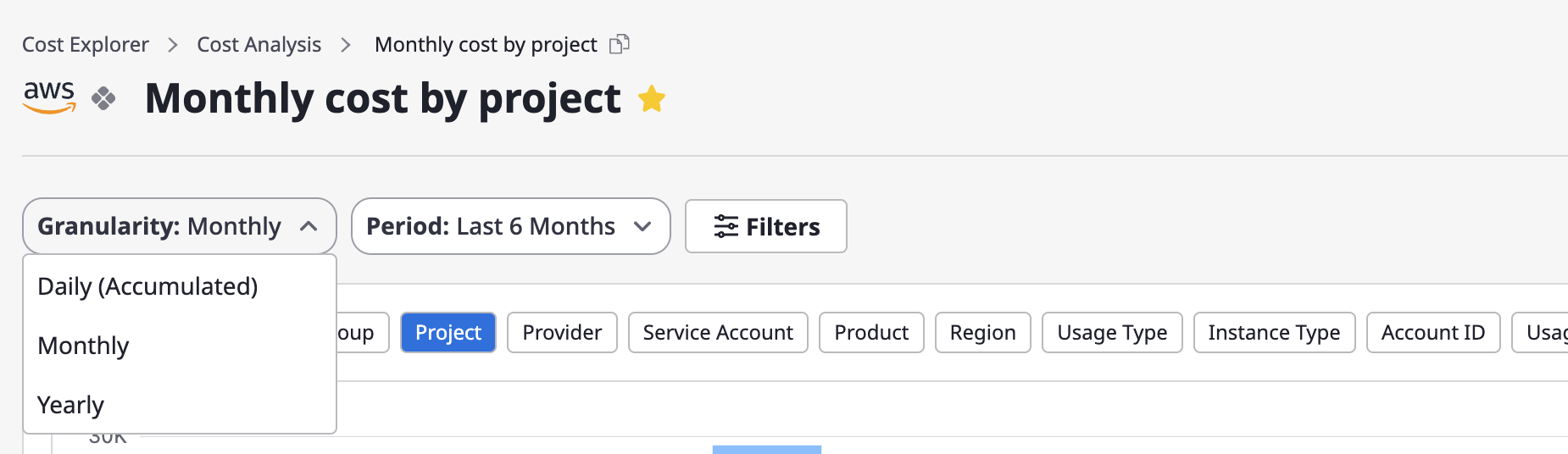
Daily: You can review daily accumulated data for a specific month.Monthly: You can check monthly data for a specific period (up to 12 months).Yearly: You can examine yearly data for the most recent three years.
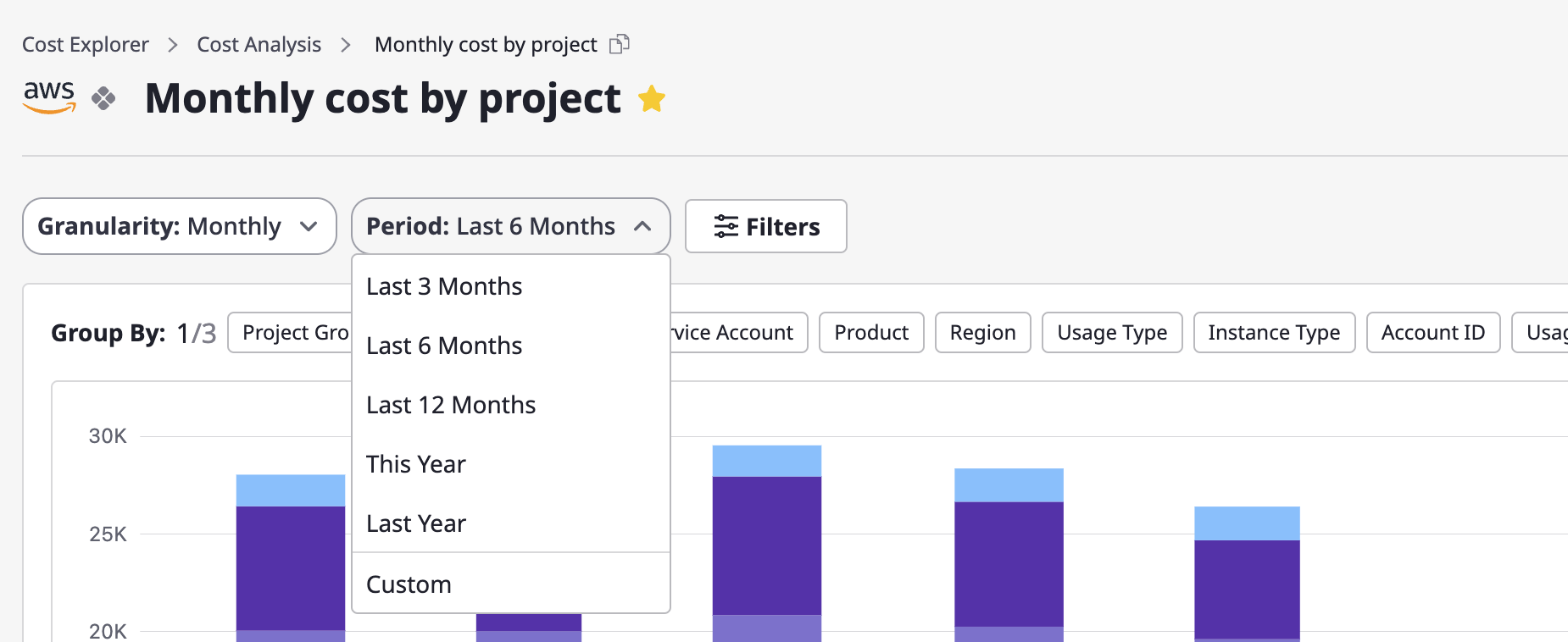
Selecting the period
The available options in the "Period" menu vary depending on a granularity you choose. You can select a menu from the [Period] dropdown or configure it directly through the "Custom" menu.
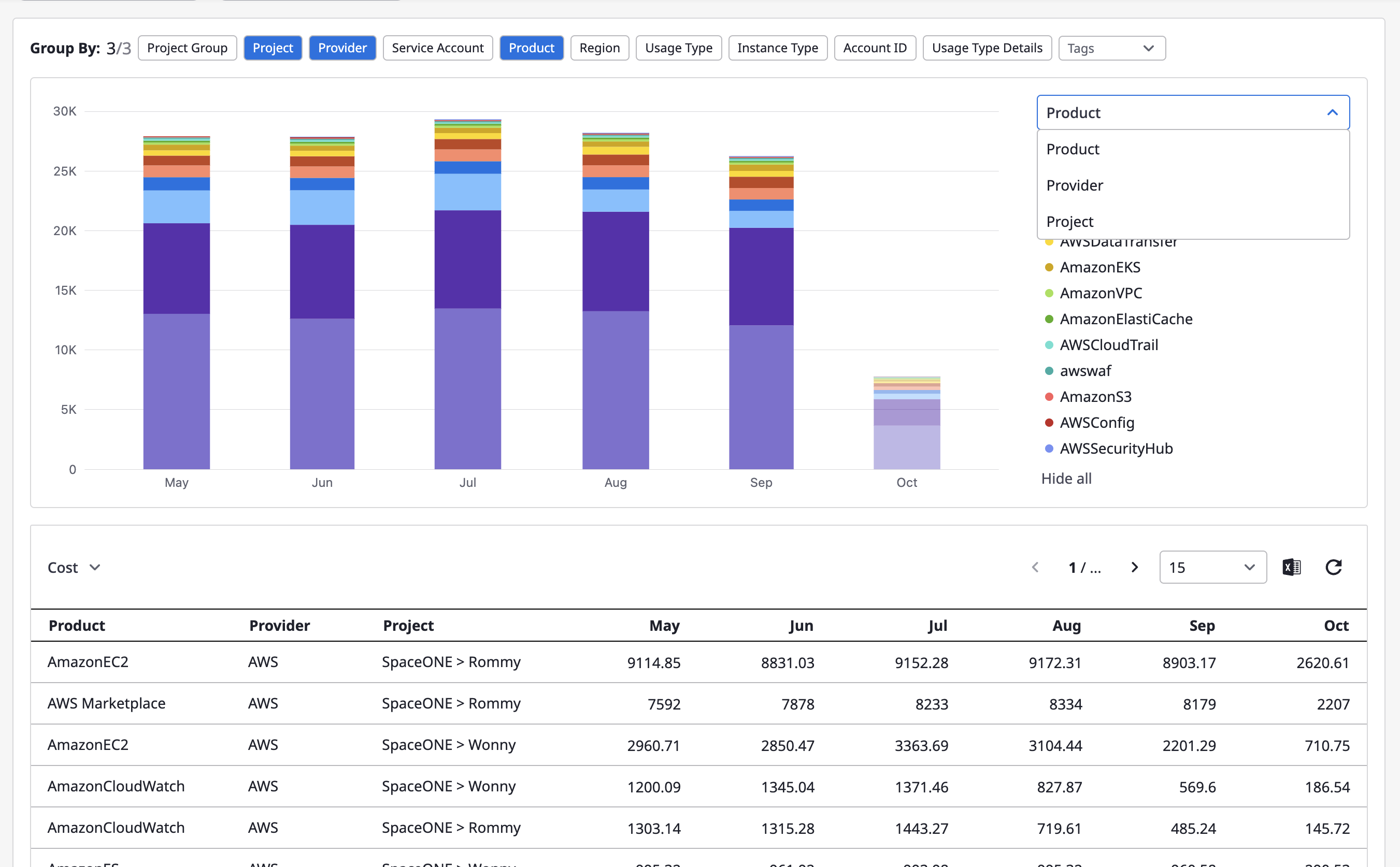
Group-by settings
You can select more than one result from group statistics. In the chart, only one selected result of group statistics is displayed, and in the table, you can see all the results from group statistics that you select.
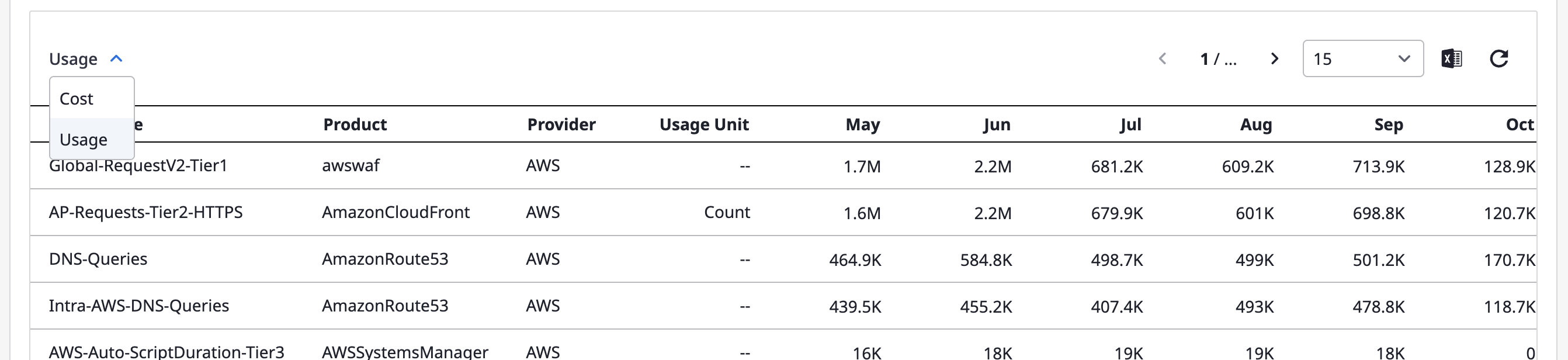
Filter settings
Filters, similar to group-by, can be selected one or more at a time, and your configured values are used for filtering with an "AND" condition.
(1) Click the [Filter] button at the top of the page.
(2) When the "Filter Settings" window opens, you can choose the desired filters, and the selections will be immediately reflected in the chart and table.
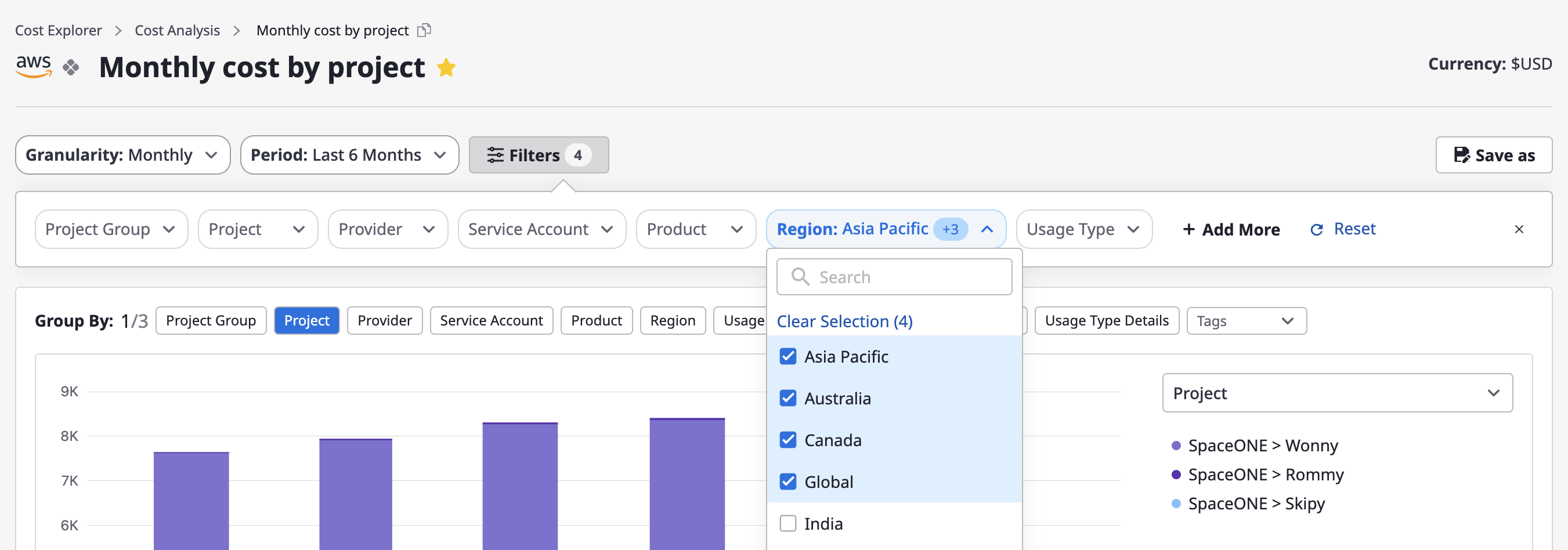
Creating/managing custom cost analysis
Creating a custom analysis page
To alleviate the inconvenience of having to reset granularity and period every time you enter the "Cost Analysis" page, a feature is provided that allows you to save frequently used settings as custom analysis pages.
(1) Click the [Save As] button in the upper-right corner of a specific cost analysis page.
(2) After entering a name and clicking the [Confirm] button, a new analysis page is created.
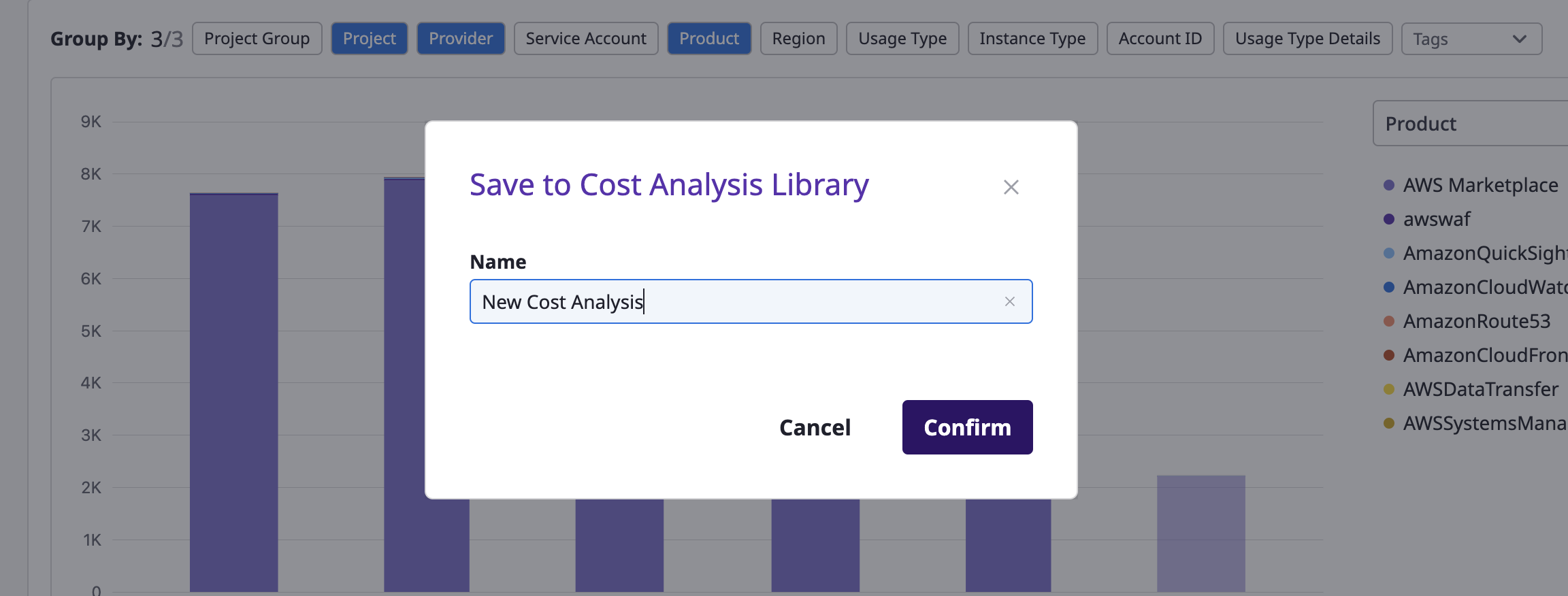
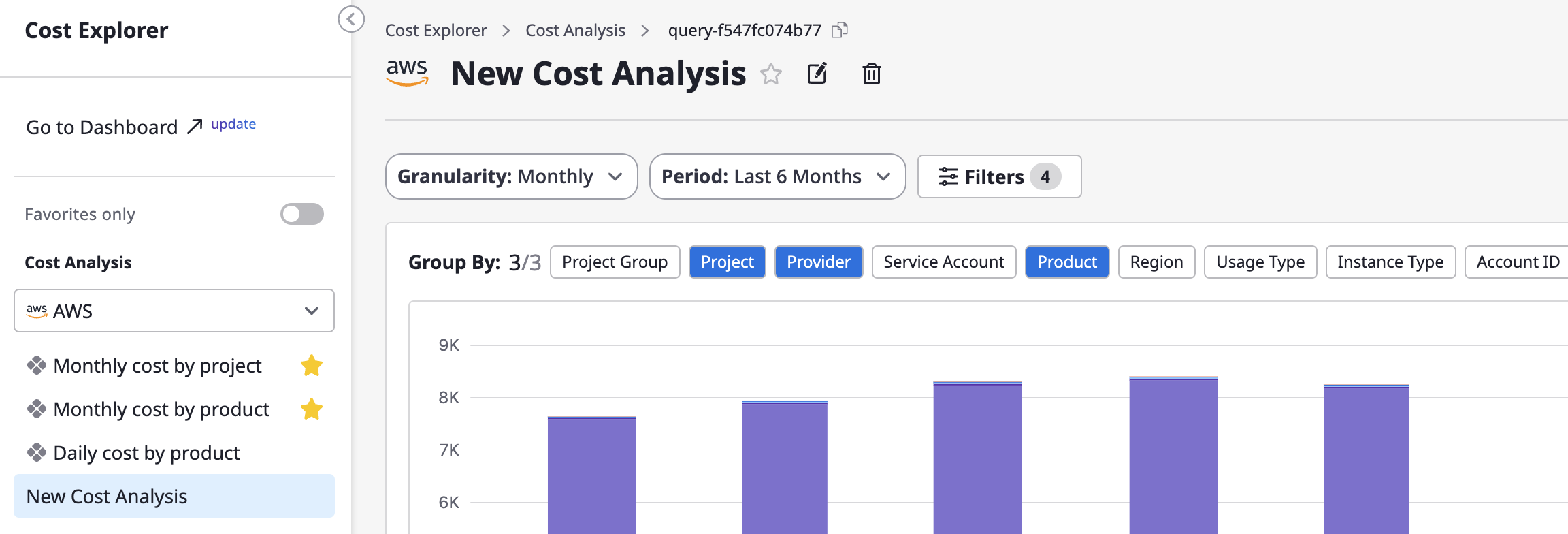
(3) Custom cost analysis pages can be saved with settings like name, filters, group-by, etc., directly using the [Save] option, and just like the default analysis pages, you can also create new pages by using [Save As].
Editing the custom analysis name
You can edit the name by clicking the [Edit] button at the top of the page.

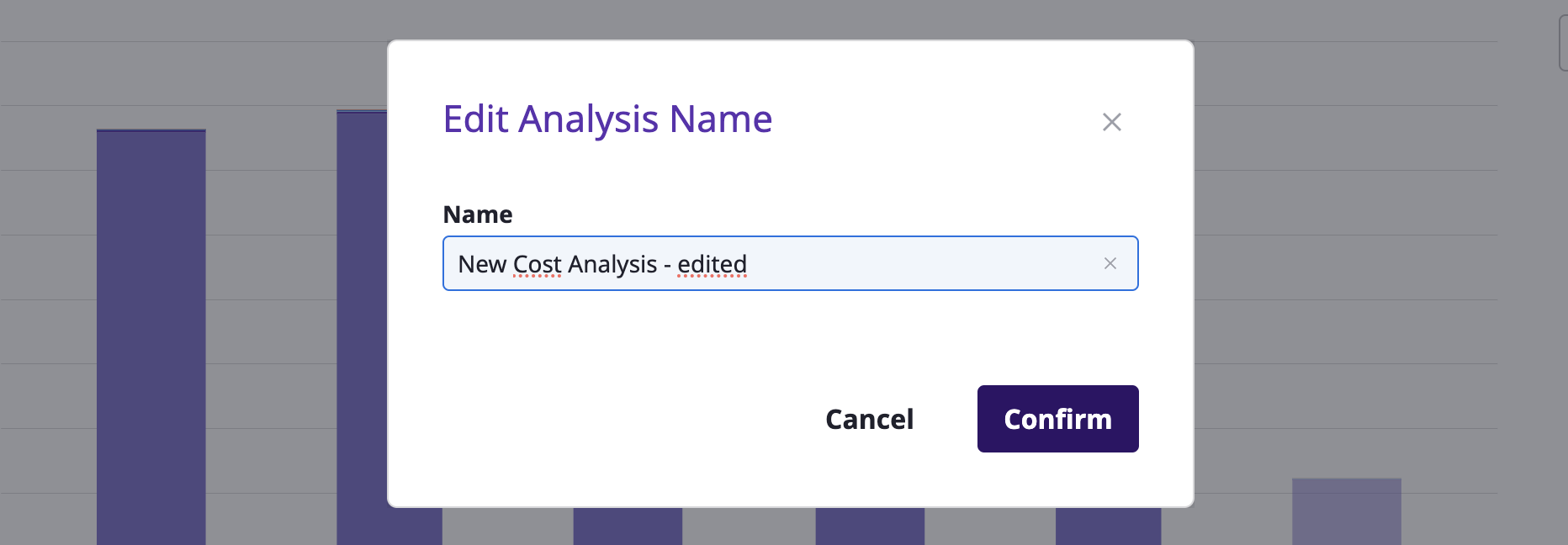
Deleting the custom analysis name
You can delete the page by clicking the [Delete] button at the top of the page.

5.2 - Budget
Creating a budget
(1) Click the [Create budget] button at the top right of the [Cost Explorer > Budget] page.
(2) Enter basic information
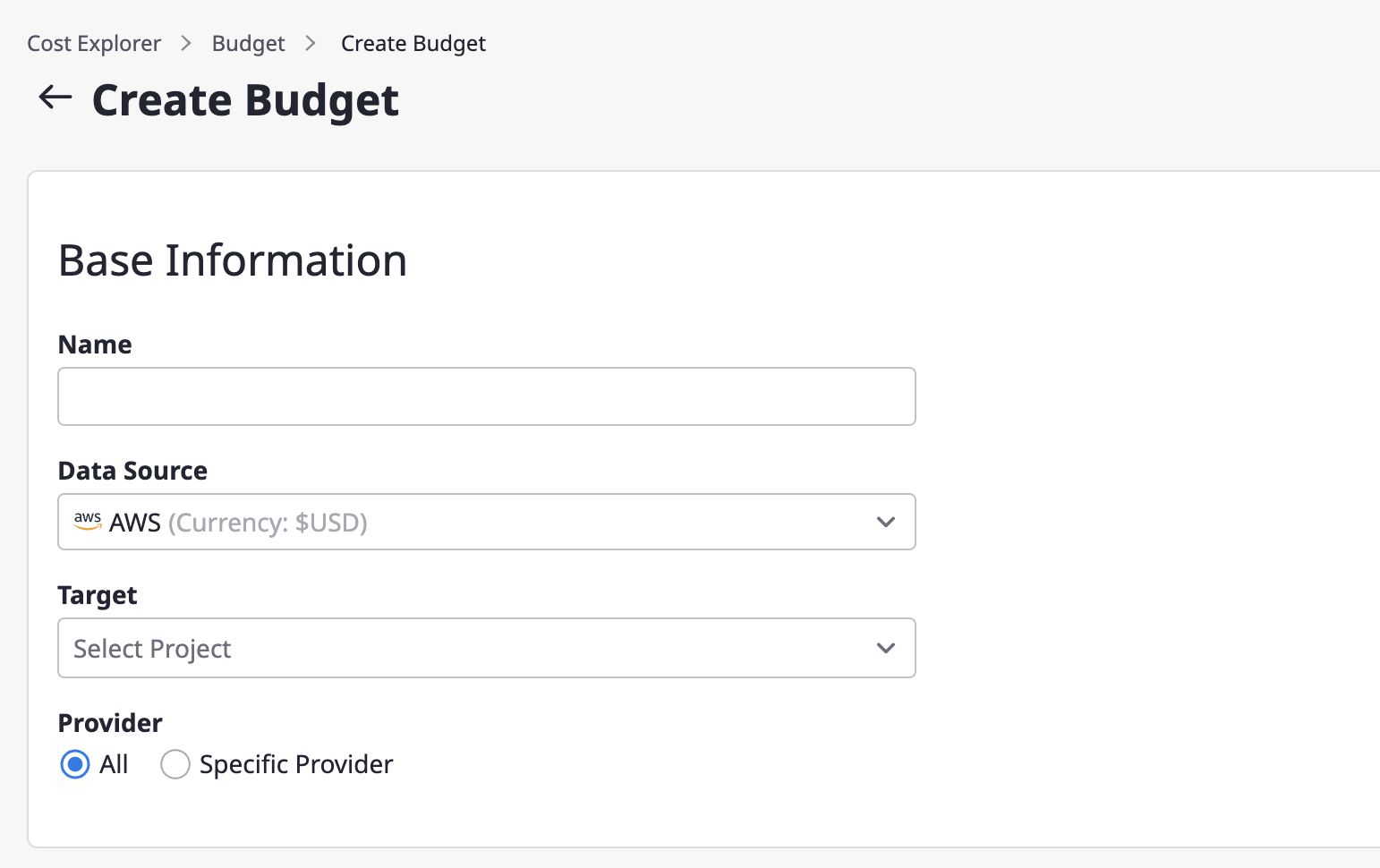
(2-1) Enter the name of the budget.
(2-2) Select a billing data source.
(2-3) Select the project to be the target of budget management in the target item.
(2-4) Select the cost incurring criteria. If you select all as the cost type, all cost data related to the corresponding project will be imported.
(3) Enter the budget plan
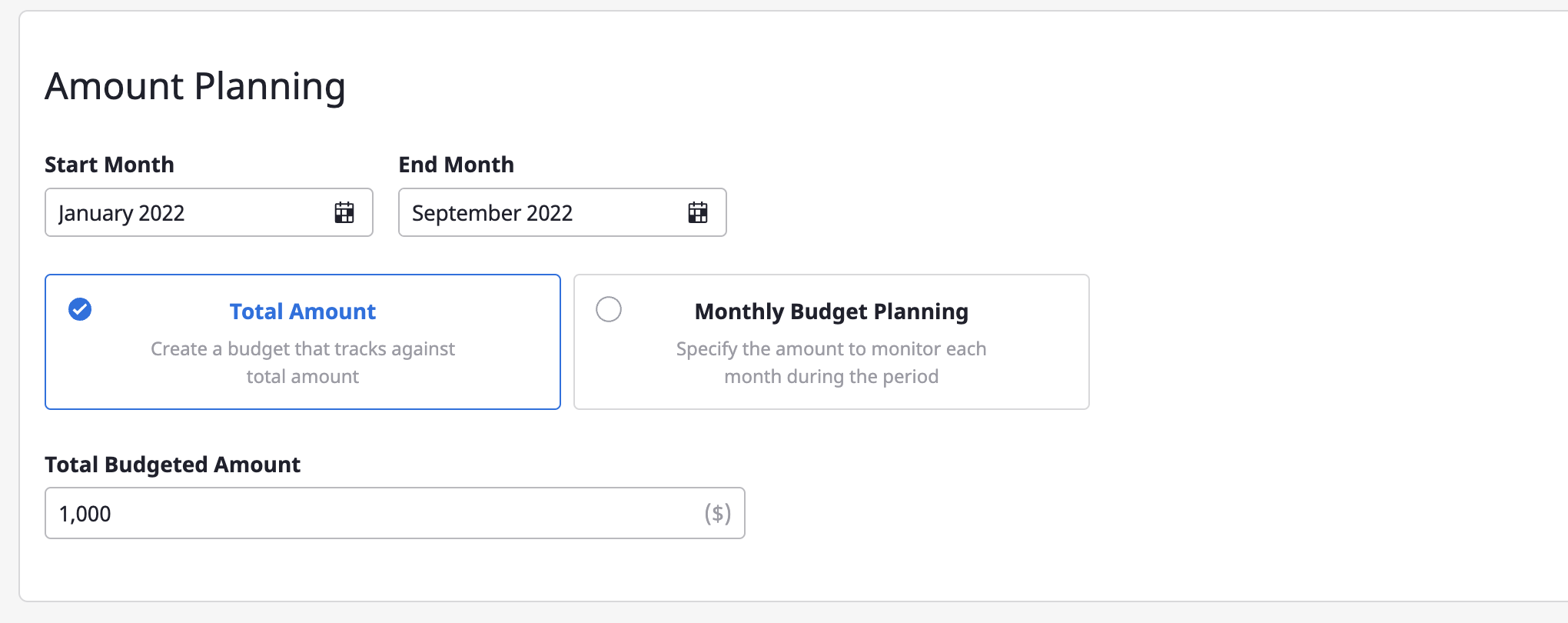
(3-1) Set a period for managing the budget.
(3-2) Choose how you want to manage your budget.
(3-3) Set the budget amount. If you selected Set total budget, enter the total budget amount. If you selected Set monthly budget, enter the monthly budget amount.
Check the set budget and usage status
The budget page provides a summary of your budget data and an overview of your budget for each project at a glance. You can use filters at the top to specify a period or apply an exchange rate, and you can search for a specific project or name using an advanced search.
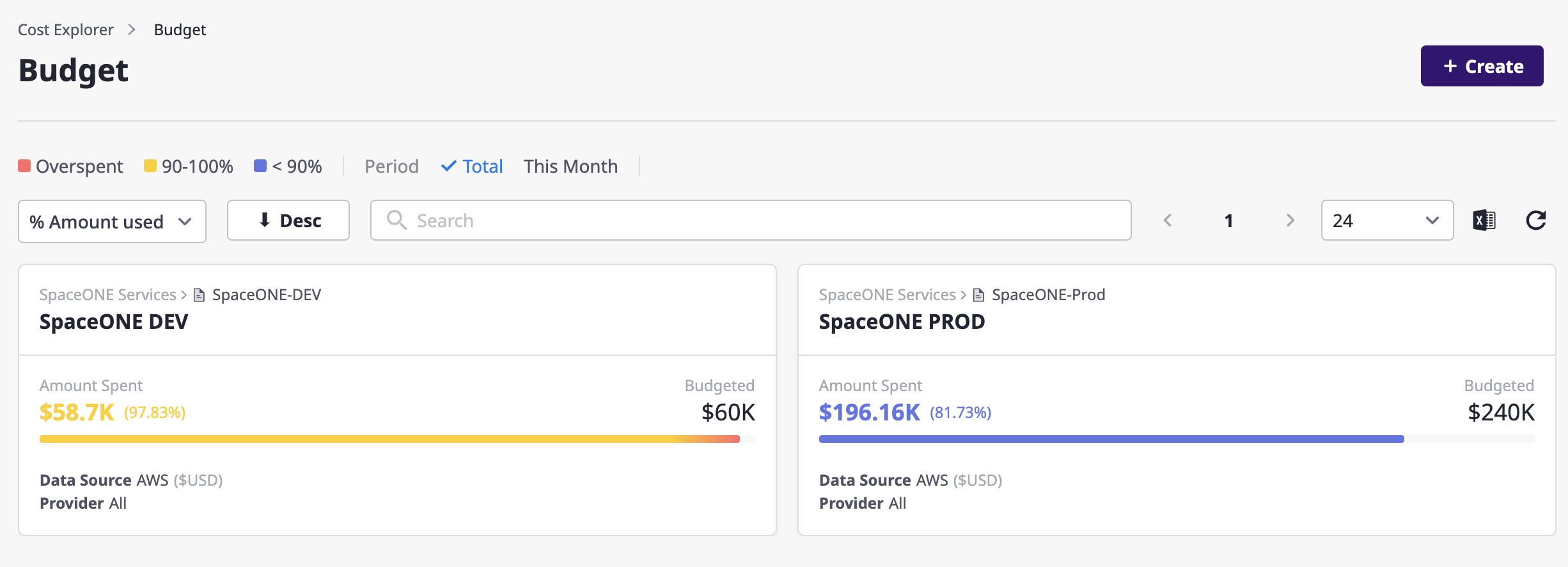
Budget detail page
On the budget detail page, you can view specific data for the created budget.
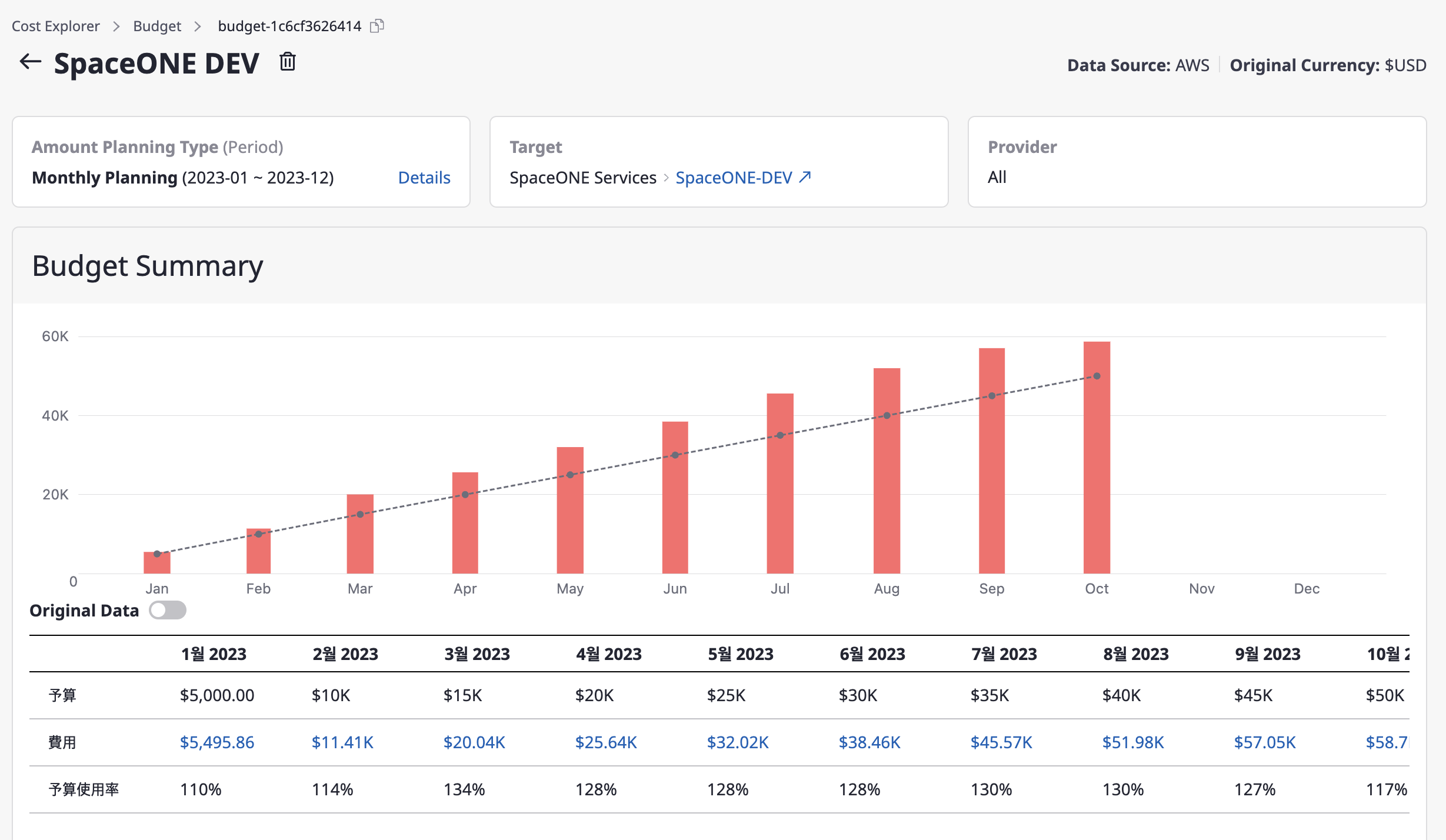
Budget summary
Under [Budget summary], you can check the monthly budget and cost trends through charts and tables.
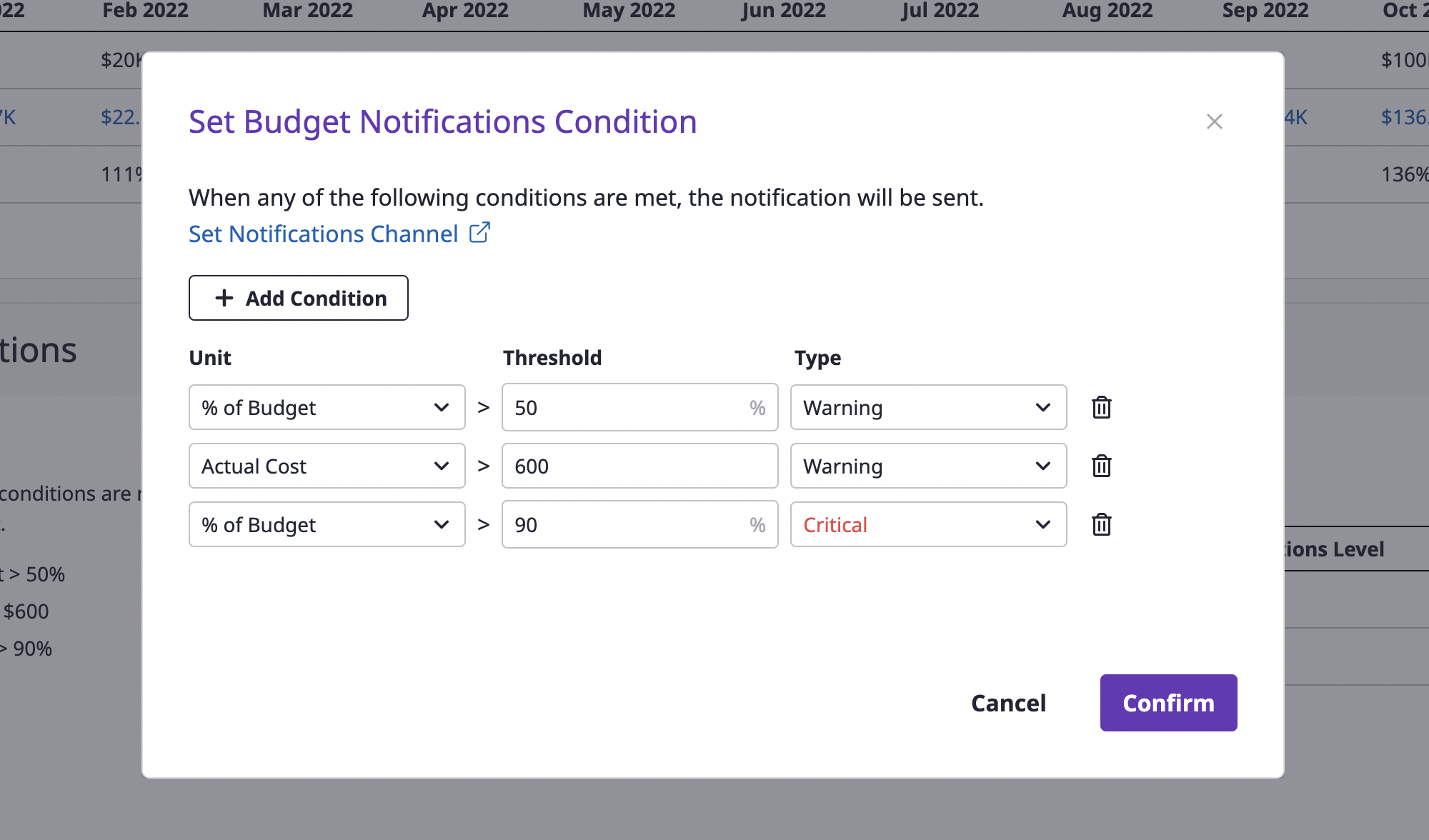
Set budget usage notifications
In [Budget usage notification settings], you can adjust the settings to receive a notification when the budget has been used up over a certain threshold. When the budget amount used goes over a certain percentage or the actual amount exceeds a certain amount, you can receive a notification through the notifications channel registered in advance.
6 - Alert manager
6.1 - Quick Start
Creating alerts
Alerts can be created in two ways:
- Create an alert manually in the Cloudforet console.
- Automatically create through an external monitoring service connection
Creating an alert manually from a console
(1) Go to the [Alert manager > Alert] page and click the [Create] button.
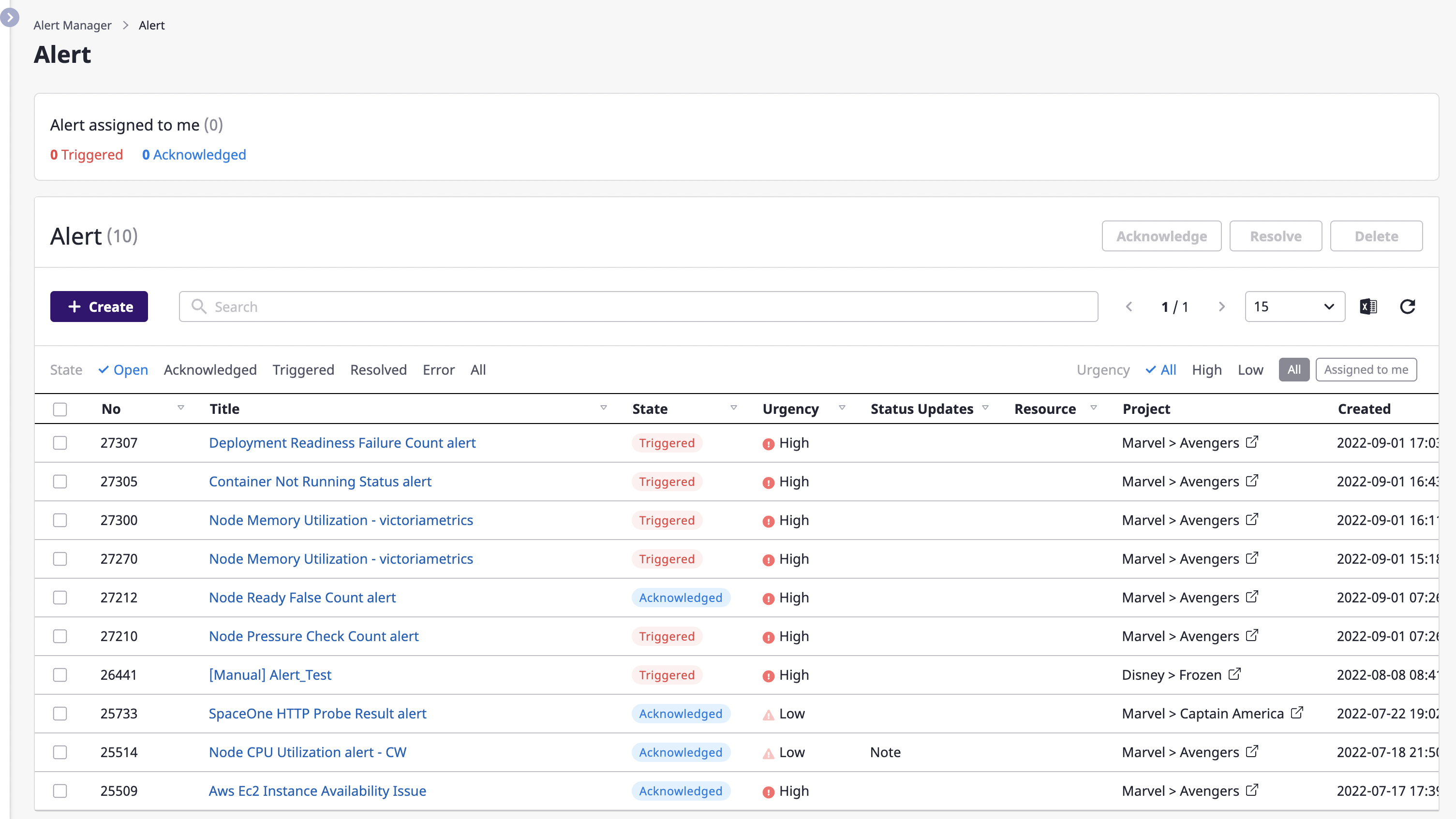
(2) When the [Create alert] modal dialog opens, fill in the input form.
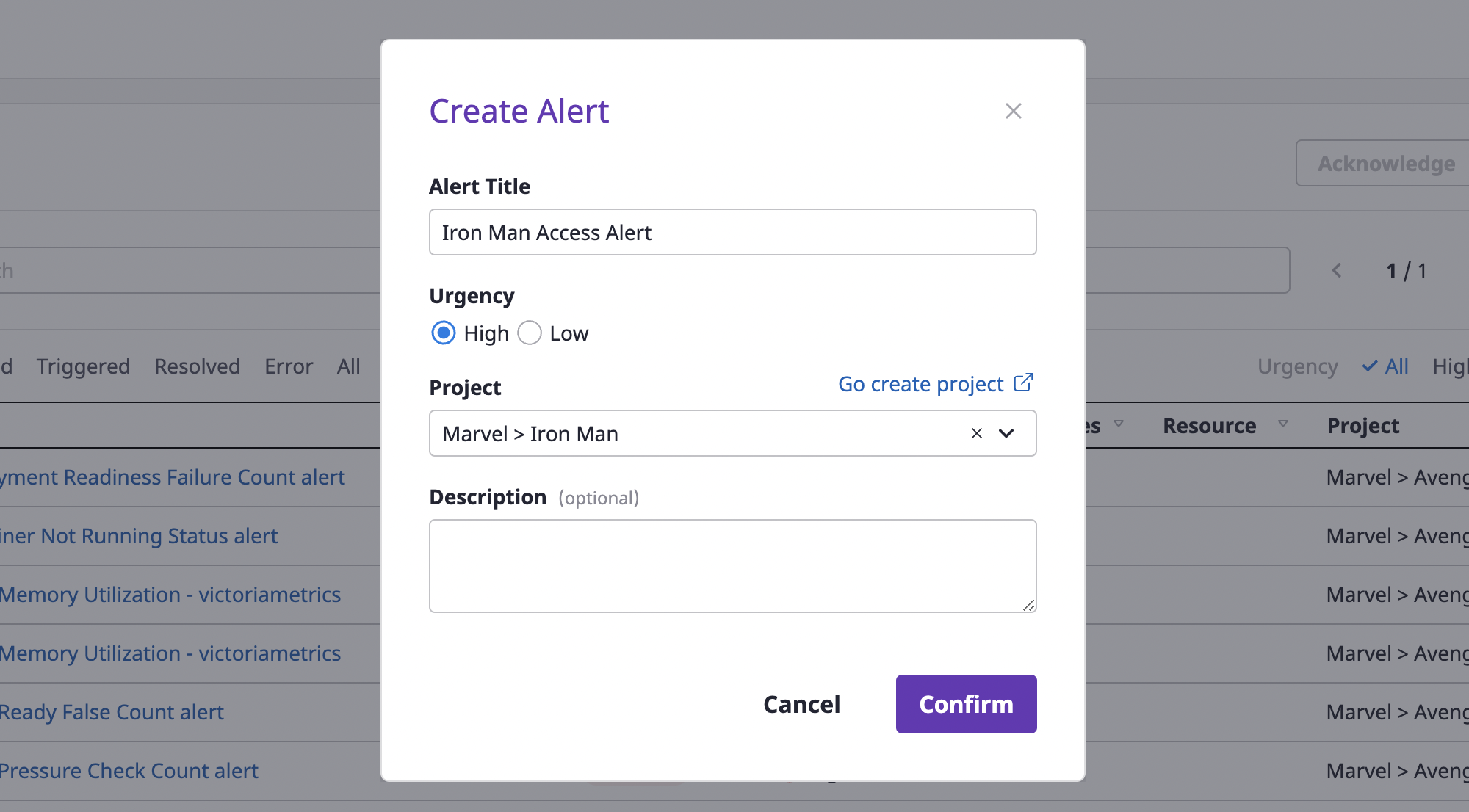
(2-1) Enter an [Alert title] and select [Urgency].
(2-2) Designate the project for which the alert occurred.
(2-3) Write [Comment] if an additional explanation is needed.
(3) Click the [OK] button to complete alert creation.
Connecting to an external monitoring service to receive alerts
When an external monitoring service is connected, an event message occurring in the service is automatically generated as an alert.
To receive alerts from the external monitoring, Webhook creation and Connection settings are required.
Webhook creation is performed in the Cloudforet console, but Connection settings must be done directly in the Cloud Service console that provides external monitoring services.
For more on how to connect an external monitoring service, see here.
Creating a webhook
To receive event messages from an external monitoring service, you need to create a webhook.
Webhooks can be created on the project detail page.
(1) Go to the [Alerts] tab of the project detail page and select the [Webhook] tab.
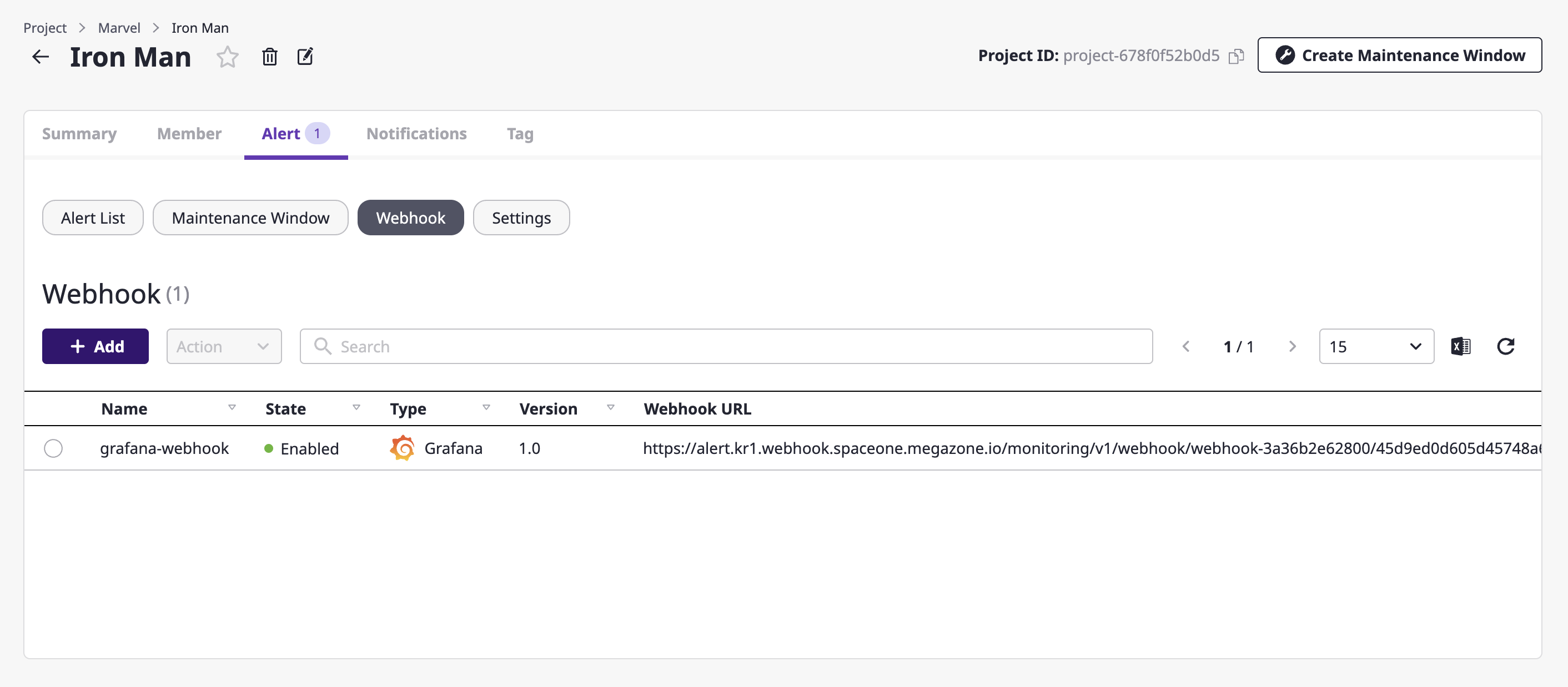
(2) Click the [Add] button.
(3) Write a name in an [Add webhook] modal dialog and select the plug-in of the external monitoring service to be connected.

(4) Click the [OK] button to complete set up.
Escalation policy settings
Whether an alert received via a webhook is sent as a notification to project members is determined by escalation policy.
(1) Inside the [Alert] tab of the project detail page, move to the [Settings] tab.
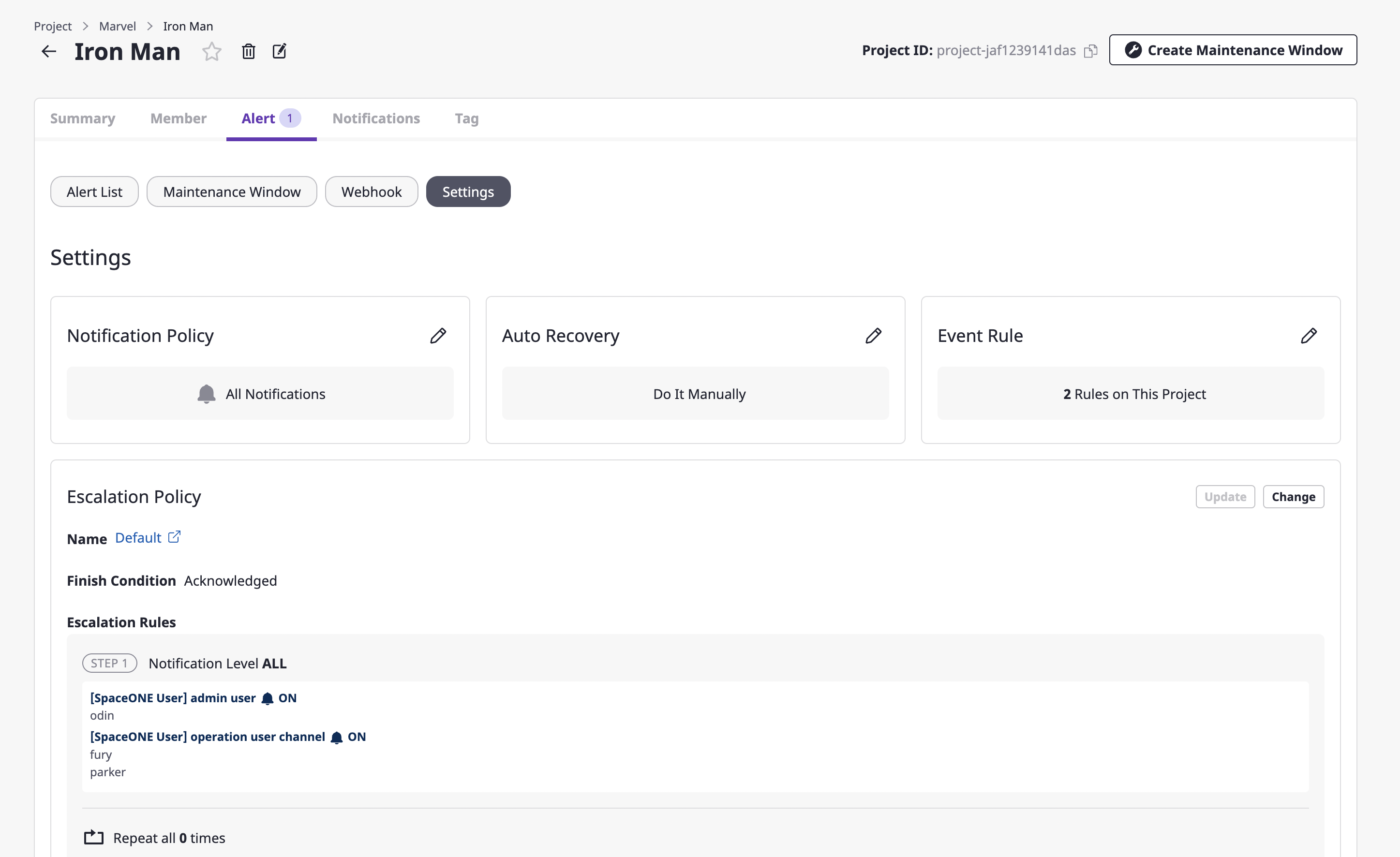
(2) Click the [Change] button in the escalation policy area.

(3) After selecting the [Create new policy] tab, enter the settings to create an escalation policy.
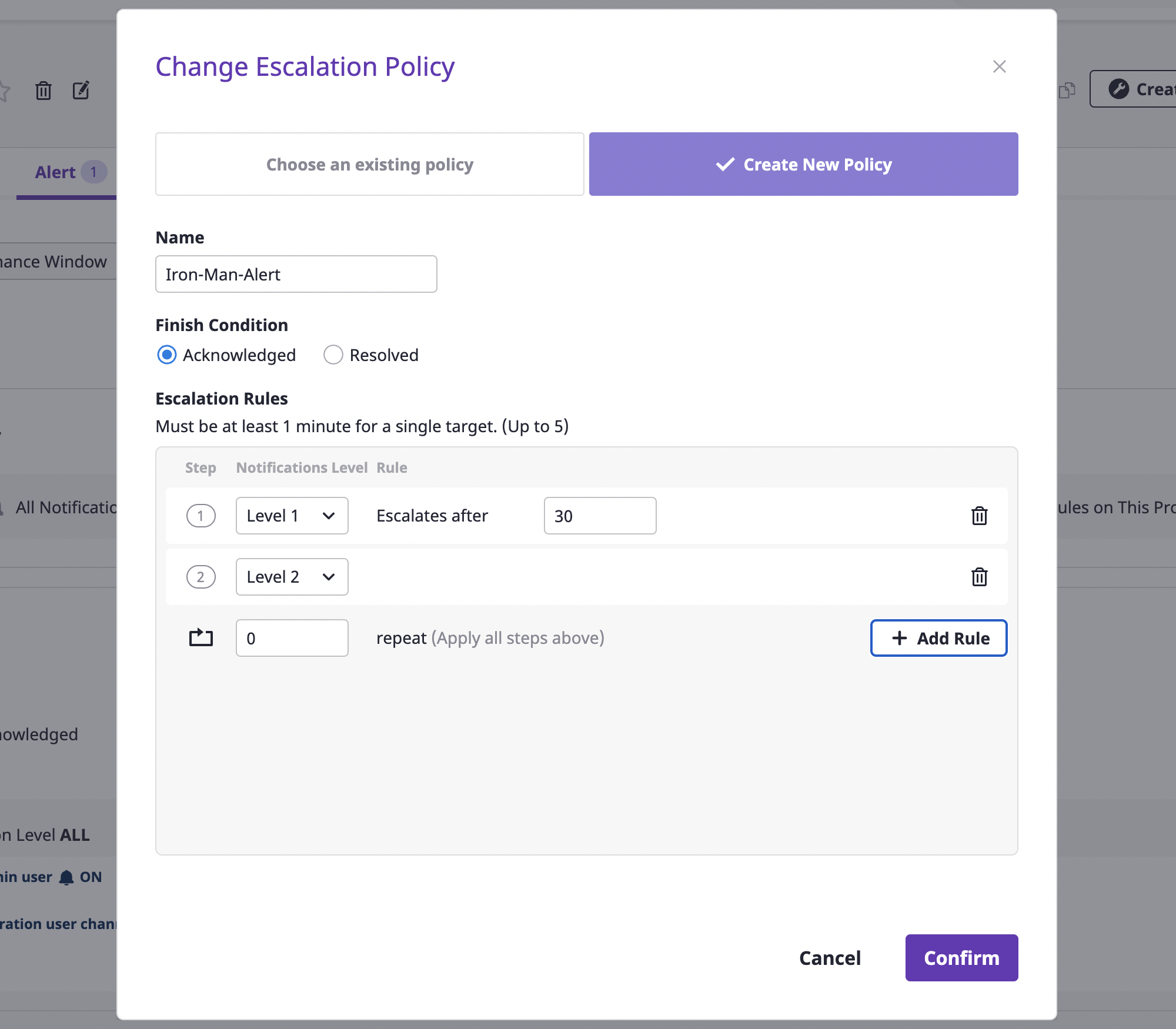
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Exit condition (status) | Define the condition to stop the generated alarm. |
| Range | Indicate the scope in which escalation policy can be used. In case of "global," the policy can be used in all projects within the domain, and in case of "project," within the specified project. |
| Escalation Rules | All levels from LV1 to LV5 can be added. Alerts are sent to a notifications channel belonging to a set level, and a period between steps can be given in minutes from step 2 or higher. |
| Number of repetitions | Define how many times to repeat an alert notification. Notifications can be repeated up to 9 times. |
| Project (if you create it from the escalation rules page) | If the scope is a project, this indicates the project being targeted. |
(4) When all settings are completed, click the [OK] button to create the escalation policy.
Notifications settings
In the [Notification] tab of the project detail page, you can decide whether or not to Create a notifications channel and enable it.
Notifications channel is a unit that expresses the systematic recipient area, including the method and level of notifications transmission. It helps to transmit alerts according to the level set in the escalation rule.
(1) On the project detail page, select the [Notification] tab and click the [Add channel] button of the desired notifications channel.
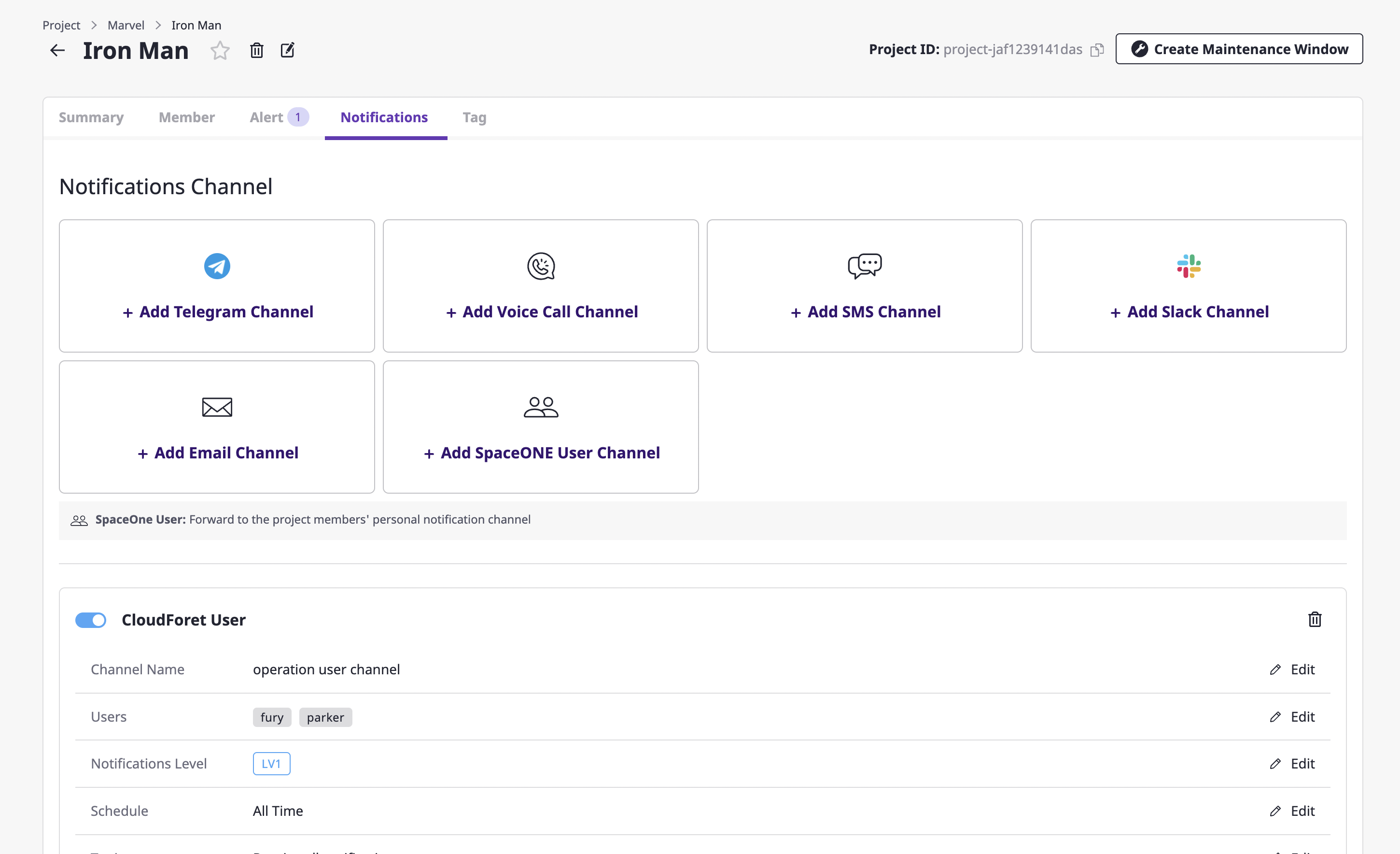
(2) On the notification creation page, enter the settings to create a notifications channel.
(2-1) Enter the basic information about the notifications channel you want to create, such as the required channel name and notification level. The [Channel name] and [Notification level] comprise the basic setting fields, and afterward, the remaining fields receive different information per channel.
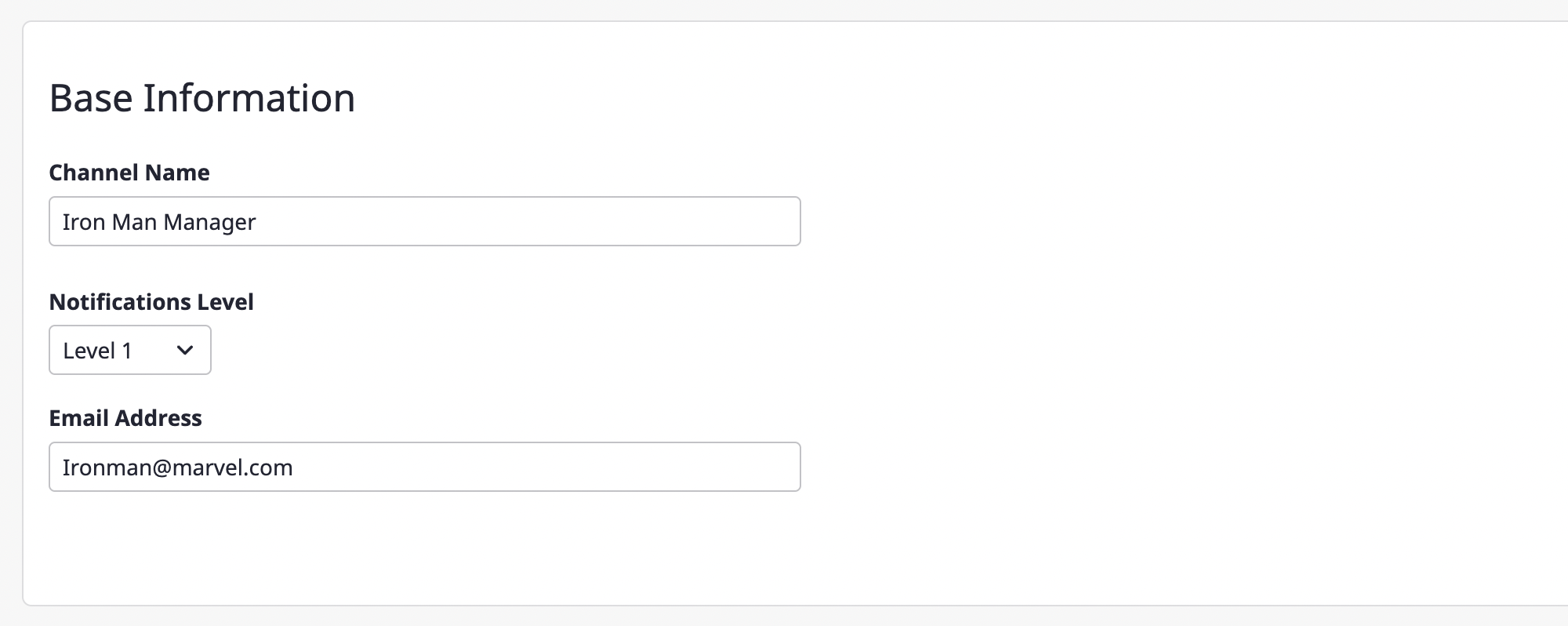
(2-2) You can set a schedule to receive notifications only at certain times.
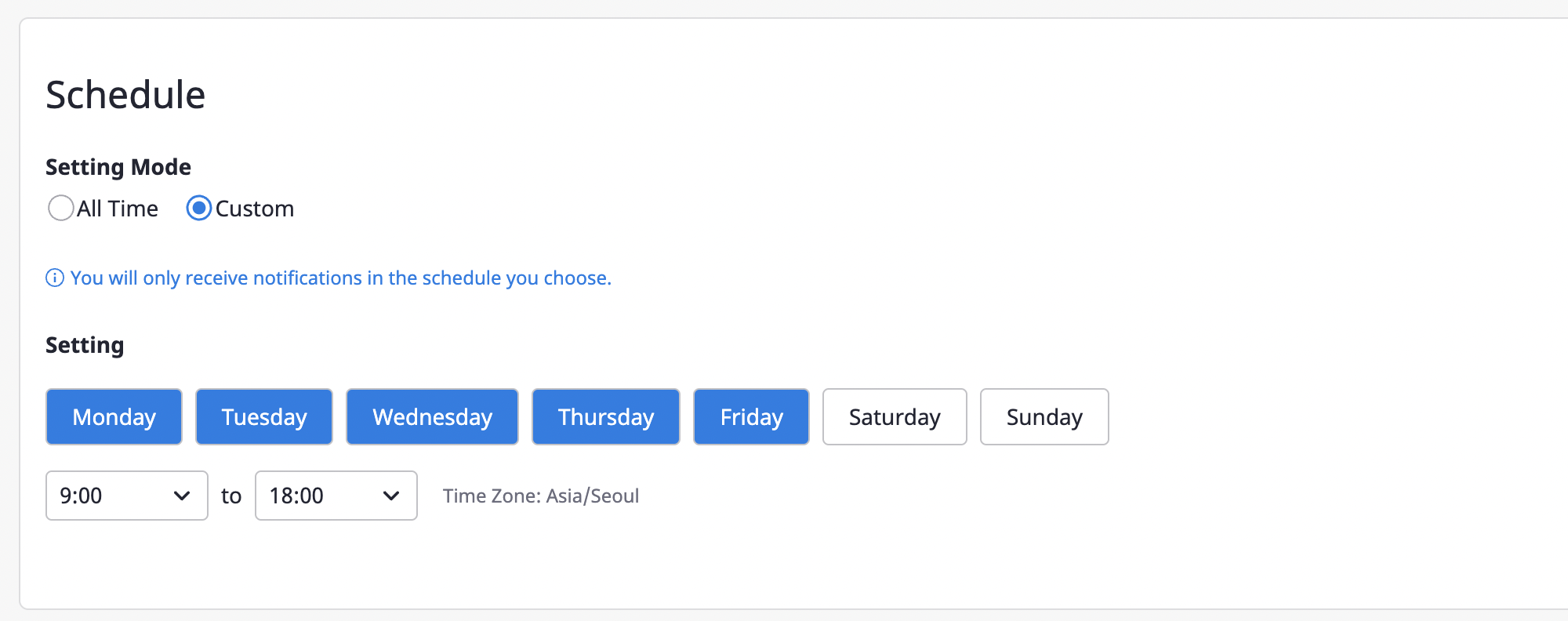
(2-3) Notifications can be received when an alert occurs or when a threshold for budget notifications was reached. You can set the occasions when you receive notifications in [Topic].
(3) Click the [Save] button to complete the notifications channel creation.
(4) Notifications channels that have been created can be checked at the bottom of the [Notification] tab.
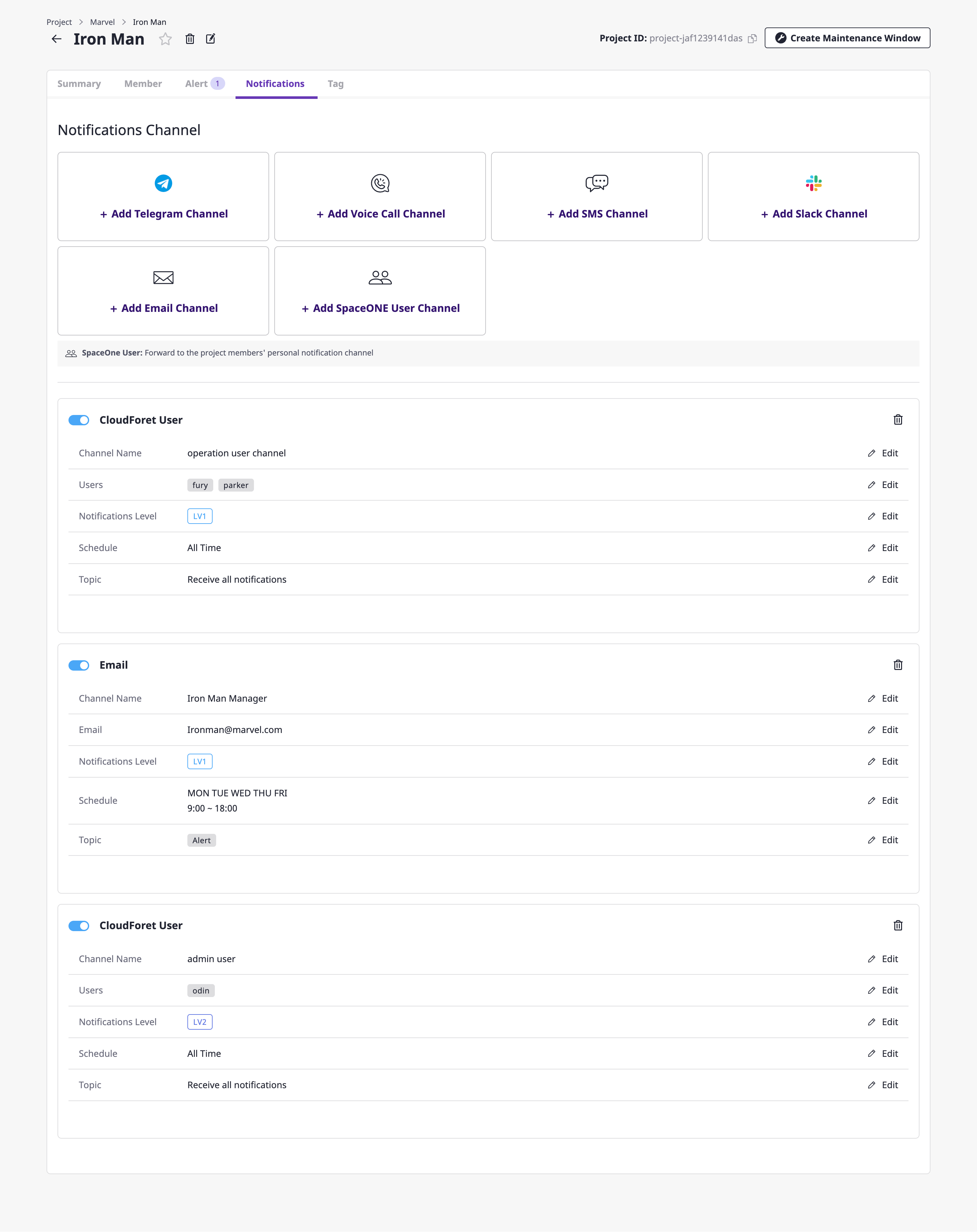
You can control whether to activate the corresponding notifications channel through the toggle button at the top left. Even if there is a level set up under the escalation policy, without activating the notifications channel, notifications will not go out.
6.2 - Dashboard
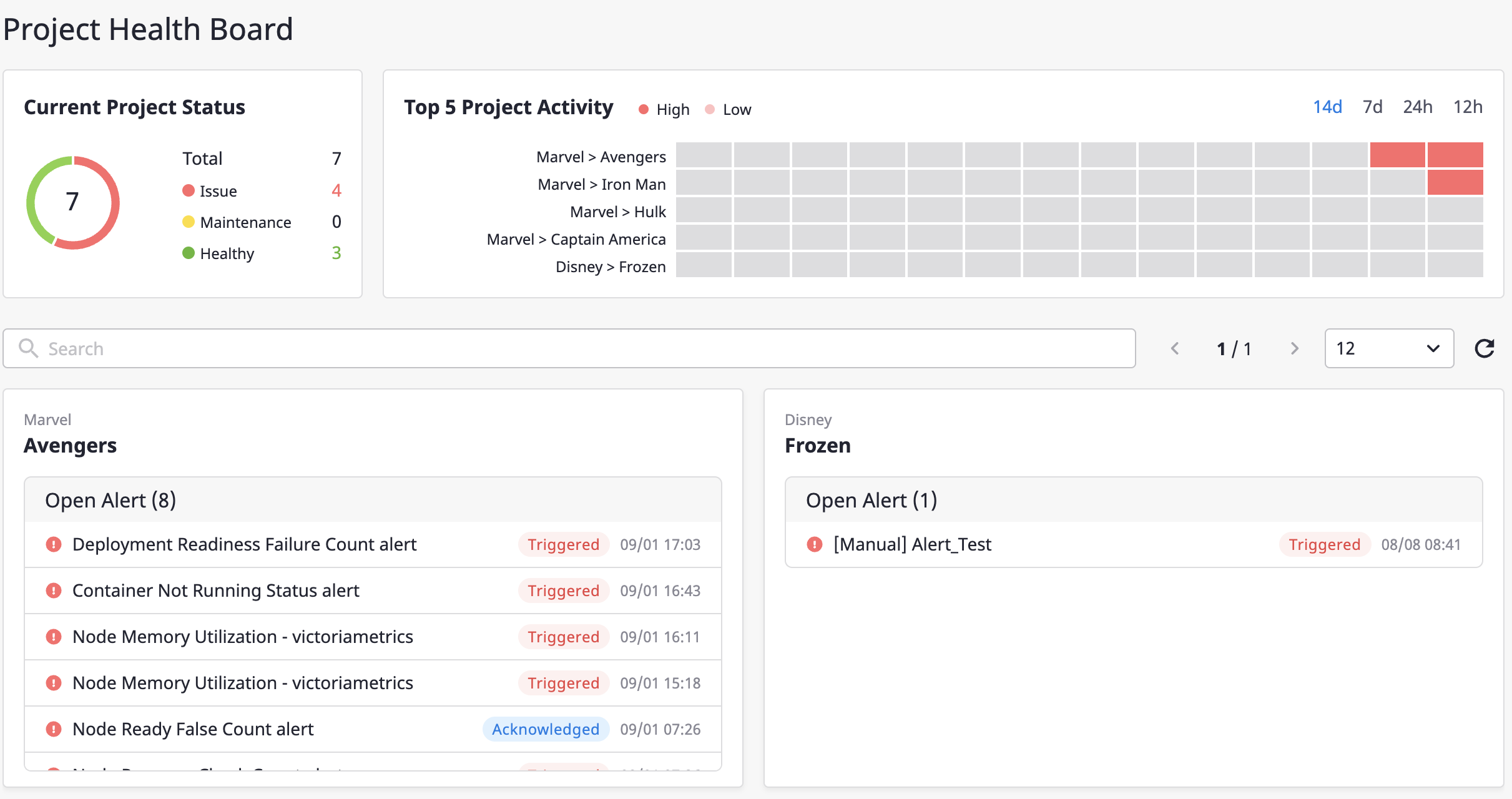
You can check alerts for each of the three main parts, as follows:
Check alerts by state
At the top of the dashboard, you can view alerts by State.
Click each item to go to the Alert details page, where you can check detailed information or implement detailed settings.
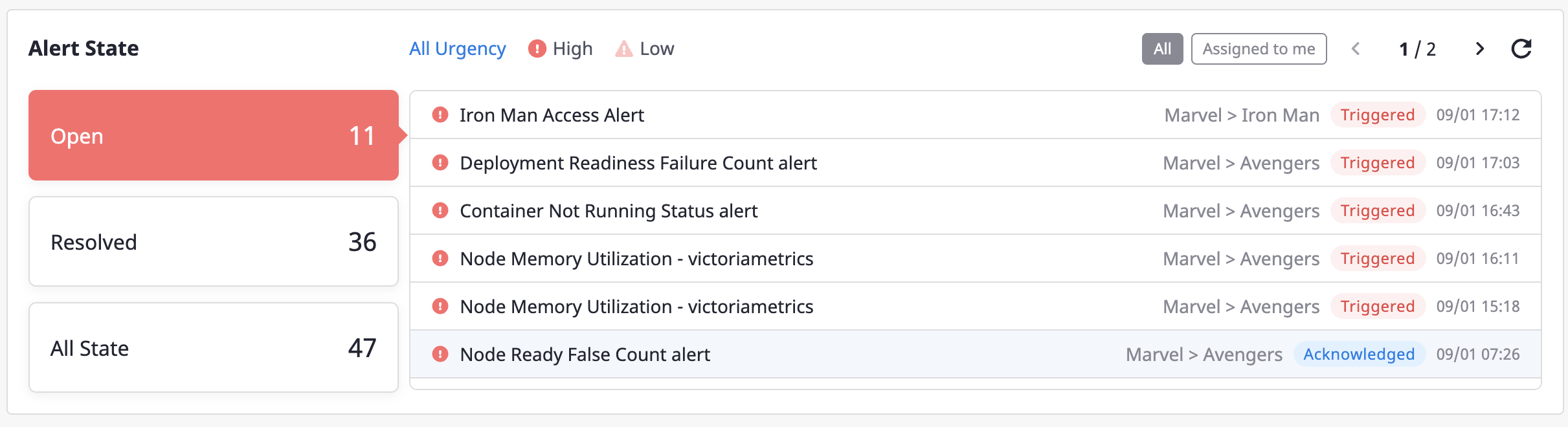
Alerts history
Alert history occurred in Project is displayed.
You can see the daily data on the chart, and the increase/decrease in alerts on the card compared to the previous month.
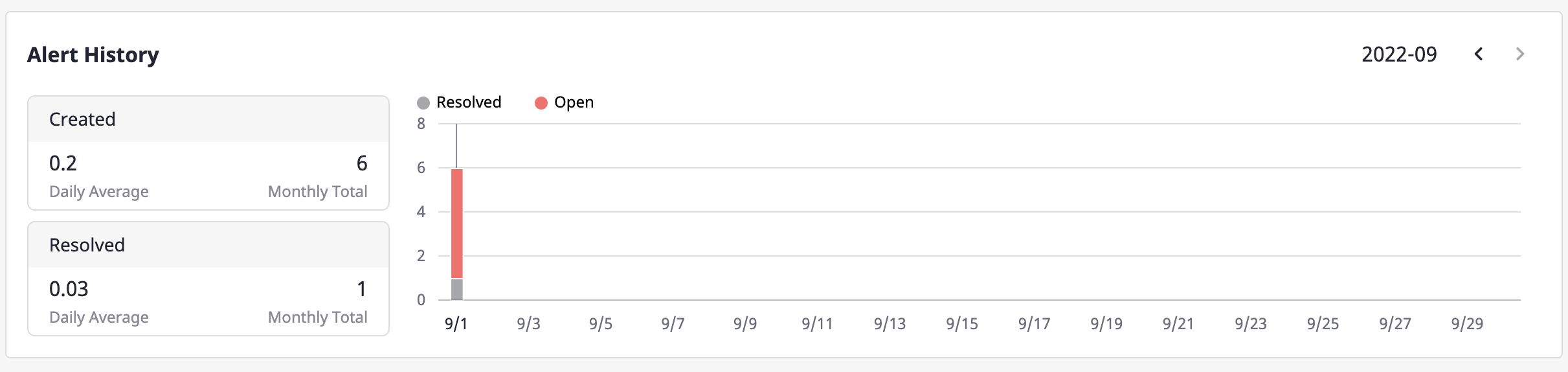
Project dashboard
[Project dashboard] shows the alert information of each project related to a user.
In the case of [Top 5 project activities], projects are displayed in the order of having the most alerts in the [Open] state.
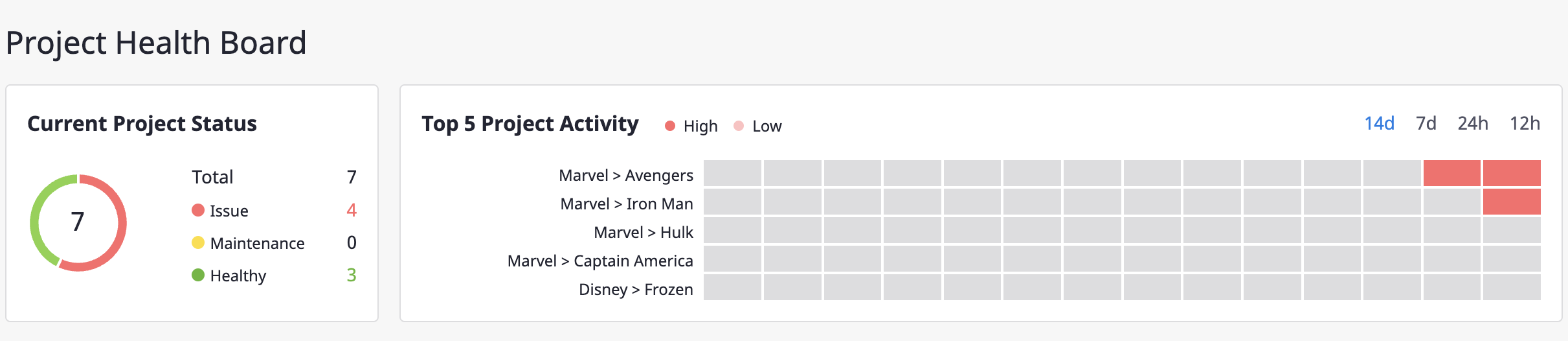
At the bottom of the search bar, the alerted projects are displayed in the order of highest activity.
Only projects marked with an issue status are visible, and when all the alerts reach a cleared status, they are changed to normal status and are no longer visible on the dashboard.
6.3 - Alert
State
Alerts have one of the following states:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| OK | State in which an alert has been assigned and is being processed |
| Created | State in which alert was first registered |
| Resoled | State in which the contents of alerts such as faults, inspection, etc., have been resolved |
| Error | State in which an event has been received through webhook connections but alerts were not normally registered due to error |
Urgency
There are two types of urgent alerts in Cloudforet: high and low.
Whereas in the case of the Manual creation of alerts, it is created as one of two types, high and low, in the case of automatic creation through webhook connections, urgency is measured according to Severity.
Severity
Severity indicates the intensity of the risk of an event coming from a typical external monitoring hook.
There are five severity levels: critical, error, warning, info,andnot_available,` and, when creating alerts from them, Cloudforet sets the urgency level based on the following criteria:
• High : critical, error, and not available
• Low: warning and info
Creating alerts
Alerts can be created in two ways:
- Manual creation: create an alert manually in the Cloudforet console.
- Auto generation: create a webhook and receives events from an external monitoring service connected to the webhook. And it automatically generates an alert by purifying the received event message.
Creating an alert manually from a console
(1) Go to the [Alert manager > Alerts] page and click the [Create] button.

(2) When the [Create alert] modal dialog opens, fill in the input form.

(2-1) Enter an [Alert title] and select [Urgency].
(2-2) Designate the project for which the alert occurred.
(2-3) Write [Comment] if an additional explanation is needed.
(3) Click the [OK] button to complete alert creation.
Connecting to an external monitoring service to receive alerts
When an external monitoring service is connected, an event message occurring in the service is automatically generated as an alert.
To receive alerts from the external monitoring, Webhook creation and Connection settings are required.
Webhook creation is performed in the Cloudforet console, but Connection settings must be done directly in the Cloud Service console that provides external monitoring services.
For more on how to connect an external monitoring service, see here.
Creating a webhook
To receive event messages from an external monitoring service, you need to create a webhook.
Webhooks can be created on the project detail page.
(1) Go to the [Alerts] tab of the project detail page and select the [Webhook] tab.

(2) Click the [Add] button.
(3) Write a name in an [Add webhook] modal dialog and select the plug-in of the external monitoring service to be connected.

(4) Click the [OK] button to complete set up.
Using Alerts
Let's take a brief look at various ways to use the alert features in Cloudforet.
- Notifications channel: set up how and when to send alerts to which users.
- Escalation policy: apply step-by-step rules to effectively forward received alerts to project members.
- Event rules: events received through webhooks are generated as Alerts according to the circumstances.
- Maintenance period: register regular and irregular system task schedules to guide tasks and block Alerts that occur between tasks.
Getting a list of alerts
You can view alerts from all projects on the [Alert manager > Alerts] page.
You can search for alerts or change the state of an alert.
Searching for alerts
You can enter a search term to see a list of alerts that match your criteria and click the title of an alert you want to check on an alert detail page.
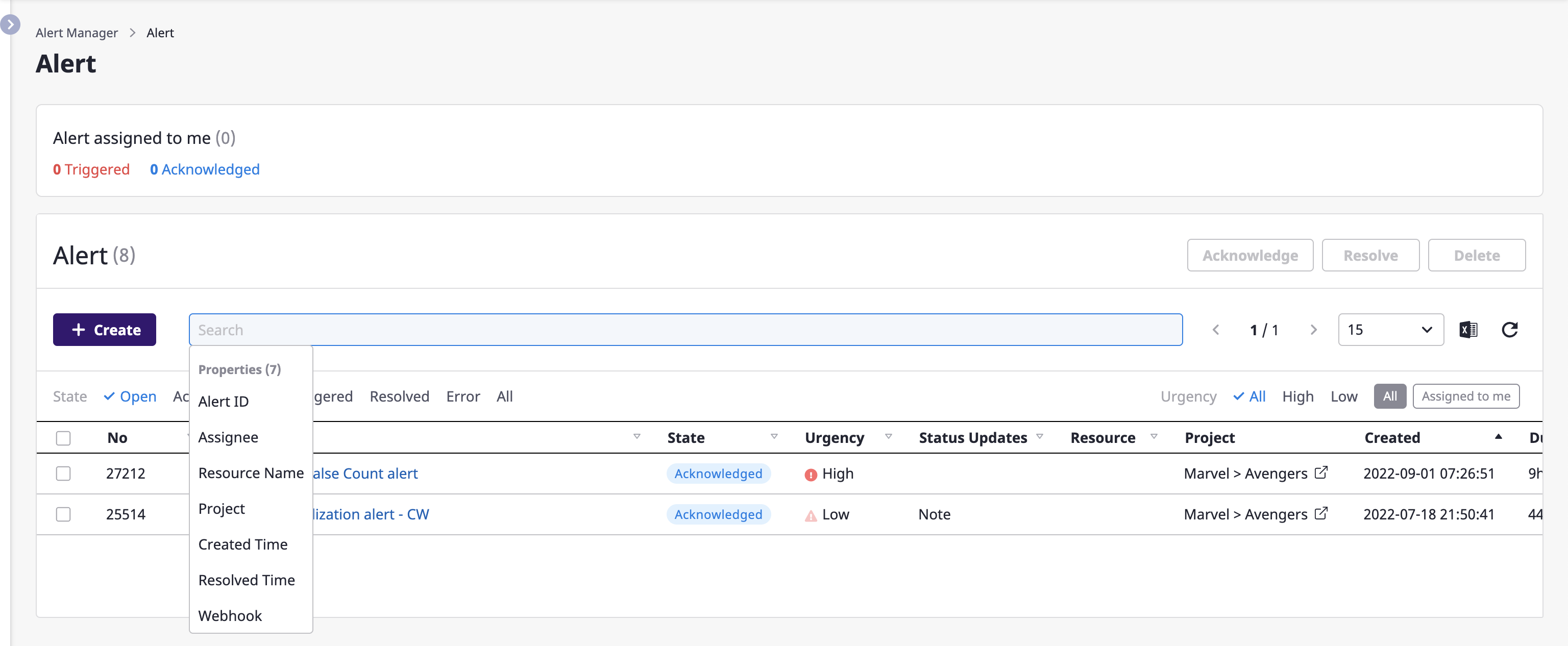
Also, the built-in filtering feature makes it convenient to filter alerts.
For a detailed description on advanced search, see here.
Changing alert state in lists
You can edit an alert state right from the list.
(1) Select an alert to edit the state, and click the desired button from among [OK], [Resolved], and [Delete] in the upper right corner.
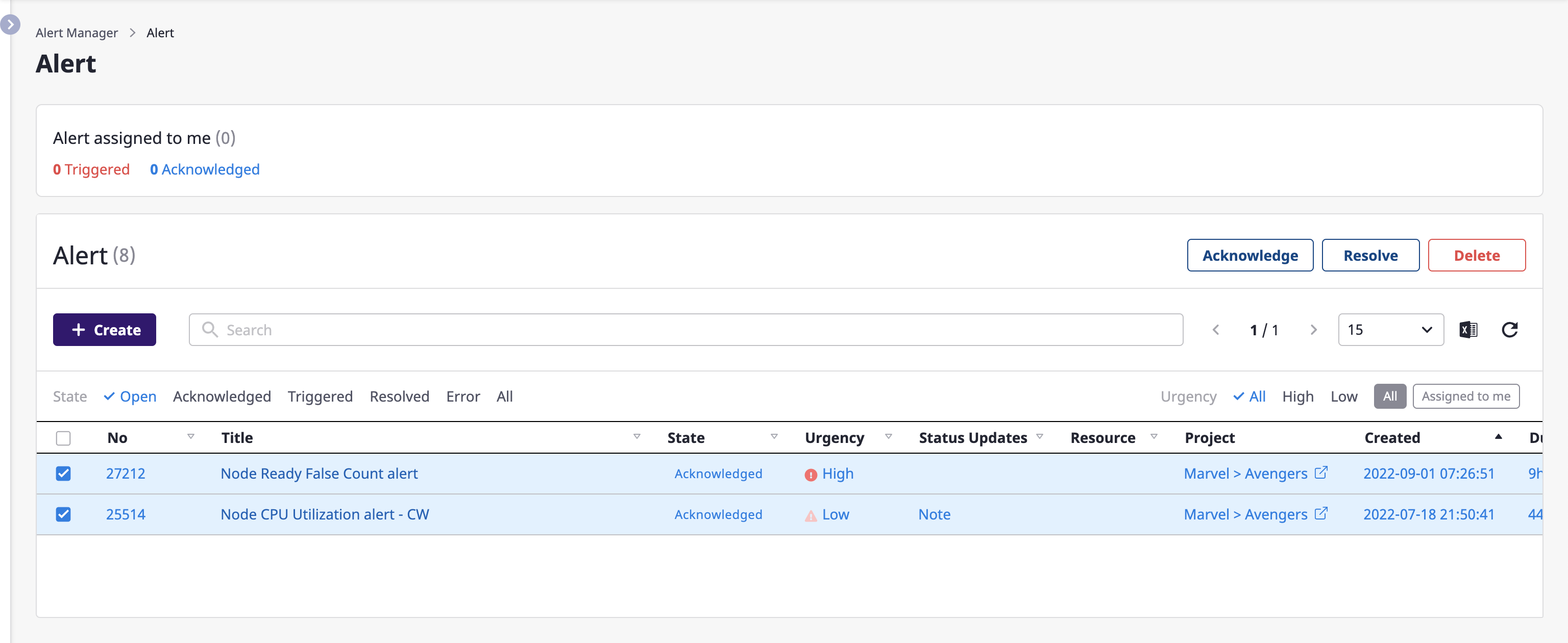
(1-1) Click the [OK] button to change the state to OK
The OK state is a state in which the alert has been assigned and is being processed by a person in charge.
As soon as you change the state, you can set the person in charge of the selected alert to yourself, and click the [OK] button to complete.
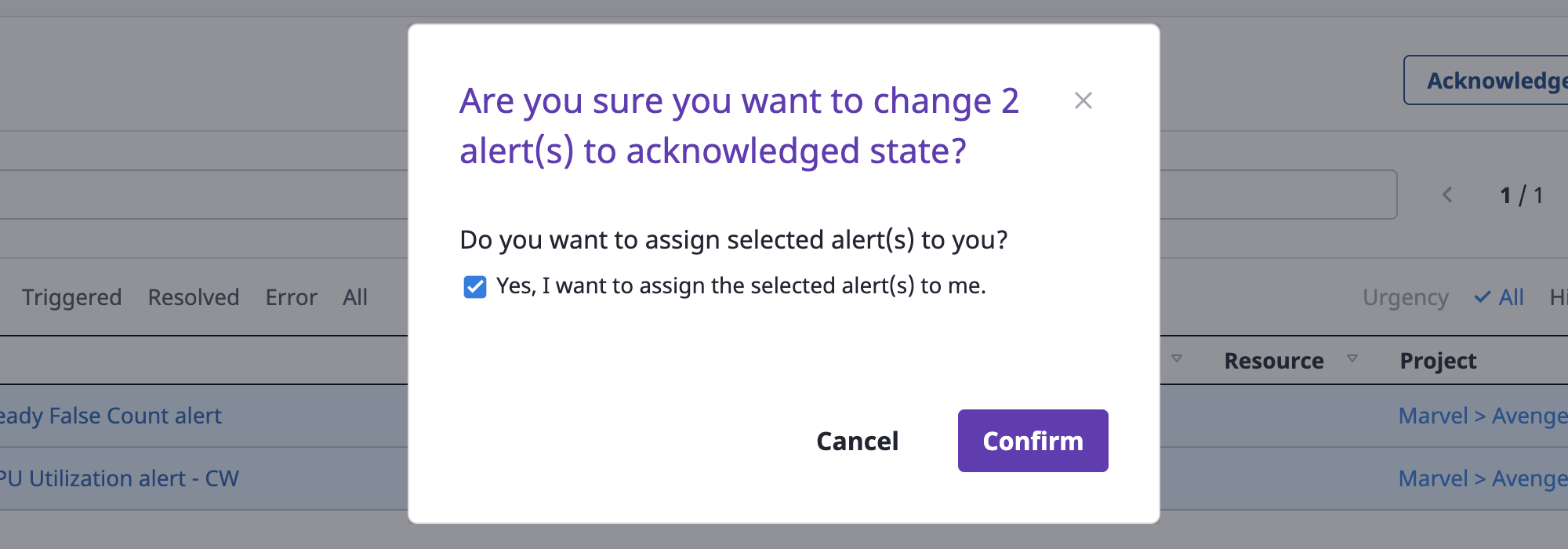
(1-2) Click the [Revolved] button to change the state to `resolved’
The resolved state means that the issue that caused the alert has been processed.
You can write a note as soon as the state changes, and click the [OK] button to complete.
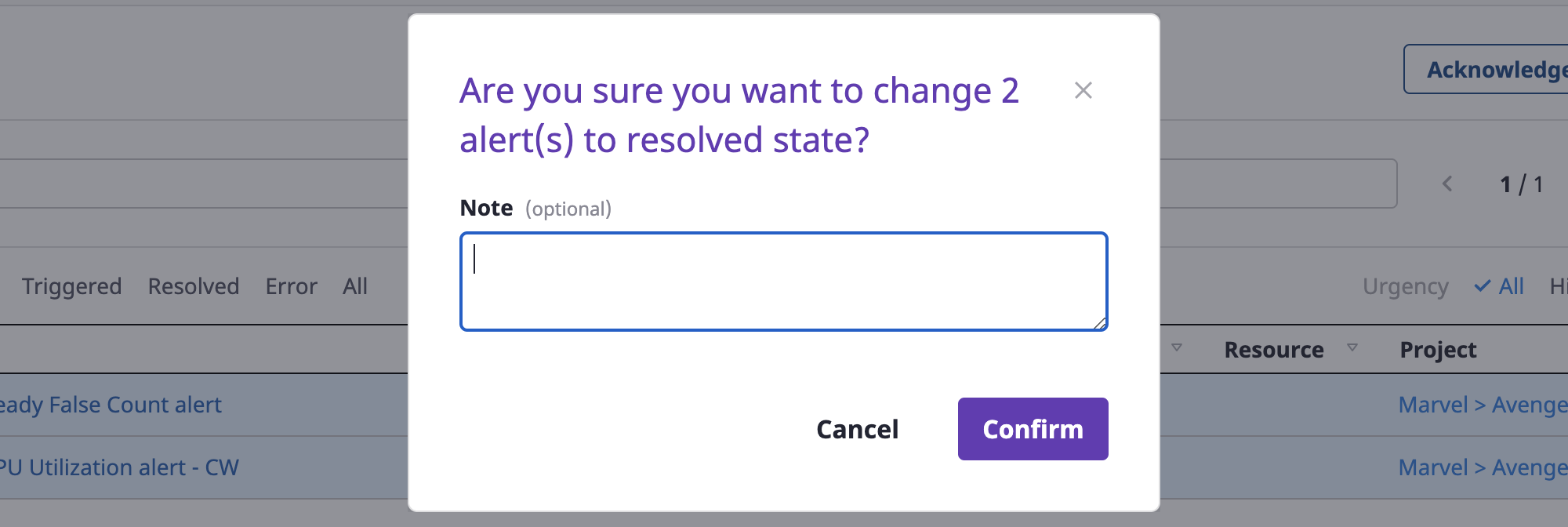
(1-3) Click the [Delete] button to delete an alert
You can check the alert list to be deleted once again, and click the [OK] button to delete it.
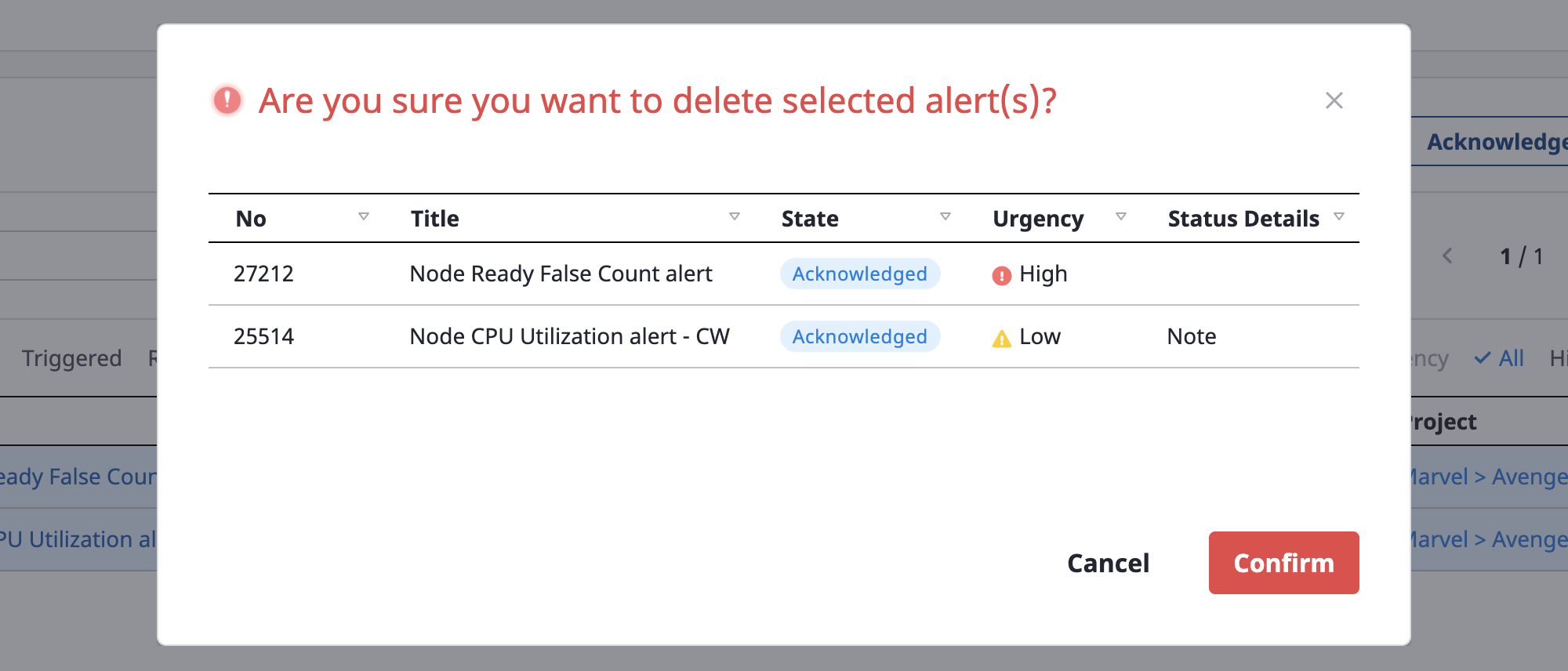
Viewing alerts
You can view and manage details and alert history on the alert detail page.
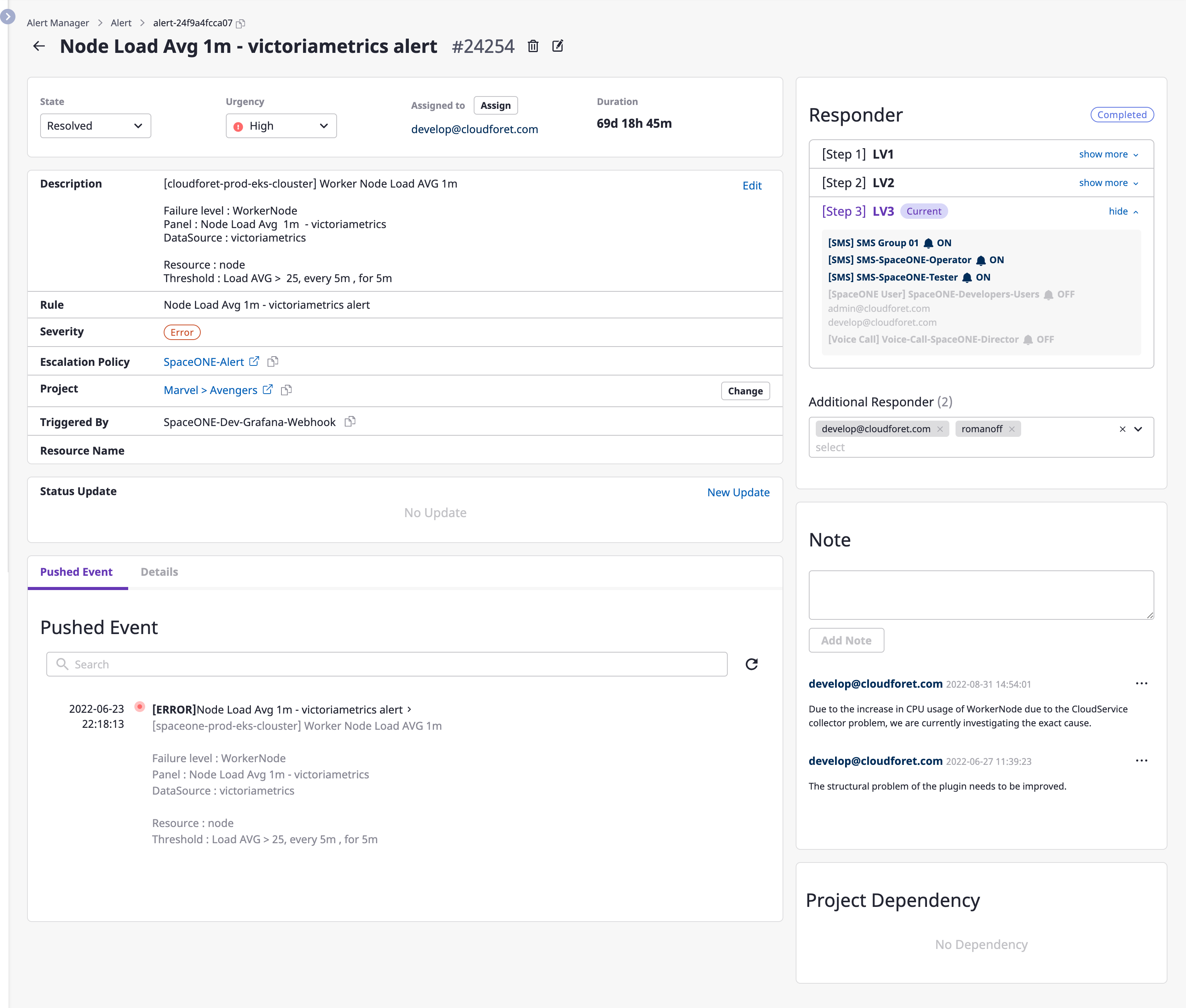
| Items | Description |
|---|---|
| Duration | Time during which an alert lasted |
| Description | As a description of an alert, the content written by a user or that of an event received from an external monitoring service |
| Rules | Conditions alerted by an external monitoring service |
| Severity | Level of seriousness of data received from a webhook event |
| Escalation policy | Applied escalation policy |
| Project | Alerted project(s) |
| Create | Monitoring services that sent alerts |
| Resource name | Alert occurrence target |
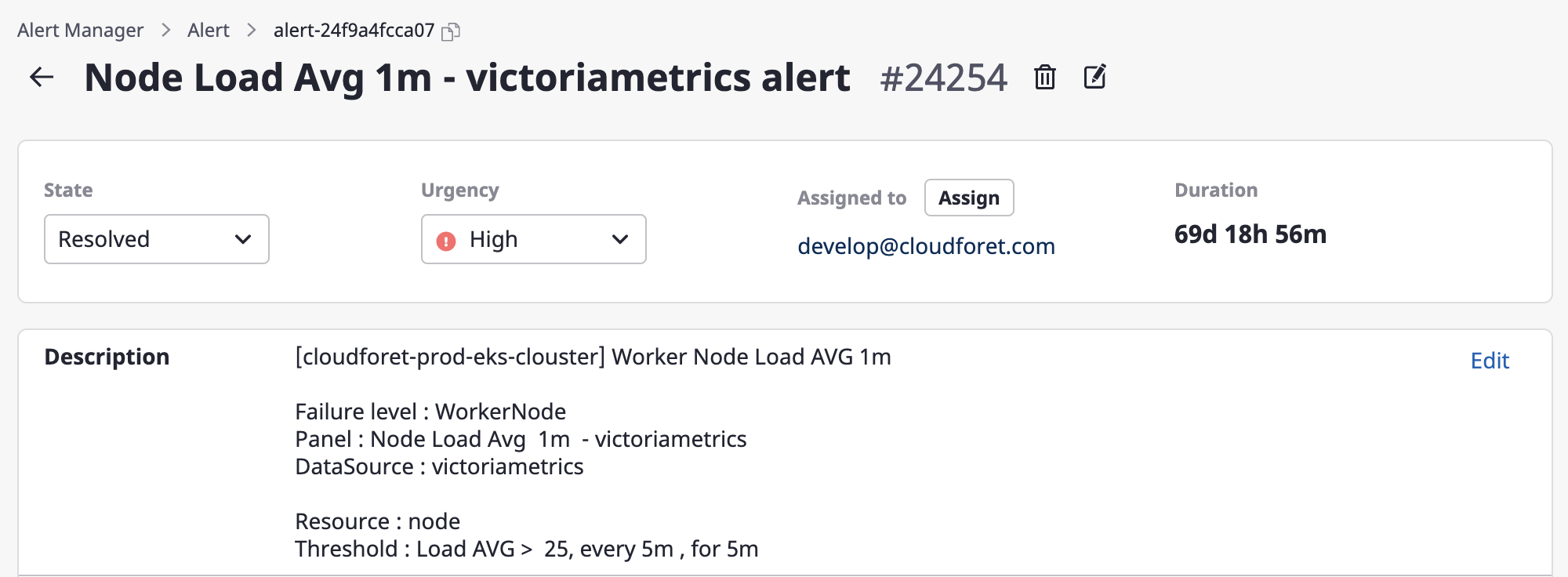
Renaming and deleting alerts
You can change the name of an alert or delete an alert through the [Edit] and [Delete] icon buttons for each.
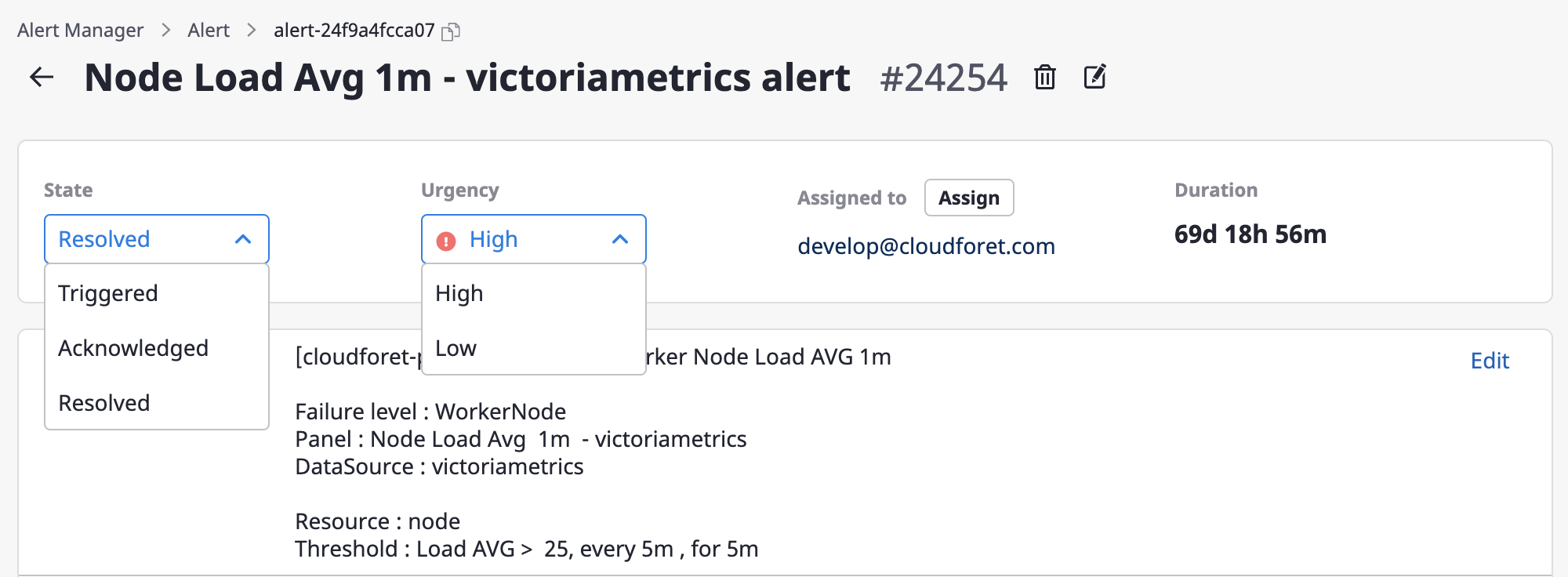
Changing state/urgency
State and urgency can be easily changed via the dropdown menus.
Changing the person in charge
(1) Click the [Assign] button.
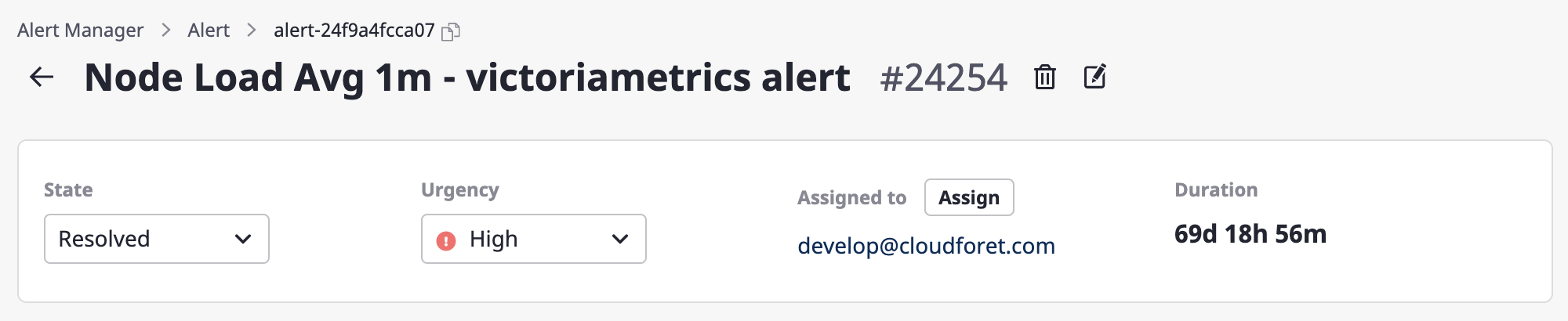
(2) Select a person in mind and click the [OK] button to complete the assignment of the person in charge.
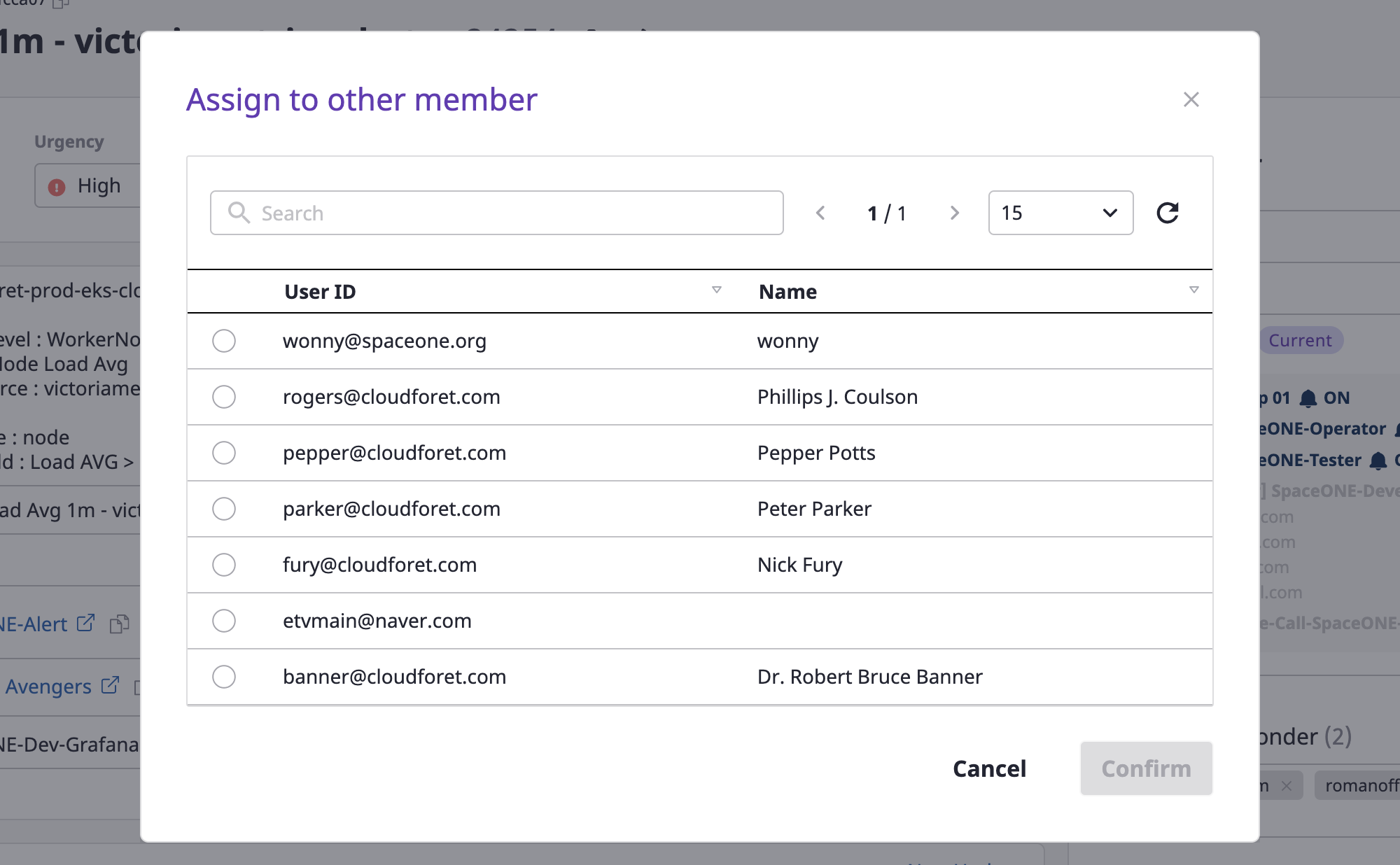
Editing description
Only users with an administrative role for the alert can edit it.
(1) Click the [Edit] button.
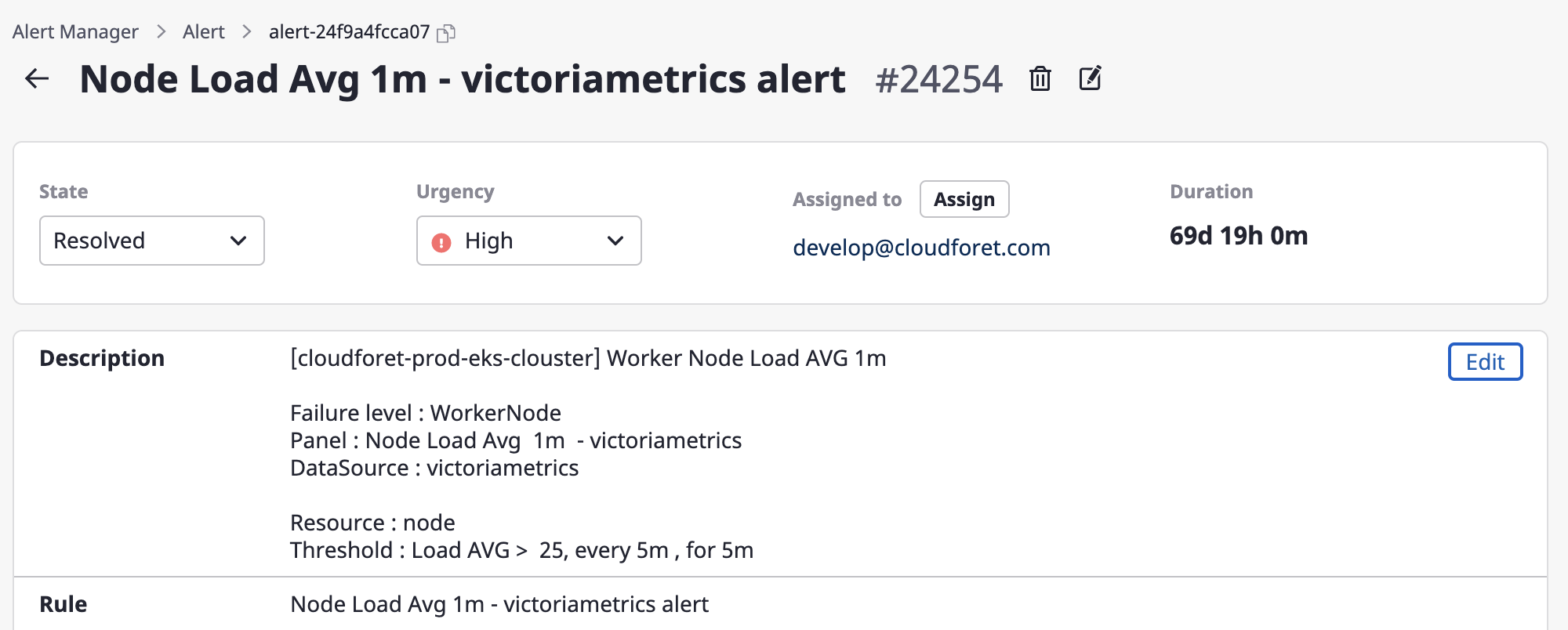
(2) Write changes through a form in an alert description field and click the [Save changes] button to complete such changes.
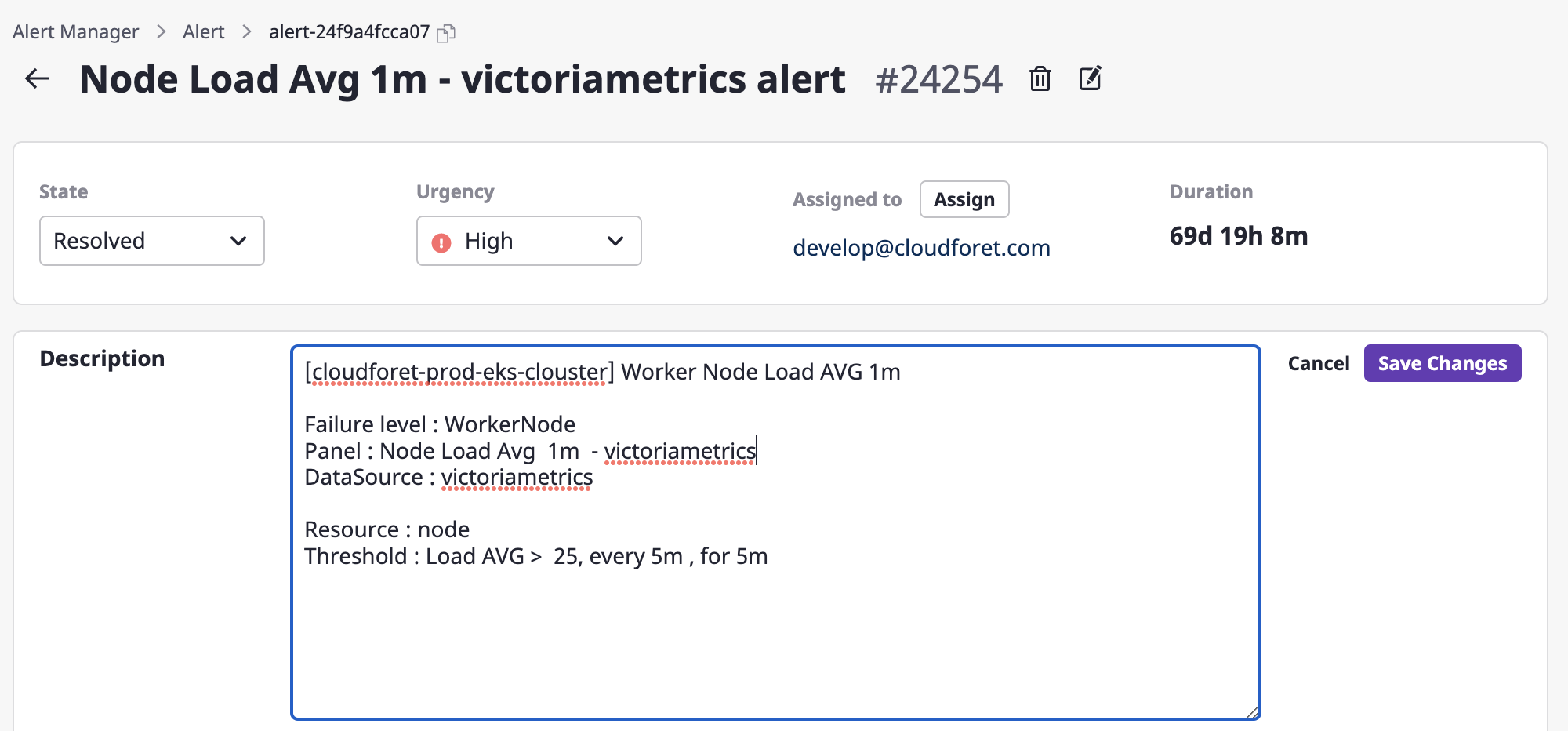
Changing a project
You can change the project linked with an alert.
(1) Click the [Change] button to change a project.
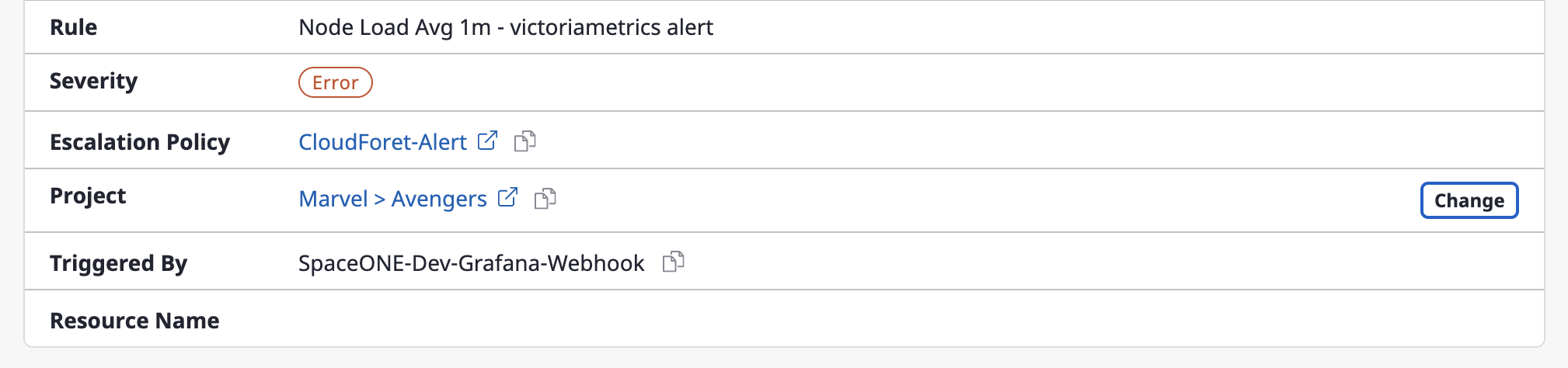
(2) After selecting a project from a [Select project] dropdown menu, click the [Save changes] button to complete the project change.
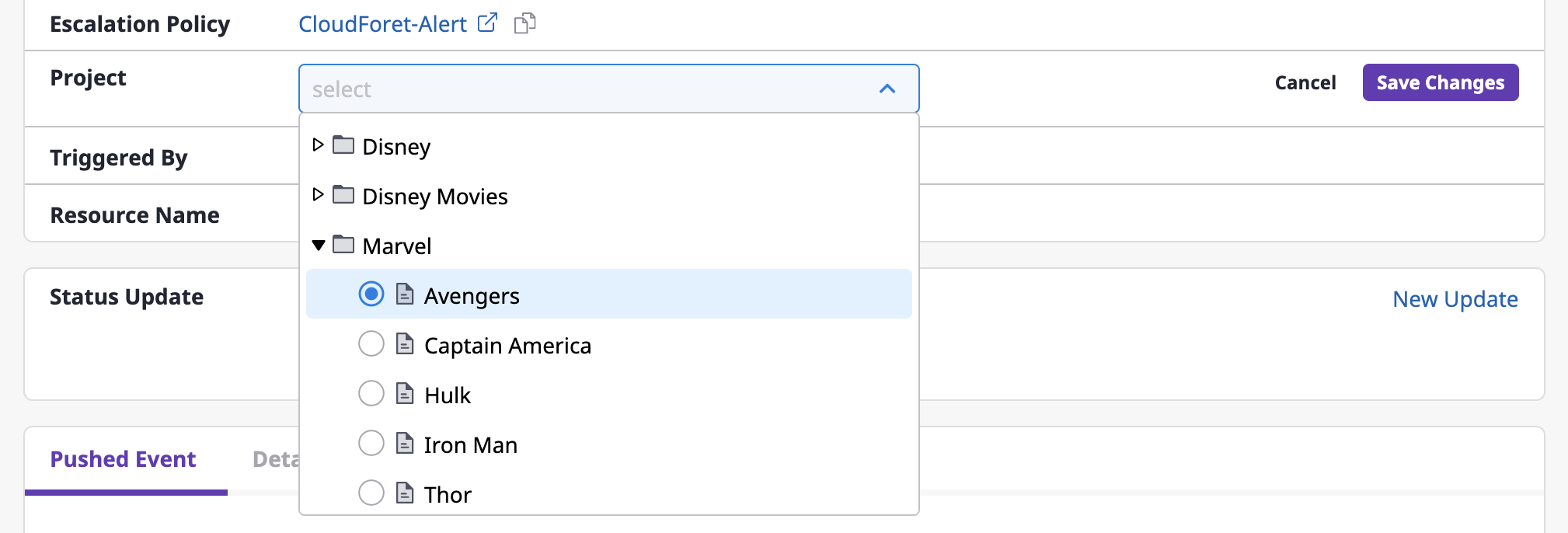
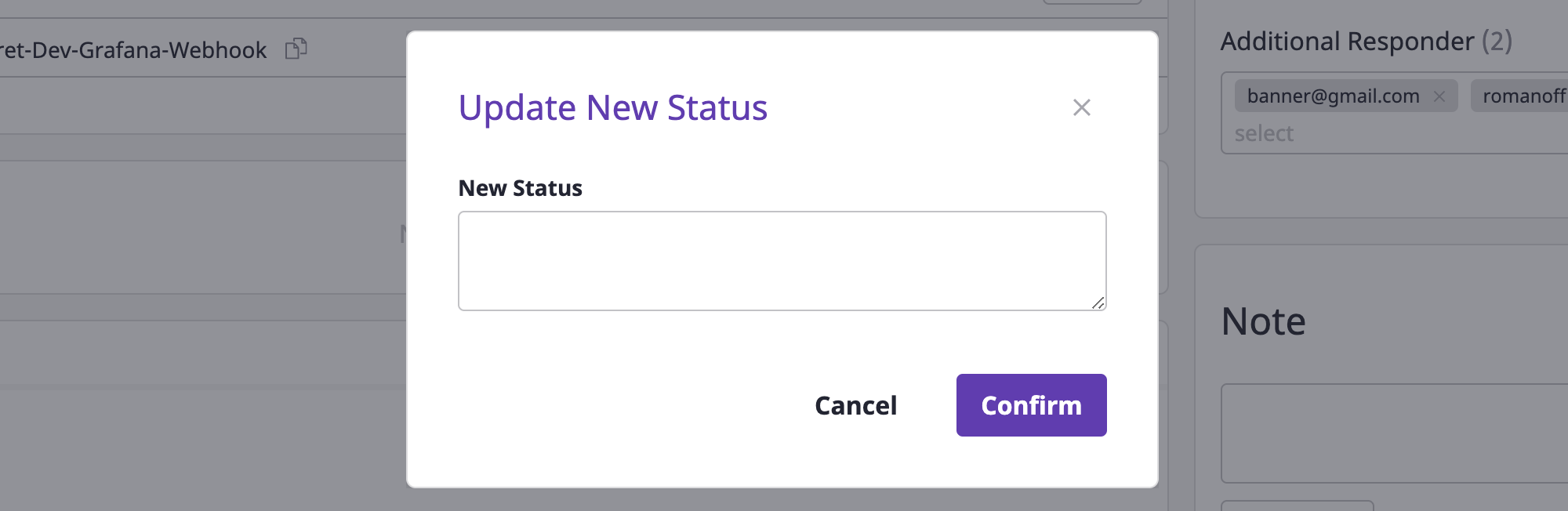
Updating to a new state
By recording the progress in the state of alerts field, you can quickly grasp their state.
If you change the content, the previous state history will be lost.
(1) Click the [New update] button.
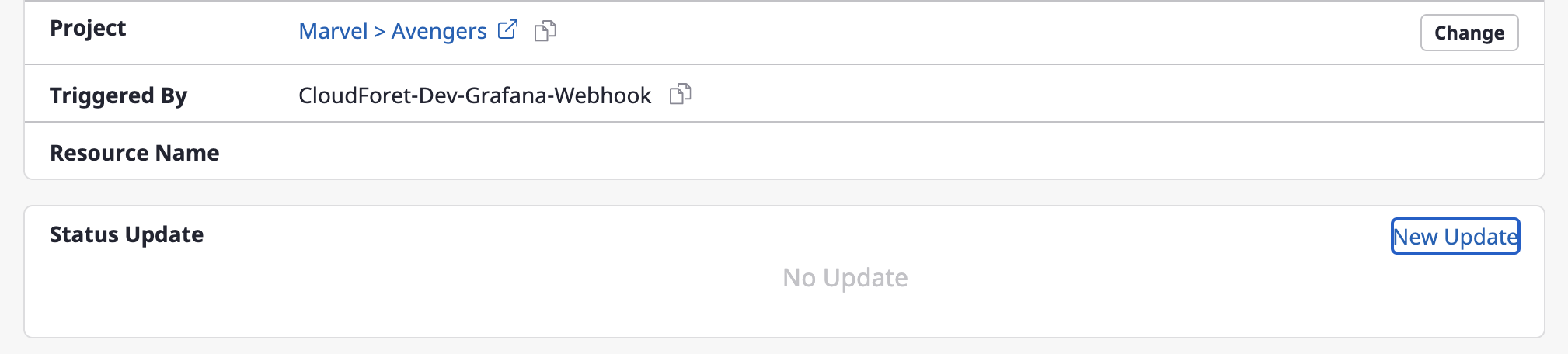
(2) Input the state in the [New state update] modal dialog, and click the [OK] button to complete the state update.
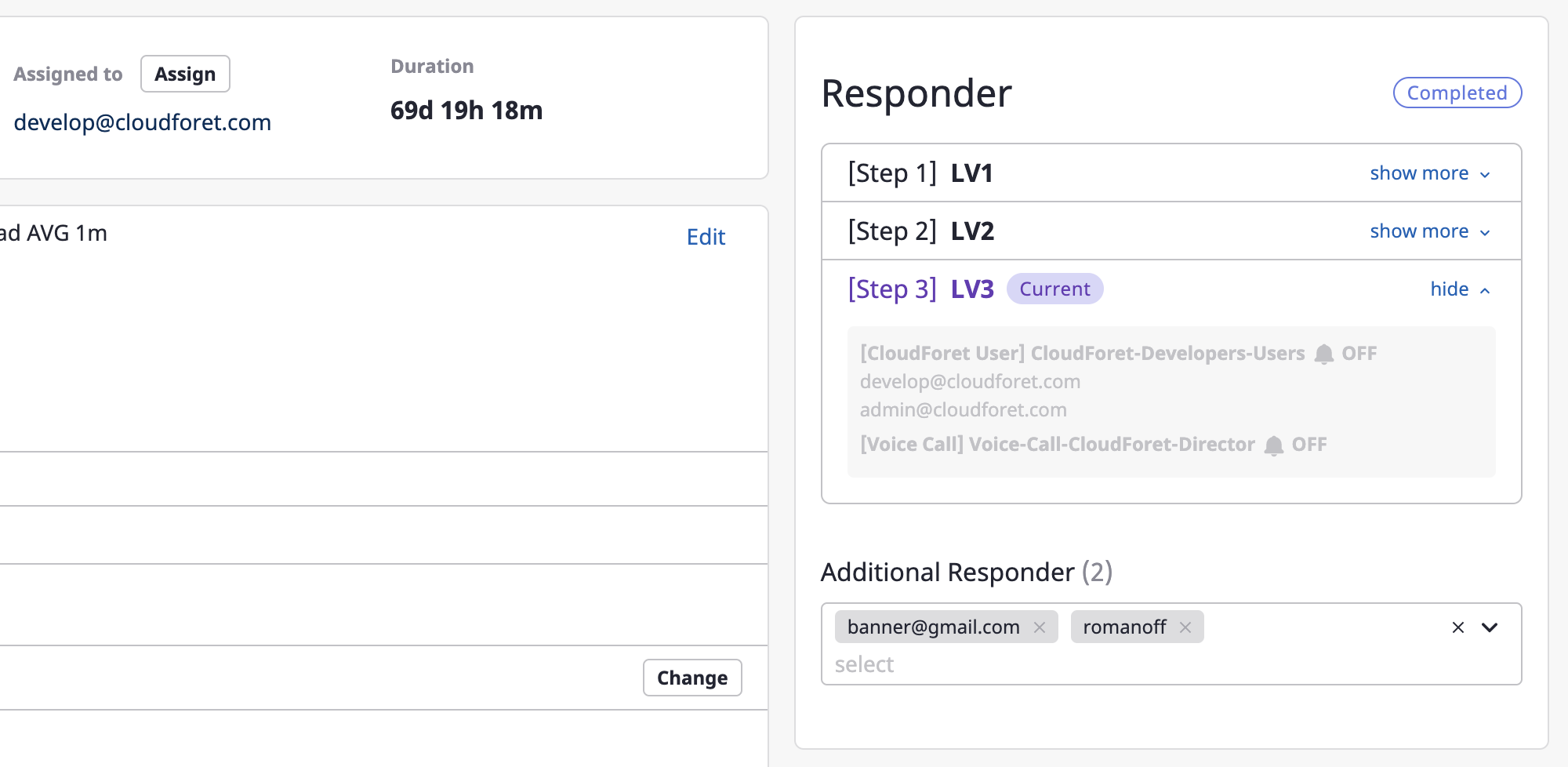
Adding recipients
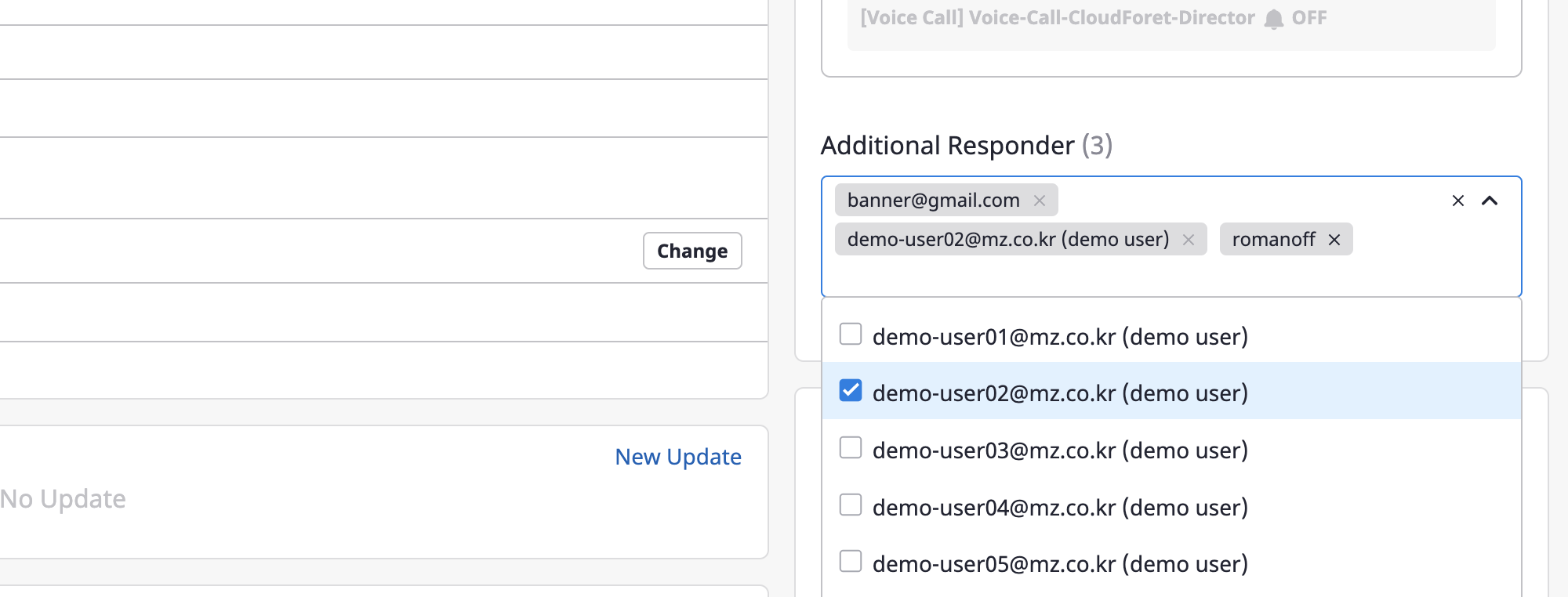
Alerts are sent to recipients via Escalation policy.
If you need to send an alert to additional users for that alert, set up [Additional recipients].
You can view and search a list of available users by clicking the search bar, where multiple selections are possible.
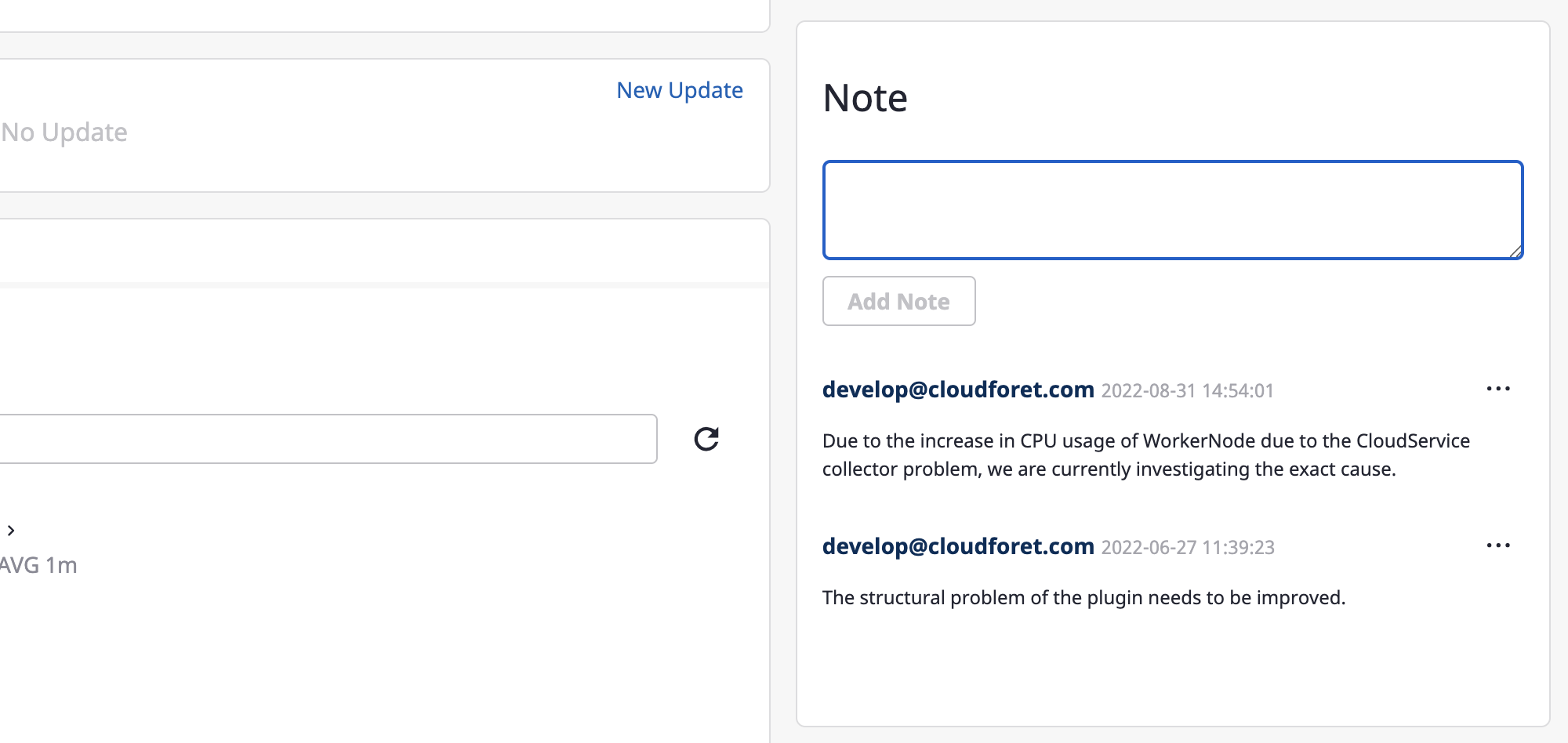
Adding notes
Members can communicate by leaving comments on alerts, registering inquiries and answers to those inquiries during processing.
Viewing occurred events
You can view history by logging events that occurred in one alert.
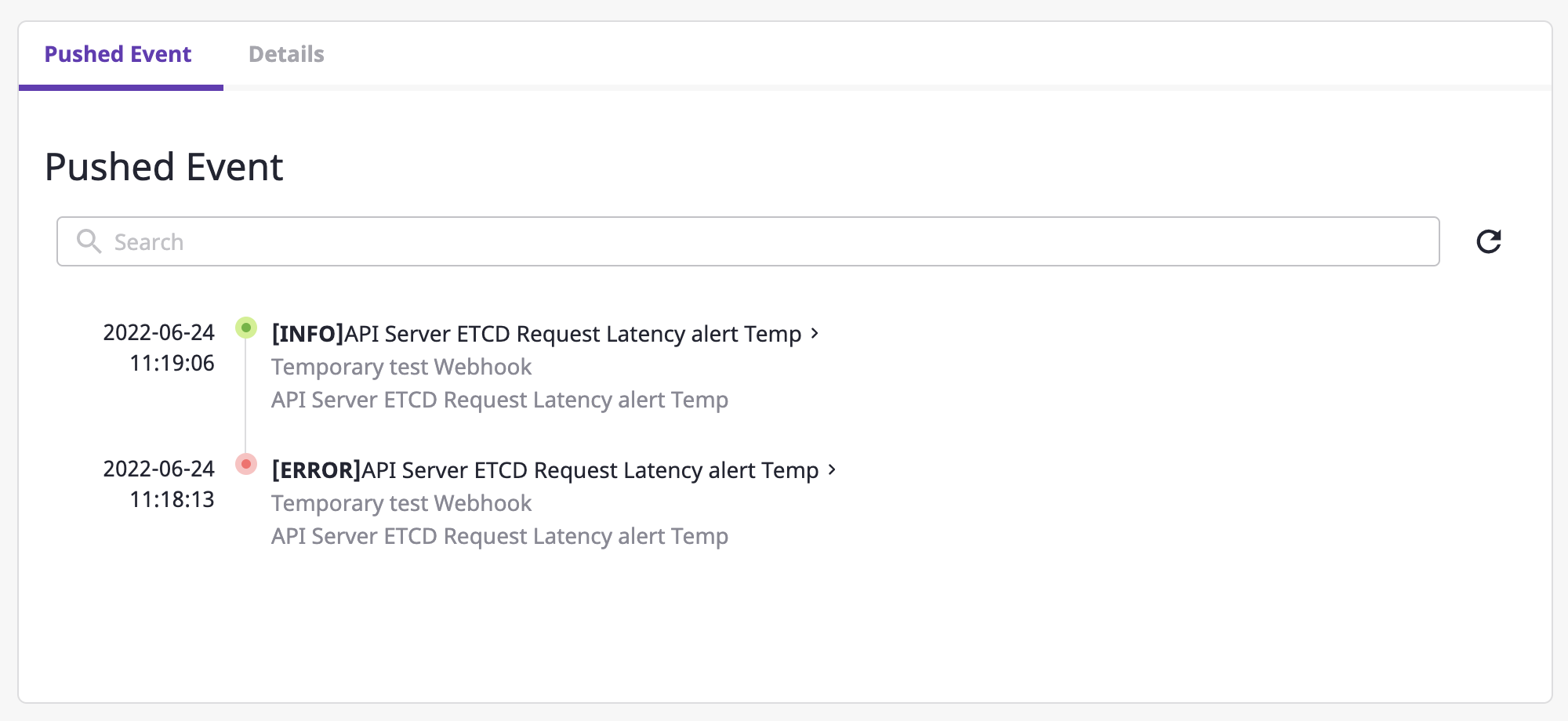
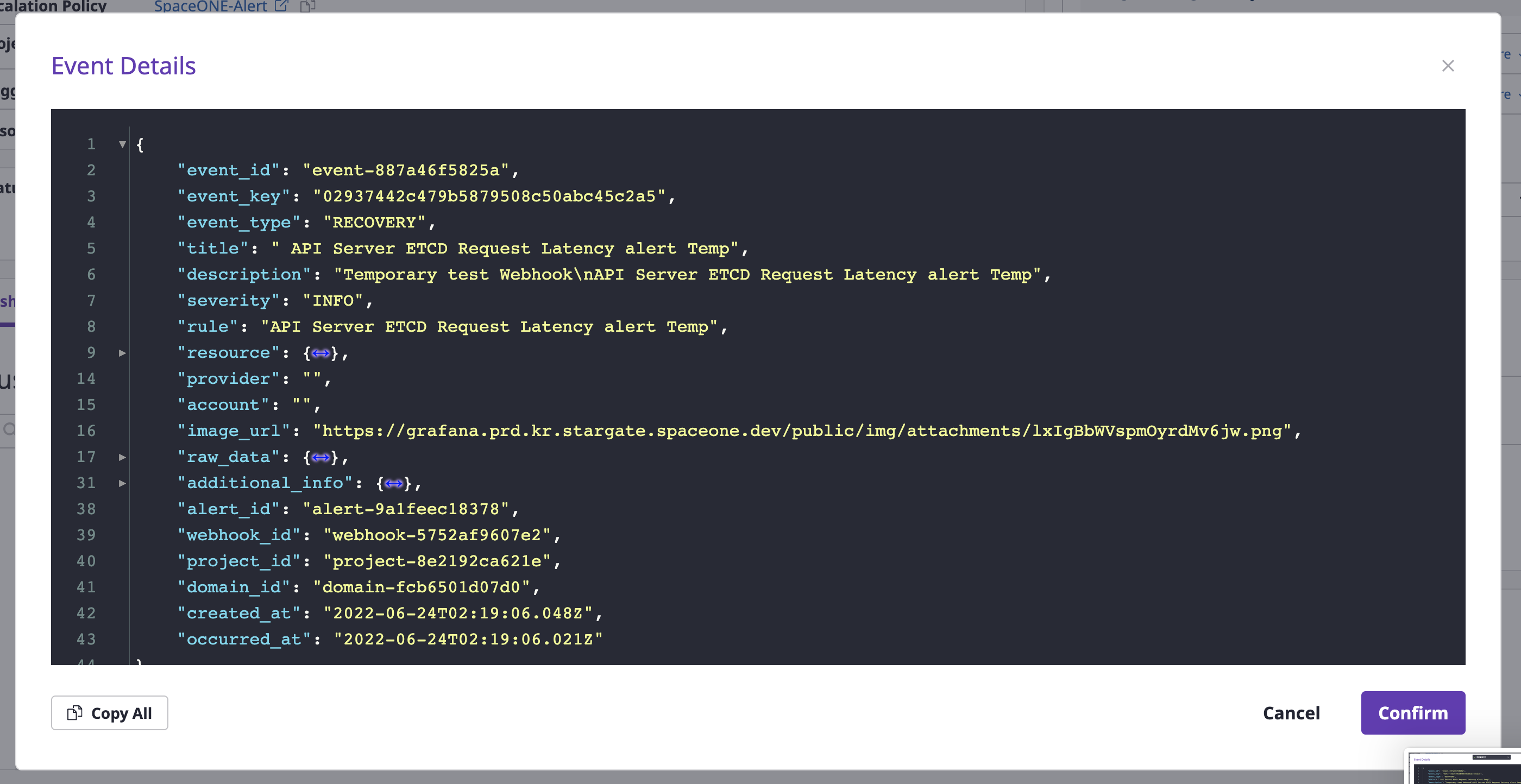
If you click one event from a list, you can view the details of that event.
Notification policy settings
You can set an alert to occur only when the urgency of the alert that has occurred in the project is urgent.
(1) Inside the [Alerts] tab of the project detail page, go to the [Settings] tab.
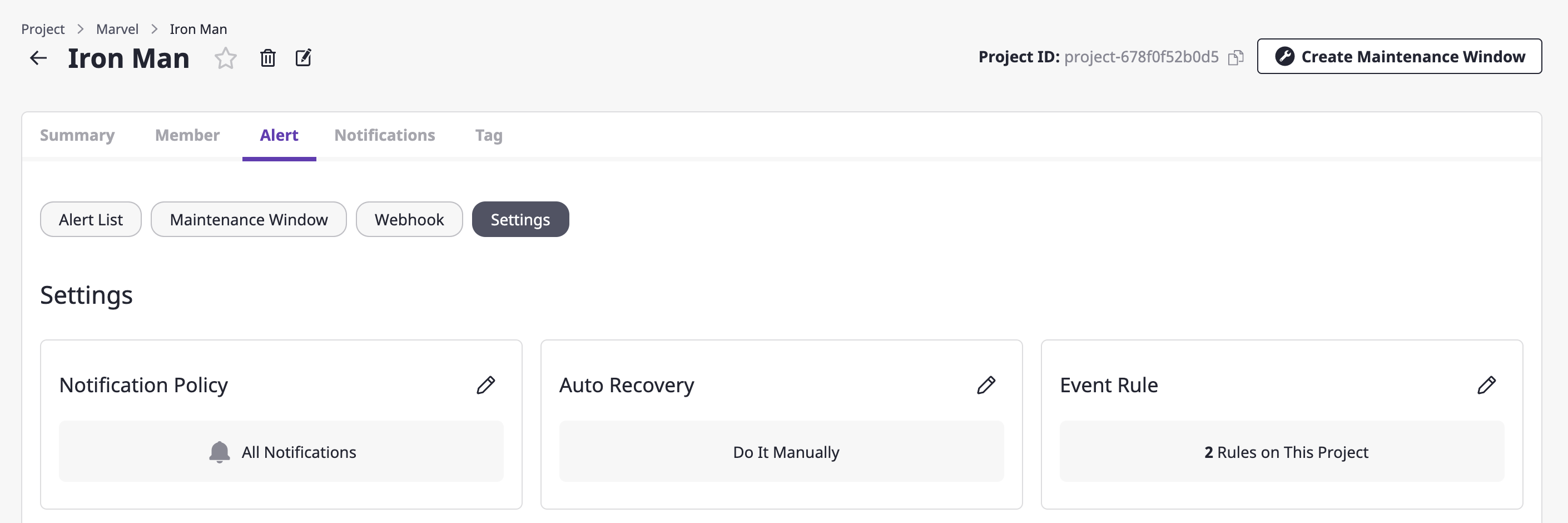
(2) Click the [Edit] icon button in the notification policy area.

(3) Select the desired notification policy.
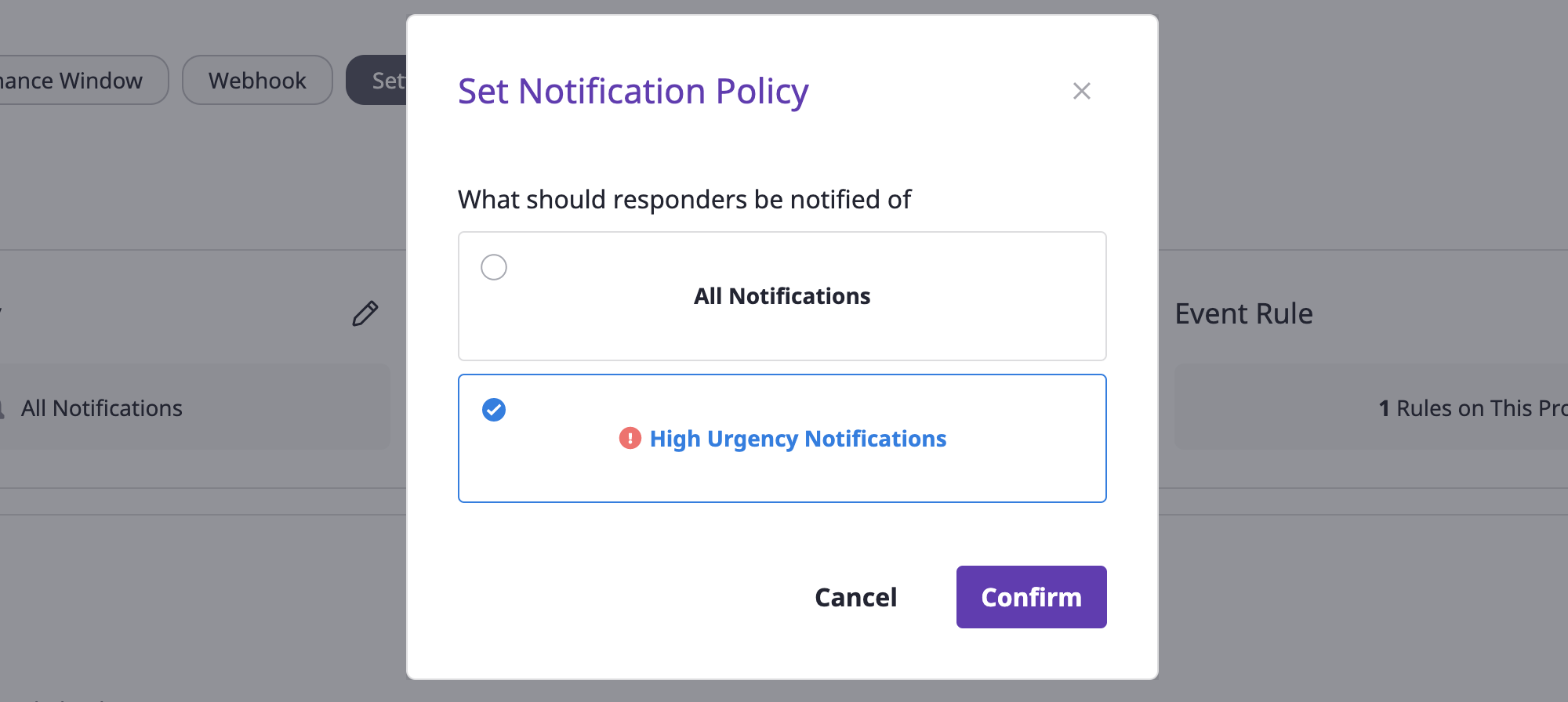
(4) Click the [OK] button to complete policy settings.
Auto recovery settings
The auto recovery feature automatically places the alert into a resolved state when the system crashes.
How auto recovery works
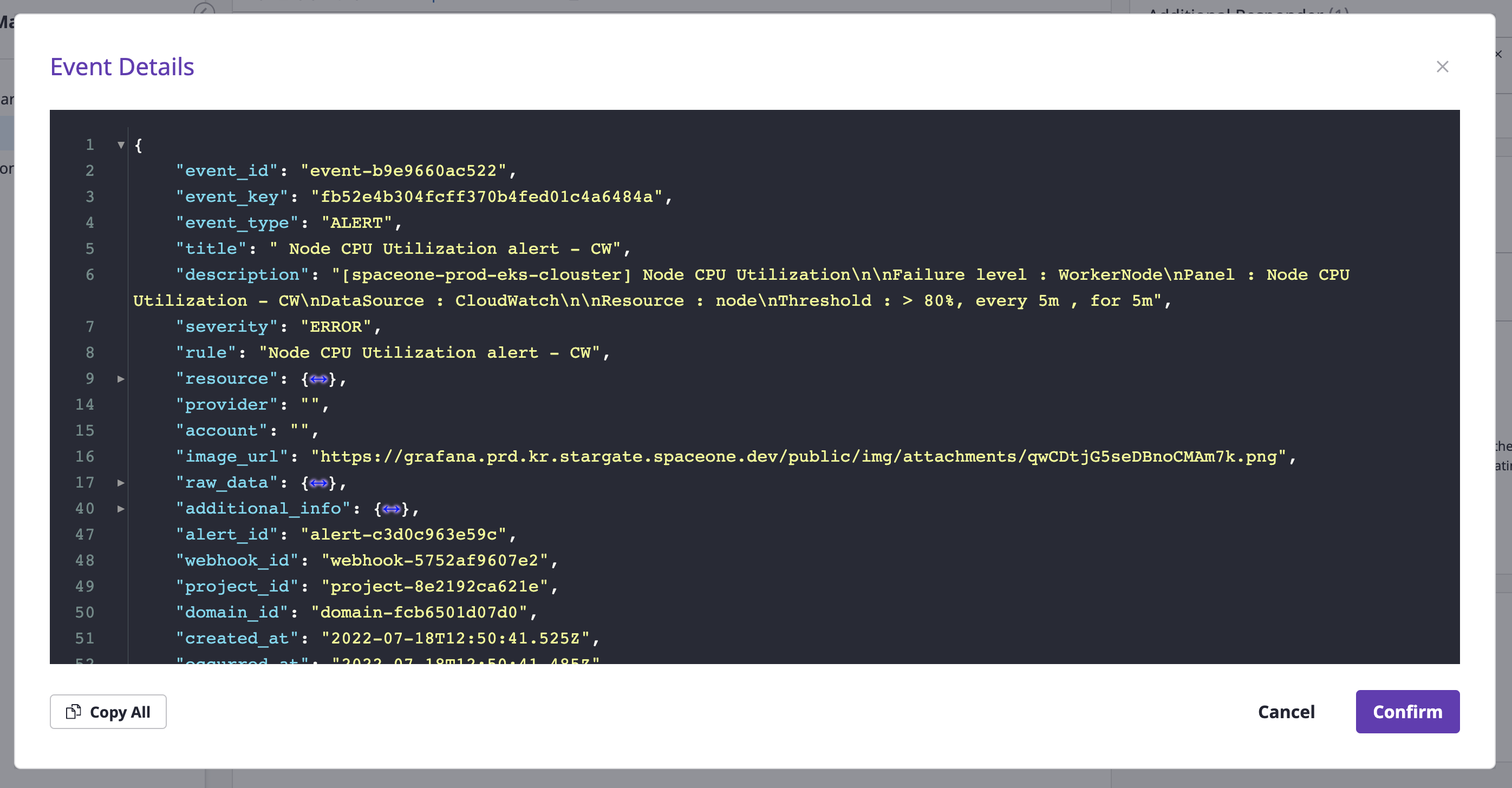
When an alert of the project for which the auto recovery is set receives an additional event, provided that the event type value of that event is recovery, the alert state is automatically switched to resolved.
(1) Inside the [Alerts] tab on the project detail page, move to the [Settings] tab.
(2) Click the [Edit] icon button in the auto recovery area.

(3) Select the desired auto recovery settings.
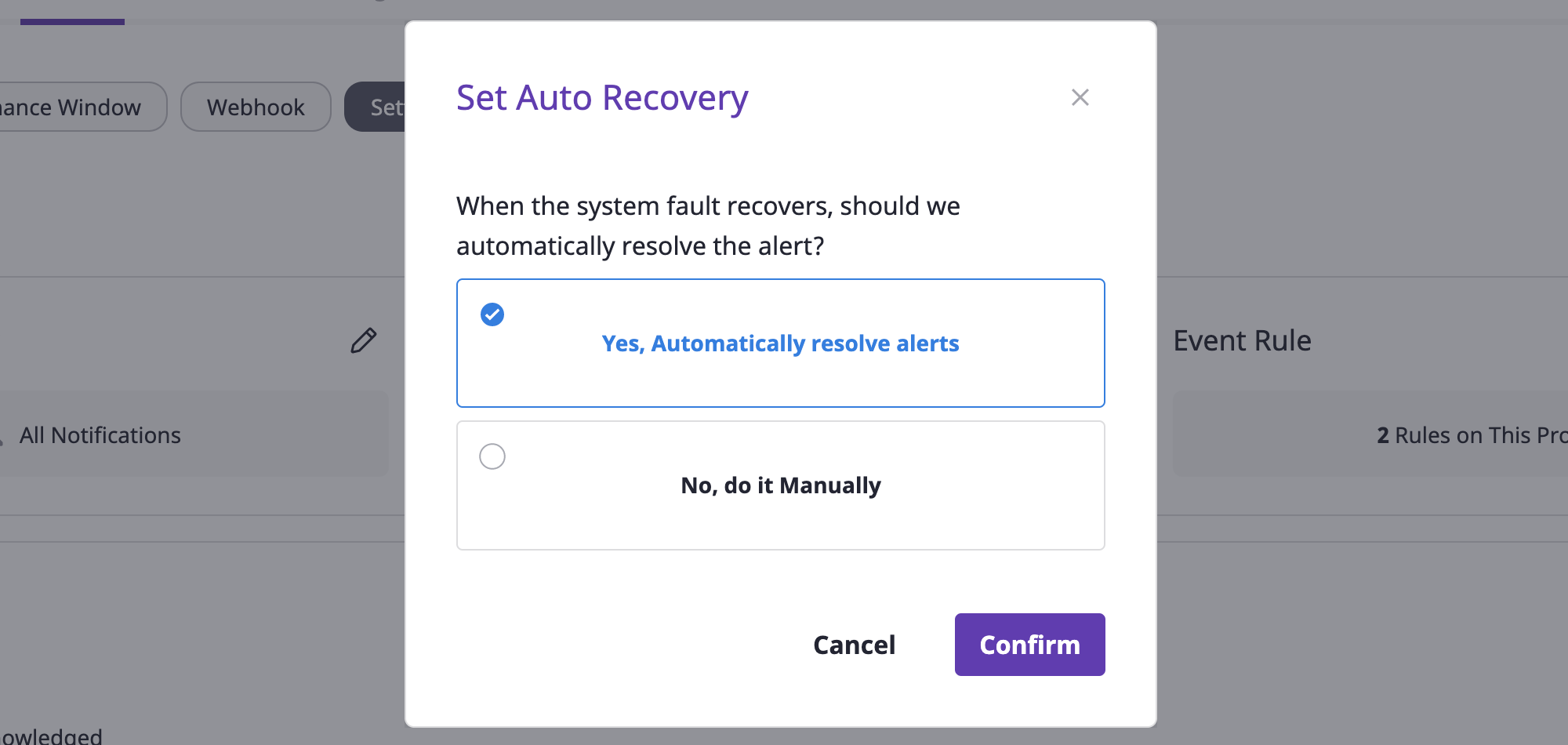
(4) Click the [OK] button to complete auto recovery settings
6.4 - Webhook
Creating a webhook
To receive event messages from an external monitoring service, you need to create a webhook.
Webhooks can be created on the project detail page.
(1) Go to the [Alerts] tab of the project detail page and select the [Webhook] tab.

(2) Click the [Add] button.
(3) Write a name in an [Add webhook] modal dialog and select the plug-in of the external monitoring service to be connected.

(4) Click the [OK] button to complete set up.
Connect external monitoring service
To use a webhook, you should connect to an external monitoring service through the URL of the created webhook.
For more on how to connect an external monitoring service, see here.
Getting a list of webhooks
Advanced search
You can enter a search word in the search bar to see a list of webhooks that match your criteria. For a detailed description on advanced search, see here.
Editing and deleting webhook
You can enable, disable, change, or delete a webhook viewed from the list.
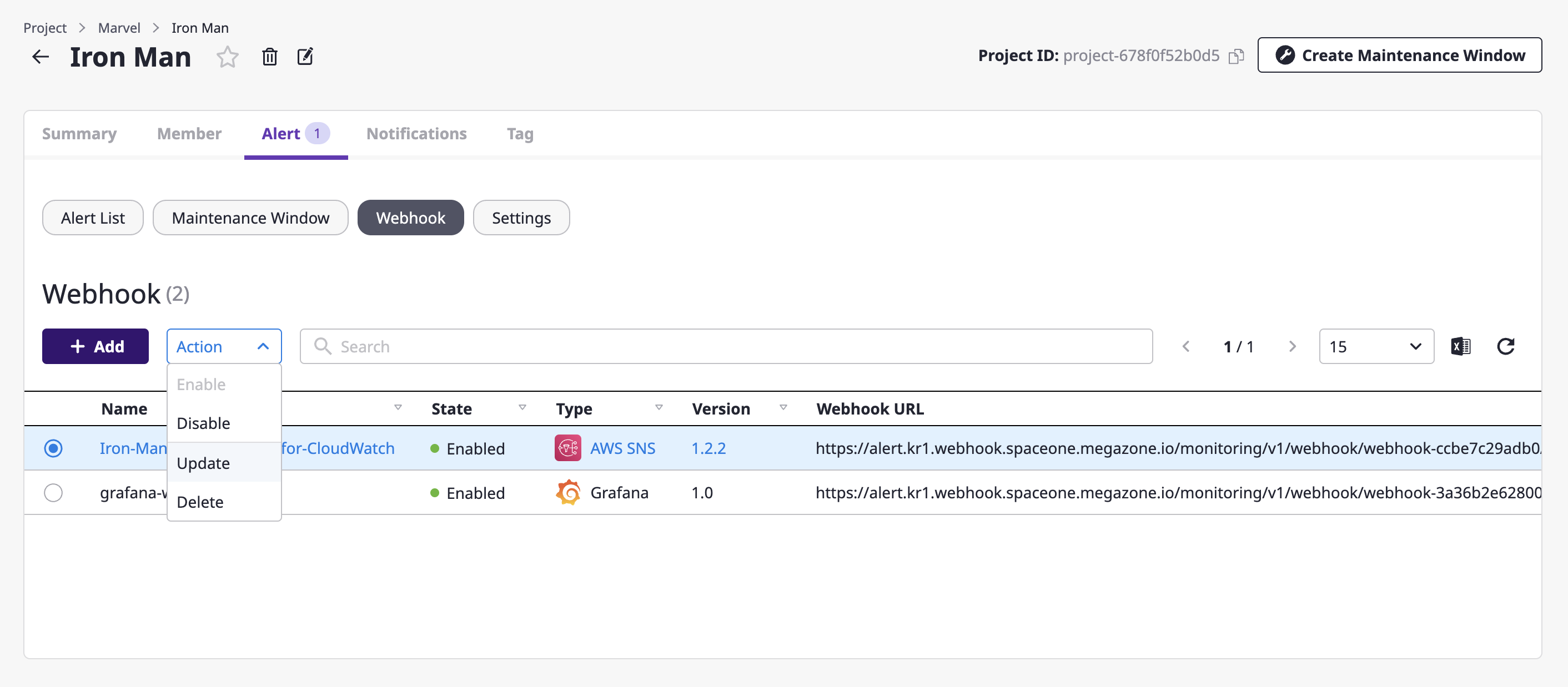
Enabling/disabling a webhook
If you enable a webhook, you can receive events from an external monitoring service connected to the webhook at Alerts.
On the contrary, if you disable a webhook, incoming events are ignored and no alerts are raised.
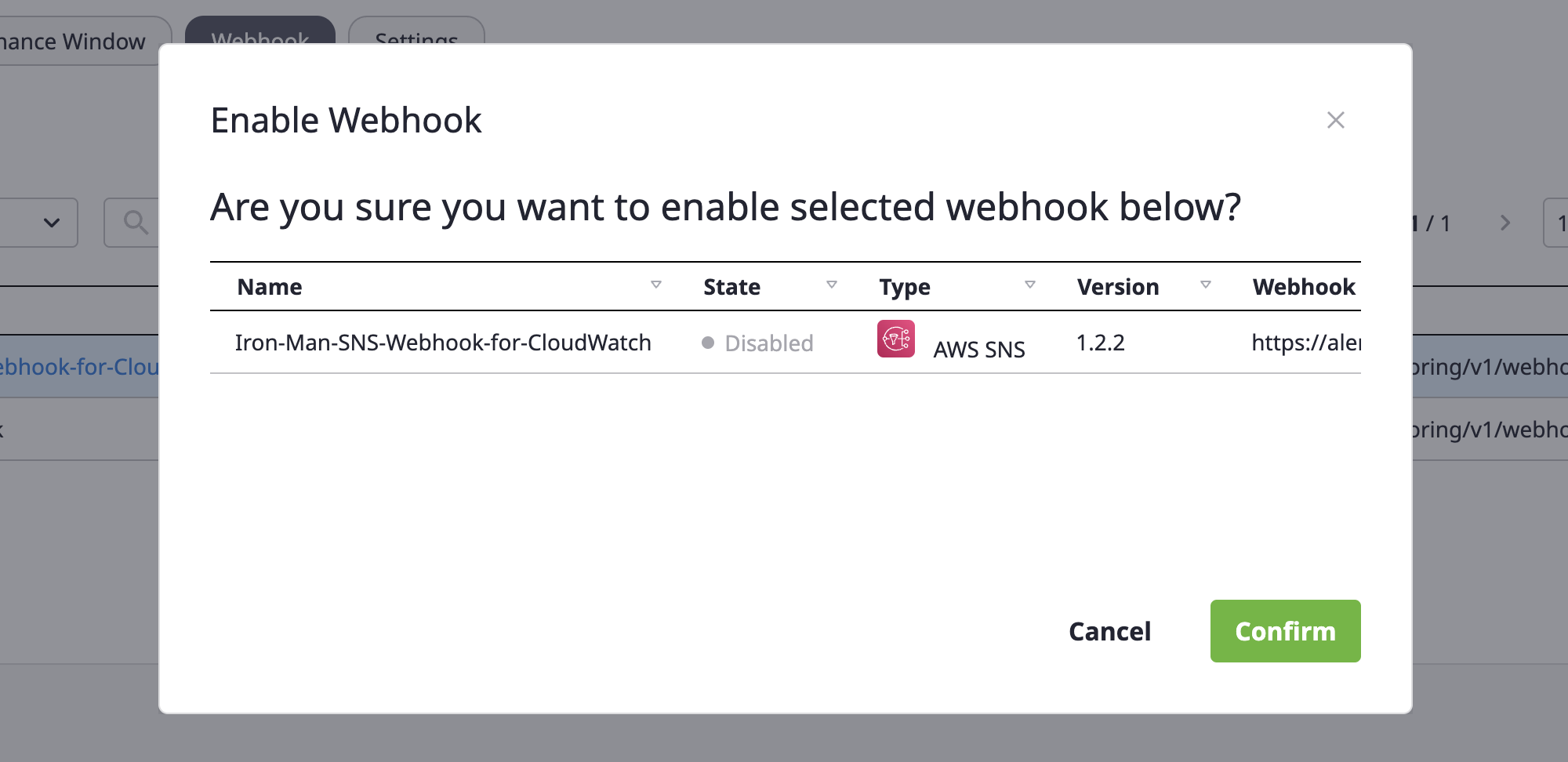
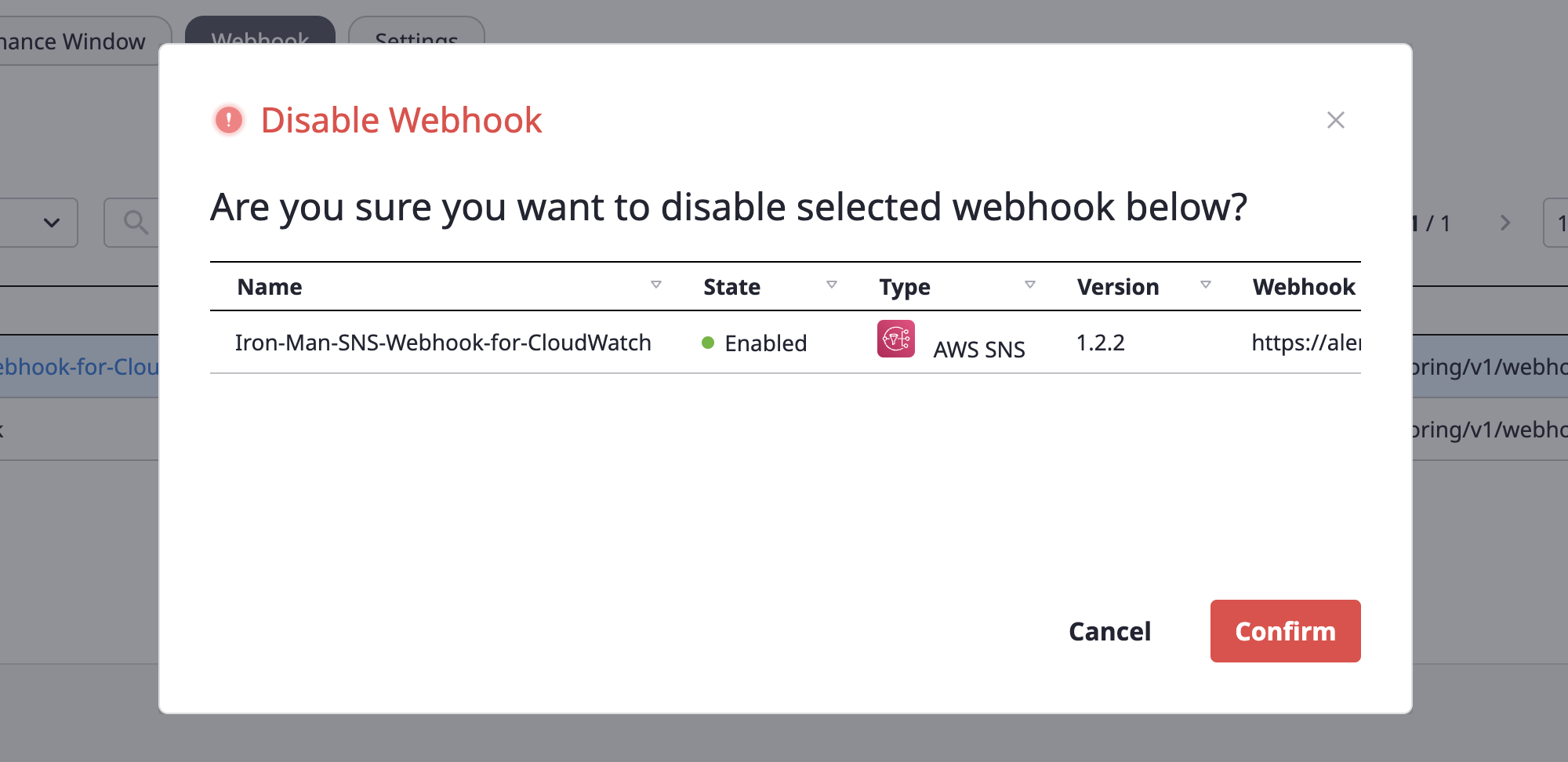
(1) Select the webhook to enable and choose the [Enable]/[Disable] menu from the [Action] dropdown.
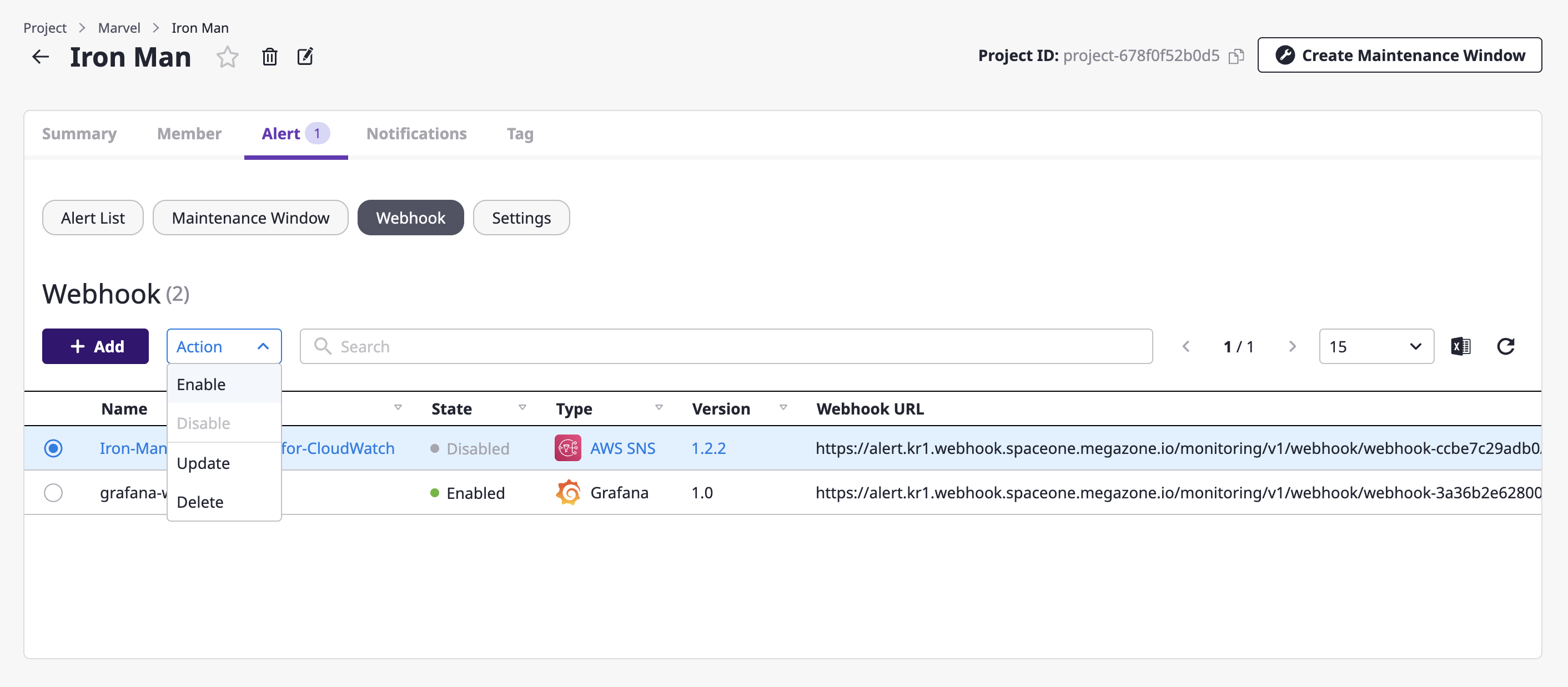
(2) Check the content in the [Enable/disable a webhook] modal dialog and click the [OK] button.
Renaming a webhook
(1) Select the webhook to change from the webhook list, and select the [Change] menu from the [Action] dropdown.
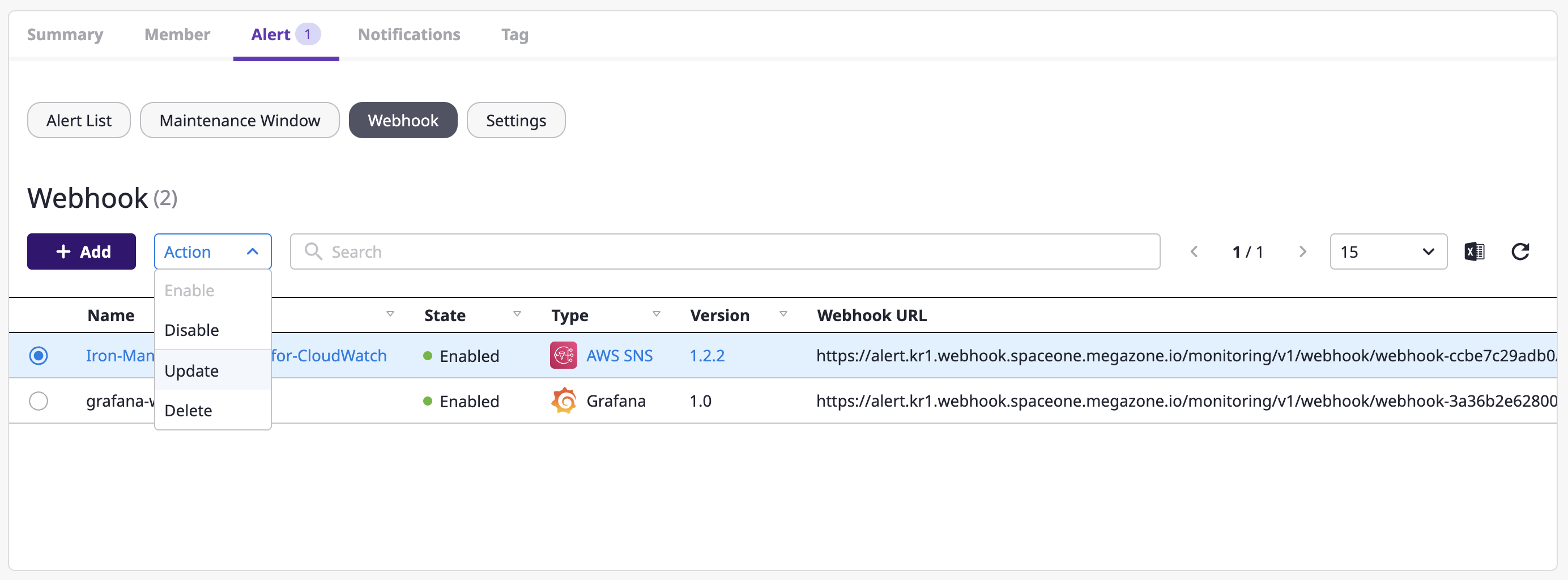
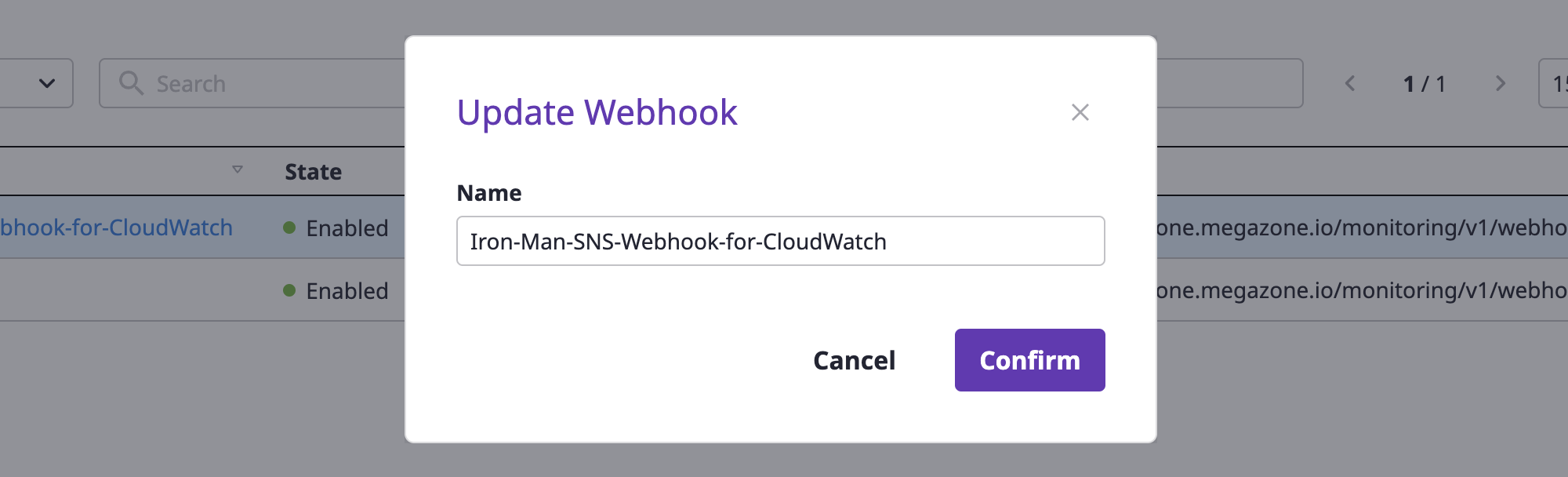
(2) Write a name to be changed and click the [OK] button to complete the change.
Deleting a webhook
(1) Select the webhook to delete from the webhook list, and choose the [Delete] menu from the [Action] dropdown.
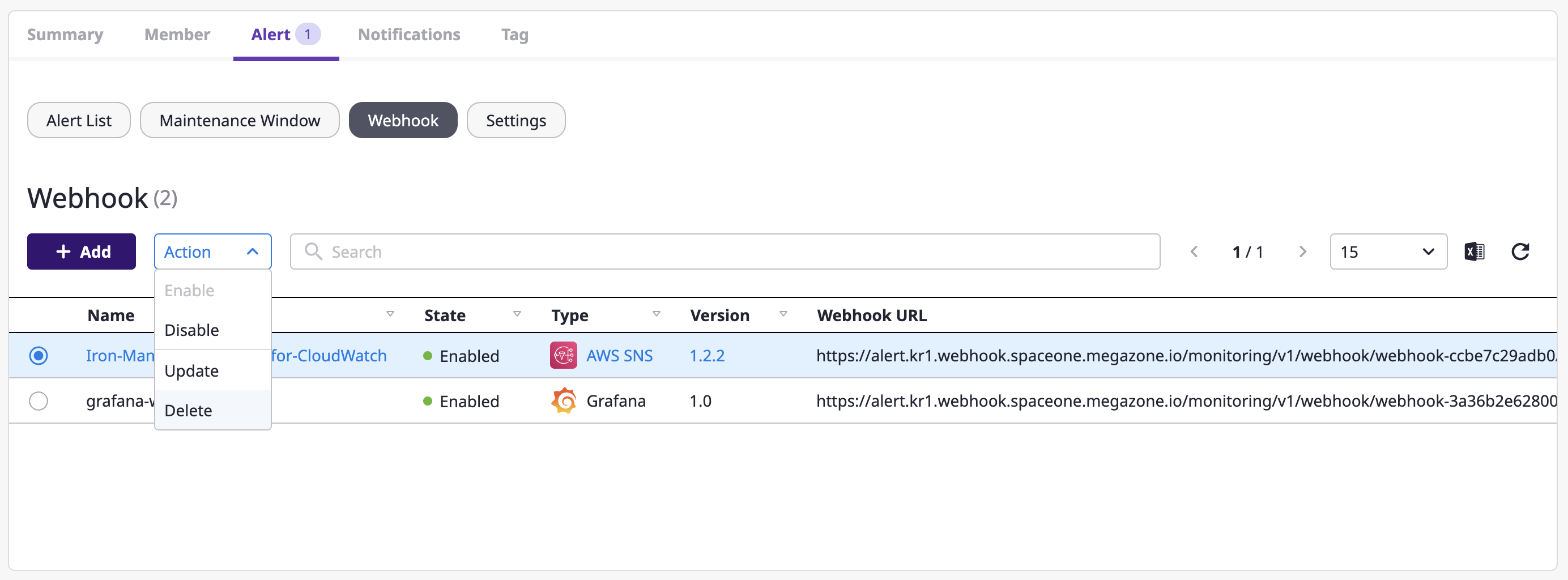
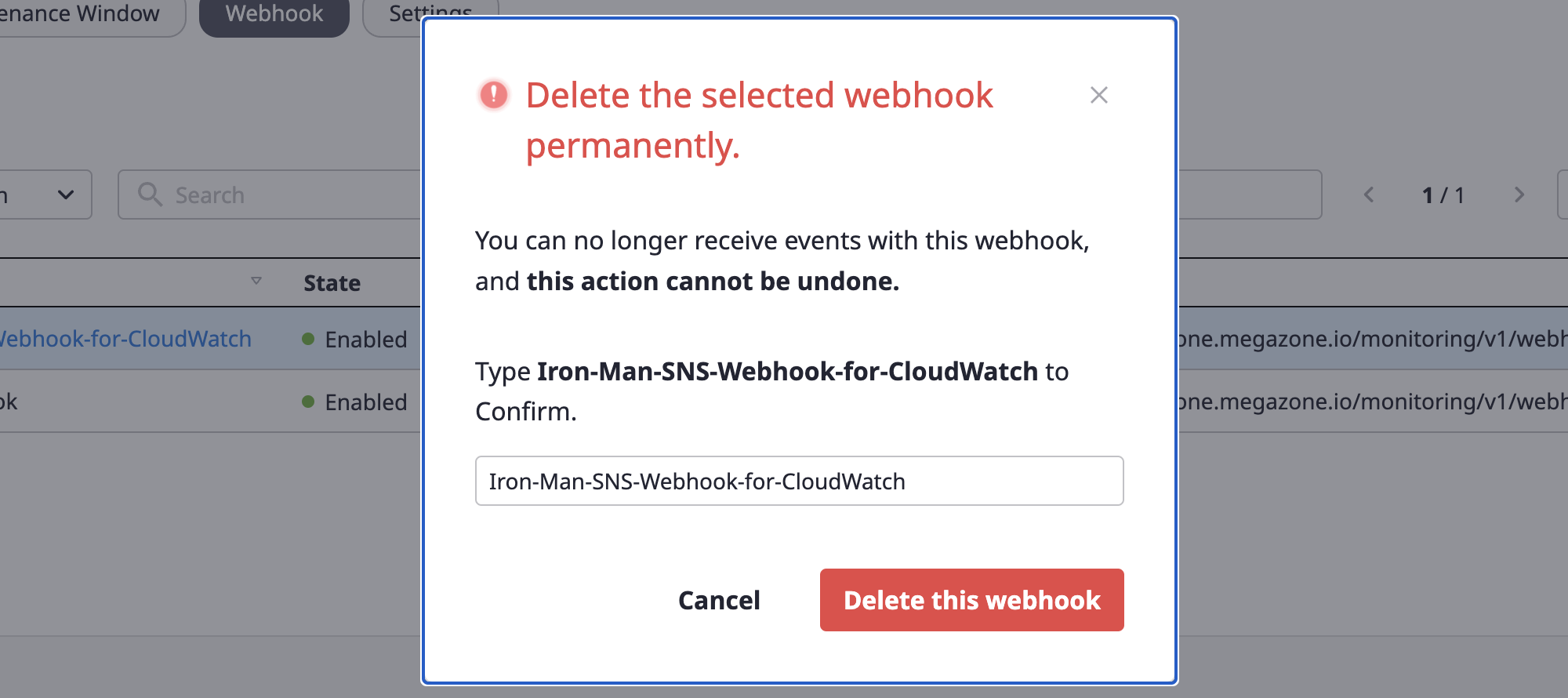
(2) After entering the accurate name of the selected webhook, click the [Delete] button to delete the webhook.
6.5 - Event rule
Event rules are project dependent and can be managed on the project detail page.
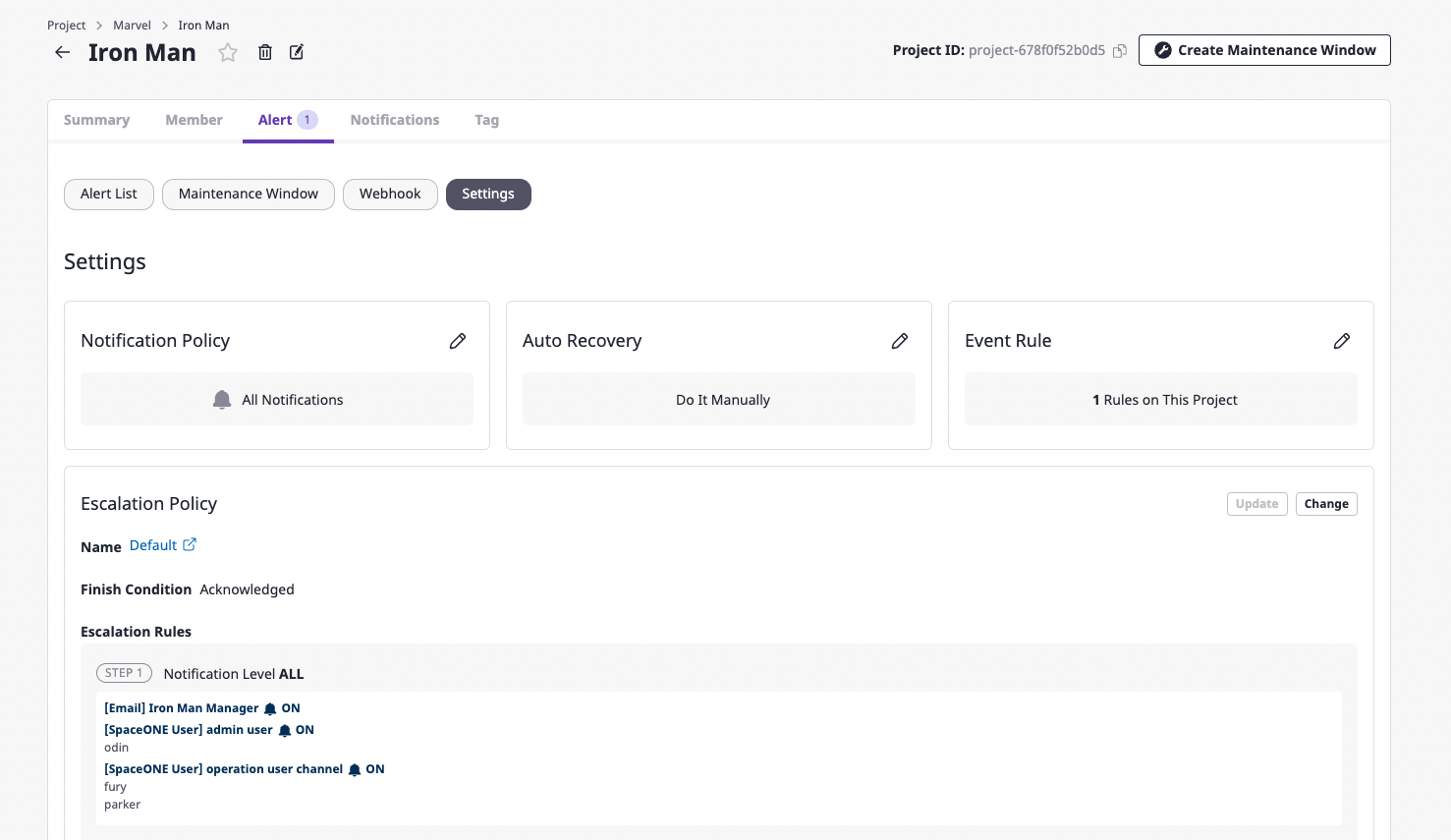
Create event rules
(1) In the [Settings] tab found in the [Alert] tab of the project detail page, click the [Edit] button of the event rule.
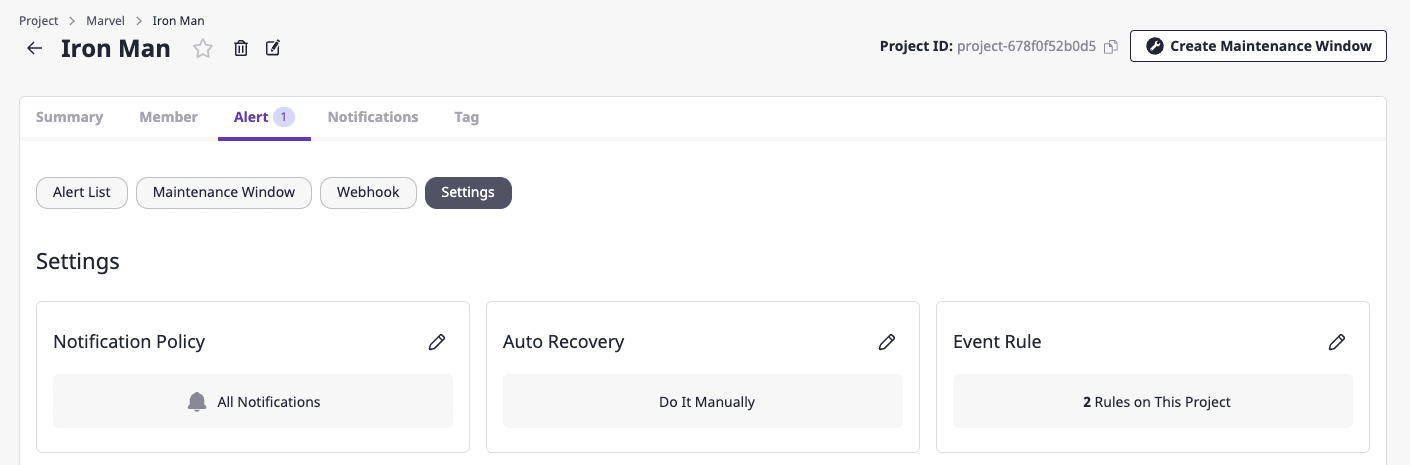
(2) Click the [Add event rule] button.
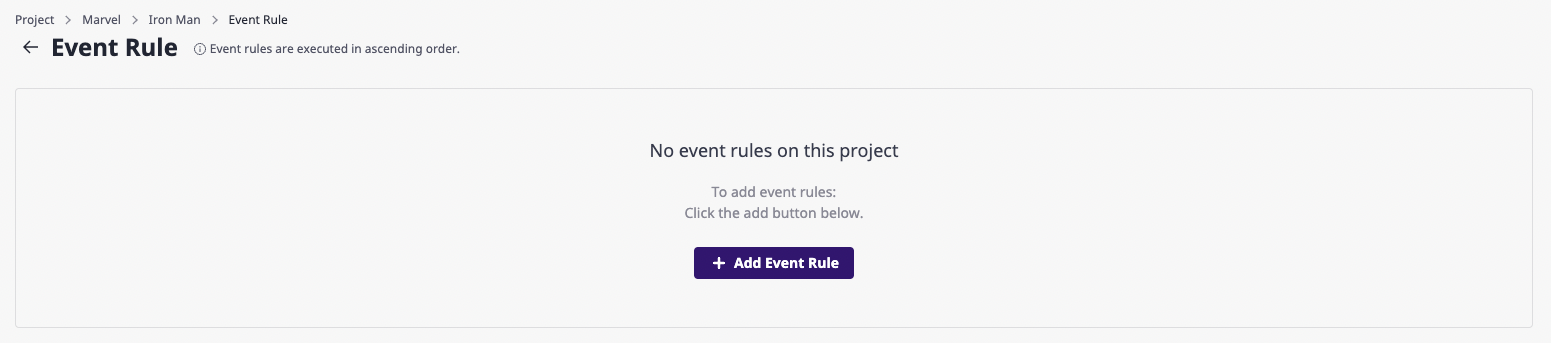
(3) Enter desired setting values on the event rule page.
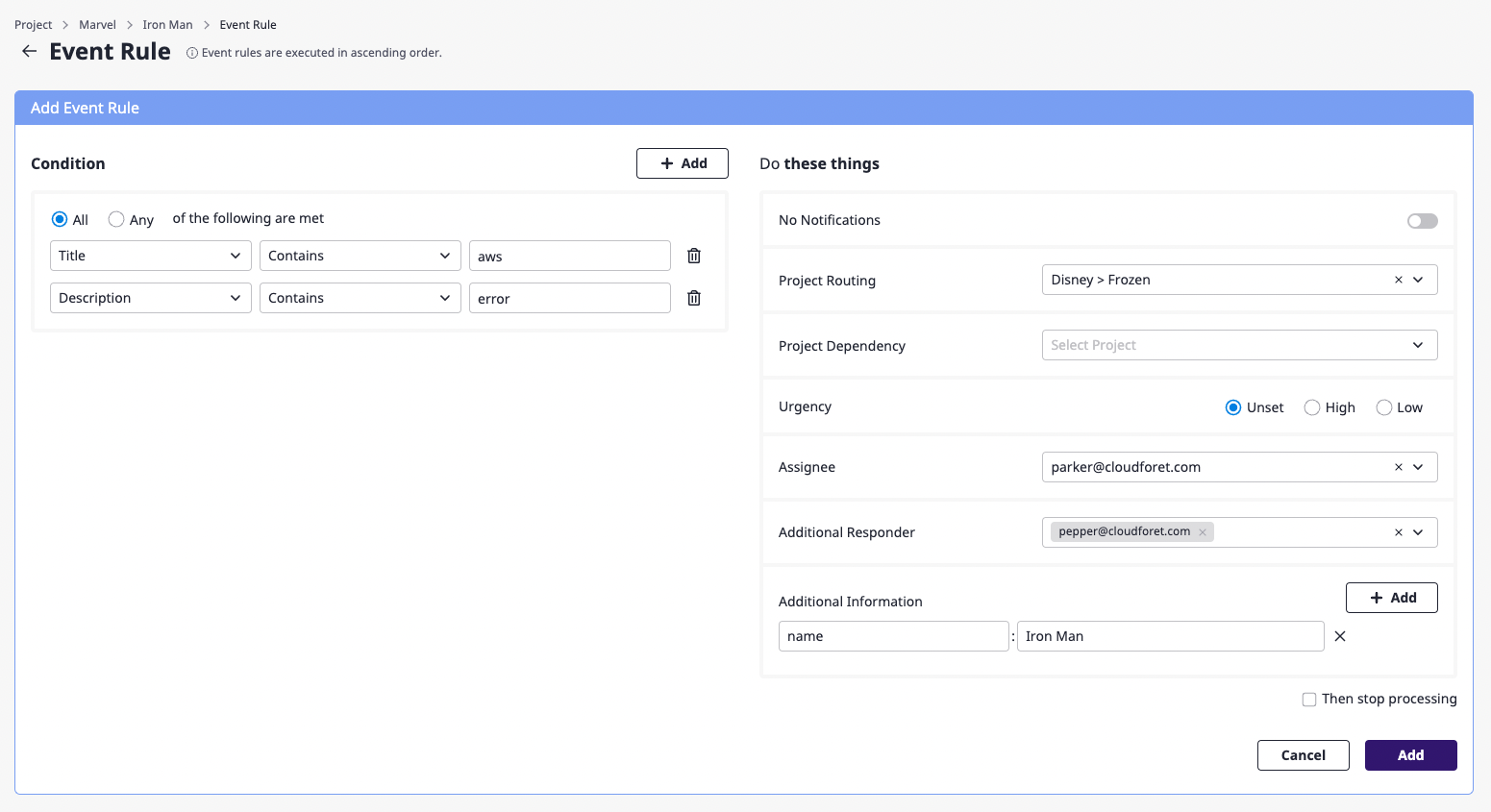
(3-1) Set the conditions to perform additional actions on the received alert.
At least one condition must be written, and you can add conditions by clicking the [Add] button on the right or delete them by clicking the [Delete] icon button.
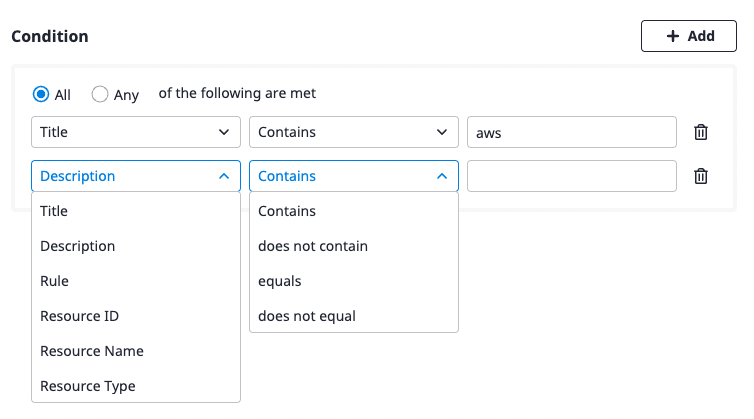
(3-2) Specify the action to be performed on the alert that meets the conditions defined above.
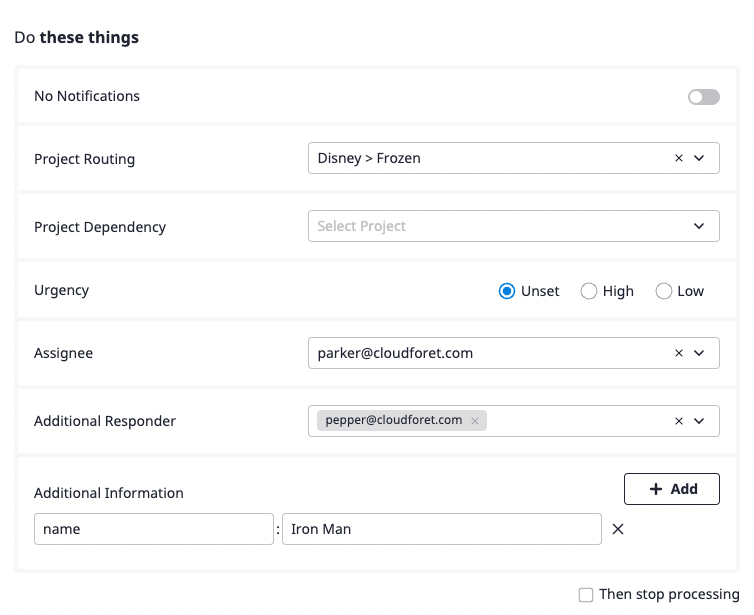
List of event rules settings
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Stop notifications | Suppress Notification for alerts for the corresponding conditions |
| Project routing | Alerts of the corresponding conditions are not received by current project but by project selected under project routing (no alert is created in the current project) |
| Project Dependencies | Alerts of the corresponding conditions can be viewed from the projects registered in project dependency. |
| Urgency | Automatically assign urgency to alerts of the corresponding conditionsHigh, low, or none-set can be specified and in case of none-set, rules are applied as follows• External monitoring alert: Urgency of an object • Direct creation: High (default) |
| Person in charge | Automatically assign a person in charge of the alert for the corresponding condition(s): |
| Additional recipients | When Notification occurs with the alert of the corresponding condition(s), send a notification to specified users together |
| Additional information | Automatically add information to alerts for the corresponding conditions |
| Stop executing further actions | If the event rule is executed, subsequent event rules are ignored (See Ways and order of event rules action) |
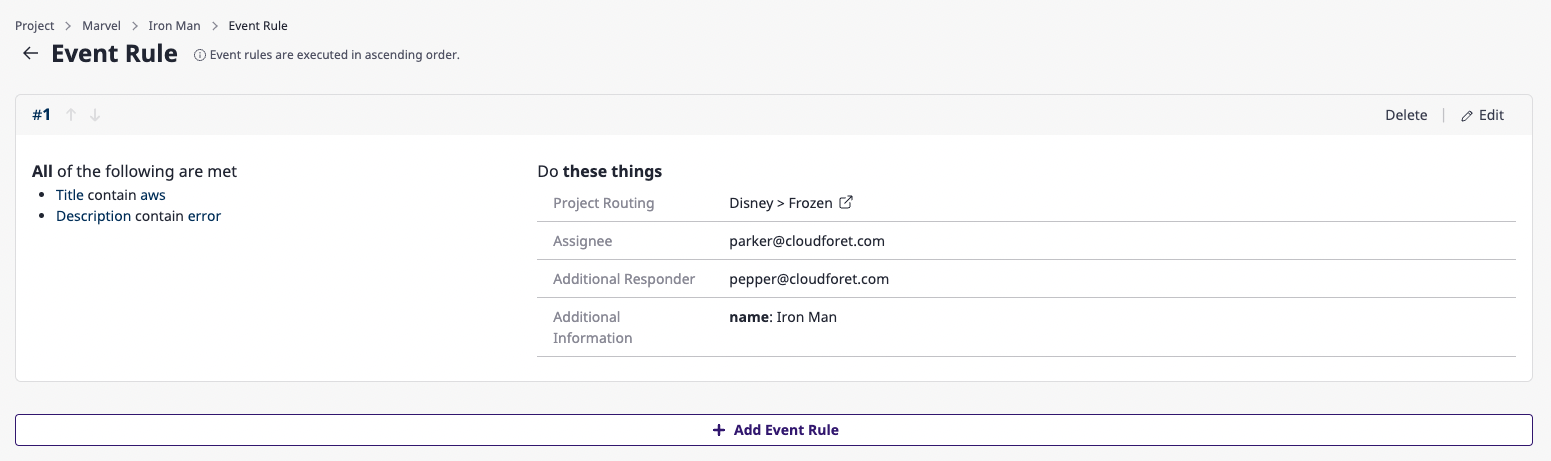
Edit event rules
(1) Click the [Edit] button on the event rules page.
(2) Enter the setting values you wantfor the event rule.
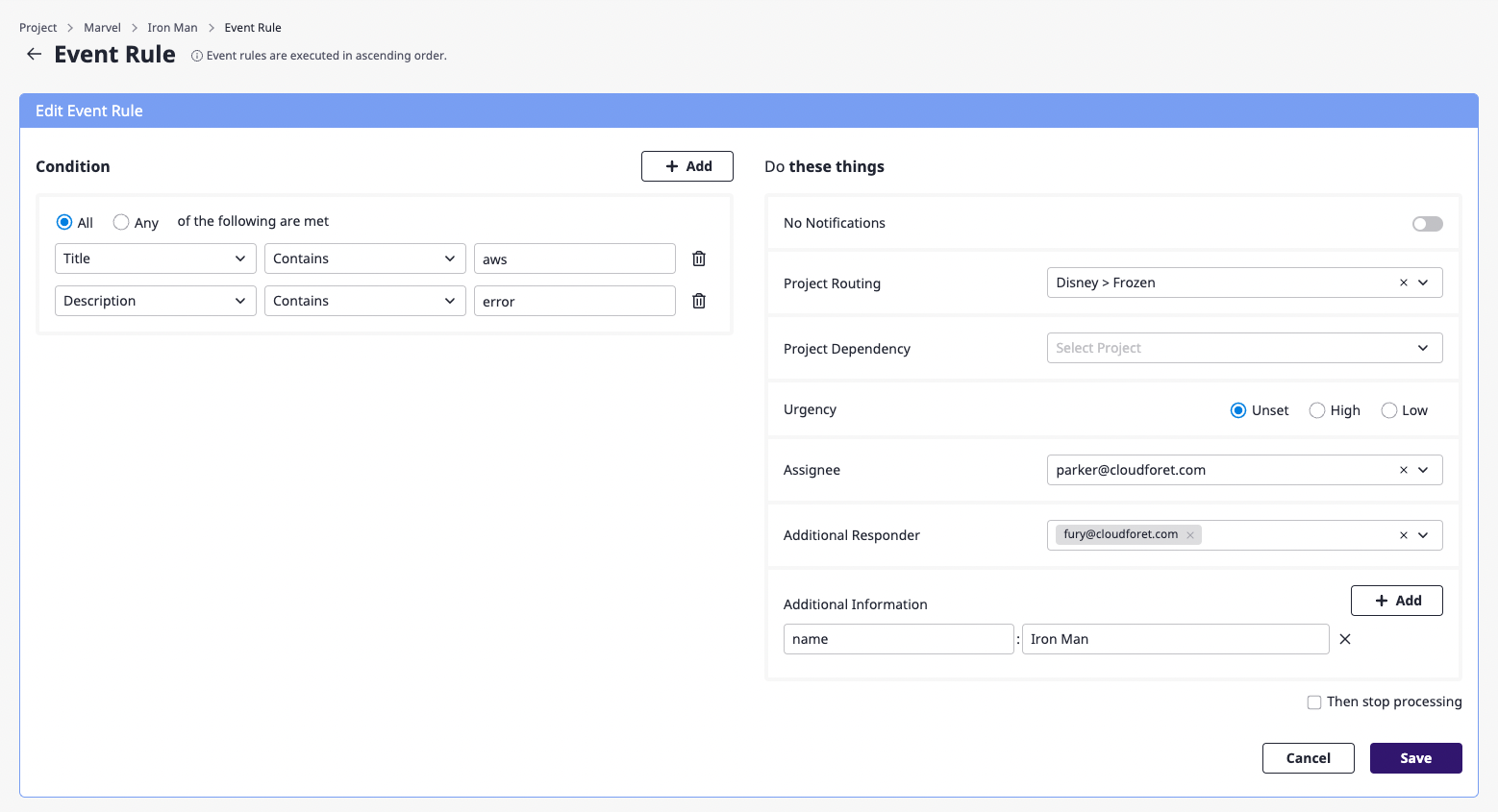
(3) Click the [Save] button to complete editing the event rules.
Delete event rules
(1) Click the [Delete] button on the event rules page.
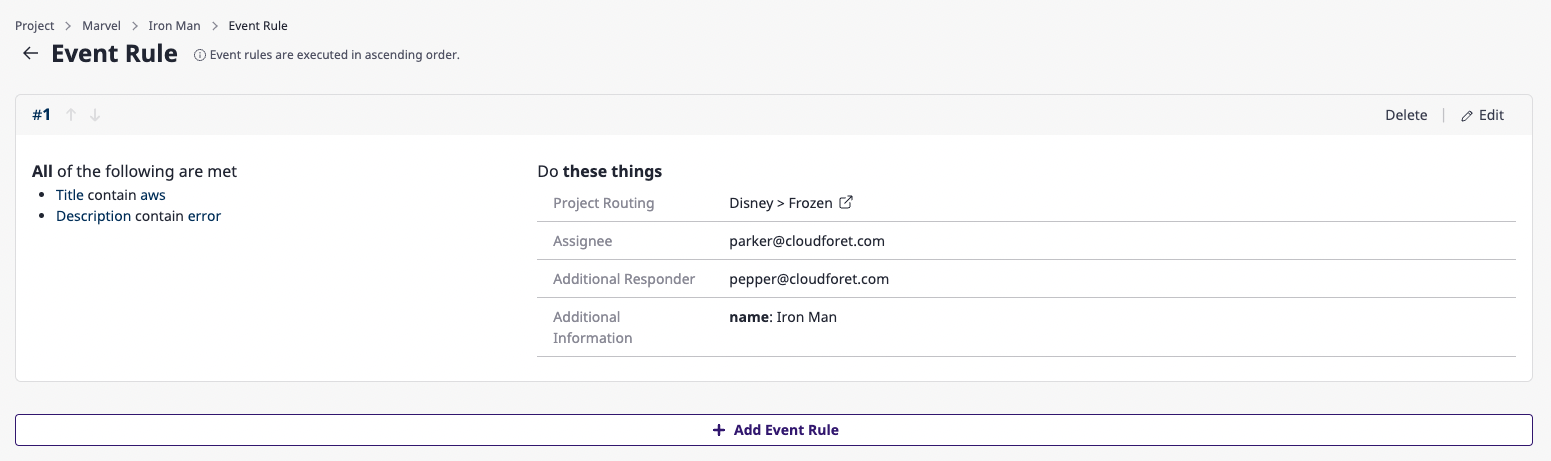
(2) In the [Delete event rule] modal dialog, click the [OK] button to complete the deletion.
Ways and order of event rules action
Event rules set by a user for when an alert occurs will be executed sequentially.
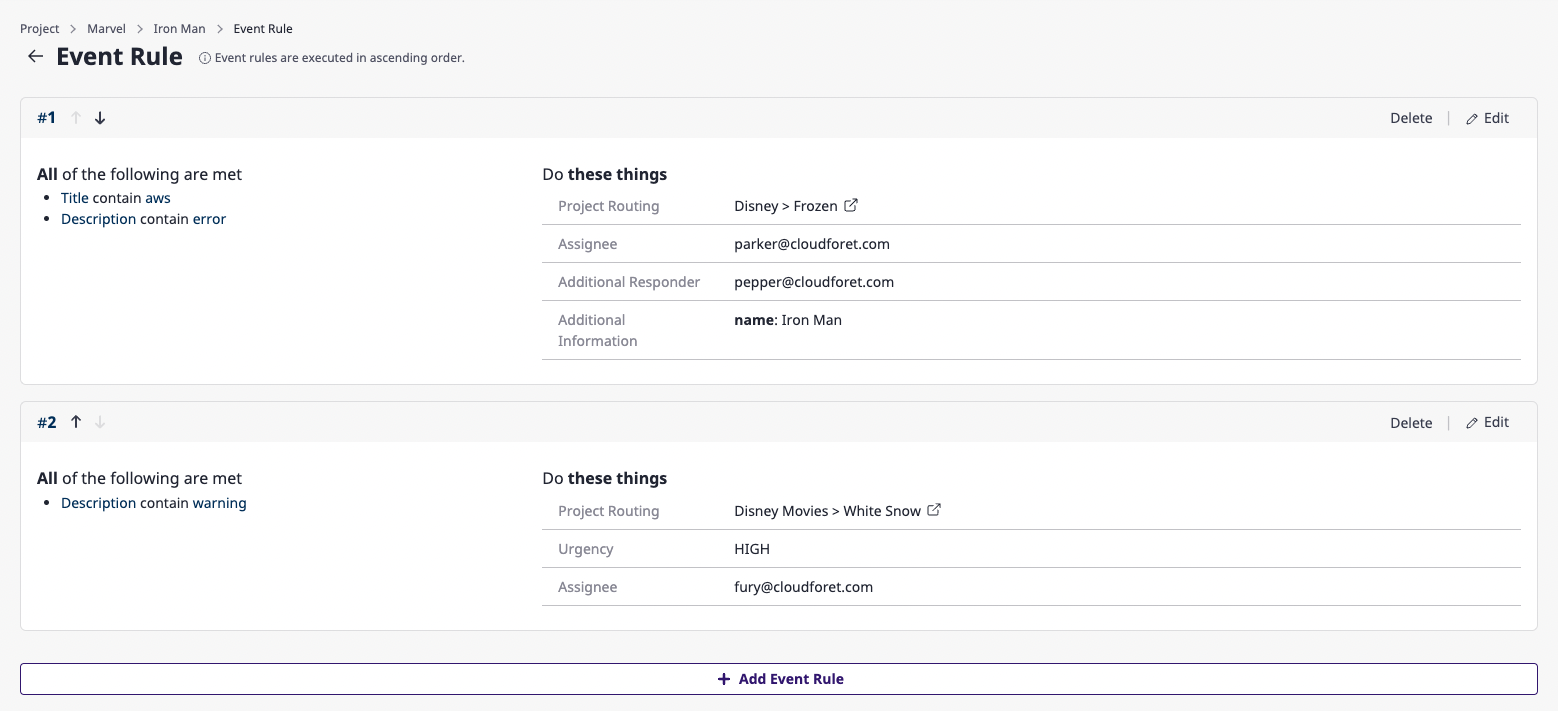
If event rules are created as in the example above, they are executed in the order of [#1], [#2], etc., starting from the highest event rule.
You can easily change the order of the event rules by clicking the [↑] and the [↓] buttons.
6.6 - Maintenance window
Setting a Maintenance window allows you to block sending notifications during that period.
The maintenance window is project dependent and can be managed on the project detail page.
Create maintenance window
(1) Click the [Create maintenance window] button at the top right of the project detail page.
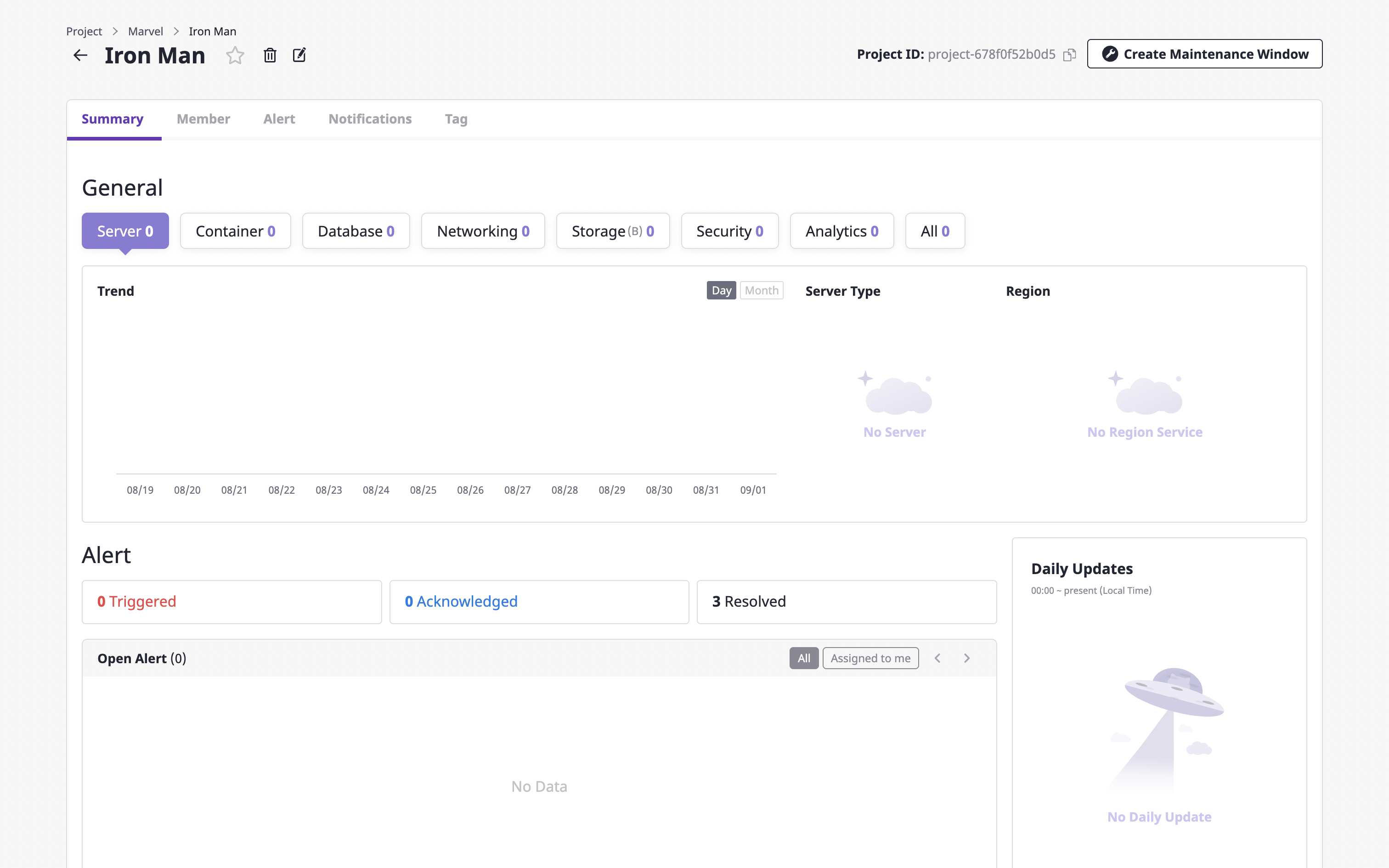
(2) Enter a [Title] for a maintenance window and set the schedule to limit the occurrence of the alert.
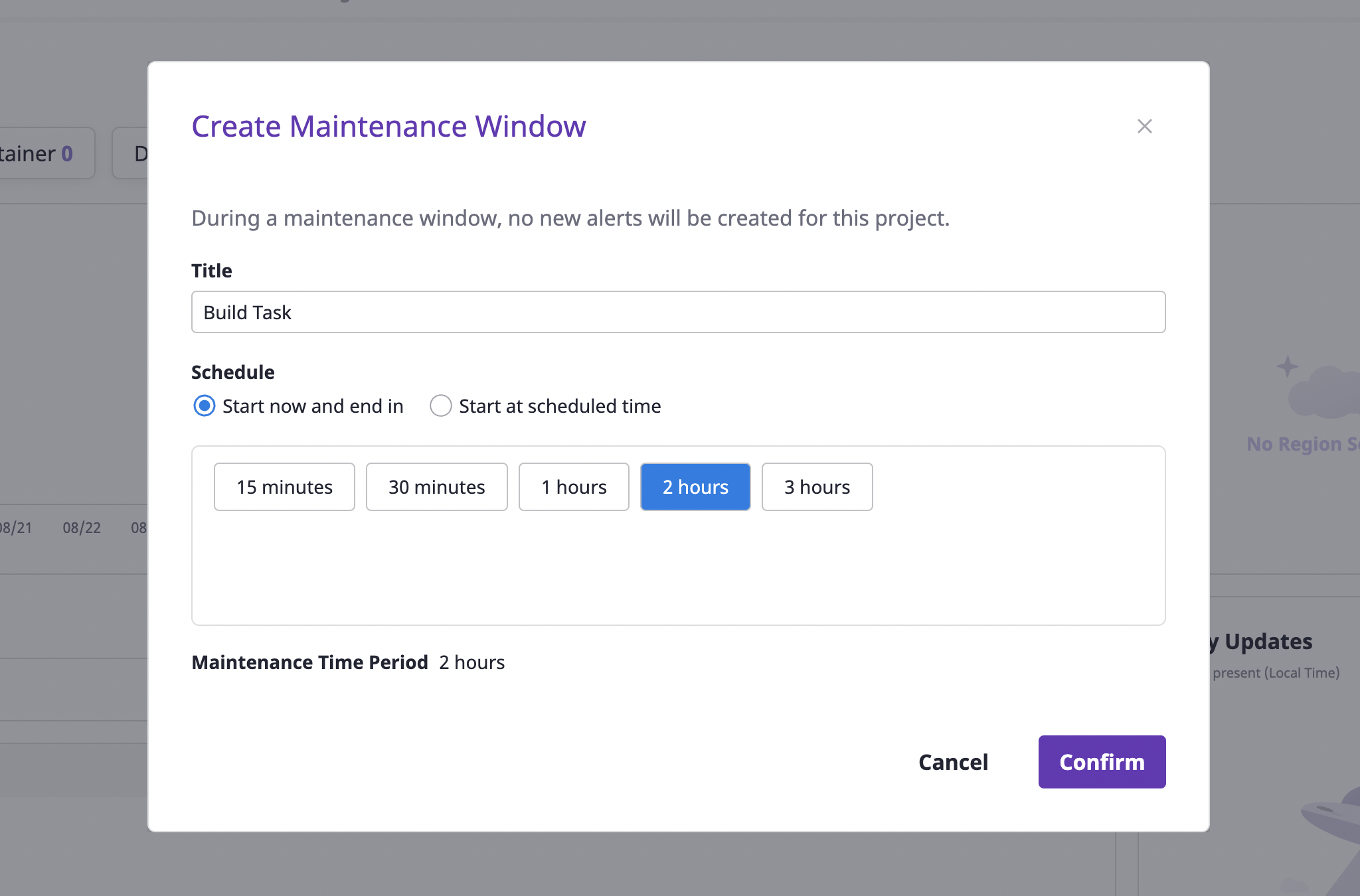
When you set the schedule, you can start right away or have it start at a scheduled time.
Select the [Start and end now] option if you want to start immediately, or the [Start at scheduled time] option if you want to schedule an upcoming task
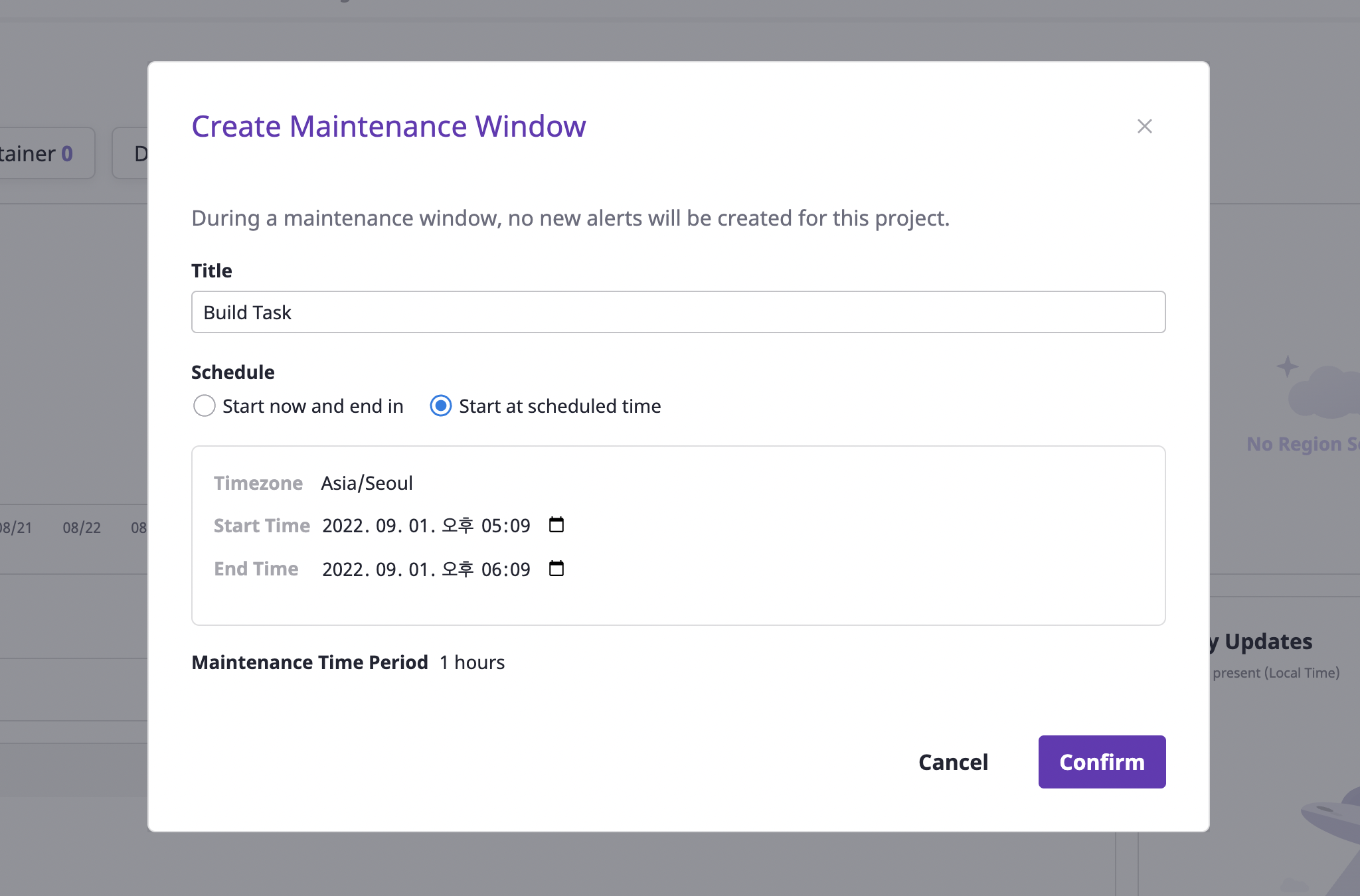
(3) Click the [OK] button to complete the creation.
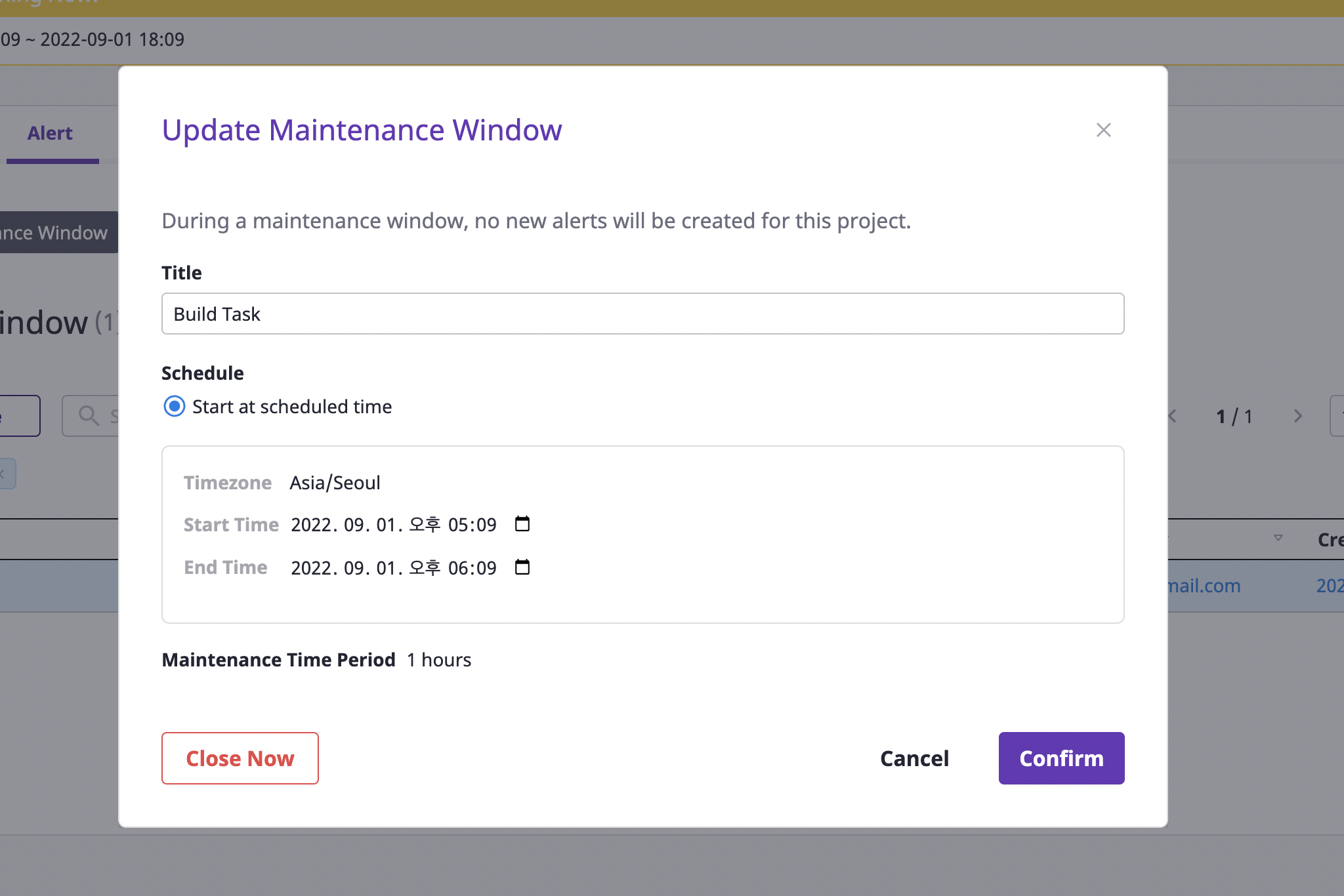
Edit maintenance window
You can only edit maintenance windows that have not yet ended.
(1) Select the [Maintenance window] tab under the [Alerts] tab on the project detail page.
(2) Select the object you want to edit and click the [Edit] button.
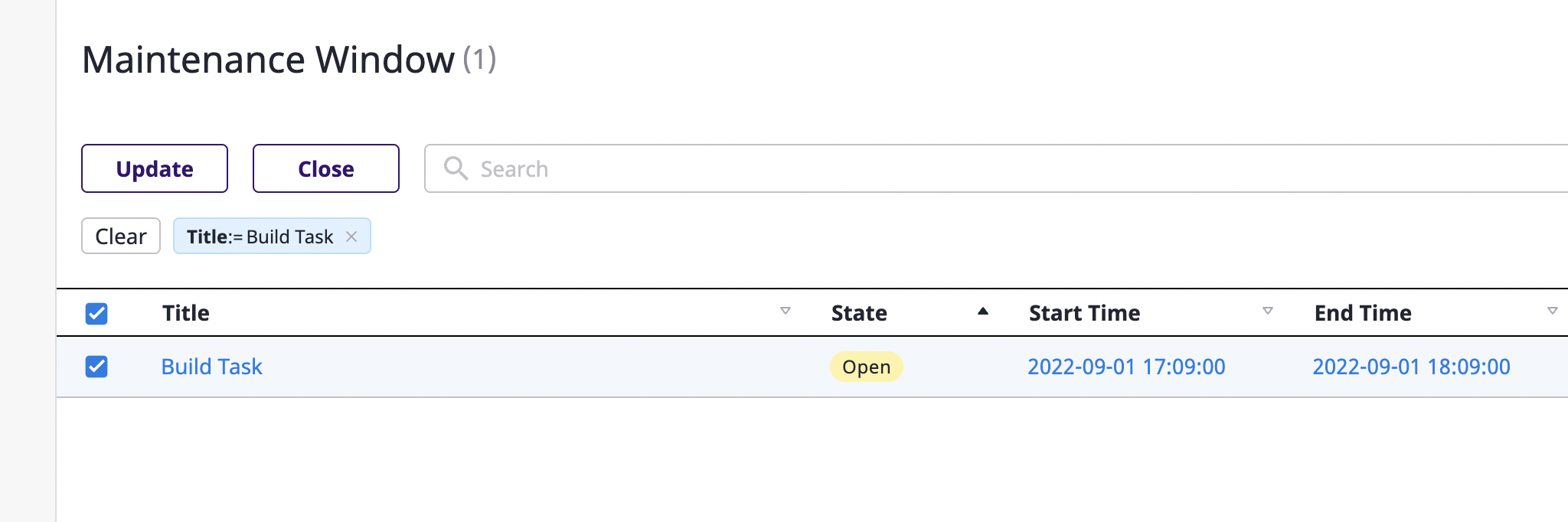
(3) After changing the desired items, click the [OK] button to complete.
Closing maintenance window
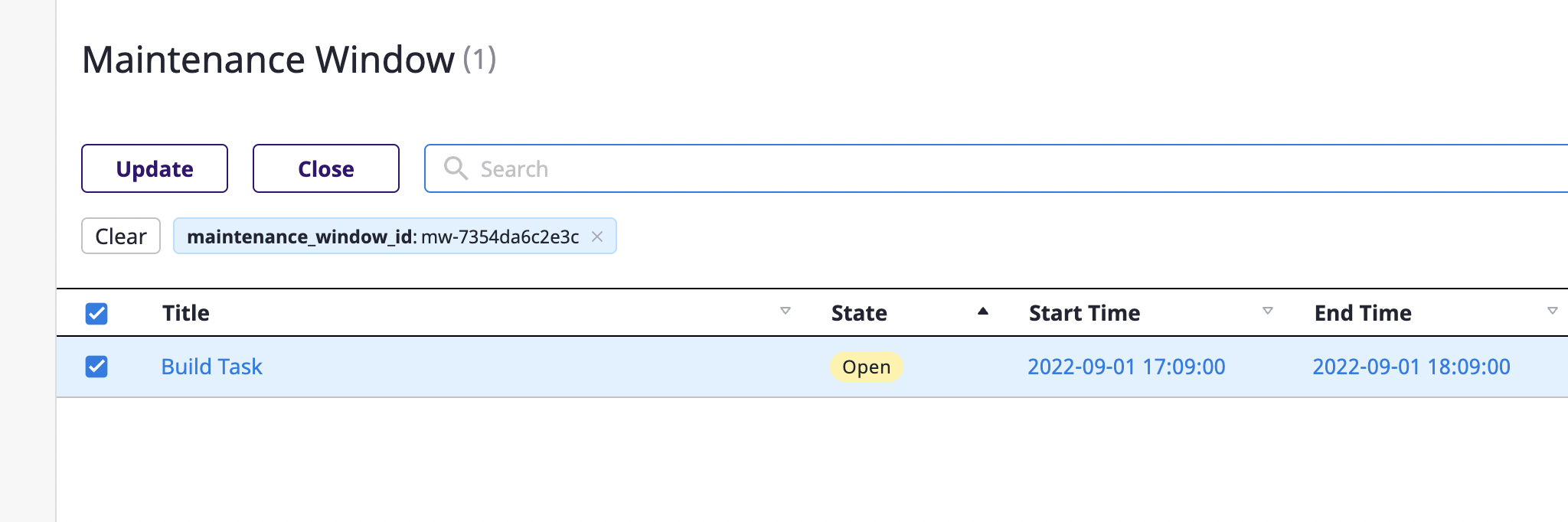
(1) Select the [Maintenance window] tab under the [Alerts] tab on the project detail page.
(2) Select the object to be edited and click the [Exit] button to exit.
6.7 - Notification
Notifications are a means to deliver alerts.
In the Notifications channel page, you can set up how and when to send alerts to which users.
The notifications channel is project dependent and can be managed on the project detail page.
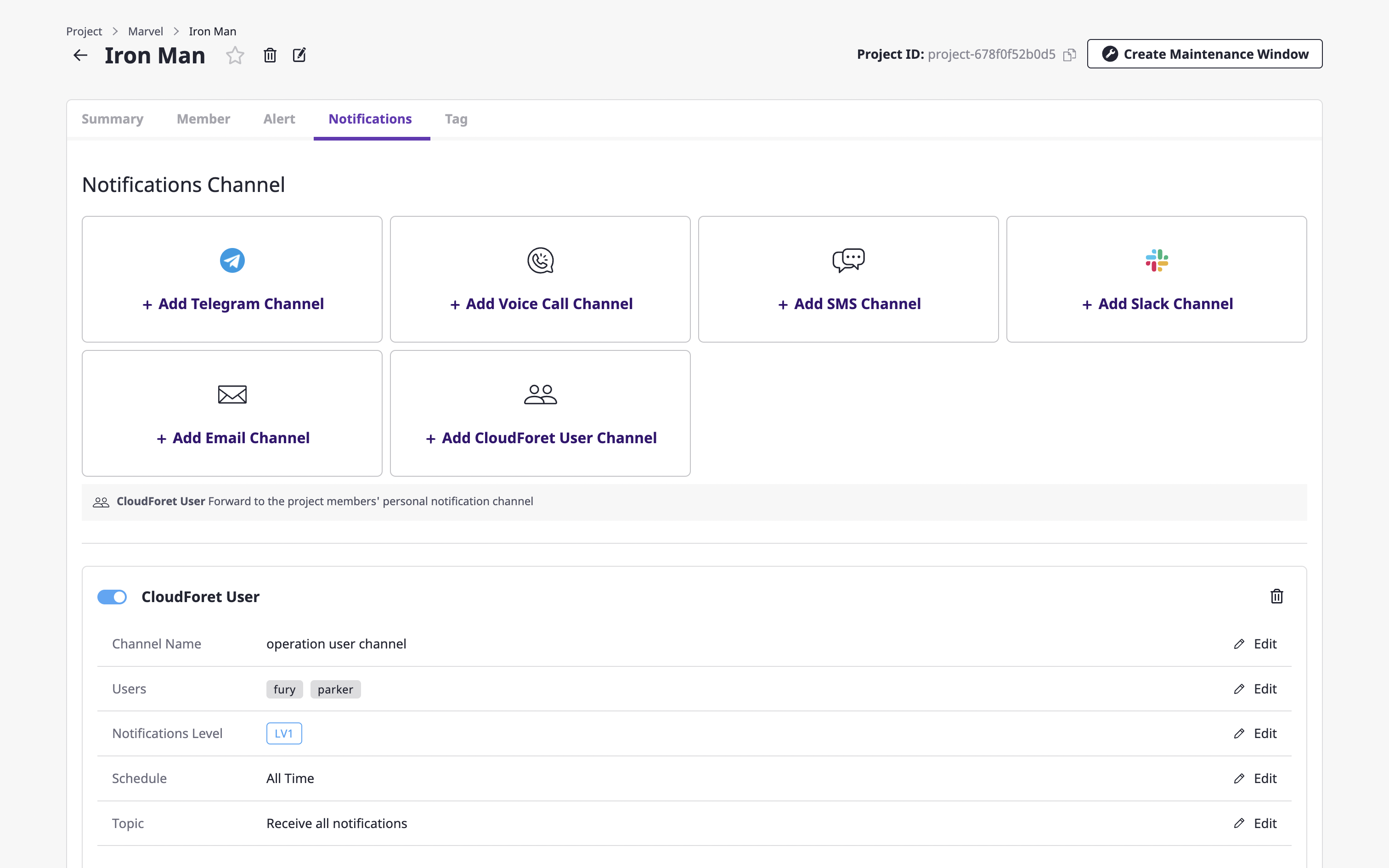
Creating a notifications channel
In the [Notification] tab of the project detail page, you can decide whether or not to Create a notifications channel and enable it.
Notifications channel is a unit that expresses the systematic recipient area, including the method and level of notifications transmission. It helps to transmit alerts according to the level set in the escalation rule.
(1) On the project detail page, select the [Notification] tab and click the [Add channel] button of the desired notifications channel.
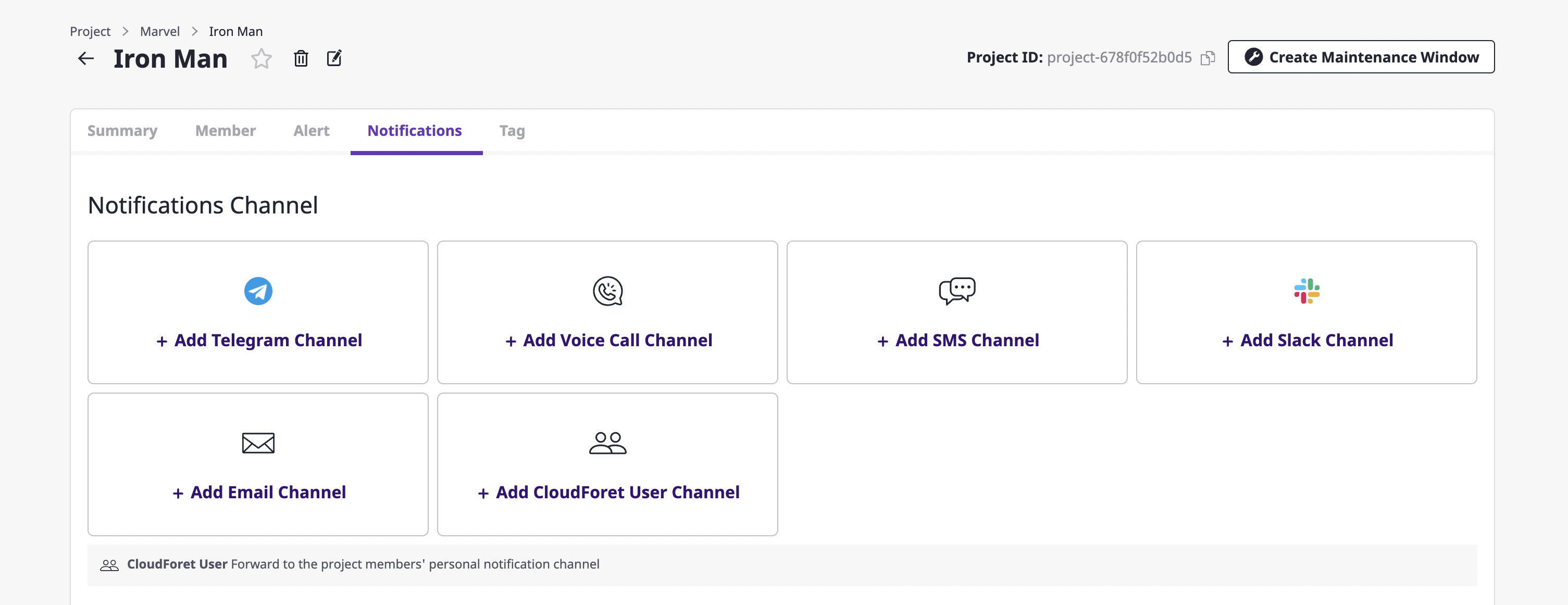
(2) On the notification creation page, enter the settings to create a notifications channel.
(2-1) Enter the basic information about the notifications channel you want to create, such as the required channel name and notification level. The [Channel name] and [Notification level] comprise the basic setting fields, and afterward, the remaining fields receive different information per channel.
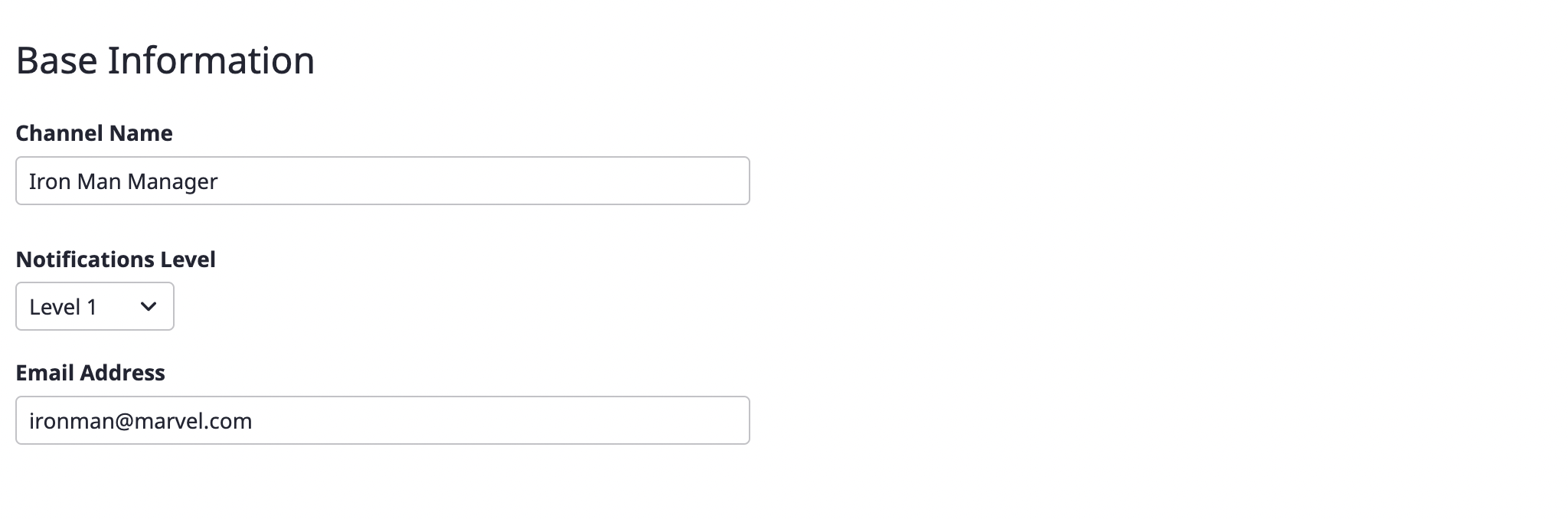
Notification level
Notification levels correlate to the escalation policy (/ko/docs/guides/alert-manager/escalation-policy/) that defines rules for spreading alerts.
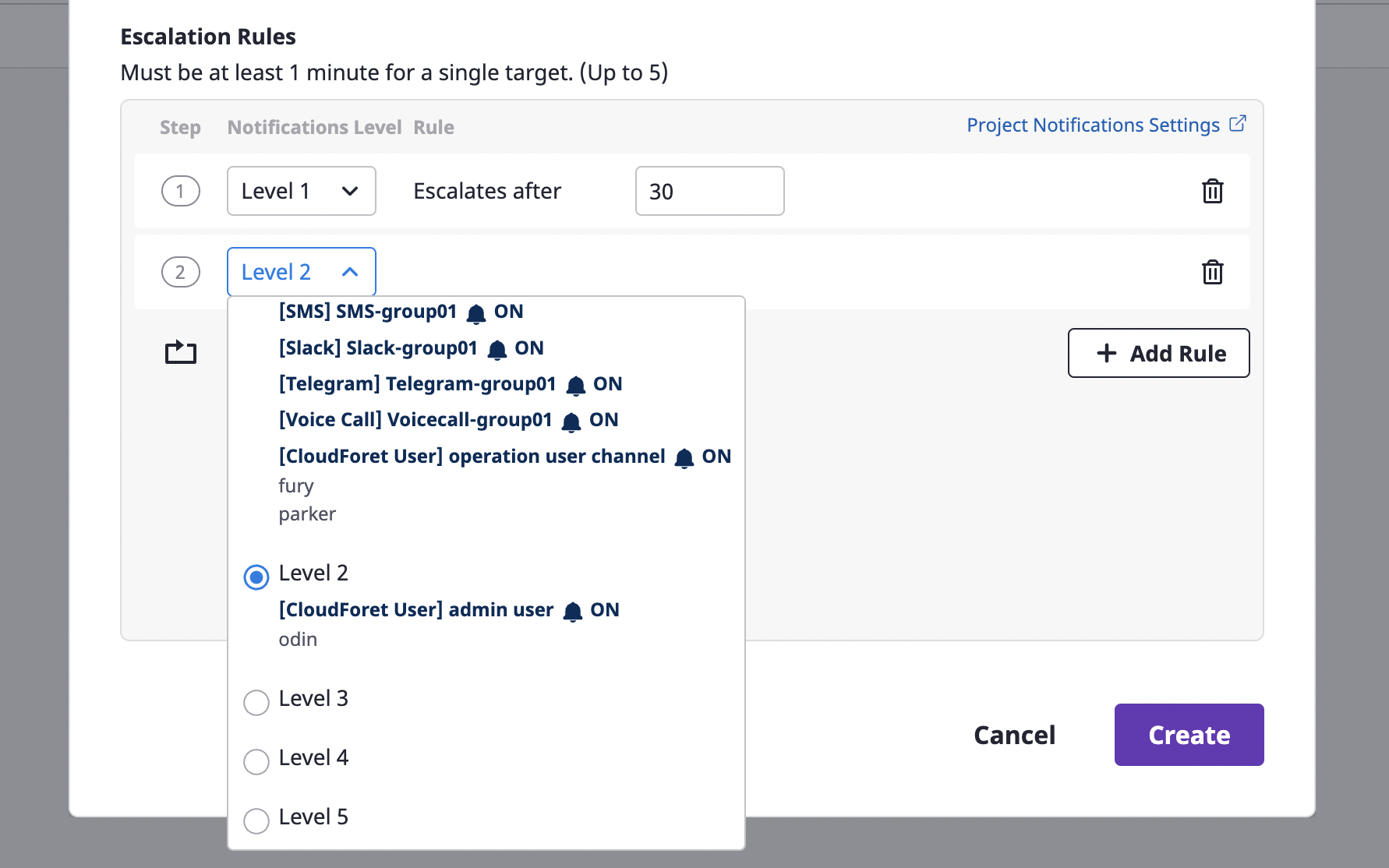
Based on the notification level specified in the escalation policy, the alert is spread to the notifications channel belonging to that level.
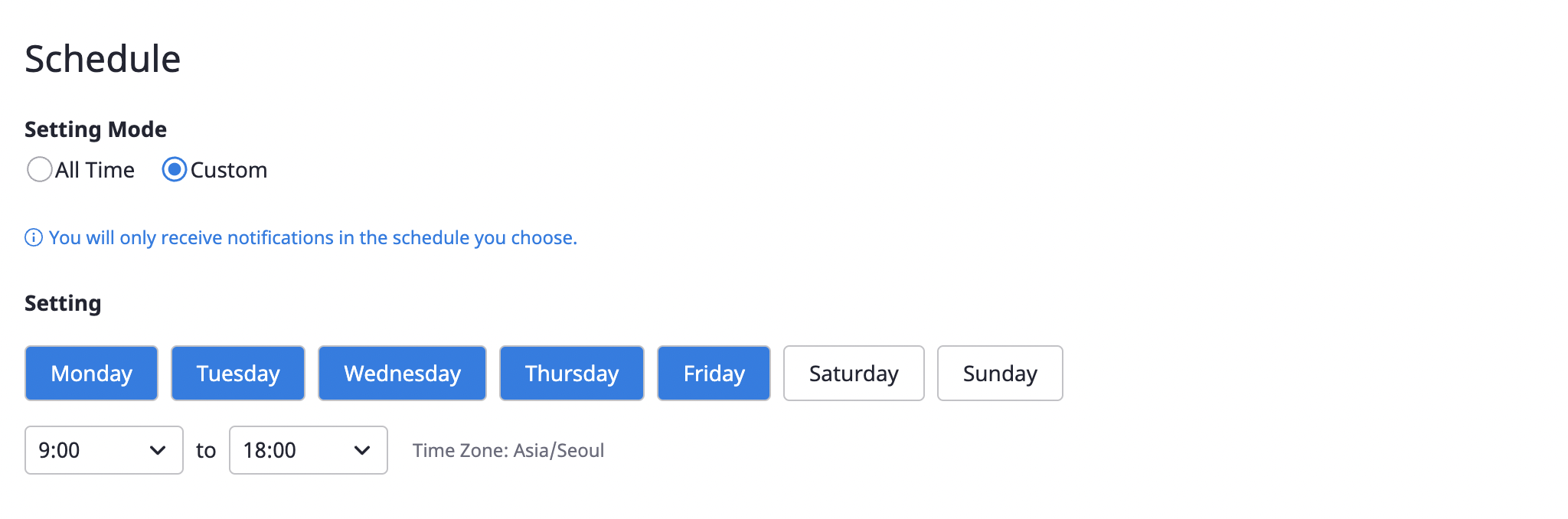
(2-2) You can set a schedule to receive notifications only at certain times.
(2-3) Notifications can be received when an alert occurs or when a threshold for budget notifications was reached. By setting up topics, you can choose which notifications you want to receive.
If you select [Receive all notifications], you will receive both types of notifications, and if you select [Receive notifications on selected topics], you will receive only notifications related to what you selected.

(3) Click the [Save] button to complete the notifications channel creation.
Editing and deleting the notifications channel
Editing the notifications channel
Created notifications channels can be checked under each notifications channel selection.
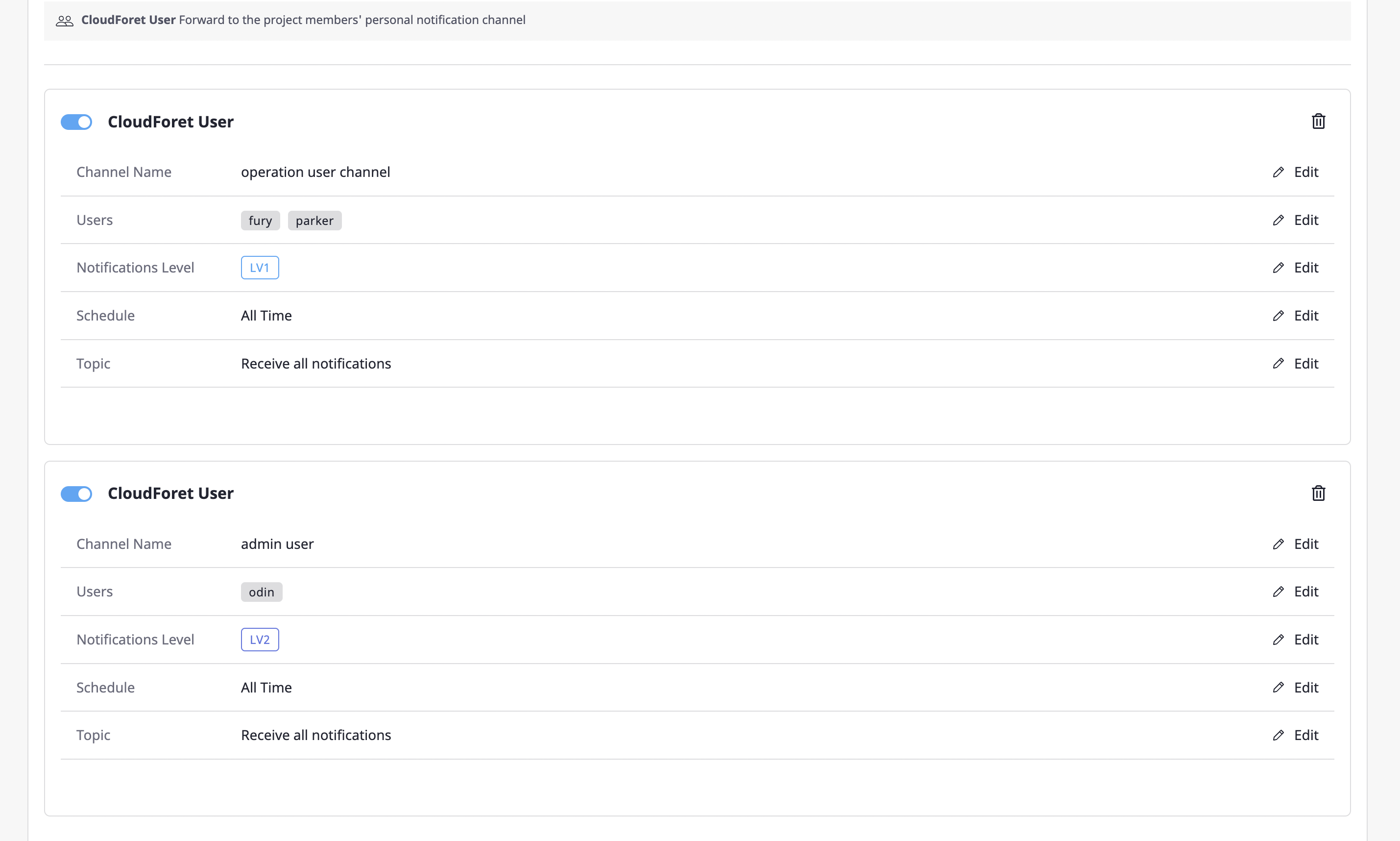
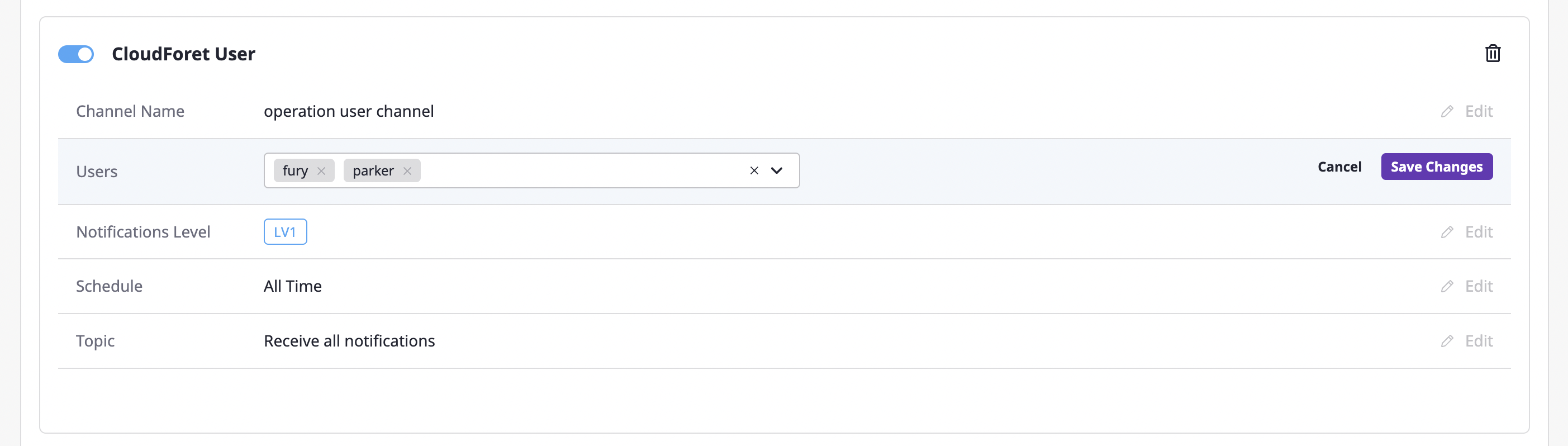
You can change the active/inactive status through the toggle button at the top left, and you can edit each item by clicking the [Edit] button of each notifications channel.
When you complete inputting the information, click the [Save changes] button to complete the editing.
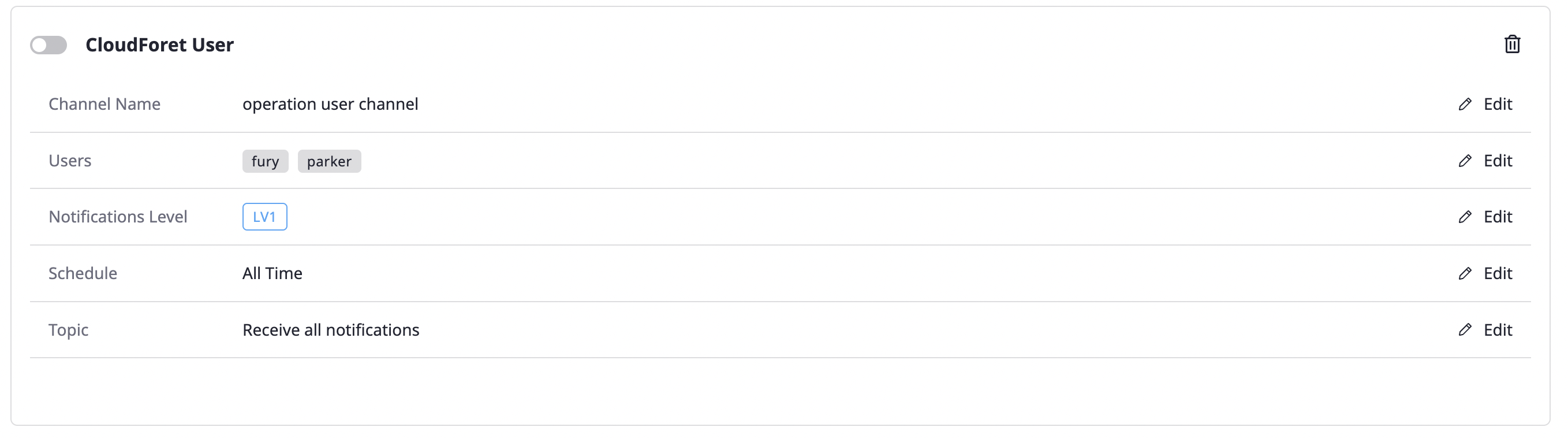
Deleting the notifications channel
You can delete the notifications channels by clicking the [Delete icon] button in the upper right corner.
Cloudforet user channel
The [Add Cloudforet user channel] button exists in the [Notifications channel] item in the project.
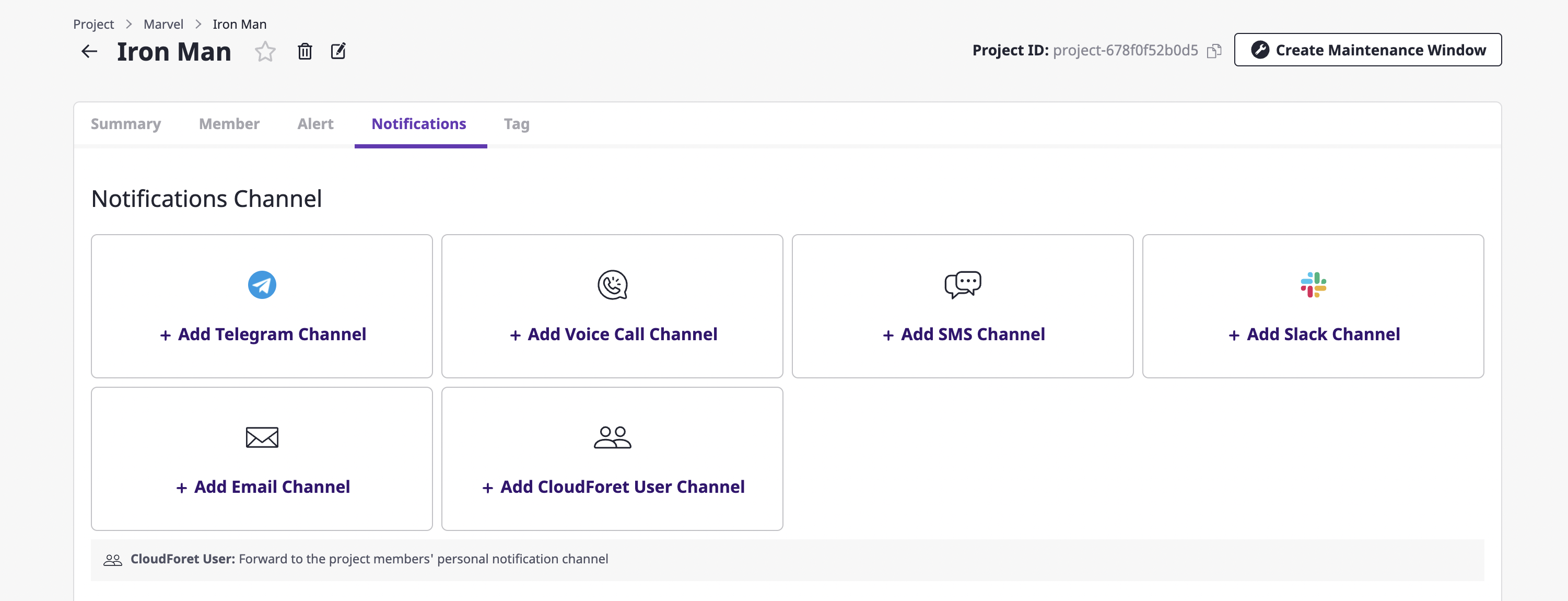
If you add a Cloudforet user channel, an alert is spread to the personal channels of project members. Afterward, alerts are forwarded via the Cloudforet user notifications channel of the user who has received it.
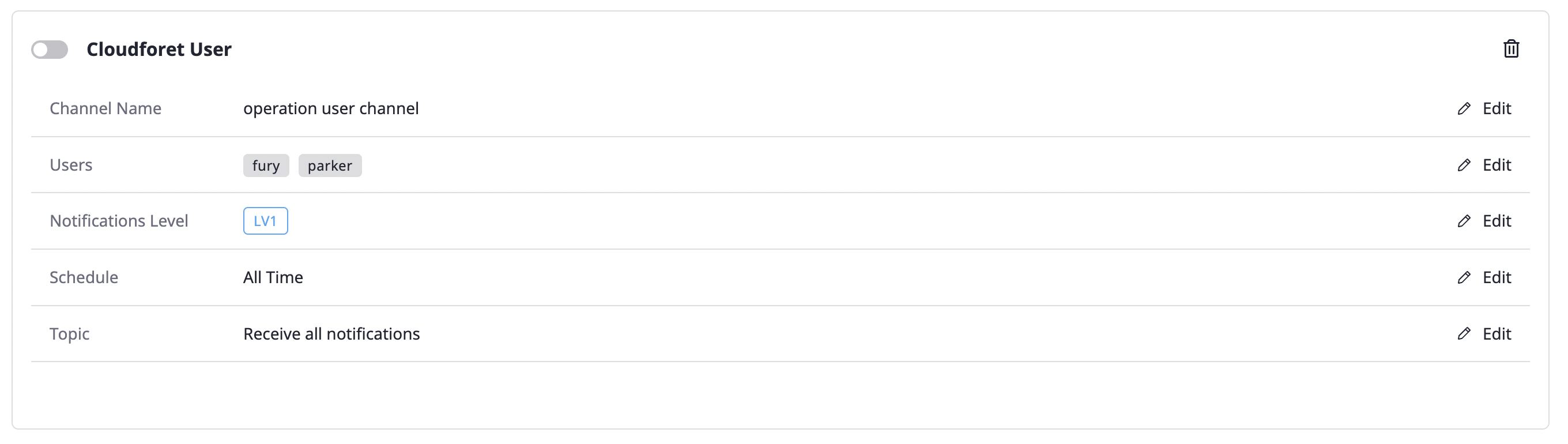
Creating a Cloudforet user notifications channel
A user notifications channel can be created in [My page > Notifications channel].
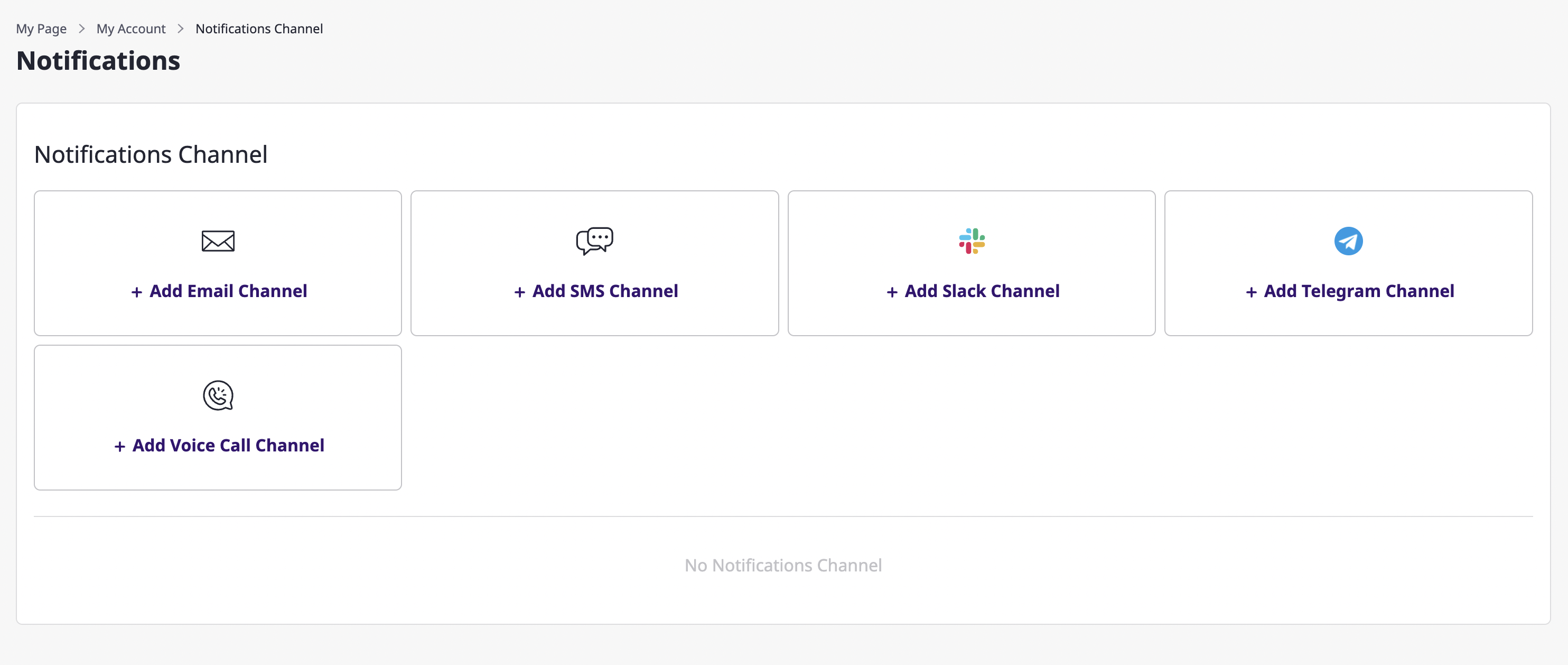
Unlike creating a project notifications channel, there are no notification level settings, and other creation procedures are the same as Creating a project notifications channel.
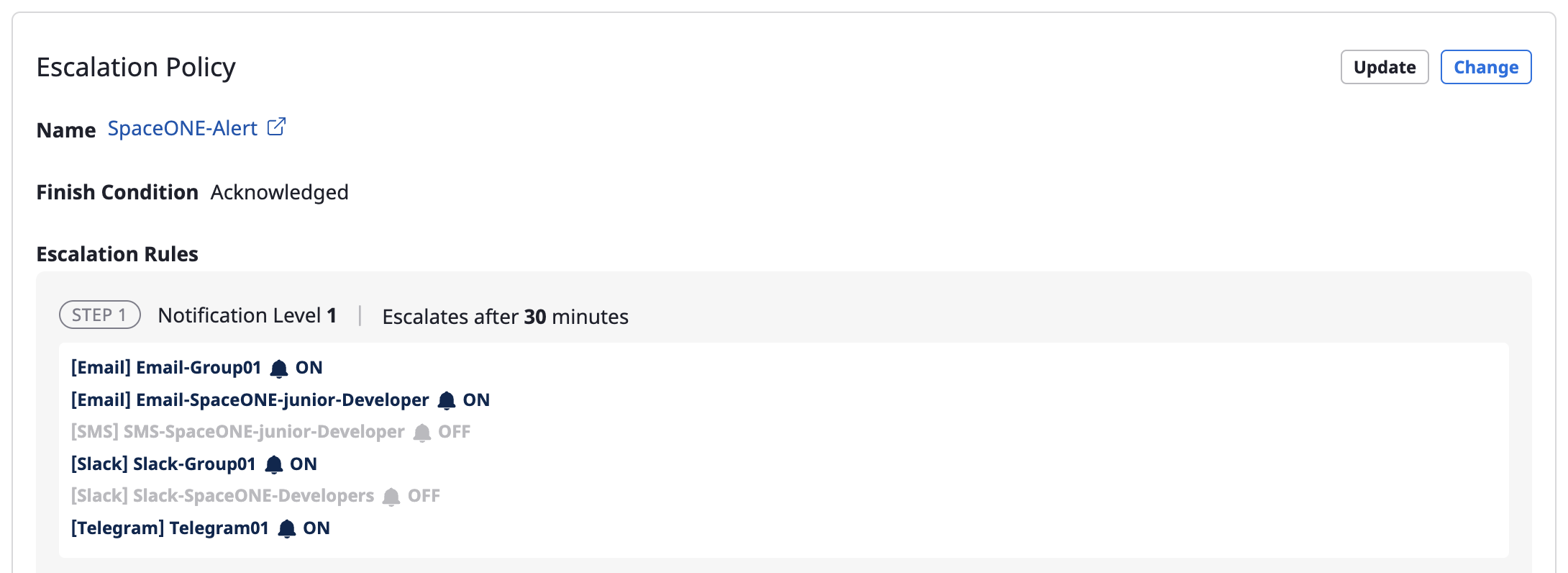
6.8 - Escalation policy
By applying stage-by-stage rules to alerts through escalation policies, alerts that have been received are effectively sent to members of the project.
Each rule has a set level, and an alert is spread to the corresponding notifications channel for each level.
Whether an alert received via a webhook is to be sent as a notification to project members is determined by Escalation policy.
Escalation policy can be managed in two places:
- [Alert manager > Escalation policy] page: Manage escalation policy under the scope of
globalandproject - [Project] detail page: Manage escalation policy under the scope of
project
Create escalation policy
If you are a user with manage permission on the [Escalation policy] page, you can create an escalation policy.
Create in an [Escalation policy] page
(1) Click the [Create] button on the [Alert manager > Escalation policy] page.
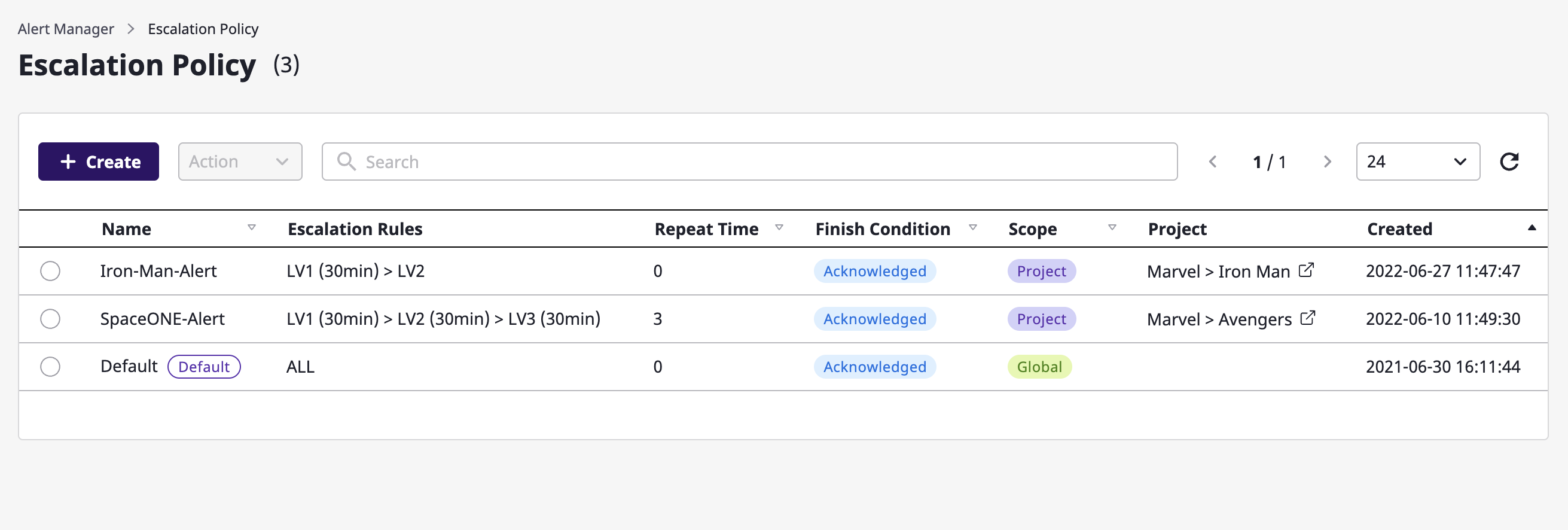
(2) Enter the settings to create an escalation policy.
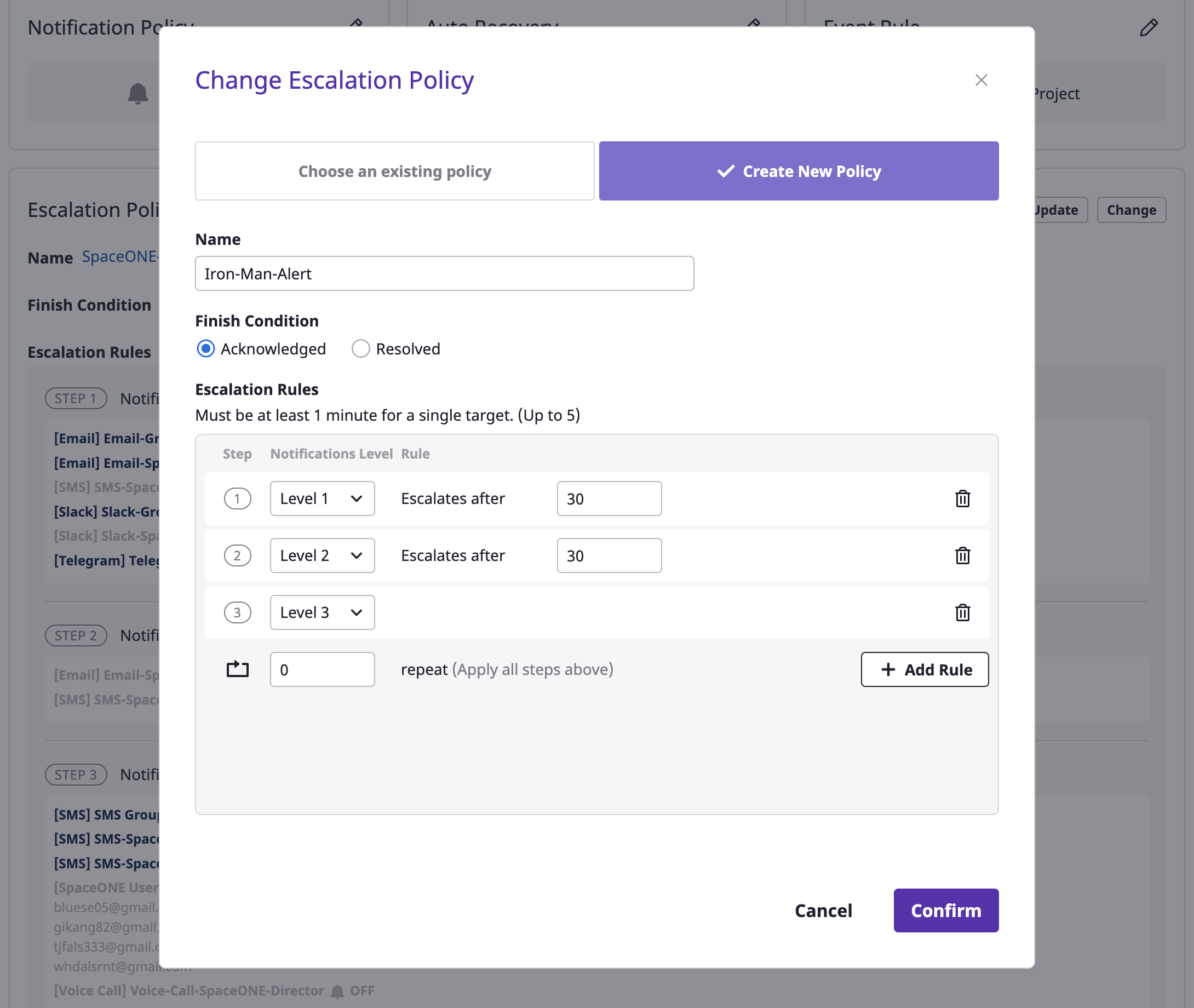
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Exit condition (status) | Define the condition to stop the generated alarm. |
| Range | Indicate the scope in which the escalation policy can be used. In case of global, the policy can be used in all projects within the domain, and in case of project, within the specified project. |
| Project | Scope defined as project indicates the project being targeted. |
| Escalation rules | Define rules for sending step-by-step notifications. Alerts are sent to a notifications channel belonging to a set level, and a period between steps can be given in minutes from step 2 or higher. |
| Number of repetitions | Define how many times to repeat an alert notification. Notifications can be repeated up to 9 times. |
When creating such items on the [Project] detail page, a
project is automatically selected for the scope, and the project is designated as the target.Create in a [Project] detail page
When you create an escalation policy on the [Project] detail page, the project is automatically designated as an escalation policy target.
(1) Inside the [Alert] tab of the project detail page, go to the [Settings] tab.
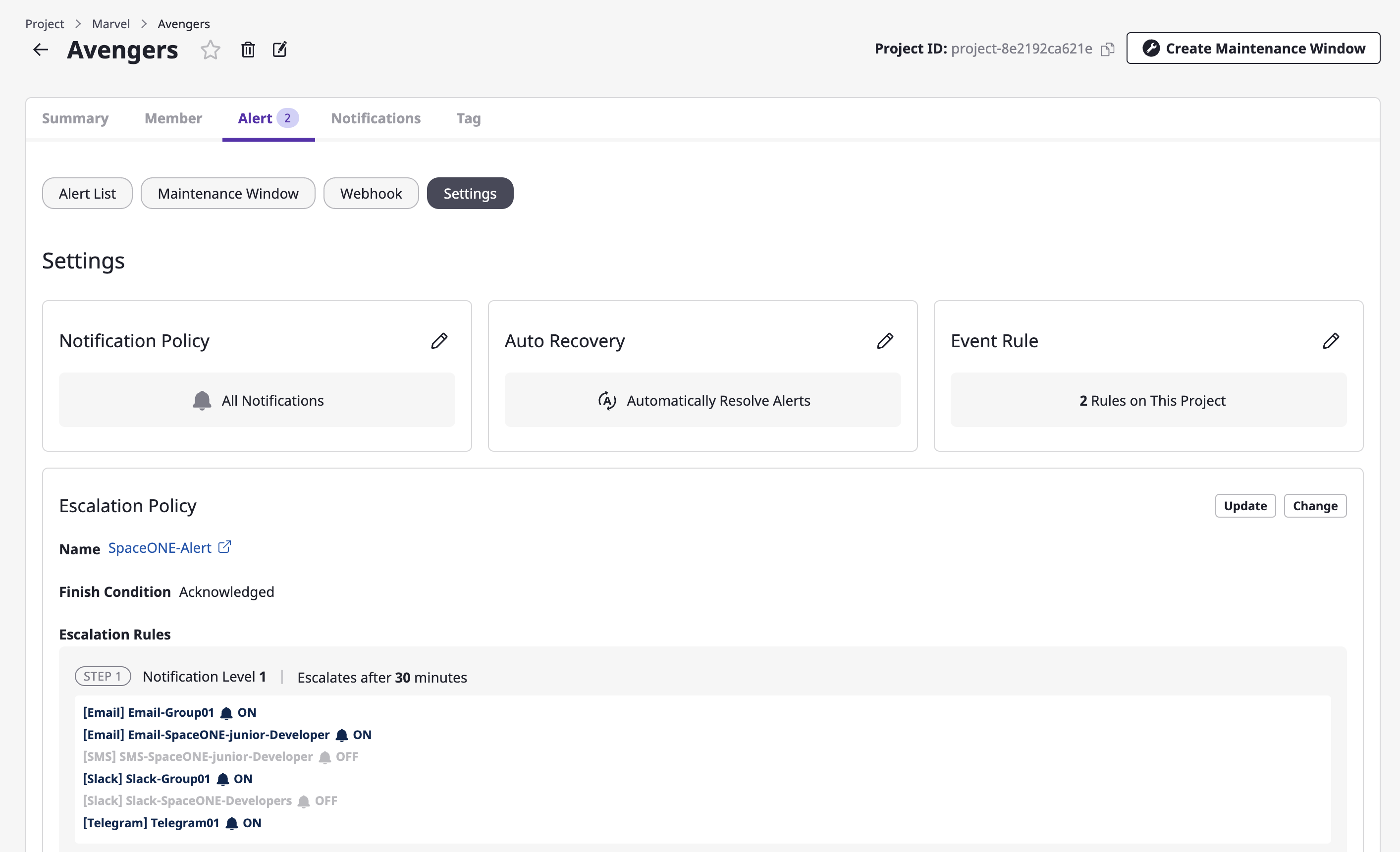
(2) Click the [Change] button in the escalation policy area.
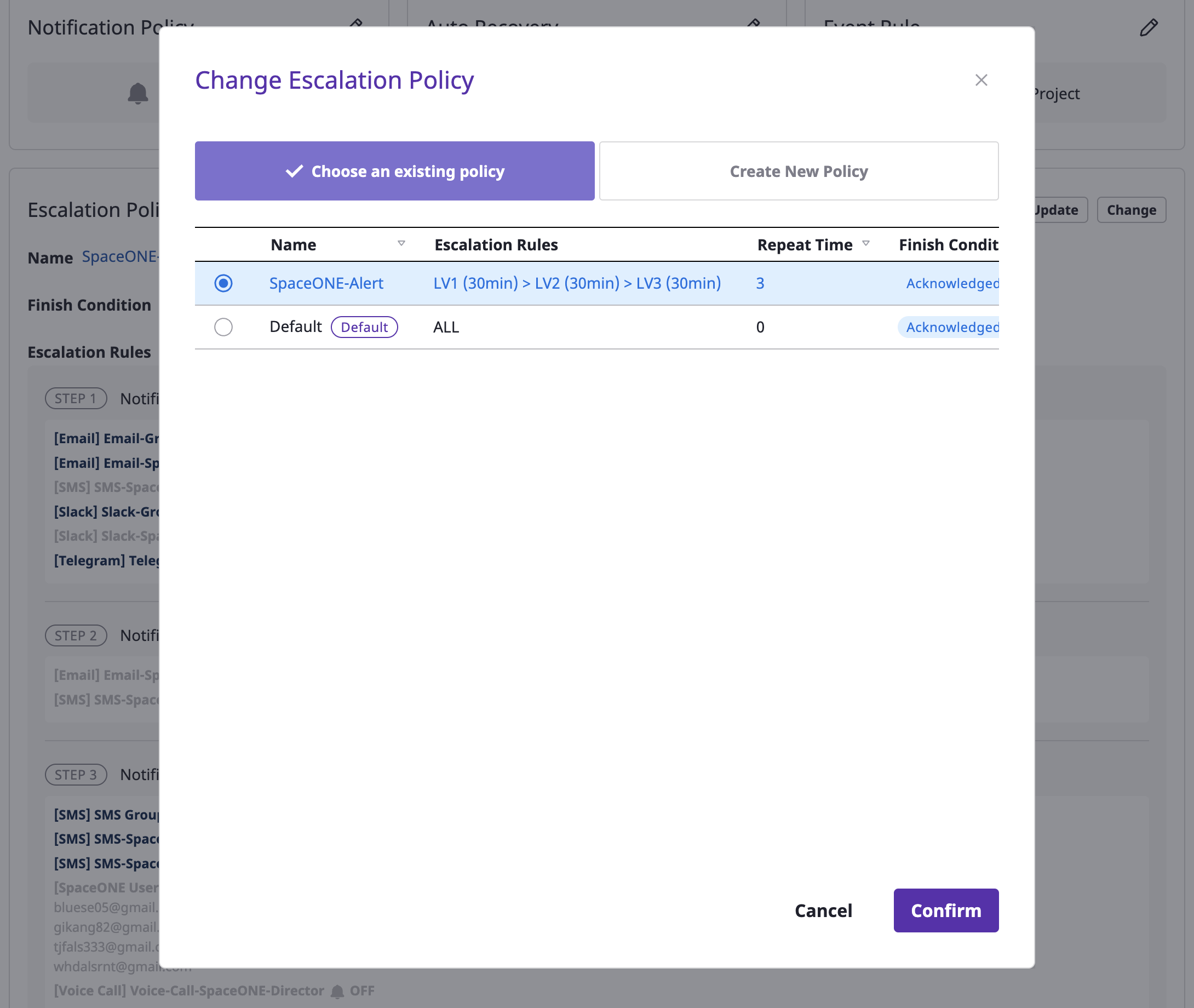
(3) Click the [Create new policy] tab.
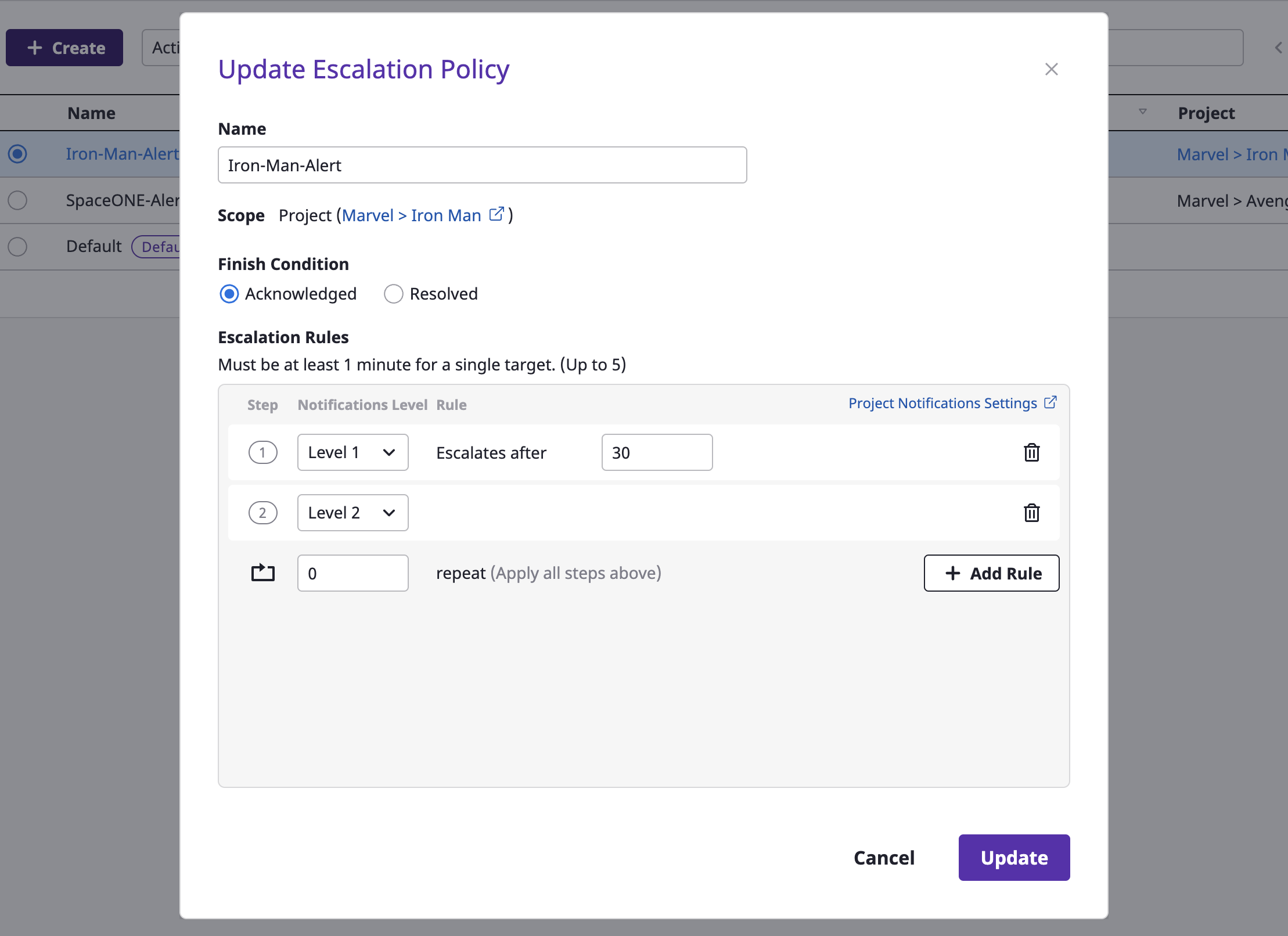
(4) Enter settings to create an escalation policy.
Level
A level is a transmission range at which you send an alert from the stage you are in when sending the alert by stage.
You can set up a notifications channel in the project, and each notifications channel has its own level.
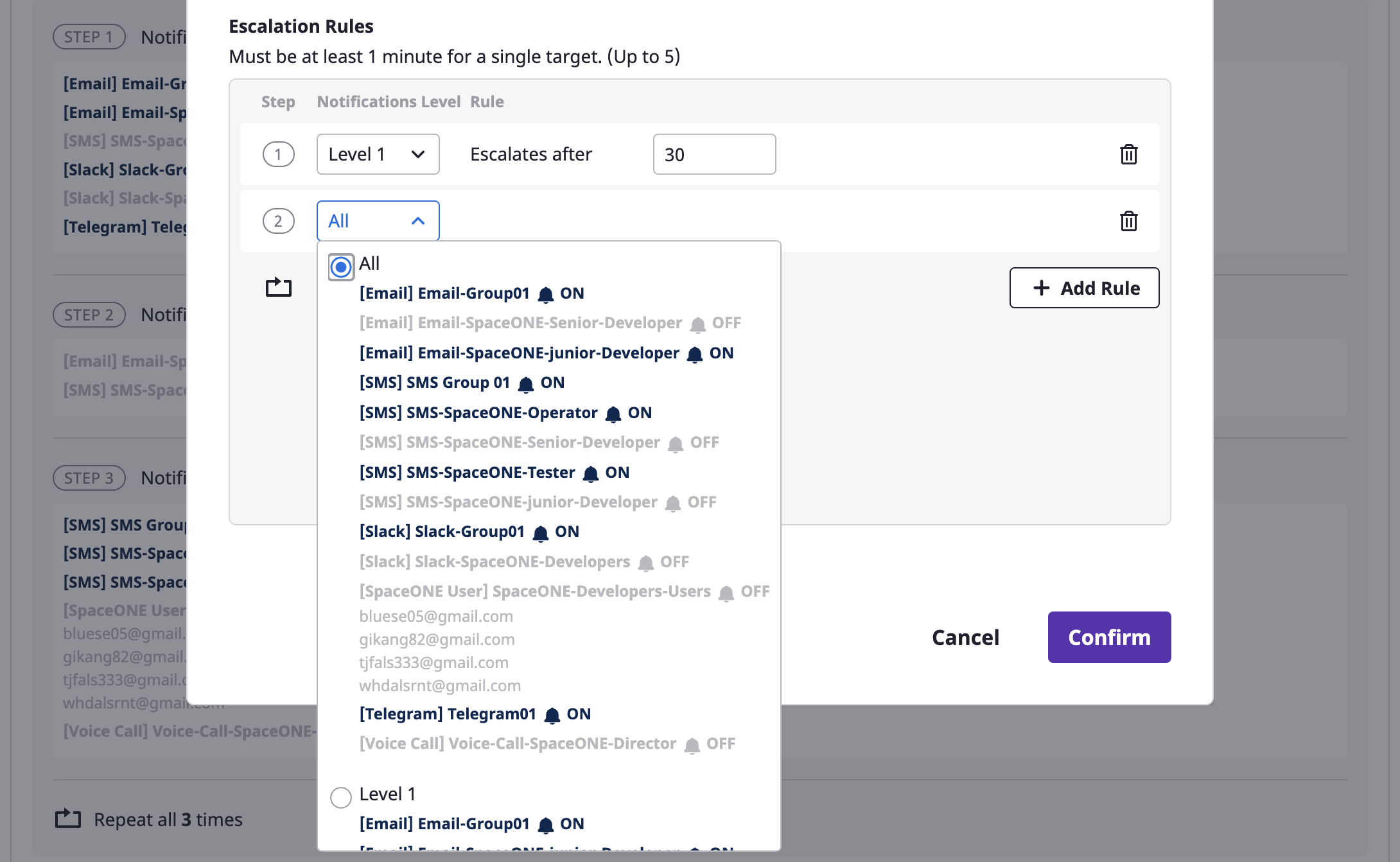
When defining the escalation rule, you set the [Notification level]. At each set stage, an alert is sent to the notifications channel of the corresponding level.
(5) When all settings are completed, click the [OK] button to create the escalation policy.
Set as default policy
After selecting one from the list of escalation policies, you can set it up as a default by selecting the [Set as default] menu from the [Action] dropdown.
When a new project is created and the alert is activated, the corresponding policy is automatically applied.
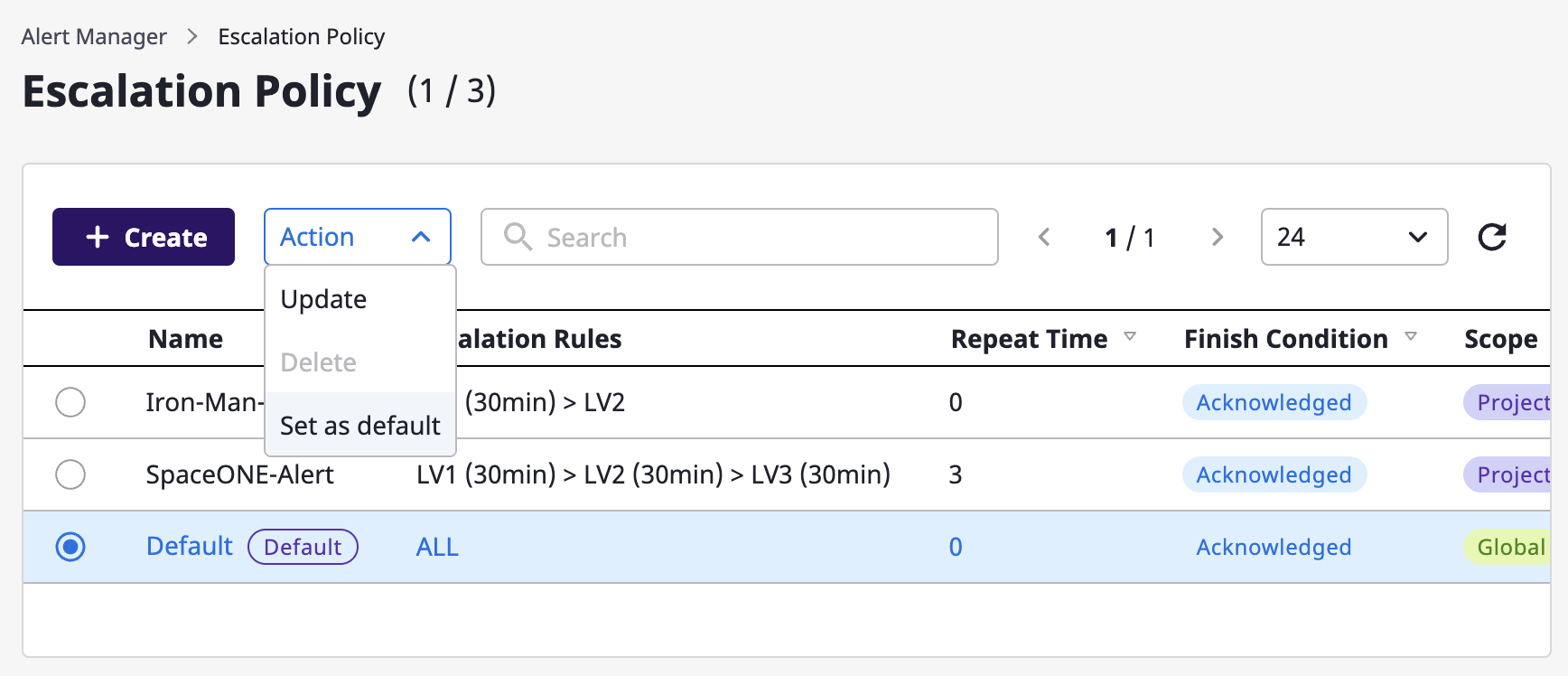
global can be selected through the [Set as default] menu.Modify and delete escalation
Once you select a target from the escalation policy list, [Modify] and [Delete] become available from the [Action] dropdown.
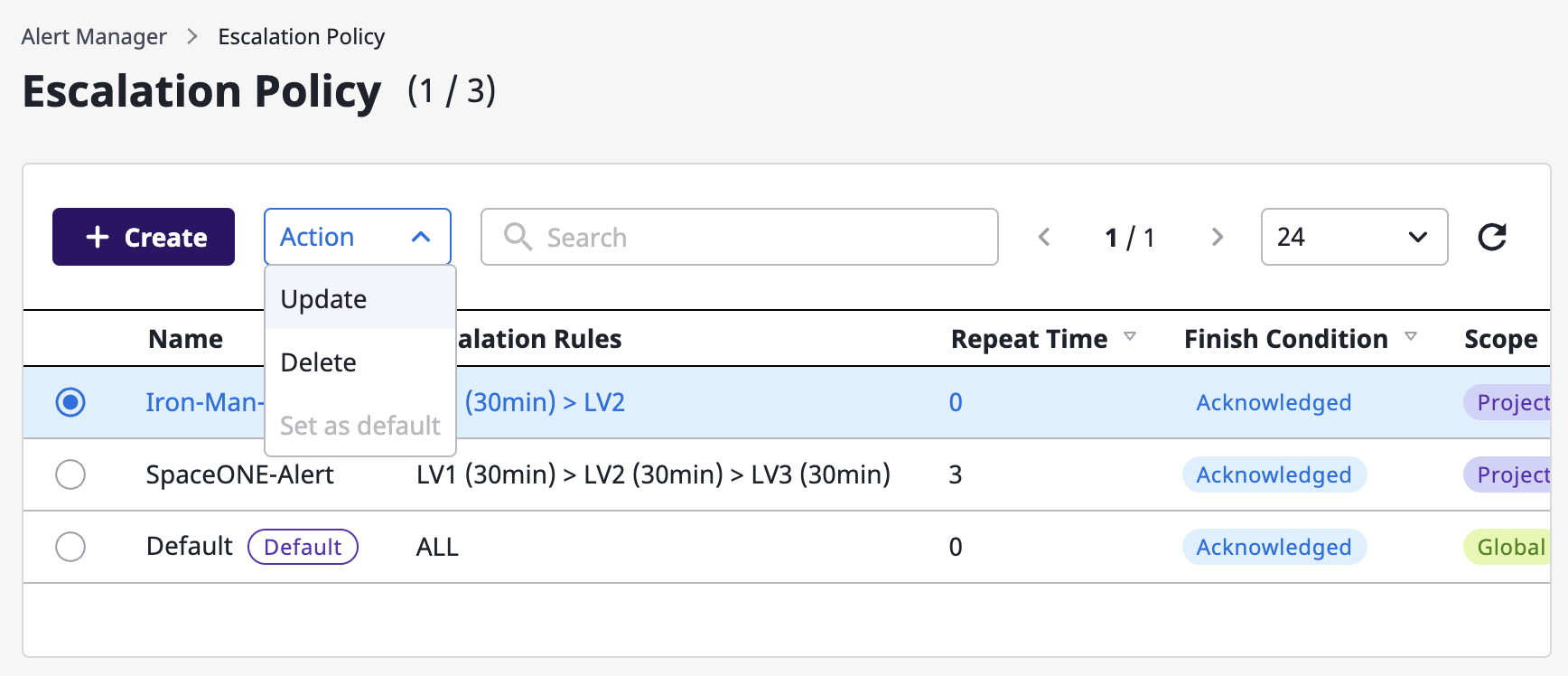
Edit
In the case of editing, you can use the same form as a modal dialog that is created when the [Create] button is clicked, and all items except the range can be edited.
Delete
In case of deletion, you can proceed with deletion through the confirmation modal dialog as shown below:

7 - Administration
You can create a User and designate a Role that is connected to an API policy.
7.1 - [IAM] User
You can also grant permissions to users by assigning them roles.
admin type. A user type can be assigned to a member of a project.
For how to assign roles to project members, see here.Adding users
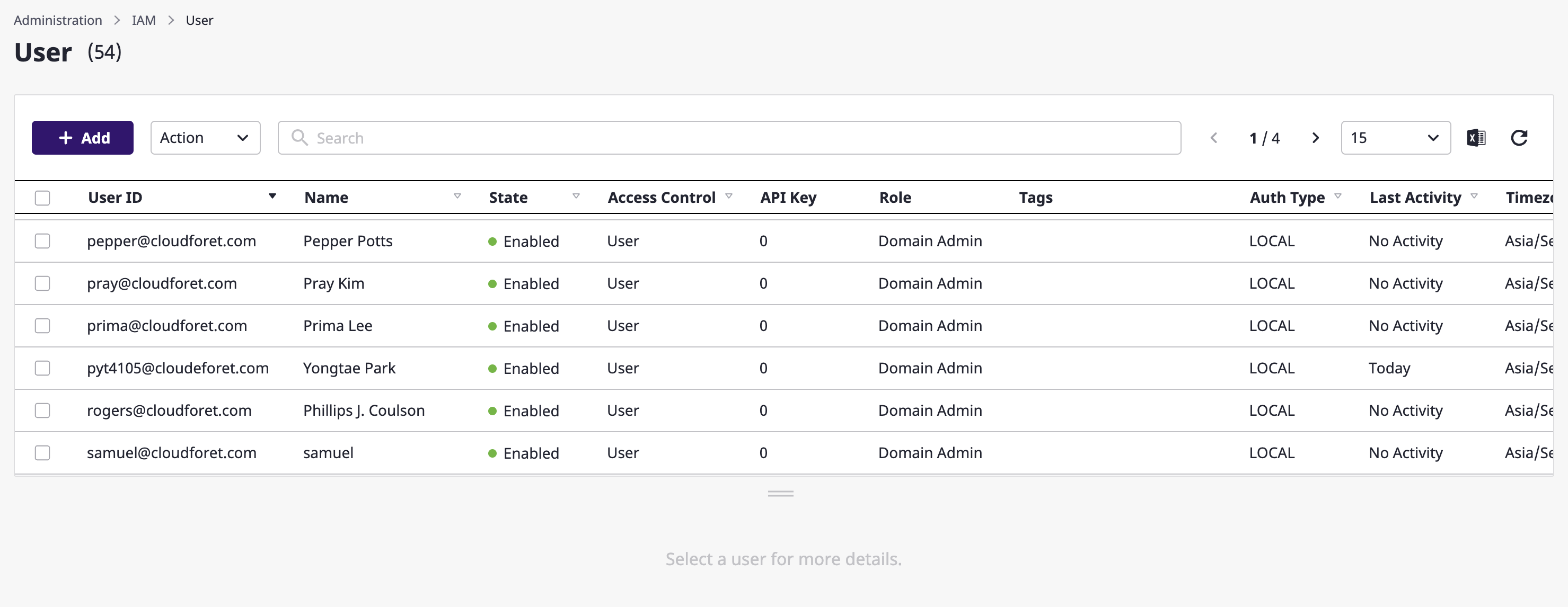
Click the [+ Add] button on the [Administration > IAM > User] page.

There are three types of users that can be added as follows:
- Internal user: users who can sign in by using their ID and password on the login page
- External user: users added by following the external user authentication that the domain has
- API Only: users who are only able to use API, and for whom the Cloudforet console is not accessible
1. Adding internal users
Internal users are users who can sign in by using their IDs and passwords on the login page.
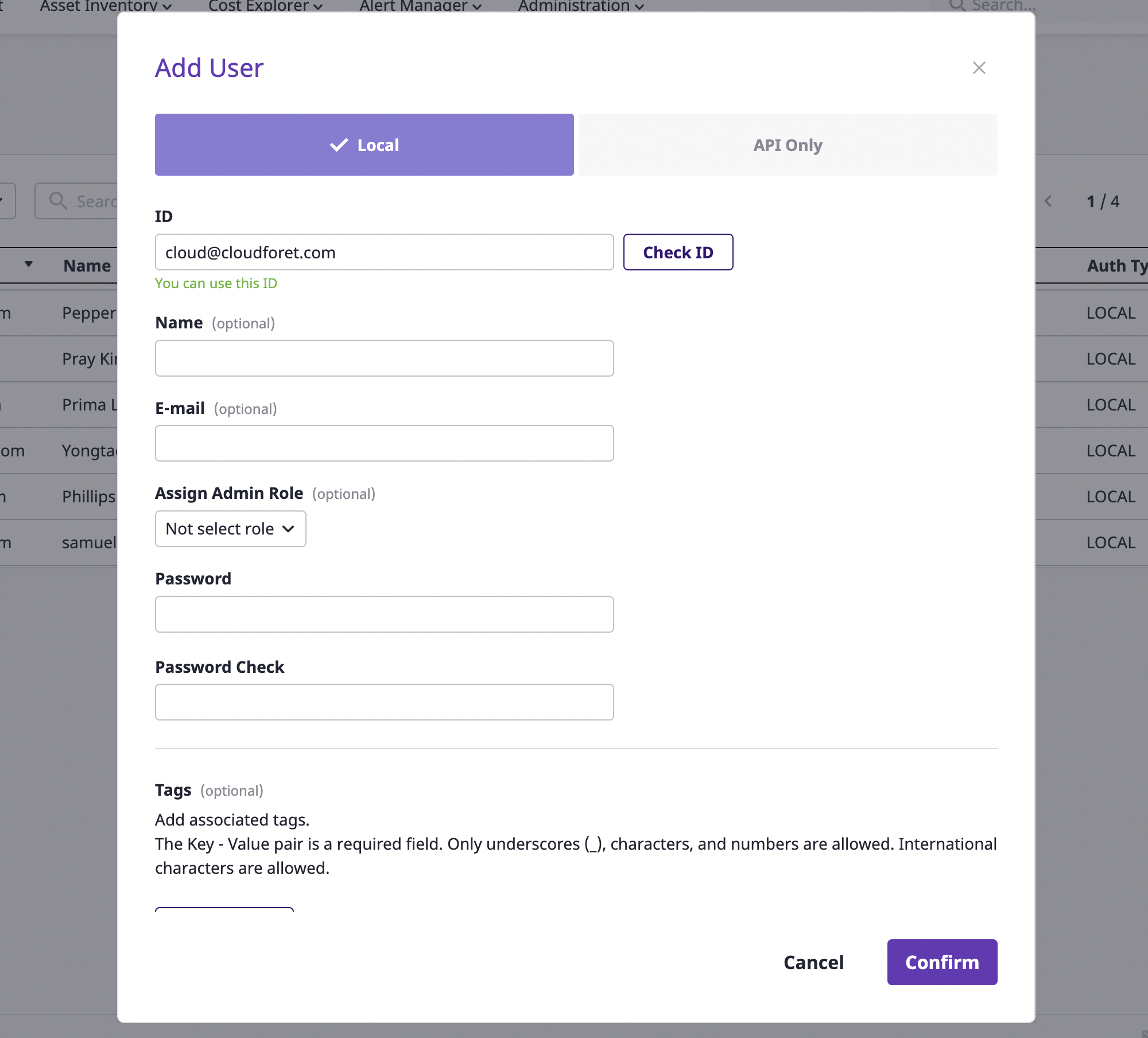
(1-1) After the [Add user] modal dialog opens, select the [Local] tab to add an internal user.

(1-2) After entering the ID of an internal user, click the [Check ID] button. The user ID must be in an email form, and not on the list of existing users.
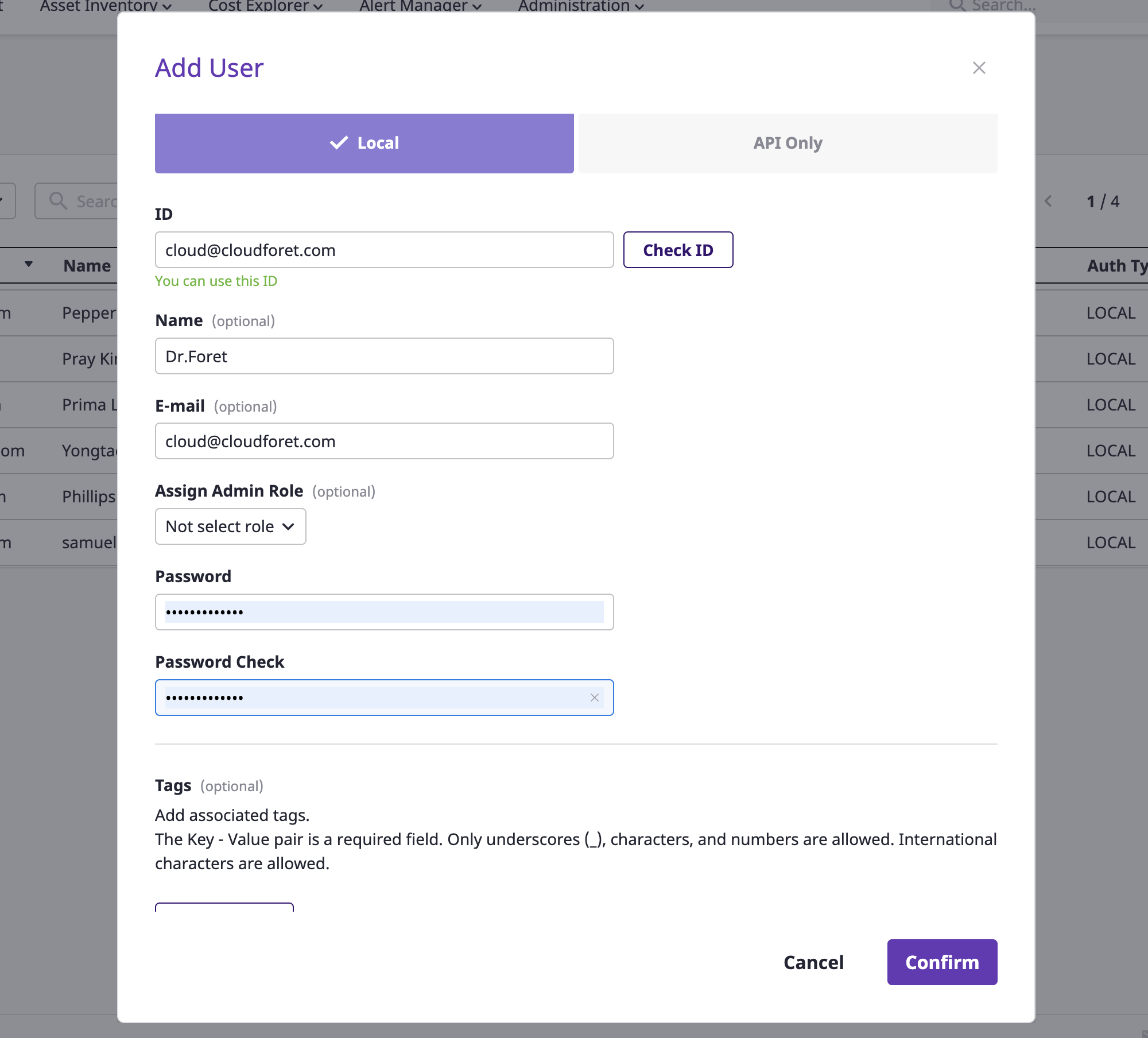
(1-3) Optionally enter user name and notification email(for receiving important system-related announcements or password reset link).
(1-4) Either send user a password reset link or, set the password on user's behalf. (※ If you set the password manually, you will need to directly inform the user of the password)
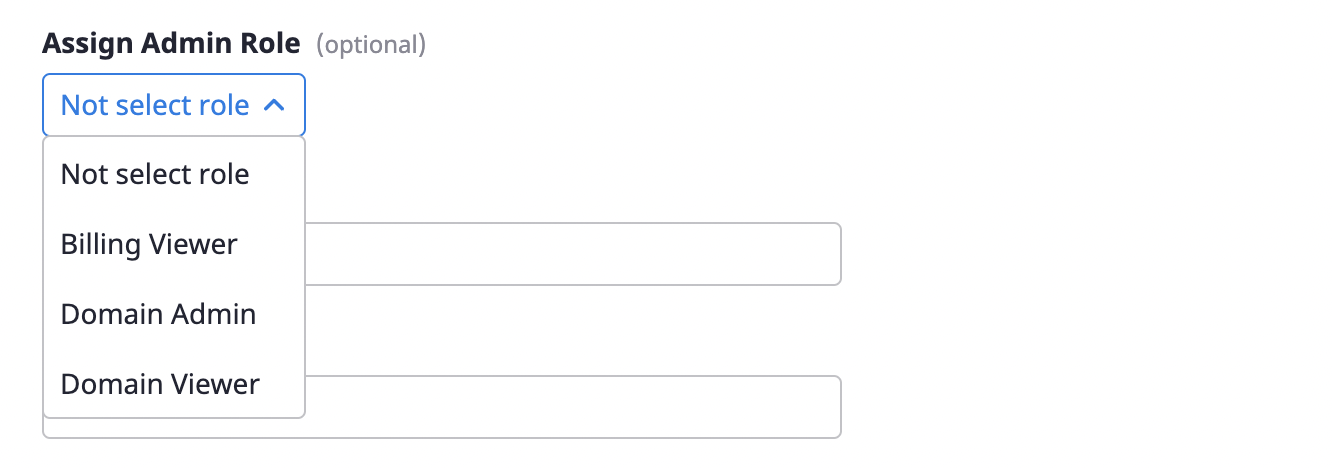
(1-5) To assign admin role to the user, you can activate the 'Admin Role' section at the bottom of the modal window and grant a specific role.

(1-6) Click the [Confirm] button to complete the user addition.
2. Adding external users
Adding an external user follows the external user authentication that the domain has. Without authentication as an external user, one cannot be added as a user.
(2-1) After opening the [Add User] modal, select a specific SSO tab for adding external users. ex. Google OAuth

(2-2) Enter an existing authenticated external user account.
(2-3) Optionally enter user name and notification email(for receiving important system-related announcements or password reset link).
(2-4) To assign admin role to the user, you can activate the 'Admin Role' section at the bottom of the modal window and grant a specific role.
(2-5) Click the [Confirm] button to complete the user addition.
3. Adding API only users
API users cannot access the Cloudforet console and can only use the API.
(3-1) After the [Add user] modal dialog opens, select the [API Only] tab.

(3-2) After entering the ID, click the [Check ID] button. The user ID must not be on the list of existing users.
(3-3) Optionally enter user name.
(3-4) To assign admin role to the user, you can activate the 'Admin Role' section at the bottom of the modal window and grant a specific role.
(3-5) Click the [Confirm] button to complete the user addition.
Viewing user details
By selecting a specific user from the table on the user page, you can view detailed information on that user.

Updating users
By selecting a specific user in the table and clicking on [Actions > Edit], you can modify the user's information.

- You can modify the user's ID, name, notification email, password, admin role (role), and tags.
- If the user encounters difficulties with verification for the notification email, you can directly verify it without sending verification code.
- For local users, you can either change the password on their behalf or send them a password reset link for the user to reset it themselves.
8 - My page
8.1 - Account & profile
[My page] can be accessed through the submenu that appears when you click the icon on the far right of the top menu.
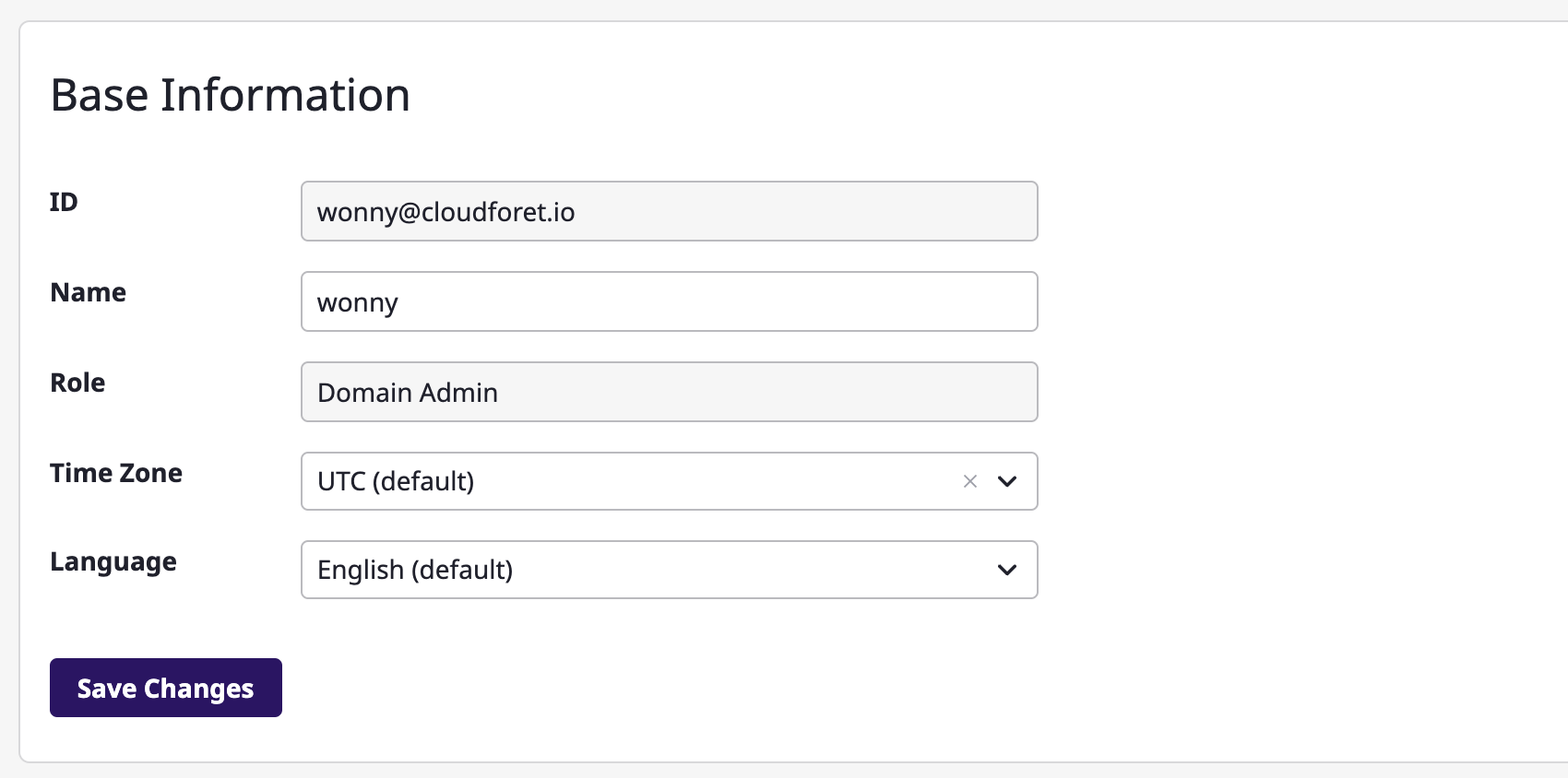
Changing settings
You can change your name, time zone, and language settings on the [My page > Account & profile] page.
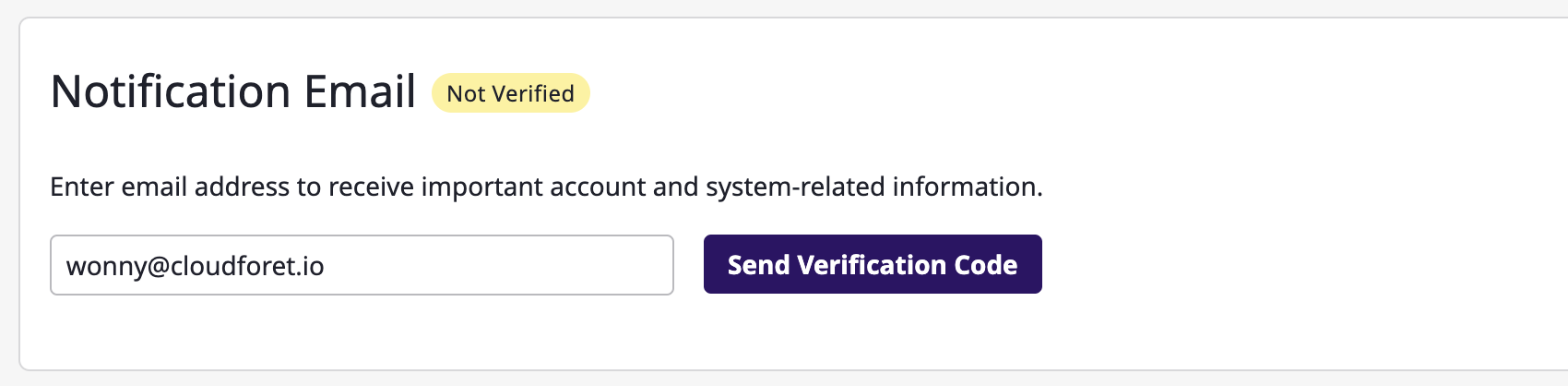
Verifying Notification Email
You can enter and verify Notification Email. If your Notification Email has not been verified yet, you won't be able to receive important system notifications or password reset link.
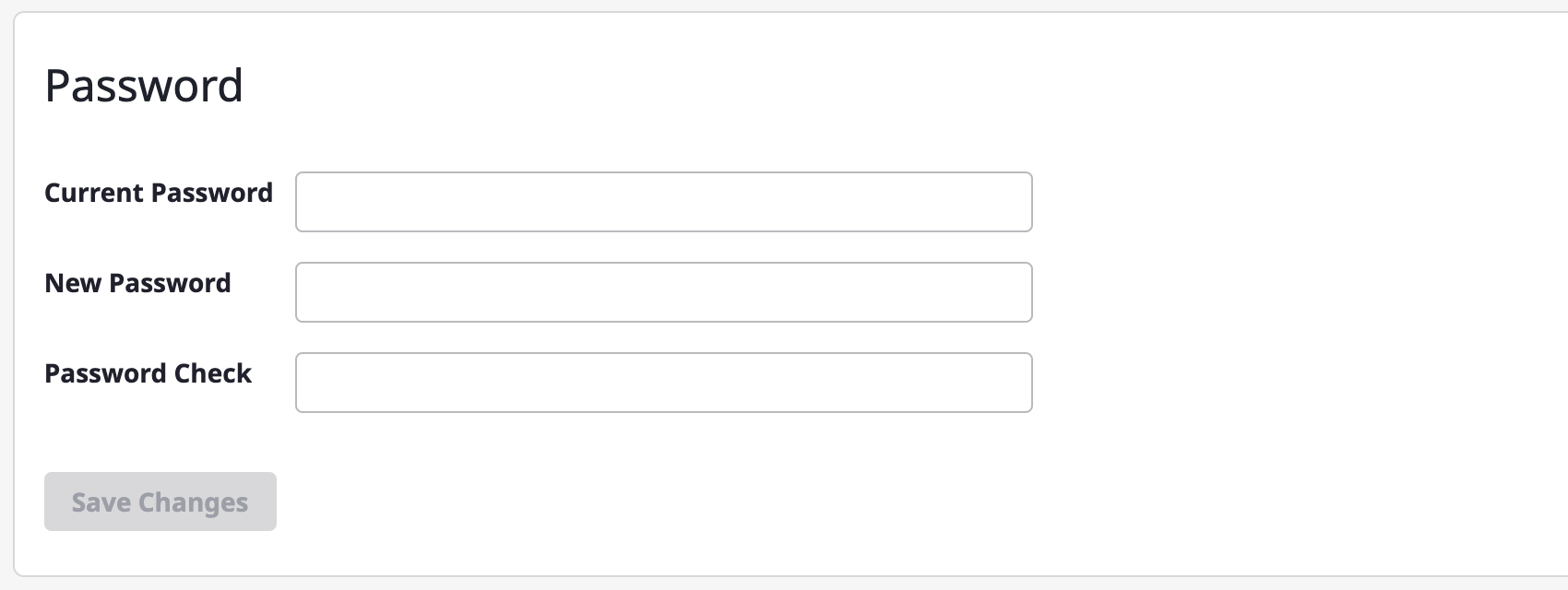
Changing the password
If you are an internal user (a user signed in with ID/password), you can change your password on this page.
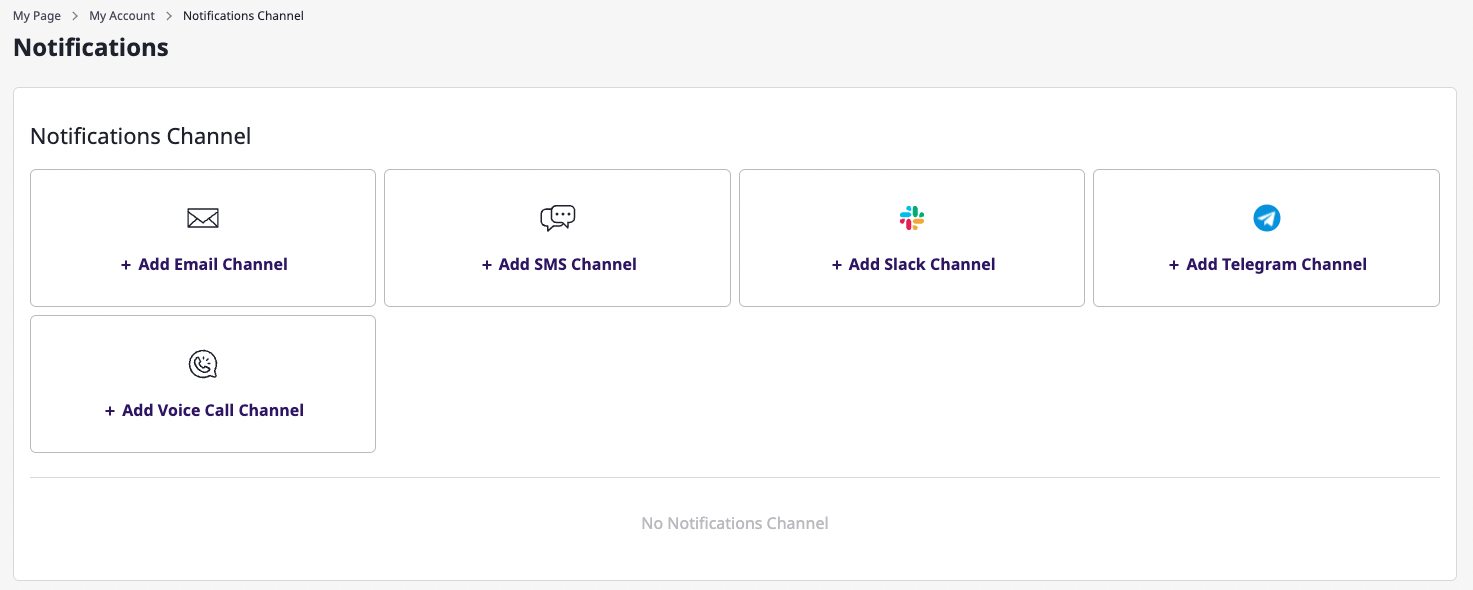
8.2 - Notifications channel
Creating notifications
On the [My page > Notifications channel] page, there is an [Add channel] button for each protocol.
As you click the [Add channel] button, you will enter the following page. The input form for basic information is different for each protocol, whereas the channel name, notification schedules, and selection boxes for topics able to subscribe to are the same for all protocols.
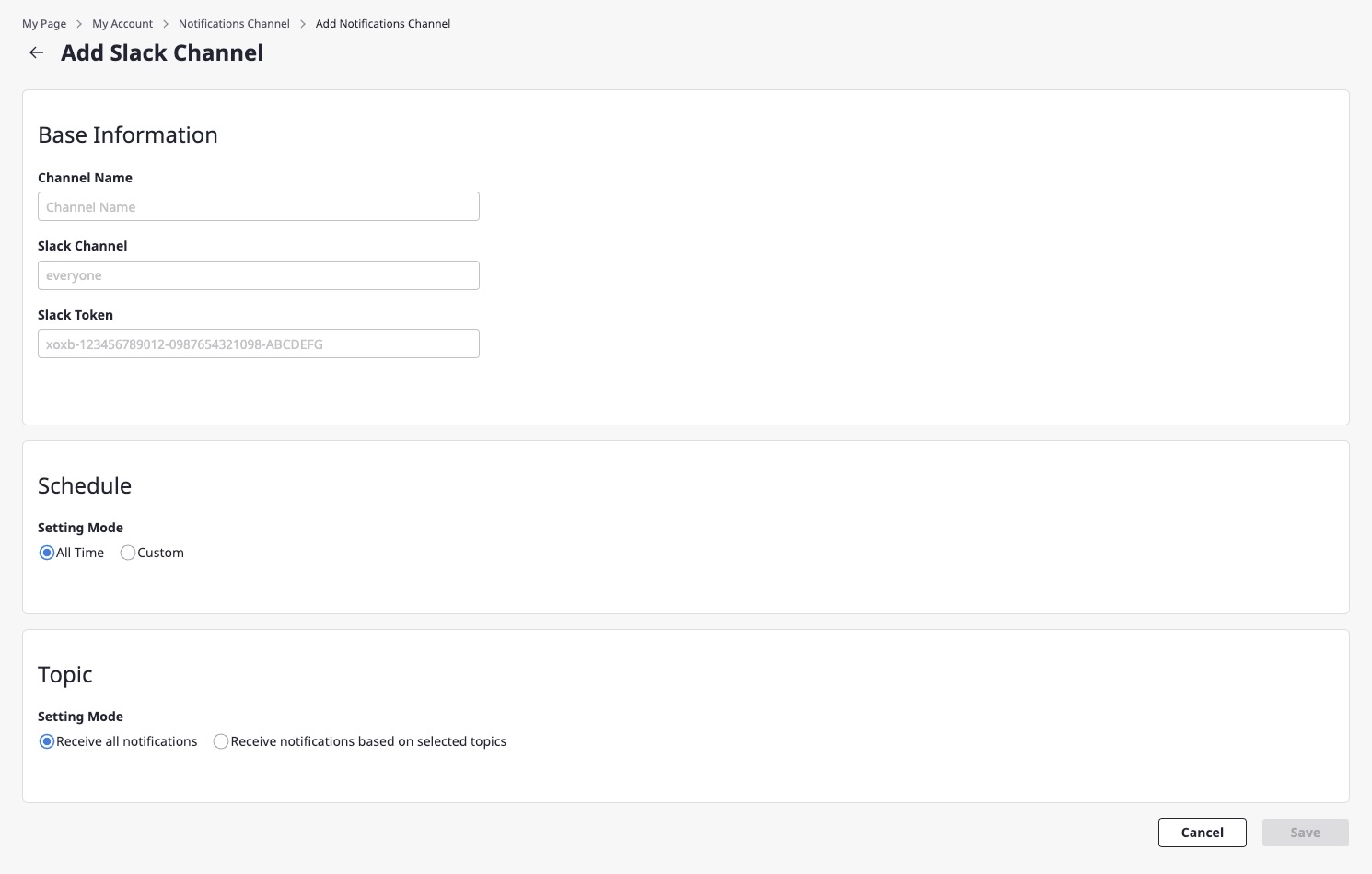
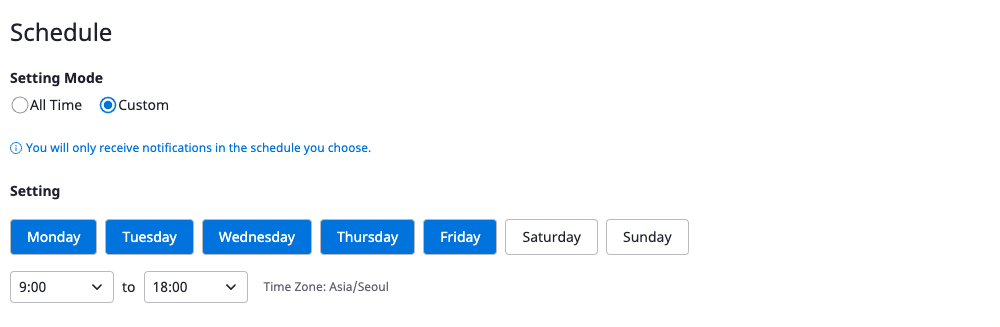
If you select anytime as the schedule, you can receive notifications at any time. If you select set time, you can select the desired day and time.
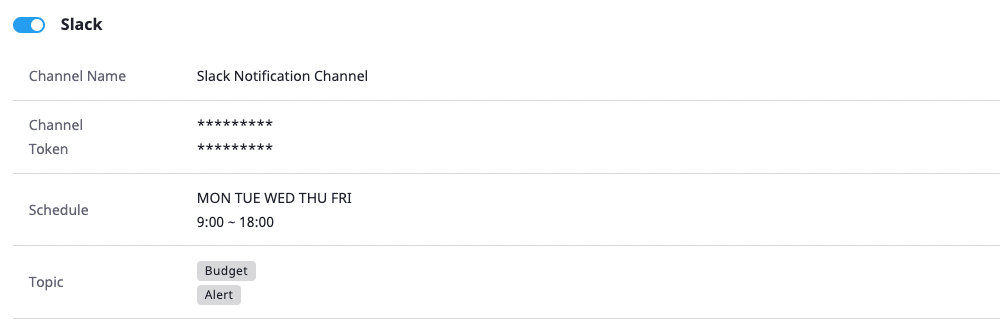
You can also select an option to receive all notifications for topics, or receive notifications only for a topic you would select between alert and budget.

Verifying the created notifications channel
When you fill out all input forms and create a notifications channel, you can check the newly created channel as follows:
Editing the notifications channel
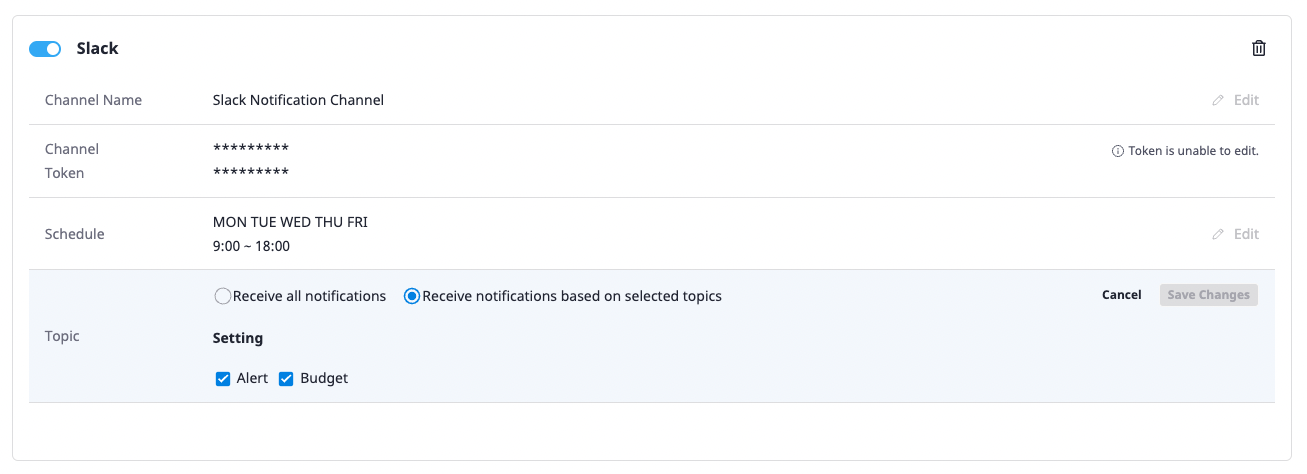
Alerts you create can be edited directly from the list.
In the case of a protocol that can edit the entered data (e.g. SMS, voice call), data, channel name(s), schedules, and topics can all be edited. For protocols where data cannot be edited (e.g., Slack, Telegram), the [Edit] button is not active.
9 - Information
9.1 - Notice
Verifying notices
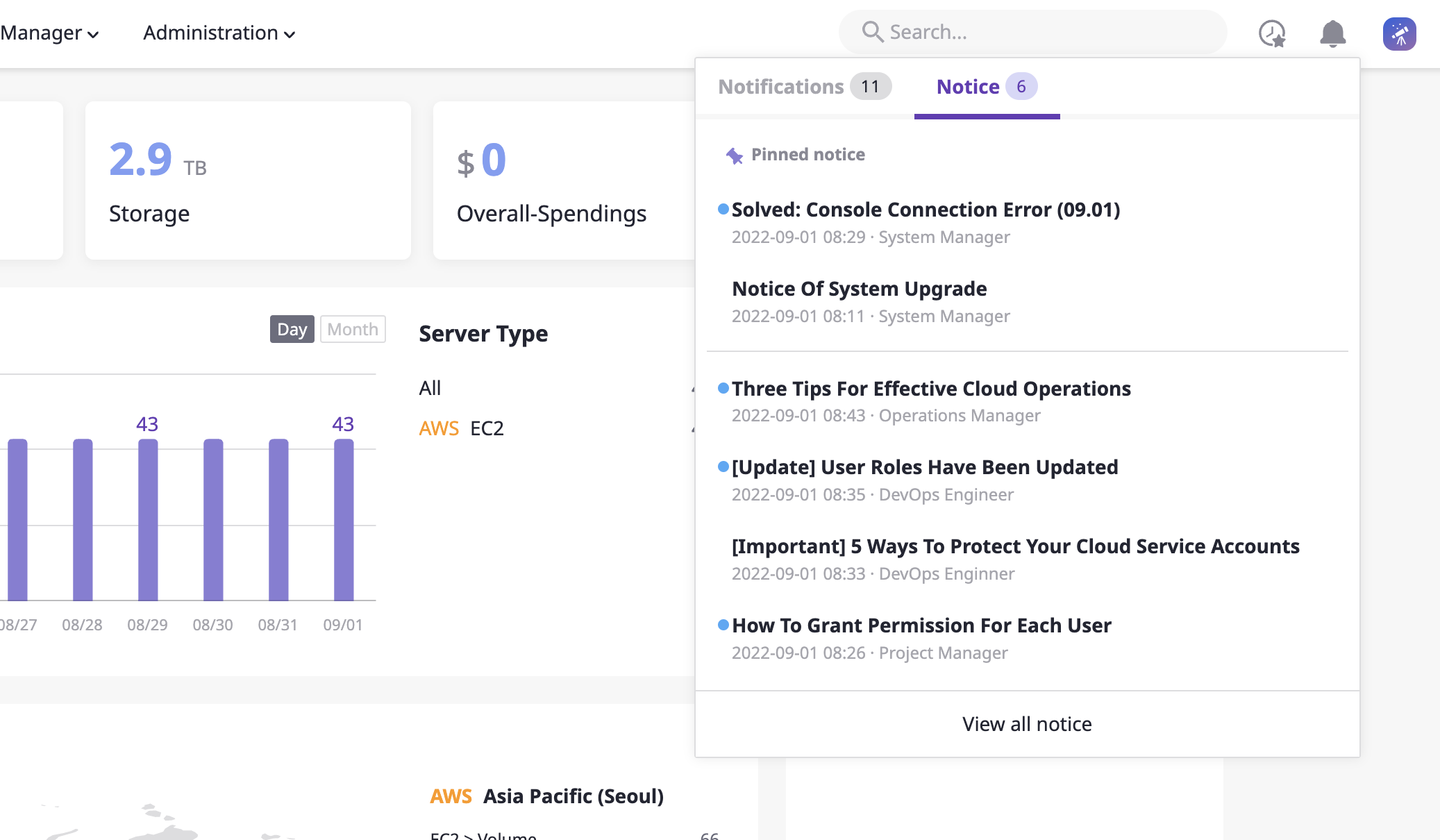
(1) Quick check for recent notices: After clicking the notification button on the top menu, click the [Notice] tab to check the recently registered notices.
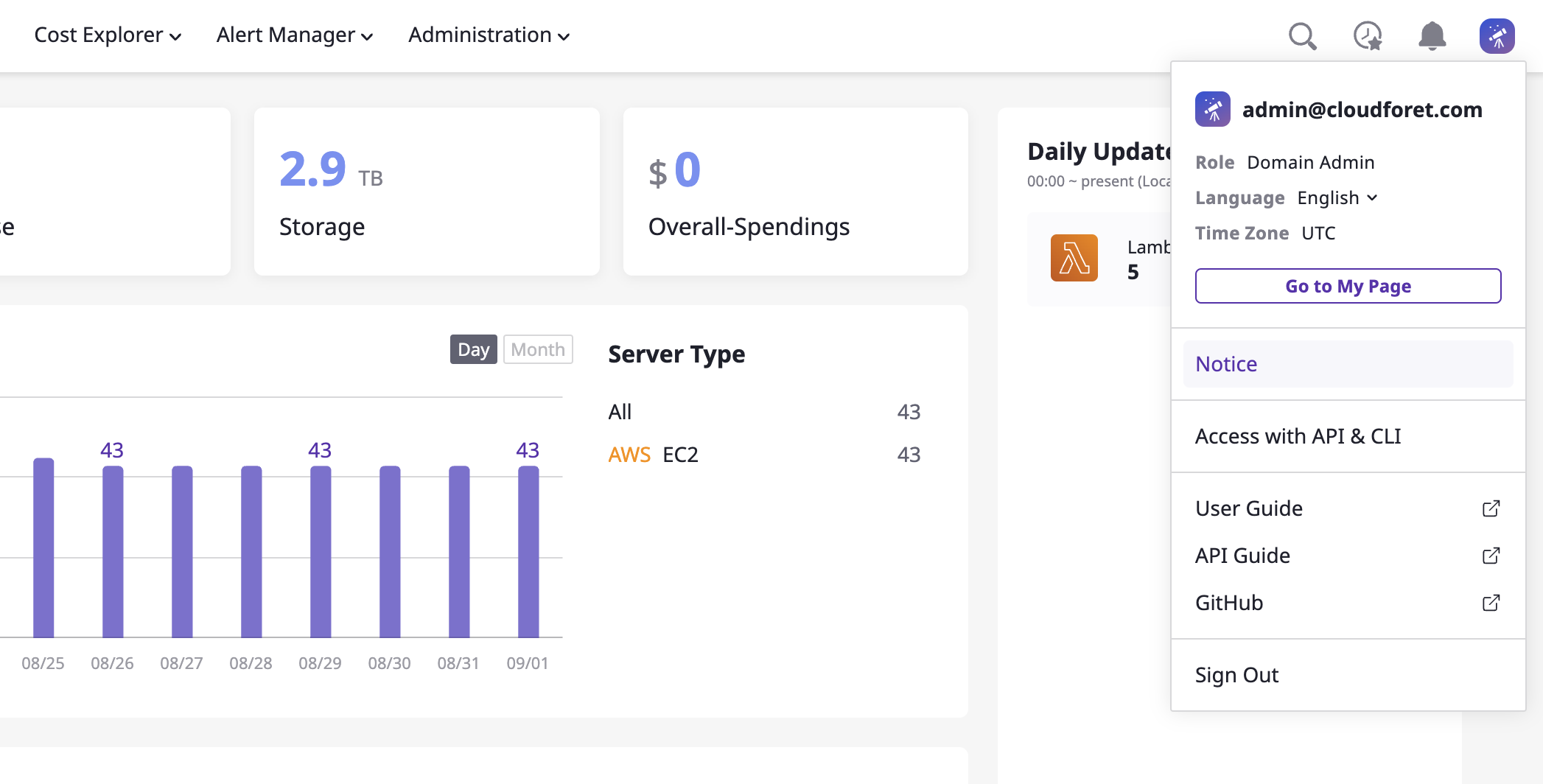
(2) Check the full list: You can move to the full list of notices page through the submenu that appears when you click the icon on the far right of the top menu.
Registering notice
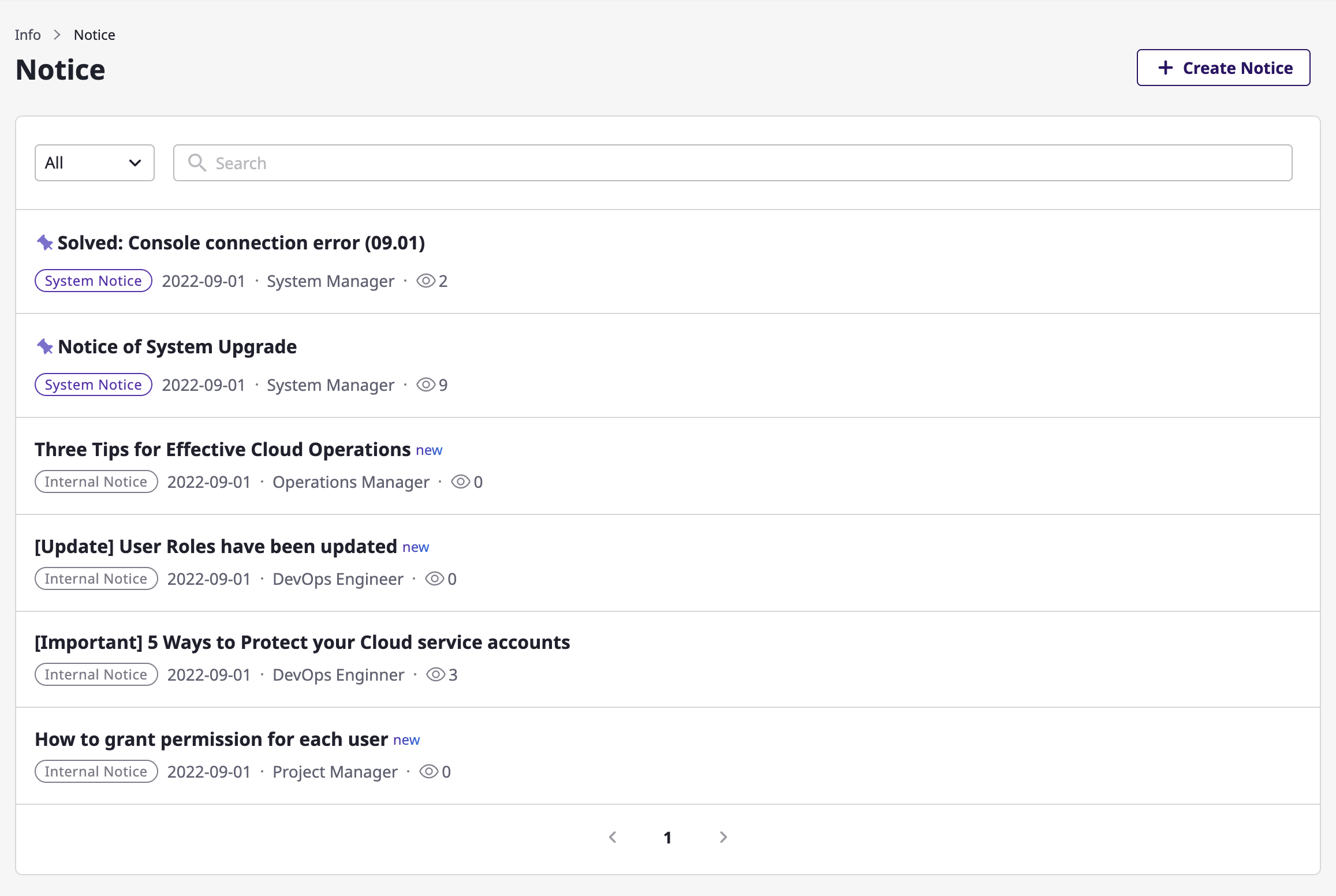
A user with a role whose type is [Admin] is permitted to directly create announcements within a related domain.
(1) Enter the [Notice] page, and click the [Register new notice] button to write a new post.
- The updated notice is open to all users assigned a specific role within a related domain.
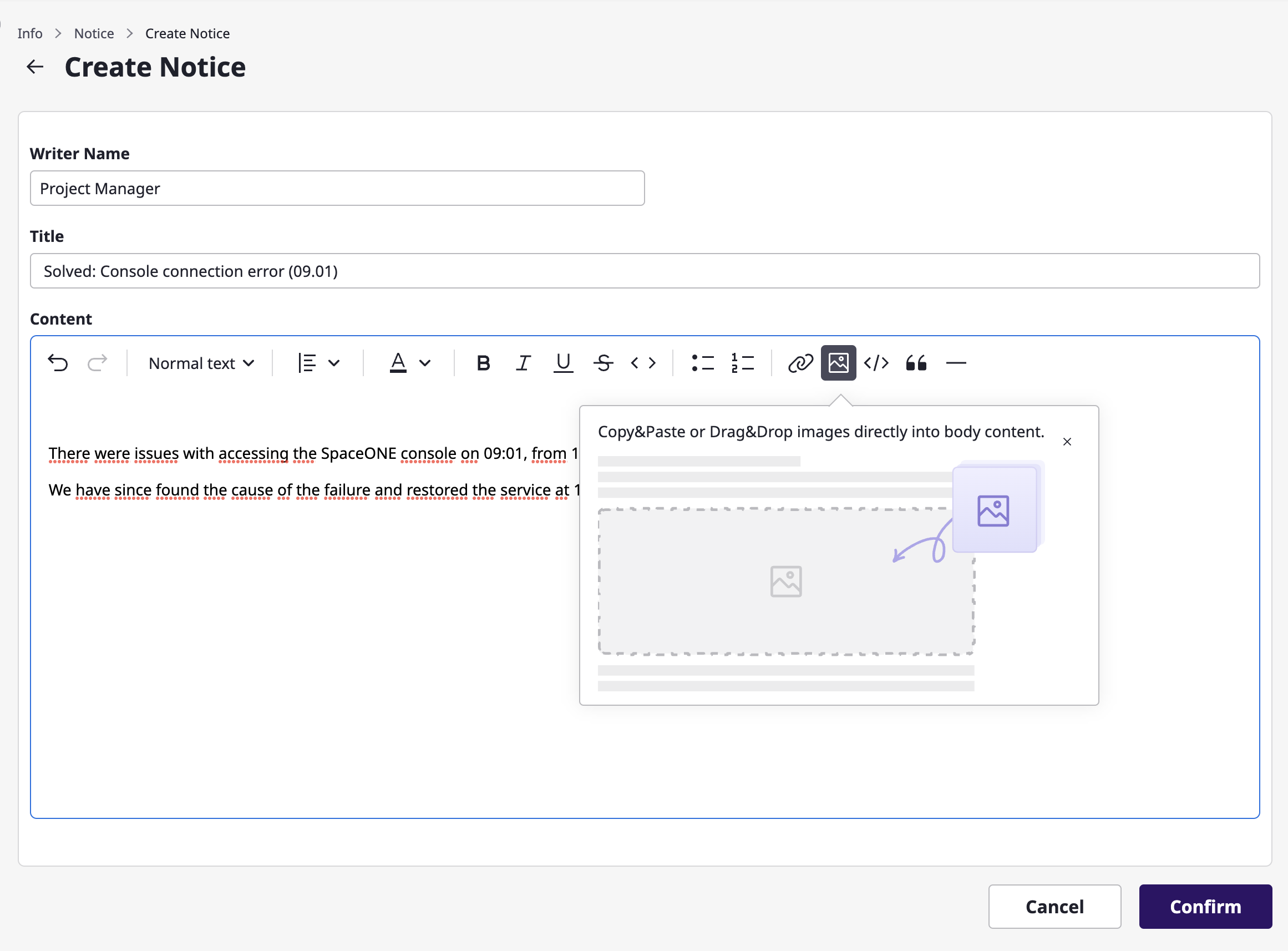
(2) The updated notice can be [modified] or [deleted] later.
10 - Advanced feature
10.1 - Custom table
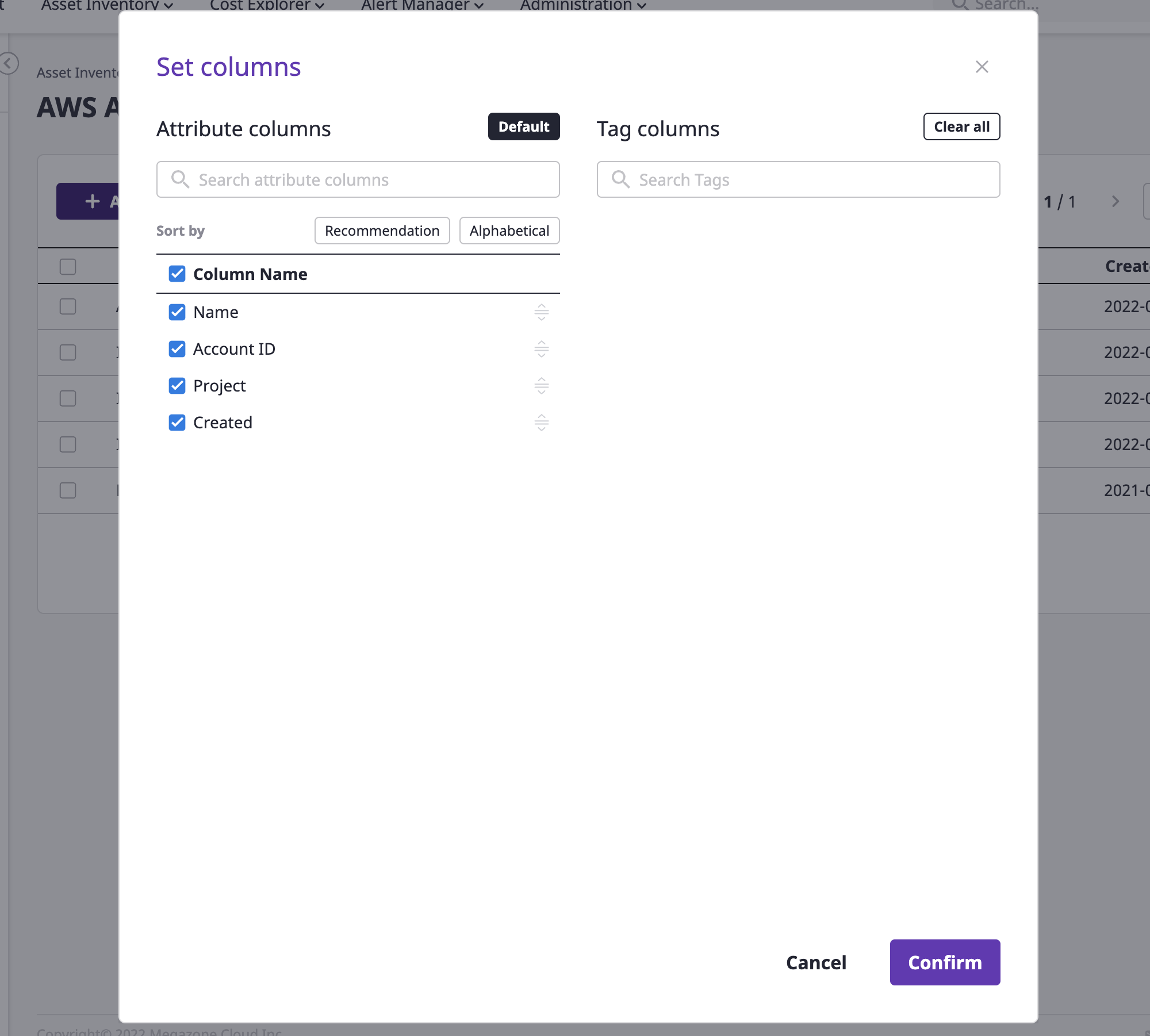
If you click the [Settings] icon button from the table, you can directly set up the table fields.
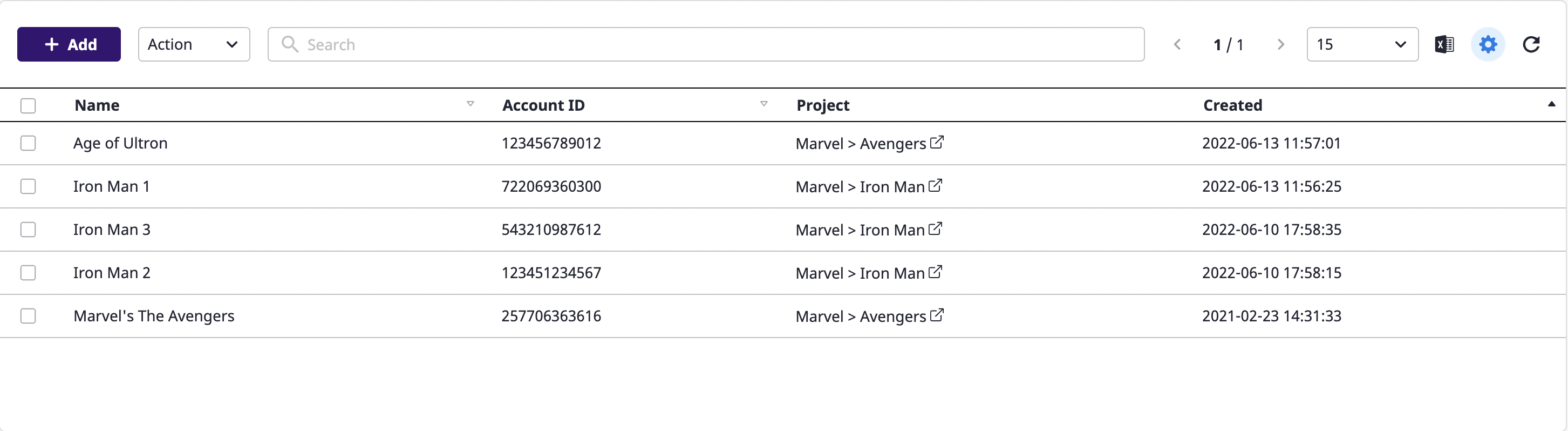
Getting field properties
You can sort fields by suggestion/alphabet or search by field name. You can also search by the tag field that you have.
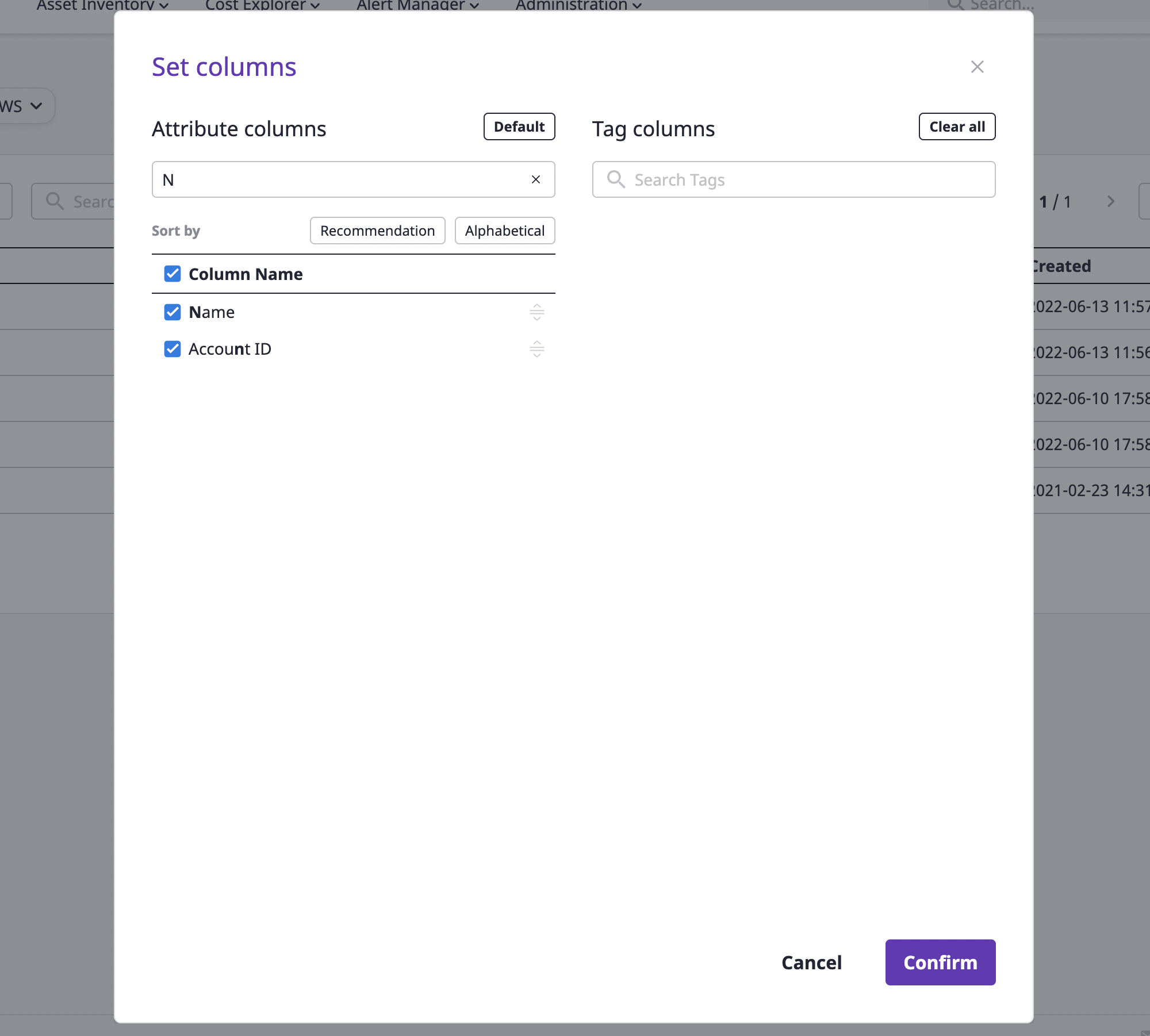
Selecting/deselecting fields
Fields can be freely deselected/selected from the field table. Select the desired field and click the [OK] button.
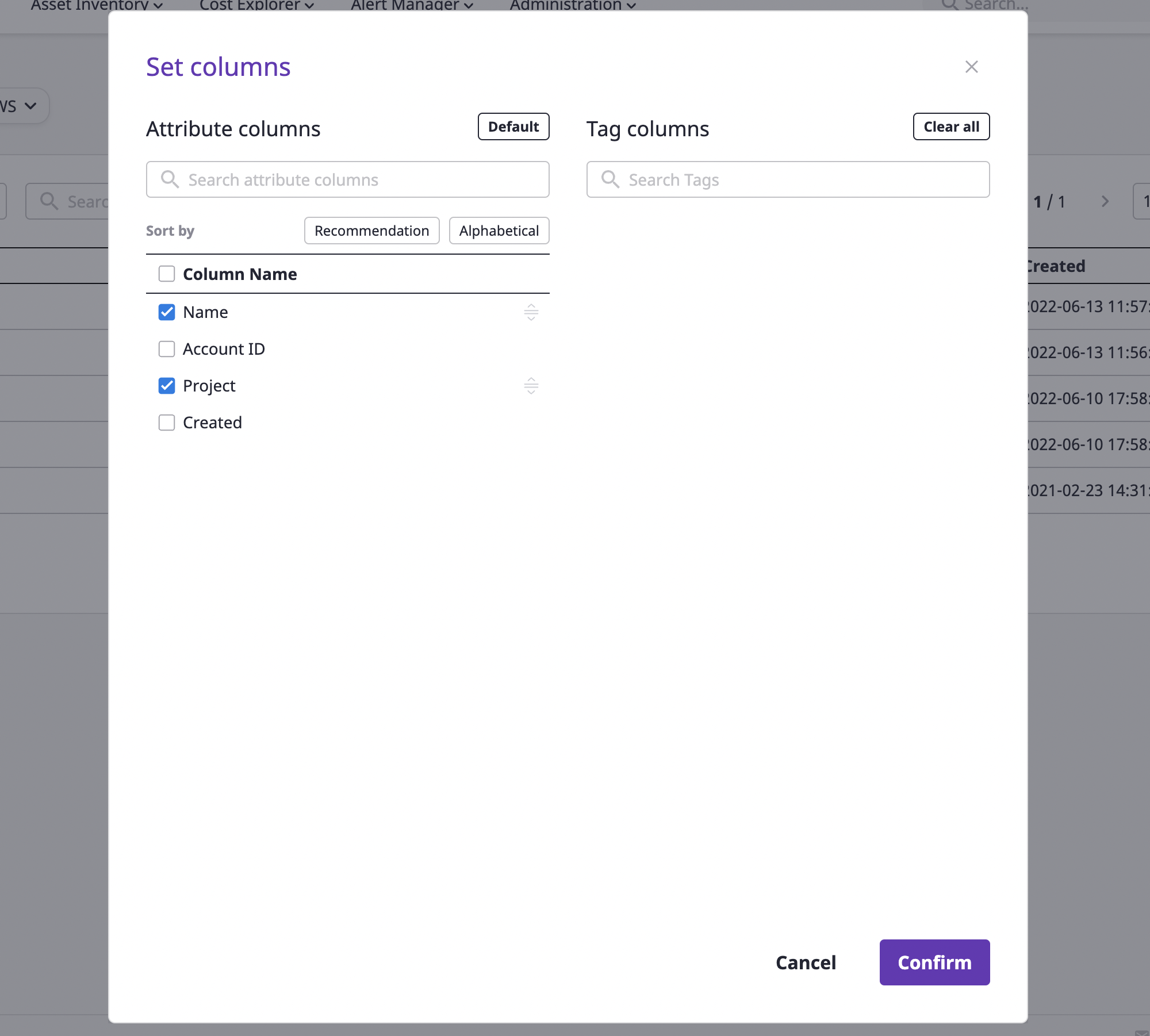
Sorting fields
Auto sort
If you click the [Recommended order] or [Alphabetical order] button at the top of the field table, the fields are sorted by the corresponding condition. The sorting only applies to the selected field.
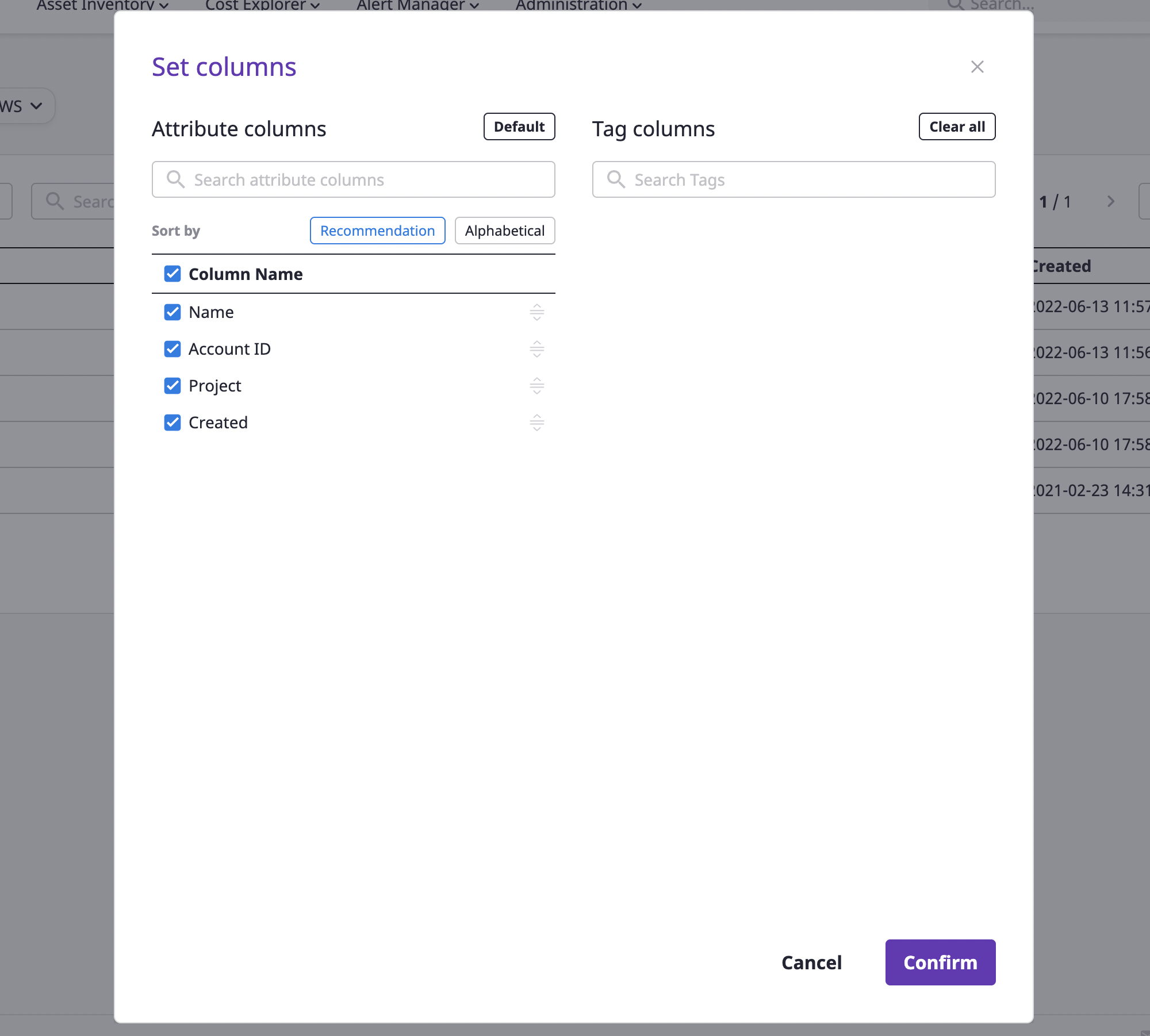
Manual sorting
You can manually sort fields by dragging and dropping the [Reorder] icon button to the right of the selected field.
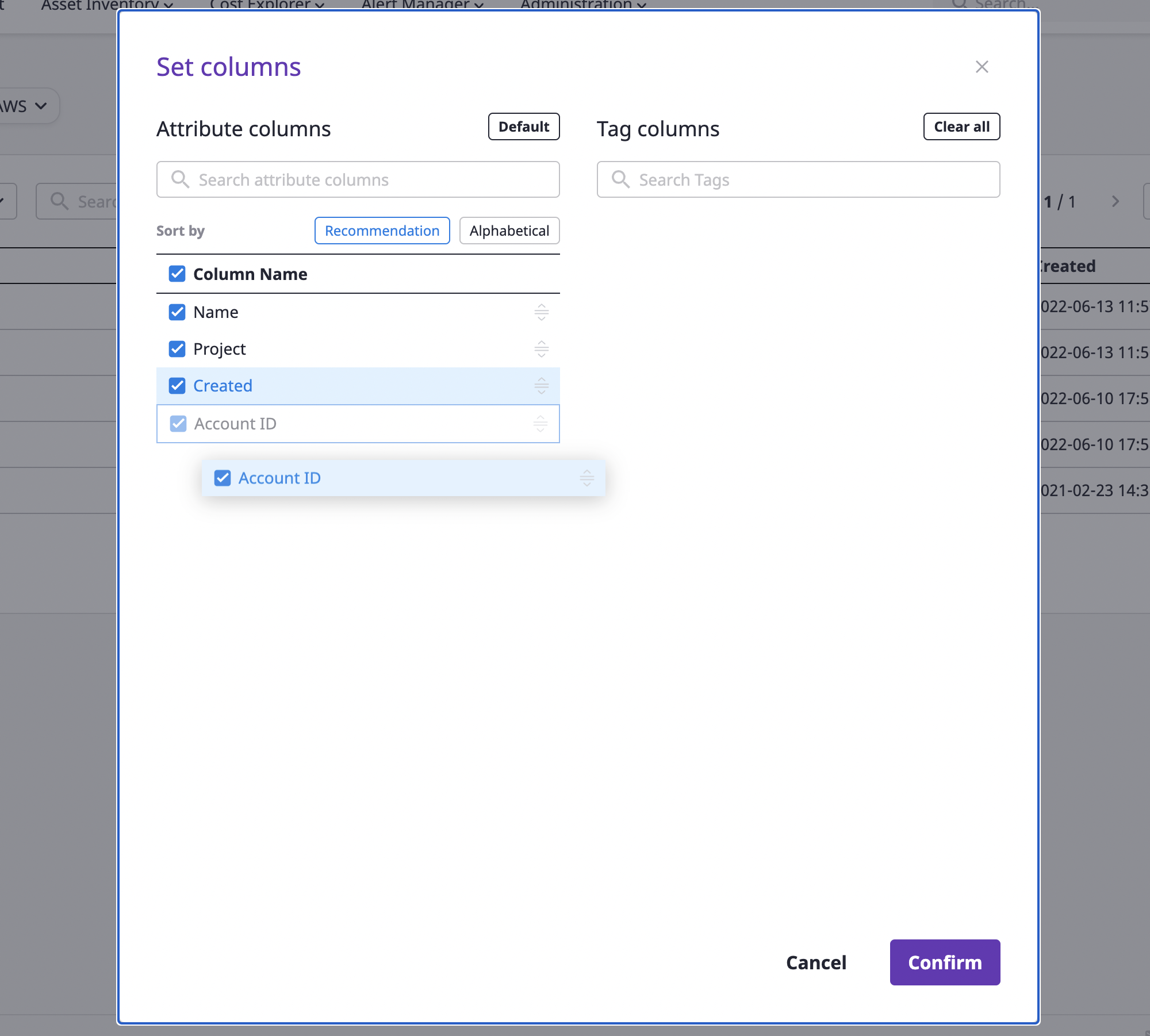
Reverting to default settings
If you want to retrieve a custom field to its default settings, click the [Return to Default] button.
10.2 - Export as an Excel file
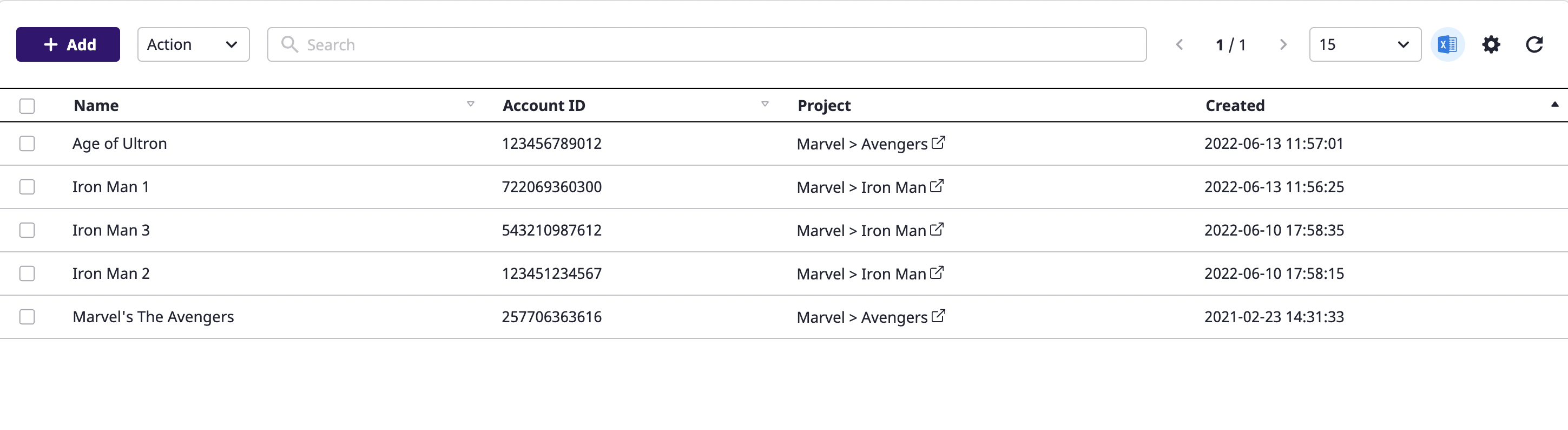
Click the [Export as an Excel file] icon button from the table.
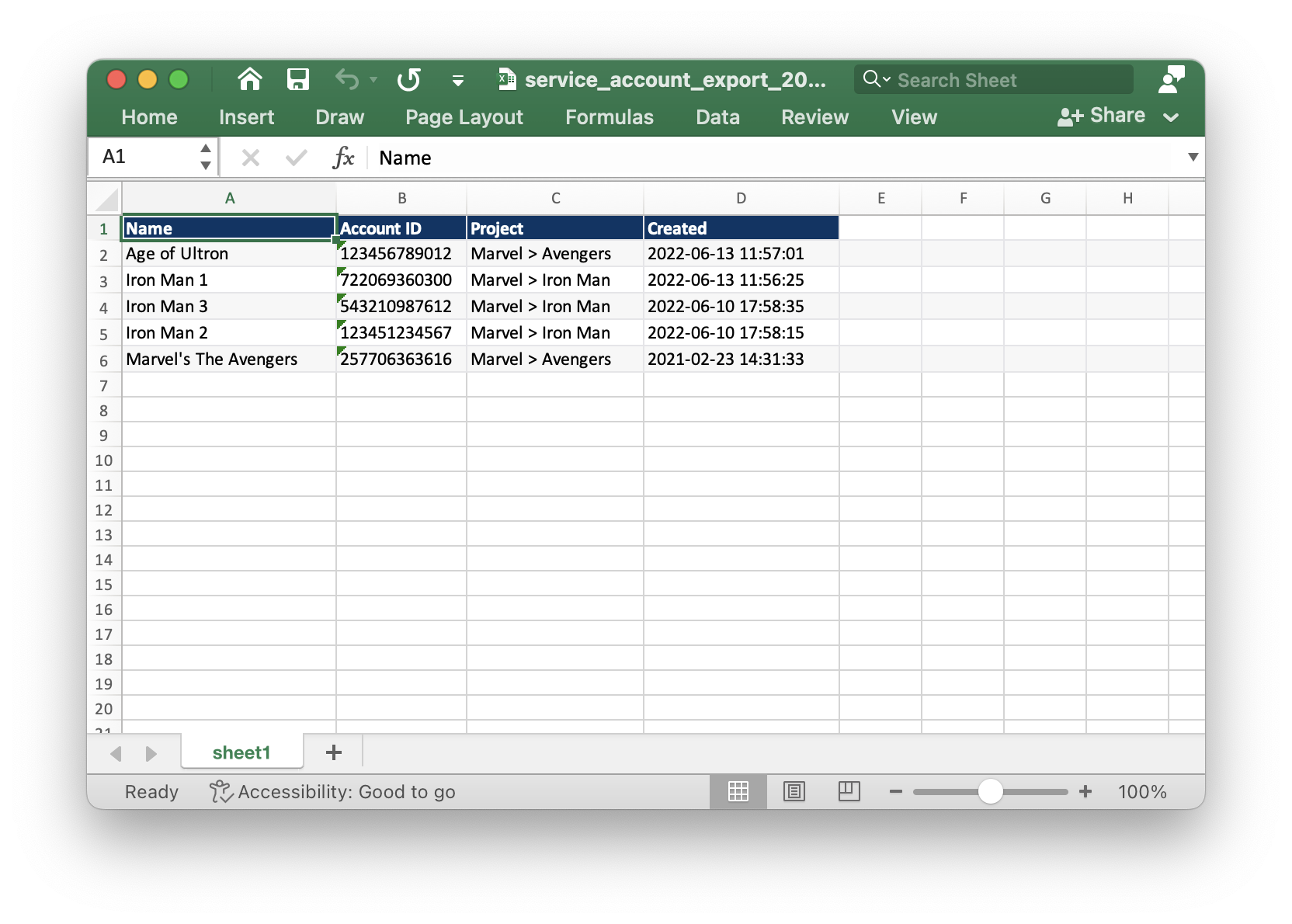
The data downloaded to Excel is as follows, and if you set it up to show only some fields as a custom table, you can see the data of that field only:
10.3 - Search
There are two ways to use the search bar from the data tables: advanced and keyword searches.
Advanced search
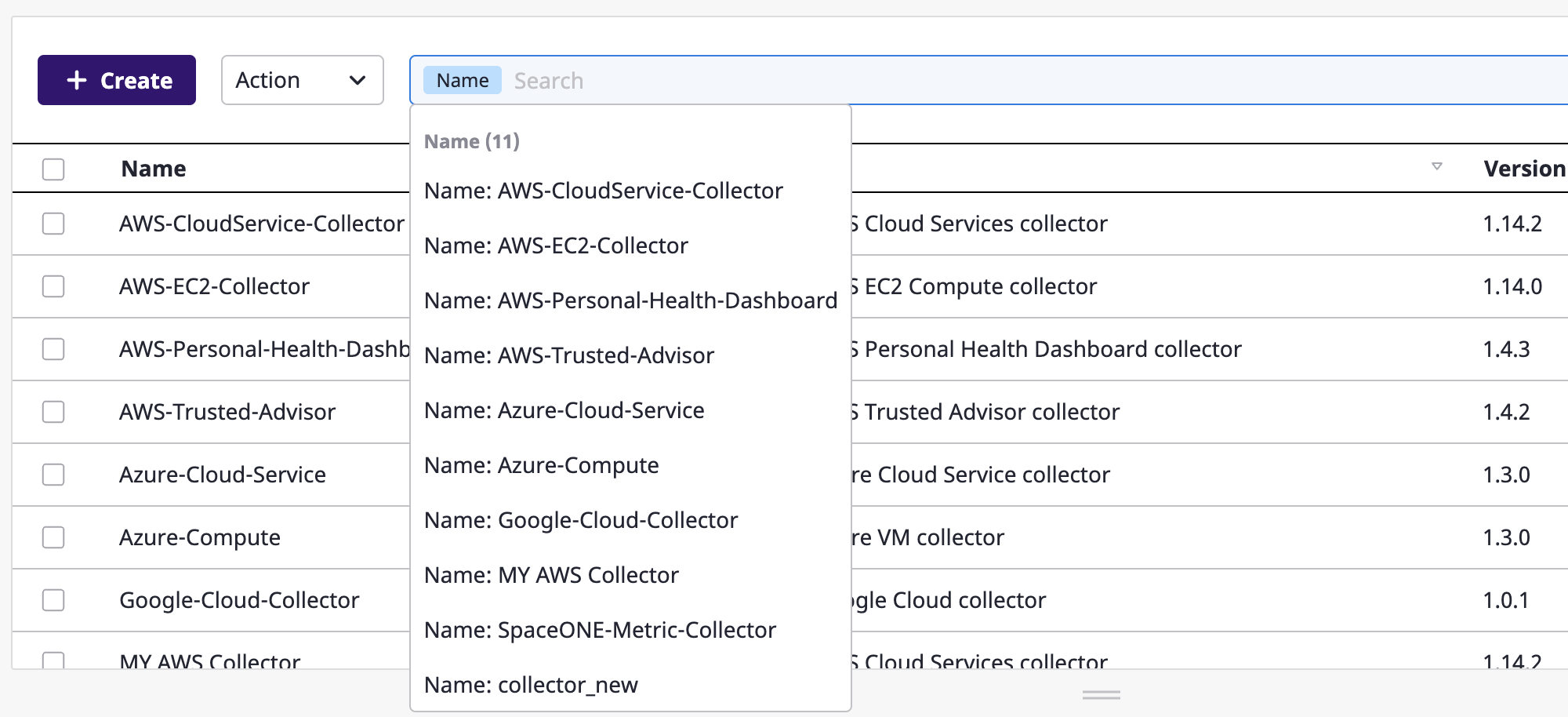
The search field provided by SpaceONE makes data searches much more convenient. All field names that can be searched would appear as you hover your mouse cursor over the search bar.
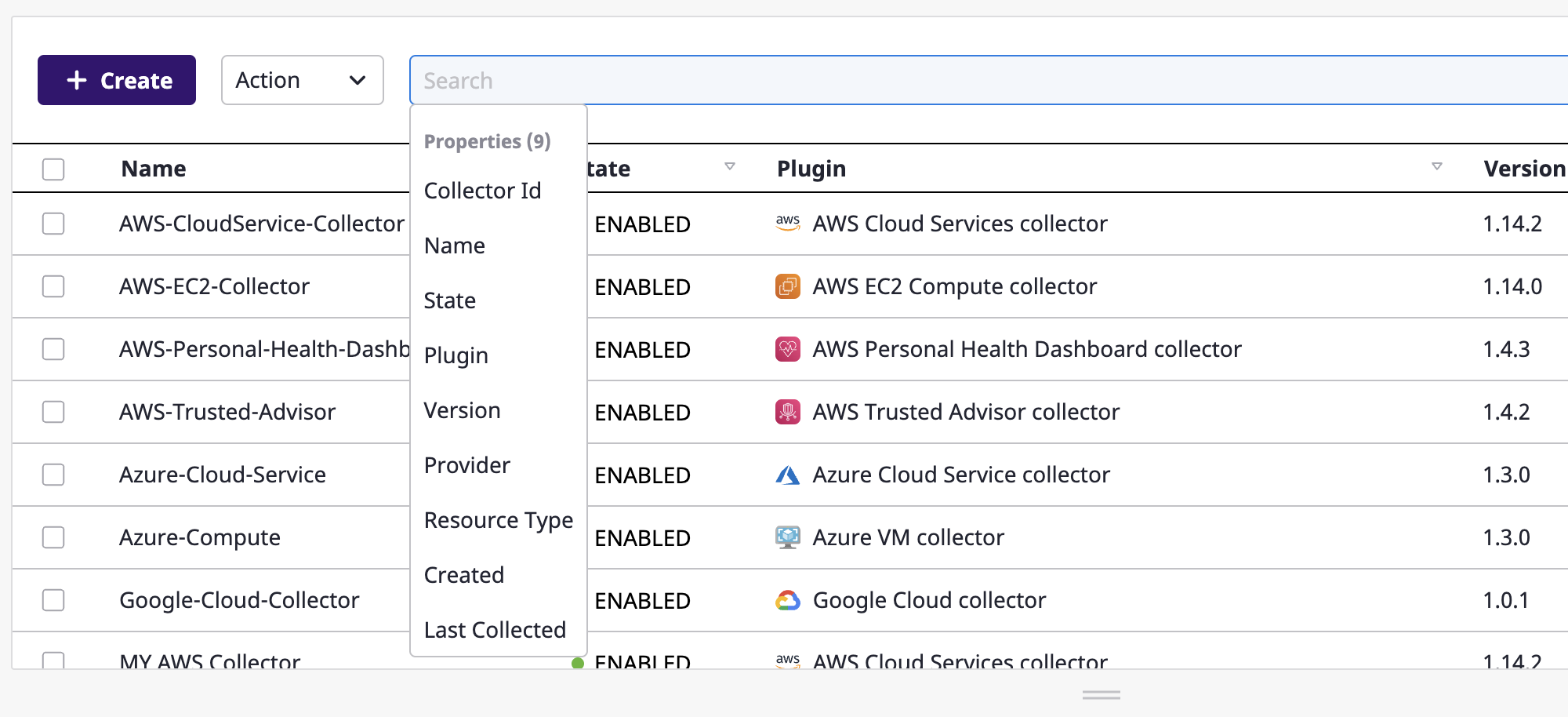
After selecting a field, you can manually enter a value for that field or choose it from a list of suggestions.
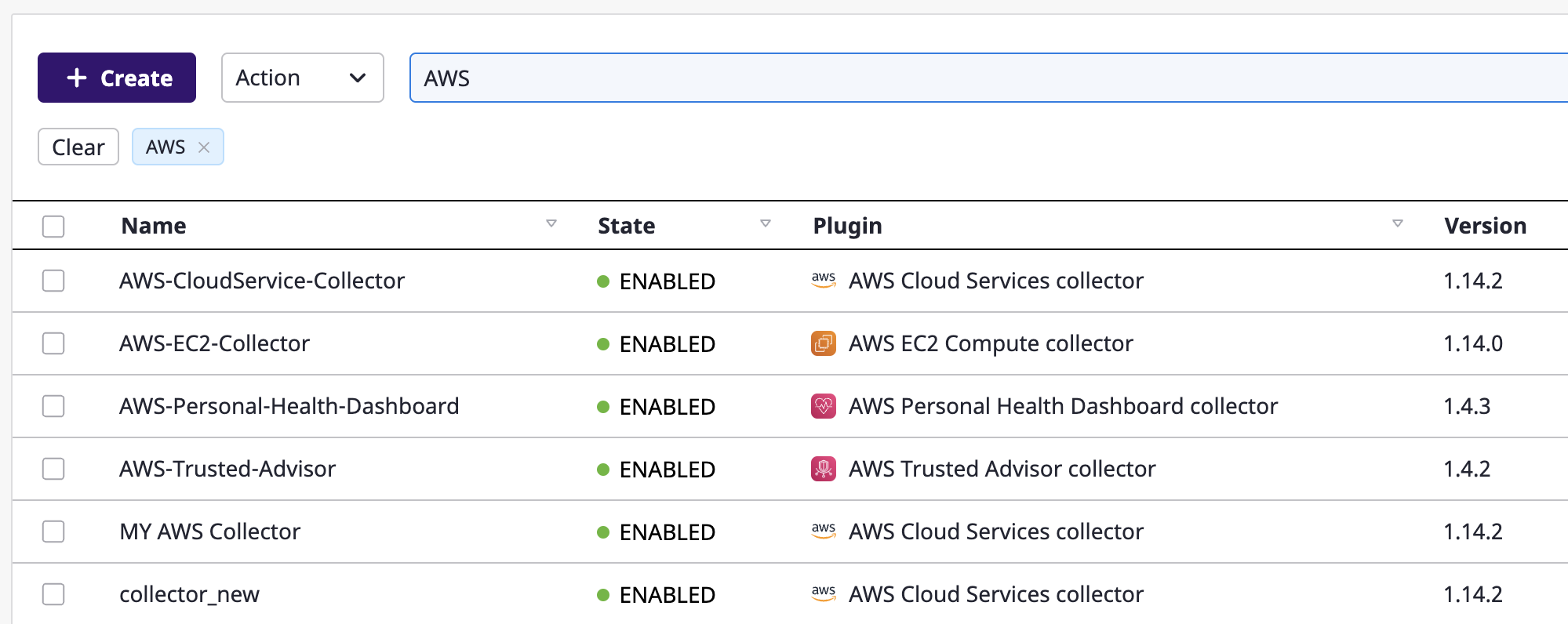
Keyword search
Use the keyword search if you want to search all fields rather than limit your search to a specific field. If you type the text in the search bar and press the enter key, the data containing the keyword is filtered in and displayed in the table.
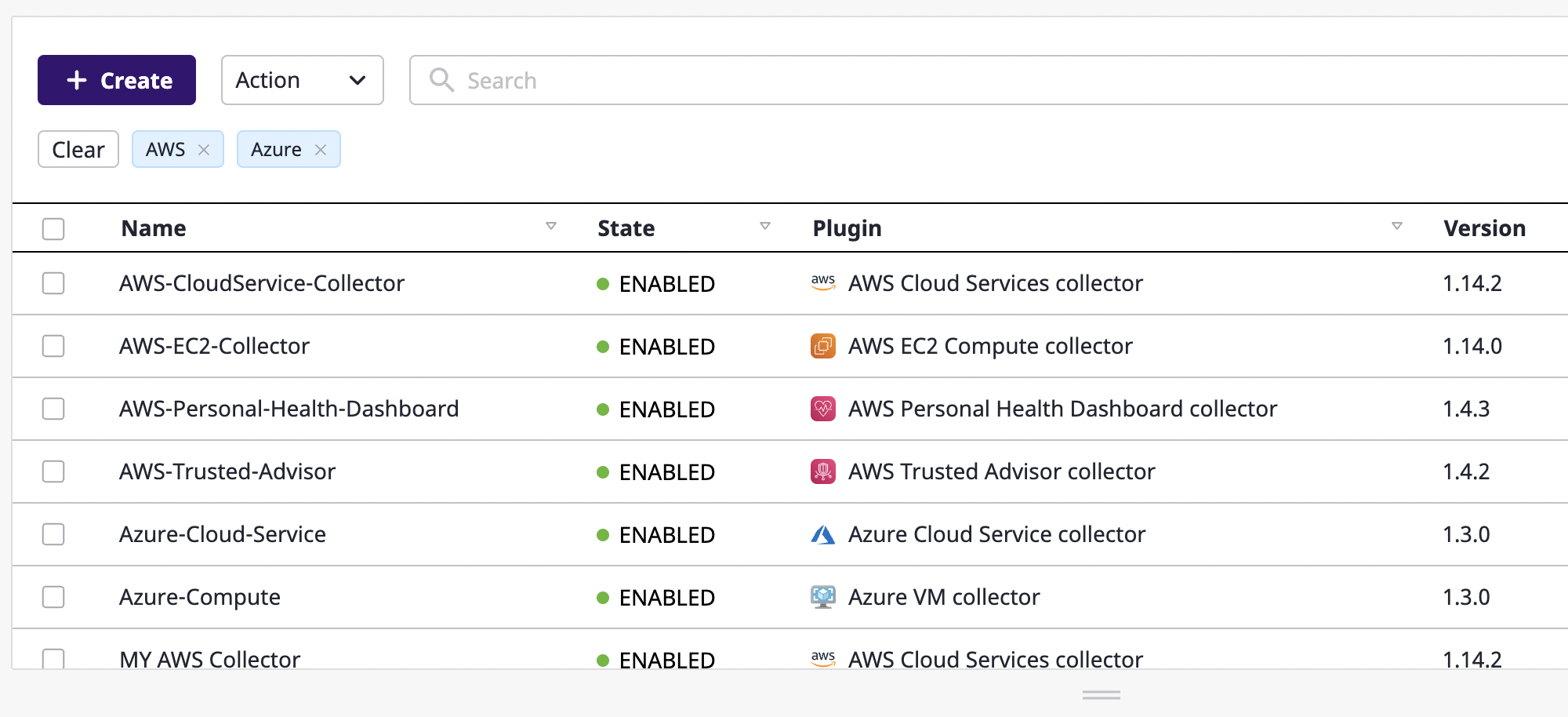
You can use both advanced and keyword searches together, and multiple searches are possible. The search word shall be displayed in the table if any of the field values are matched by filtering the data with the "or" condition.
11 - Plugin
11.1 - [Alert manager] notification
Overview
Cloudforet provides plugins as a notification method to deliver alerts to users.
For a list of plugins currently supported by Cloudforet, see the Plugin support list.
You can see more detailed descriptions on Telegram and Slack connections from the below link.
In addition, the Email, SMS and Voice call are available Without any additional settings.
Plugin support list
| Plugins | Setup guide link |
|---|---|
| Telegram | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-telegram-noti-protocol/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| Slack | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-slack-noti-protocol/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| Can be used without additional settings | |
| SMS | Can be used without additional settings |
| Voice call | Can be used without additional settings |
11.2 - [Alert manager] webhook
Overview
Cloudforet supports plugin type webhooks for you to receive event messages from Various monitoring services.
For a list of webhook plugins currently supported by Cloudforet, see the Plugin support list.
In particular, event messages generated by AWS CloudWatch and AWS PHD (PersonalHealthDashboard)
are collected by Cloudforet through the AWS SNS (Simple Notification Service) webhook.
For the settings guide for each monitoring service, see Setup guide link in the plugin support list below.
Plugin support list
11.3 - [Asset inventory] collector
Overview
Cloudforet can collect cloud resources in use by each Cloud provider through a collector plugin.
For a list of collectors currently supported by Cloudforet, see the Plugin support list below.
First, to use the collector plugin, you must register a Service account.
However, since the ways for registering a service account registration are different for each cloud provider such as AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, etc.,
see the Setup guide link in the plugin support list below for detailed settings.
Plugin support list
| Plugins | Setup guide link |
|---|---|
| AWS Cloud Services collector | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-aws-cloud-service-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| AWS EC2 Compute collector | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-aws-ec2-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| AWS Personal Health Dashboard collector | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-aws-phd-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| AWS Trusted Advisor collector | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-aws-trusted-advisor-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| Azure Cloud collector | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-azure-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| Google Cloud collector | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-google-cloud-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
| Monitoring Metric Collector of Collected Resources | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-monitoring-metric-inven-collector/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
11.4 - [Cost analysis] data source
Overview
Cloudforet collects cost data for cloud services using a plugin.
For a list of plugins currently supported by Cloudforet, see the Plugin support list.
If there is no suitable plugin, you can develop a plugin fit for your company's billing system
and use it in Cloudforet.
Plugin support list
| Plugins | Setup guide link |
|---|---|
| AWS hyperbilling cost datasource | https://github.com/cloudforet-io/plugin-aws-hyperbilling-cost-datasource/blob/master/docs/ko/GUIDE.md |
11.5 - [IAM] authentication
Overview
As a means for user authentication, Cloudforet provides an authentication method using an account of other services using a plugin.
For a list of authentication plugins currently supported by Cloudforet, see the Plugin support list.
You can use the Google Oauth2 plugin,
which authenticates users through your Google account, and the Keycloak plugin, which supports a single sign-on (SSO) via standard protocols.
For more detailed settings, see the Setup guide link below